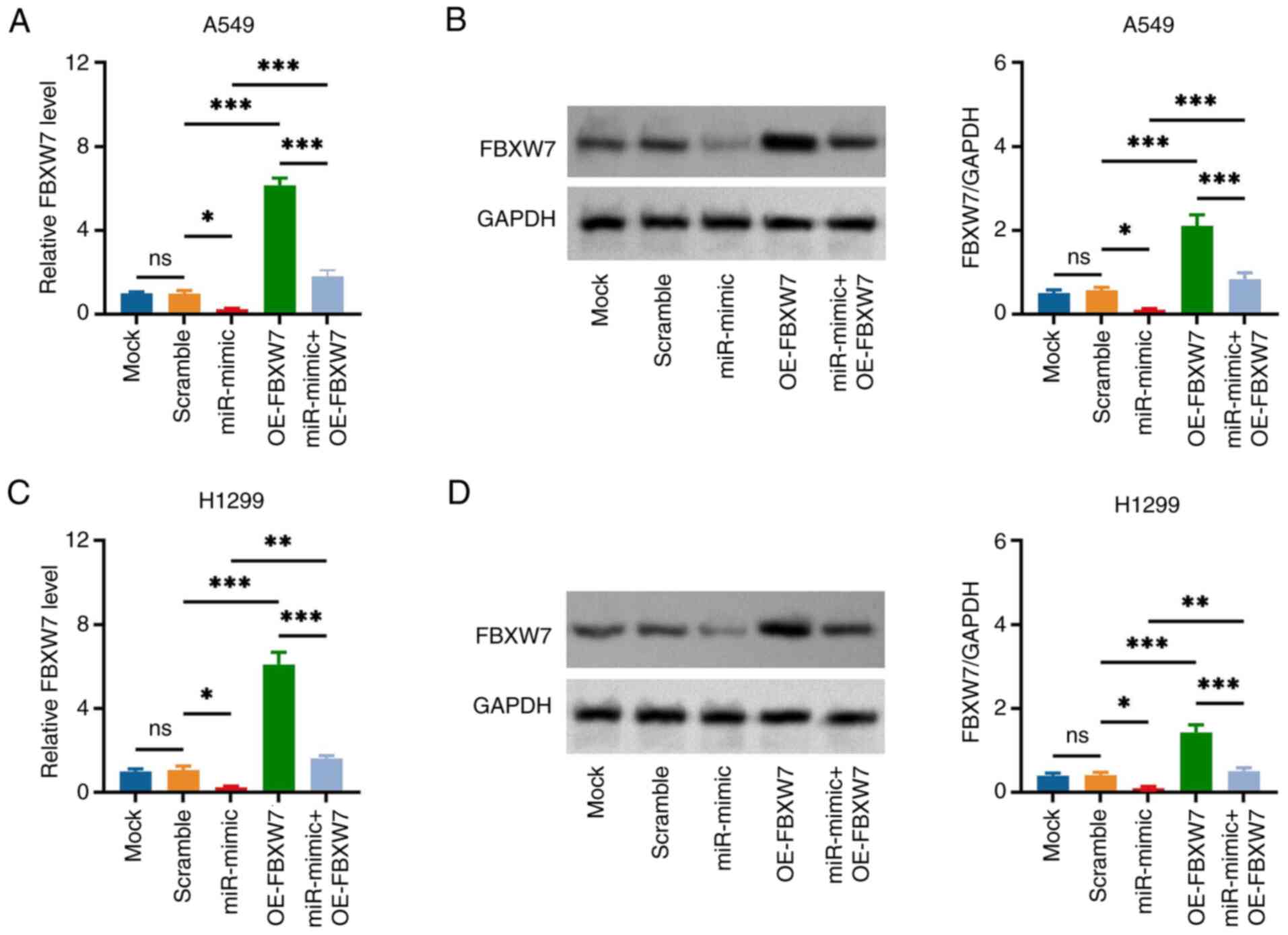
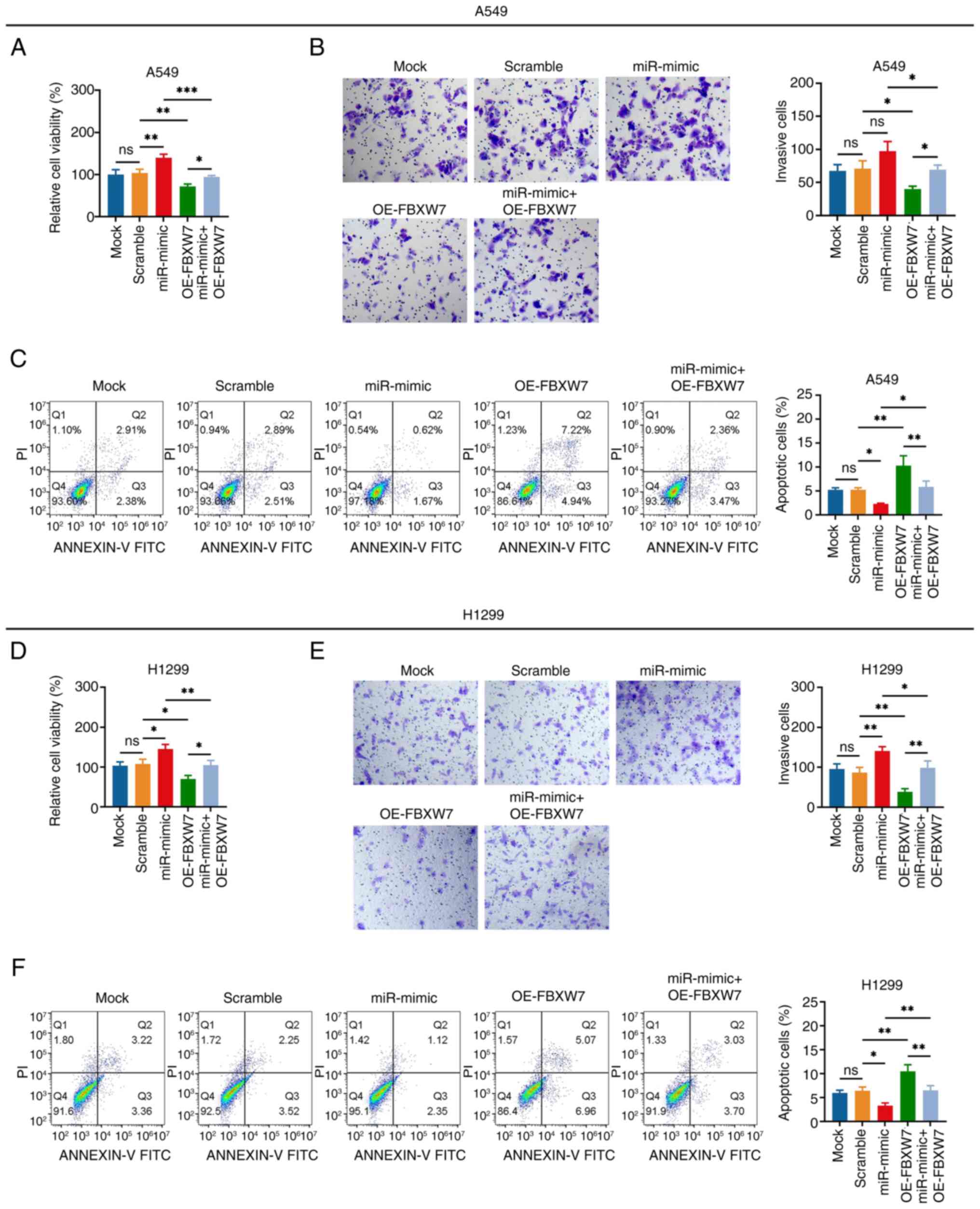
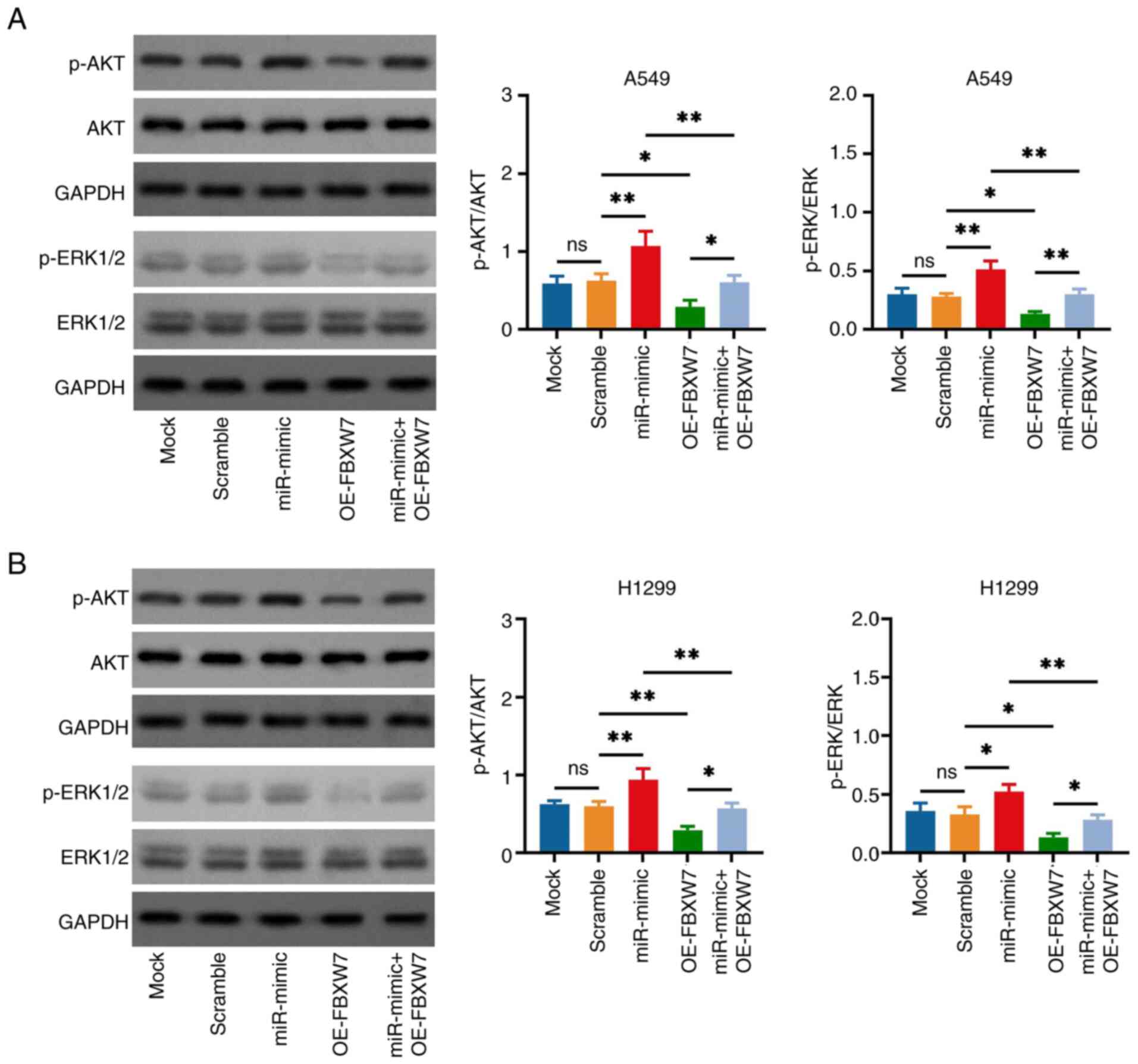
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Han B, Zheng R, Zeng H, Wang S, Sun K,
Chen R, Li L, Wei W and He J: Cancer incidence and mortality in
China, 2022. J Natl Cancer Cent. 4:47–53. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen P, Liu Y, Wen Y and Zhou C: Non-small
cell lung cancer in China. Cancer Commun (Lond). 42:937–970. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alexander M, Kim SY and Cheng H: Update
2020: Management of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung. 198:897–907.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu J and Lin Z: Non-small cell lung cancer
targeted therapy: Drugs and mechanisms of drug resistance. Int J
Mol Sci. 23:150562022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang KH and Ding DC: Role of
cancer-associated mesenchymal stem cells in the tumor
microenvironment: A review. Tzu Chi Med J. 35:24–30. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Frisbie L, Buckanovich RJ and Coffman L:
Carcinoma-associated mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: Architects of
the pro-tumorigenic tumor microenvironment. Stem Cells. 40:705–715.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Adelipour M, Lubman DM and Kim J:
Potential applications of mesenchymal stem cells and their derived
exosomes in regenerative medicine. Expert Opin Biol Ther.
23:491–507. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Papaccio F, Paino F, Regad T, Papaccio G,
Desiderio V and Tirino V: Concise review: Cancer cells, cancer stem
cells, and mesenchymal stem cells: Influence in cancer development.
Stem Cells Transl Med. 6:2115–2125. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arena S, Salati M, Sorgentoni G, Barbisan
F and Orciani M: Characterization of tumor-derived mesenchymal stem
cells potentially differentiating into cancer-associated
fibroblasts in lung cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 20:1582–1591. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hazrati A, Malekpour K, Mirsanei Z,
Khosrojerdi A, Rahmani-Kukia N, Heidari N, Abbasi A and Soudi S:
Cancer-associated mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: Role in
progression and potential targets for therapeutic approaches. Front
Immunol. 14:12806012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shang C, Ke M, Liu L, Wang C, Liu Y and
Zheng X: Exosomes from cancer-associated mesenchymal stem cells
transmit TMBIM6 to promote the malignant behavior of hepatocellular
carcinoma via activating PI3K/AKT pathway. Front Oncol.
12:8687262022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Garnier D, Ratcliffe E, Briand J, Cartron
PF, Oliver L and Vallette FM: The activation of mesenchymal stem
cells by glioblastoma microvesicles alters their exosomal secretion
of miR-100-5p, miR-9-5p and let-7d-5p. Biomedicines. 10:1122022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao MN, Zhang LF, Sun Z, Qiao LH, Yang T,
Ren YZ, Zhang XZ, Wu L, Qian WL, Guo QM, et al: A novel
microRNA-182/interleukin-8 regulatory axis controls osteolytic bone
metastasis of lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 14:2982023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang F, Pei Y, Xu W and Rong L:
hsa_circ_0003176 suppresses the progression of non-small-cell lung
cancer via regulating miR-182-5p/RBM5 axis. Dis Markers.
2022:84021162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang W, Yin Y, Bi L, Wang Y, Yao J, Xu L
and Jiao L: MiR-182-5p promotes the metastasis and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer by
targeting EPAS1. J Cancer. 12:7120–7129. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stafford MYC and McKenna DJ: MiR-182 is
upregulated in prostate cancer and contributes to tumor progression
by targeting MITF. Int J Mol Sci. 24:18242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li J, Yuan H, Xu H, Zhao H and Xiong N:
Hypoxic cancer-secreted exosomal miR-182-5p promotes glioblastoma
angiogenesis by targeting kruppel-like factor 2 and 4. Mol Cancer
Res. 18:1218–1231. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao F, Yin J, Wang Y, Li H and Wang D:
miR-182 promotes cervical cancer progression via activating the
Wnt/β-catenin axis. Am J Cancer Res. 13:3591–3598. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen G, Yu L, Dong H, Liu Z and Sun Y:
MiR-182 enhances radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer
cells by regulating FOXO3. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 46:137–143.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cascio S, Chandler C, Zhang L, Sinno S,
Gao B, Onkar S, Bruno TC, Vignali DAA, Mahdi H, Osmanbeyoglu HU, et
al: Cancer-associated MSC drive tumor immune exclusion and
resistance to immunotherapy, which can be overcome by Hedgehog
inhibition. Sci Adv. 7:eabi57902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cao J, Yu U, Li L, Yuan X, Chen S, Xu H,
Yi M and Liu S: circKL inhibits the growth and metastasis of kidney
cancer by sponging miR-182-5p and upregulating FBXW7. Oncol Rep.
47:752022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chang H, Liu YH, Wang LL, Wang J, Zhao ZH,
Qu JF and Wang SF: MiR-182 promotes cell proliferation by
suppressing FBXW7 and FBXW11 in non-small cell lung cancer. Am J
Transl Res. 10:1131–1142. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chiang CH, Chu PY, Hou MF and Hung WC:
MiR-182 promotes proliferation and invasion and elevates the
HIF-1α-VEGF-A axis in breast cancer cells by targeting FBXW7. Am J
Cancer Res. 6:1785–1798. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Razmkhah M, Abtahi S and Ghaderi A:
Mesenchymal stem cells, immune cells and tumor cells crosstalk: A
sinister triangle in the tumor microenvironment. Curr Stem Cell Res
Ther. 14:43–51. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bussard KM, Mutkus L, Stumpf K,
Gomez-Manzano C and Marini FC: Tumor-associated stromal cells as
key contributors to the tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res.
18:842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu H, Deng S, Han L, Ren Y, Gu J, He L,
Liu T and Yuan ZX: Mesenchymal stem cells, exosomes and
exosome-mimics as smart drug carriers for targeted cancer therapy.
Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 209:1121632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gemayel J, Chaker D, El Hachem G, Mhanna
M, Salemeh R, Hanna C, Harb F, Ibrahim A, Chebly A and Khalil C:
Mesenchymal stem cells-derived secretome and extracellular
vesicles: Perspective and challenges in cancer therapy and clinical
applications. Clin Transl Oncol. 25:2056–2068. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan C, Chang J, Song X, Qi Y, Ji Z, Liu T,
Yu W, Wei F, Yang L and Ren X: Lung cancer-associated mesenchymal
stem cells promote tumor metastasis and tumorigenesis by induction
of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem-like reprogram. Aging
(Albany NY). 13:9780–9800. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yassine S and Alaaeddine N: Mesenchymal
stem cell exosomes and cancer: Controversies and prospects. Adv
Biol (Weinh). 6:e21010502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lin Z, Wu Y, Xu Y, Li G, Li Z and Liu T:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in cancer therapy
resistance: Recent advances and therapeutic potential. Mol Cancer.
21:1792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu X, Wang W, Wu G, Peng C and Liu J:
miR-182-5p serves as an oncogene in lung adenocarcinoma through
binding to STARD13. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021:70743432021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang T, Goel A, Xu X, Wu Y, Tang E, Zhang
F, Li Y, Li H, Cai Y and Weng W: N-mytistoyltransferase 1 and 2 are
potential tumor suppressors and novel targets of miR-182 in human
non-small cell lung carcinomas. Lung Cancer. 171:70–81. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao J, Tang J, Men W and Ren K:
FBXW7-mediated degradation of CCDC6 is impaired by ATM during DNA
damage response in lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 586:4257–4263.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xiao G, Li Y, Wang M, Li X, Qin S, Sun X,
Liang R, Zhang B, Du N, Xu C, et al: FBXW7 suppresses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemo-resistance of
non-small-cell lung cancer cells by targeting snai1 for
ubiquitin-dependent degradation. Cell Prolif. 51:e124732018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
An HJ, Lee CJ, Lee GE, Choi Y, Jeung D,
Chen W, Lee HS, Kang HC, Lee JY, Kim DJ, et al: FBXW7-mediated ERK3
degradation regulates the proliferation of lung cancer cells. Exp
Mol Med. 54:35–46. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li C, Lin XF, Wang JN and Ren XS: FBXW7
inhibited cell proliferation and invasion regulated by miR-27a
through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 24:3701–3709. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pan Y, Liu J, Gao Y, Guo Y, Wang C, Liang
Z, Wu M, Qian Y, Li Y, Shen J, et al: FBXW7 loss of function
promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via
elevating MAP4 and ERK phosphorylation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
42:752023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Song M, Bode AM, Dong Z and Lee MH: AKT as
a therapeutic target for cancer. Cancer Res. 79:1019–1031. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ullah R, Yin Q, Snell AH and Wan L:
RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer evolution and treatment. Semin Cancer
Biol. 85:123–154. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|