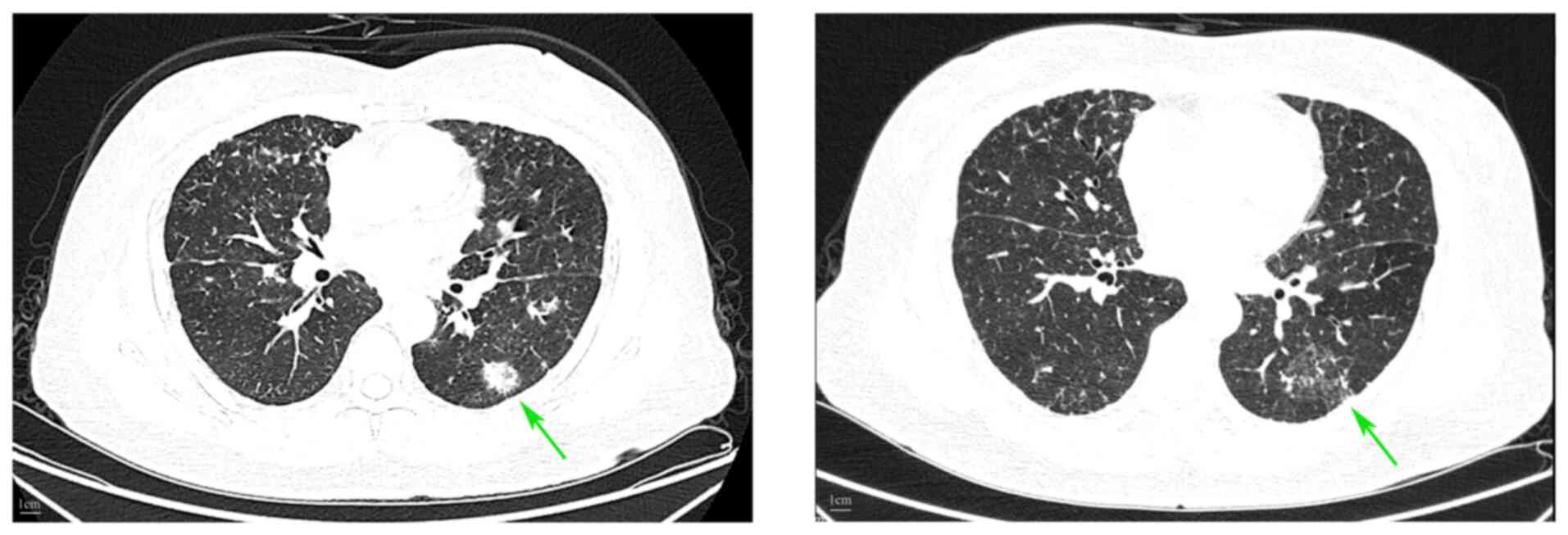
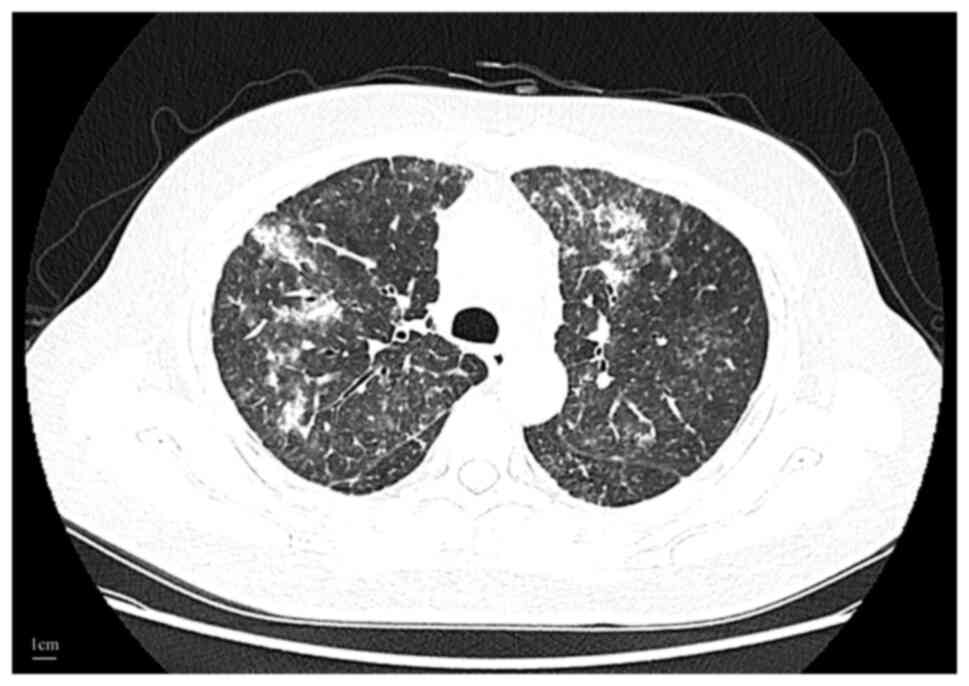
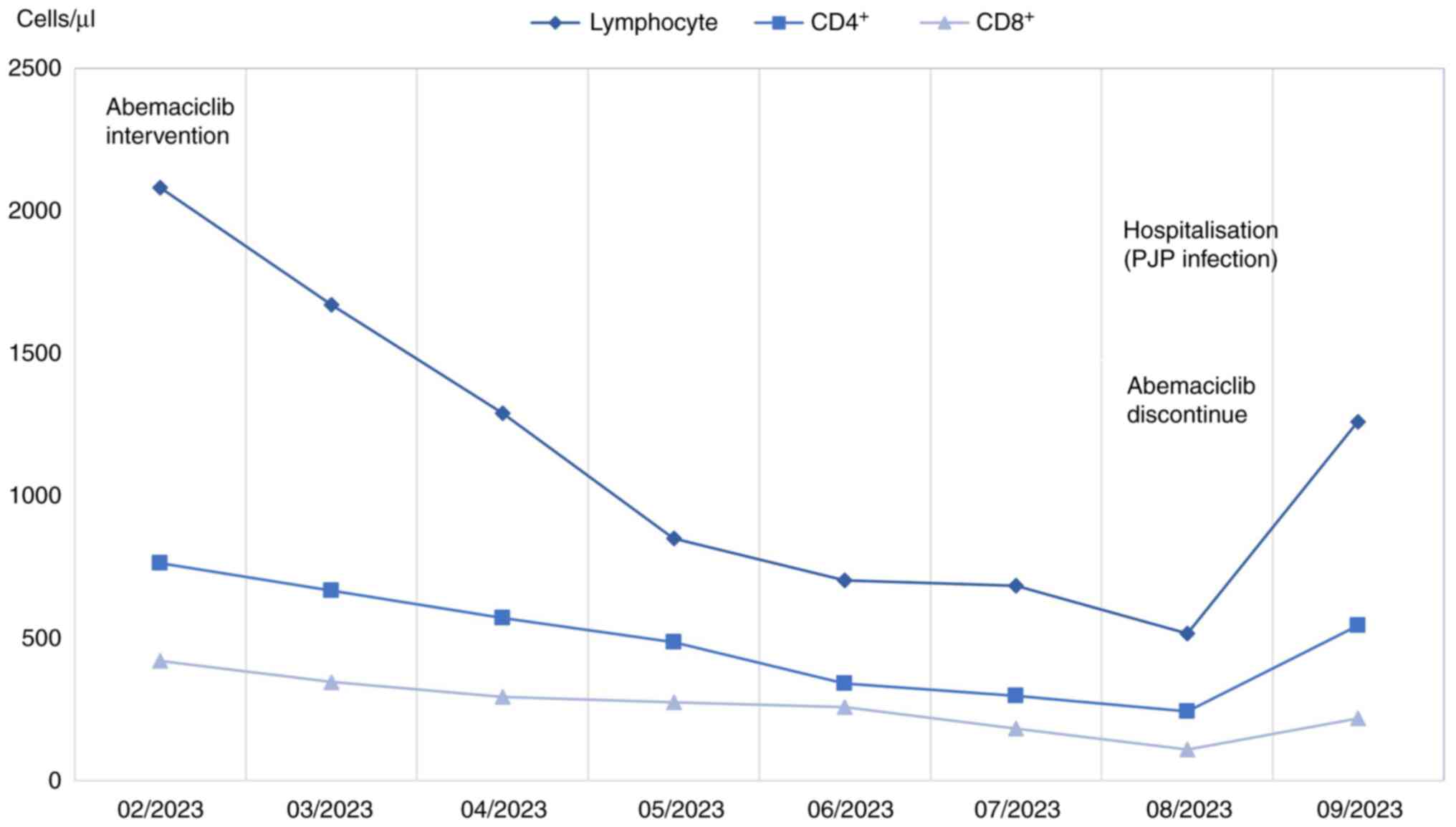
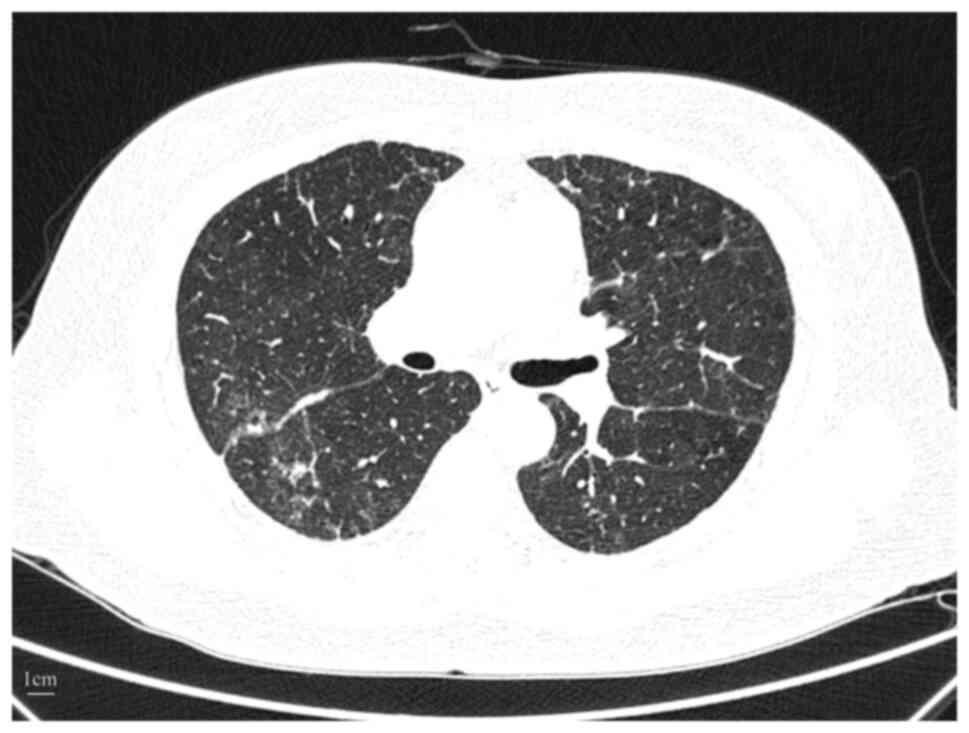
|
1
|
Zhou S and Aitken SL: Prophylaxis against
pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in adults. JAMA. 330:182–183.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Masur H, Brooks JT, Benson CA, Holmes KK,
Pau AK and Kaplan JE; National Institutes of Health, Centers for
Disease Control and Prevention HIV Medicine Association of the
Infectious Diseases Society of America, : Prevention and treatment
of opportunistic infections in HIV-infected adults and adolescents:
Updated guidelines from the centers for disease control and
prevention, national institutes of health, and HIV medicine
association of the infectious diseases society of America. Clin
Infect Dis. 58:1308–1311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gilroy SA and Bennett NJ: Pneumocystis
pneumonia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 32:775–782. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang Y, Zhou X, Saimi M, Huang X, Sun T,
Fan G and Zhan Q: Risk factors of mortality from pneumocystis
pneumonia in non-HIV patients: A meta-analysis. Front Public
Health. 9:6801082021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jerzak KJ, Bouganim N, Brezden-Masley C,
Edwards S, Gelmon K, Henning JW, Hilton JF and Sehdev S: HR+/HER2-
Advanced breast cancer treatment in the first-line setting: Expert
review. Curr Oncol. 30:5425–5447. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cooley L, Dendle C, Wolf J, Teh BW, Chen
SC, Boutlis C and Thursky KA: Consensus guidelines for diagnosis,
prophylaxis and management of pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in
patients with haematological and solid malignancies, 2014. Intern
Med J. 44:1350–1363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Johnston SRD, Harbeck N, Hegg R, Toi M,
Martin M, Shao ZM, Zhang QY, Martinez Rodriguez JL, Campone M,
Hamilton E, et al: Abemaciclib combined with endocrine therapy for
the adjuvant treatment of HR+, HER2-, node-positive, high-risk,
early breast cancer (monarchE). J Clin Oncol. 38:3987–3998. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sledge GW Jr, Toi M, Neven P, Sohn J,
Inoue K, Pivot X, Burdaeva O, Okera M, Masuda N, Kaufman PA, et al:
MONARCH 2: Abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant in women
with HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer who had progressed while
receiving endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol. 35:2875–2884. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Goetz MP, Toi M, Campone M, Sohn J,
Paluch-Shimon S, Huober J, Park IH, Trédan O, Chen SC, Manso L, et
al: MONARCH 3: Abemaciclib as initial therapy for advanced breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 35:3638–3646. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Patnaik A, Rosen LS, Tolaney SM, Tolcher
AW, Goldman JW, Gandhi L, Papadopoulos KP, Beeram M, Rasco DW,
Hilton JF, et al: Efficacy and safety of abemaciclib, an inhibitor
of CDK4 and CDK6, for patients with breast cancer, non-small cell
lung cancer, and other solid tumors. Cancer Discov. 6:740–753.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Wu J, Ji Z, Zhao Y, Li S, Li J,
Chen L, Zou J, Zheng J, Lin W, et al: Comparative efficacy and
safety of different combinations of three CDK4/6 inhibitors with
endocrine therapies in HR+/HER-2- metastatic or advanced breast
cancer patients: A network meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 23:8162023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lombardo JF: American society of clinical
oncology/college of American pathologists guidelines should be
scientifically validated. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 131:1510–1511. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guillaume Z, Medioni J, Lillo-Lelouet A,
Marret G, Oudard S and Simonaggio A: Severe cellular
immunodeficiency triggered by the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib.
Clin Breast Cancer. 20:e192–e195. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Deng J, Wang ES, Jenkins RW, Li S, Dries
R, Yates K, Chhabra S, Huang W, Liu H, Aref AR, et al: CDK4/6
inhibition augments antitumor immunity by enhancing T-cell
activation. Cancer Discov. 8:216–233. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gebbia V, Valerio MR, Firenze A and
Vigneri P: Abemaciclib: Safety and effectiveness of a unique
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. Expert Opin Drug Saf.
19:945–954. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Weyant RB, Kabbani D, Doucette K, Lau C
and Cervera C: Pneumocystis jirovecii: A review with a focus on
prevention and treatment. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 22:1579–1592.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ruhstaller T, Giobbie-Hurder A, Colleoni
M, Jensen MB, Ejlertsen B, de Azambuja E, Neven P, Láng I, Jakobsen
EH, Gladieff L, et al: Adjuvant letrozole and tamoxifen alone or
sequentially for postmenopausal women with hormone
receptor-positive breast cancer: Long-term follow-up of the BIG
1–98 trial. J Clin Oncol. 37:105–114. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pagani O, Francis PA, Fleming GF, Walley
BA, Viale G, Colleoni M, Láng I, Gómez HL, Tondini C, Pinotti G, et
al: Absolute improvements in freedom from distant recurrence to
tailor adjuvant endocrine therapies for premenopausal women:
Results from TEXT and SOFT. J Clin Oncol. 38:1293–1303. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Spagnolo P, Bonniaud P, Rossi G,
Sverzellati N and Cottin V: Drug-induced interstitial lung disease.
Eur Respir J. 60:21027762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pipavath S and Godwin JD: Imaging of
interstitial lung disease. Clin Chest Med. 25:455–465. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Conte P, Ascierto PA, Patelli G, Danesi R,
Vanzulli A, Sandomenico F, Tarsia P, Cattelan A, Comes A, De
Laurentiis M, et al: Drug-induced interstitial lung disease during
cancer therapies: Expert opinion on diagnosis and treatment. ESMO
Open. 7:1004042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Damiani C, Demey B, Pauc C, Le Govic Y and
Totet A: A negative (1,3)-β-D-glucan result alone is not sufficient
to rule out a diagnosis of pneumocystis pneumonia in patients with
hematological malignancies. Front Microbiol. 12:7132652021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu Y, Wang X, Xu J, Yang Q, Zhu H, Liu Y
and Yang J: Diagnostic value of metagenomic next-generation
sequencing of lower respiratory tract specimen for the diagnosis of
suspected pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. Ann Med.
55:22323582023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang JZ, Wang JB, Yuan D, Sun CH, Hou LL,
Zhang Y, Yang XH, Xie HX and Gao YX: Metagenomic next-generation
sequencing-based diagnosis of pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in
patients without human immunodeficiency virus infection: A
dual-center retrospective propensity matched study. J Infect Public
Health. 18:1028312025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li X, Li Z, Ye J and Ye W: Diagnostic
performance of metagenomic next-generation sequencing for
pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. BMC Infect Dis. 23:4552023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pang Y, Qiu J, Yang H, Zhang J, Mo J,
Huang W, Zeng C and Xu P: Application value of metagenomic
next-generation sequencing based on protective bronchoalveolar
lavage in nonresponding pneumonia. Microbiol Spectr.
13:e03138242025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Spring LM, Zangardi ML, Moy B and Bardia
A: Clinical management of potential toxicities and drug
interactions related to cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in
breast cancer: Practical considerations and recommendations.
Oncologist. 22:1039–1048. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen JK, Guerci J, Corbo H, Richmond M and
Martinez M: Low-dose TMP-SMX for pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia
prophylaxis in pediatric solid organ transplant recipients. J
Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 28:123–128. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hsieh CY and Tsai TF: Drug-induced
neutropenia during treatment of non-neoplastic dermatologic
diseases: A review. Clin Drug Investig. 40:915–926. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wolf R, Matz H, Orion E, Tuzun B and Tuzun
Y: Dapsone. Dermatol Online J. 8:22002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huang YS, Tseng SY, Chang TE, Perng CL and
Huang YH: Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim-induced liver injury and
genetic polymorphisms of NAT2 and CYP2C9 in Taiwan. Pharmacogenet
Genomics. 31:200–206. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Posada MM, Morse BL, Turner PK,
Kulanthaivel P, Hall SD and Dickinson GL: Predicting clinical
effects of CYP3A4 modulators on abemaciclib and active metabolites
exposure using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling. J
Clin Pharmacol. 60:915–930. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|