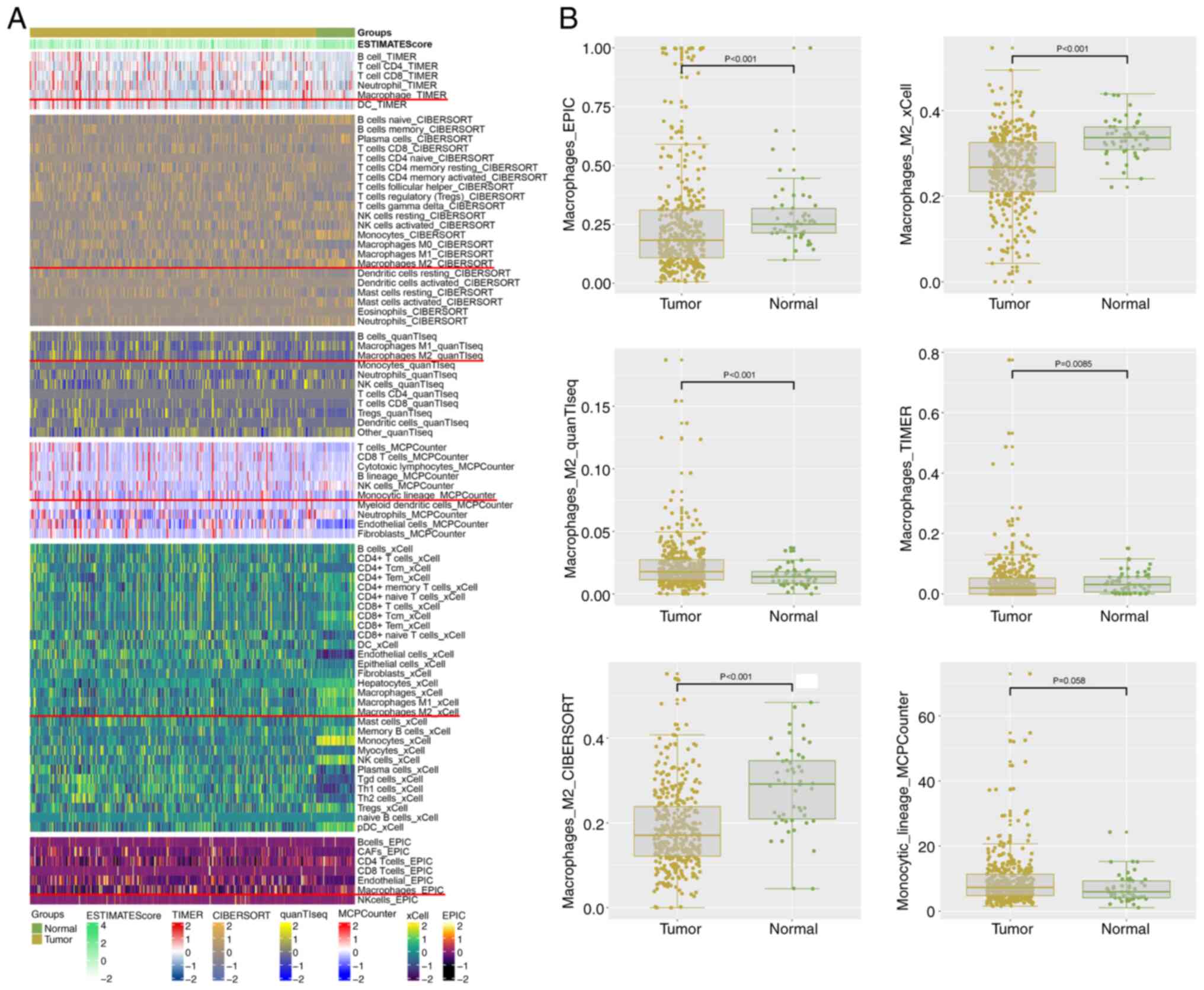
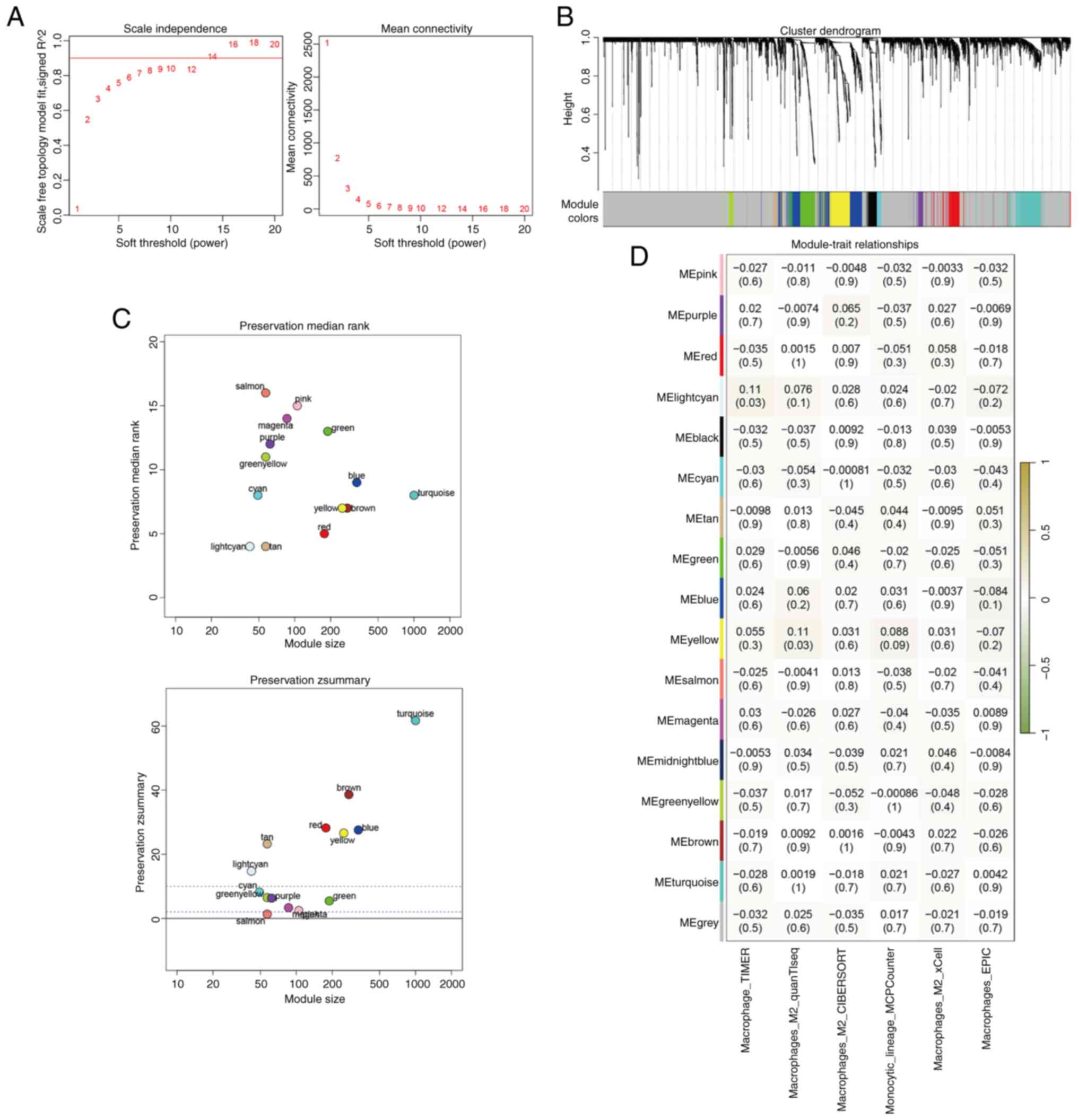
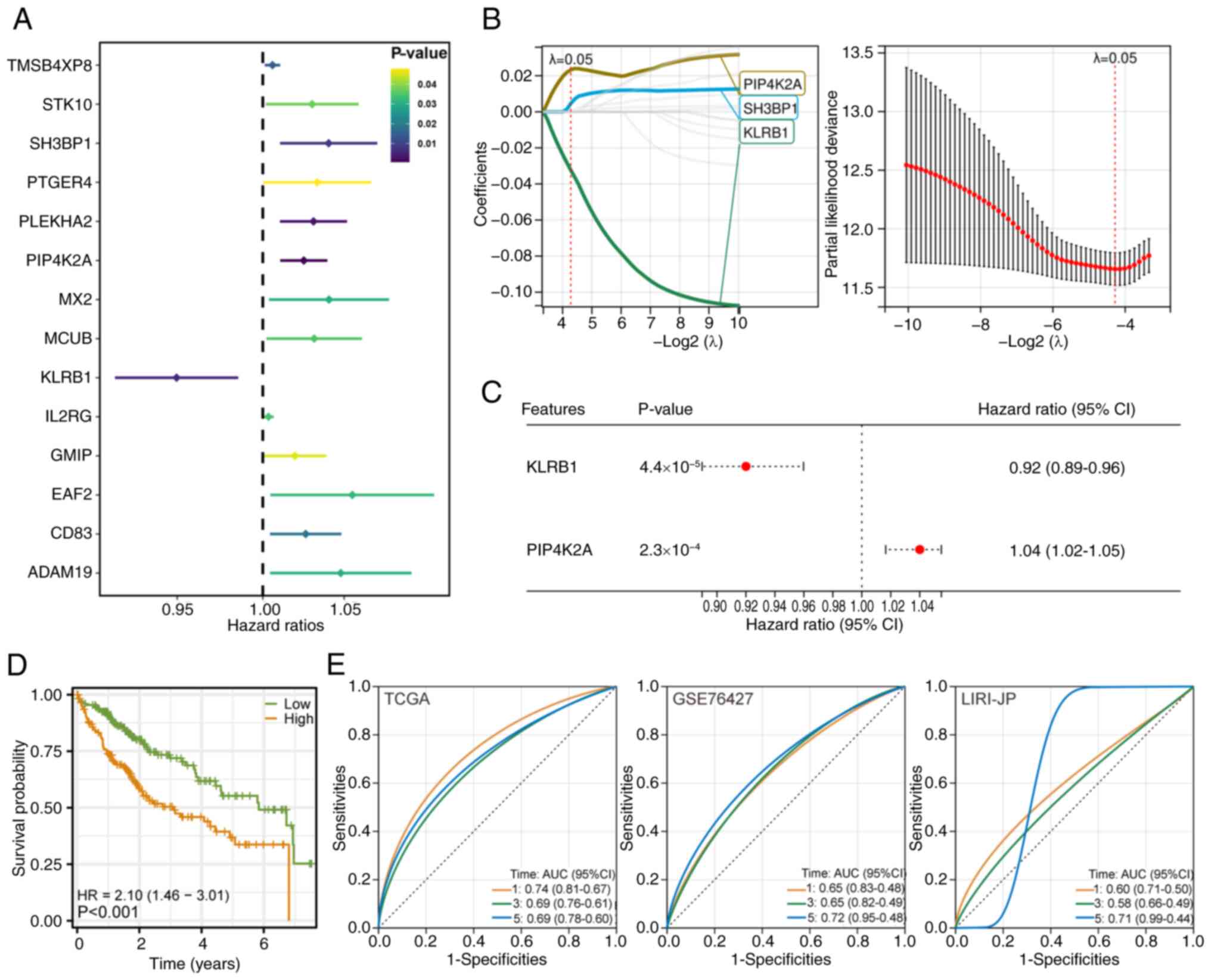
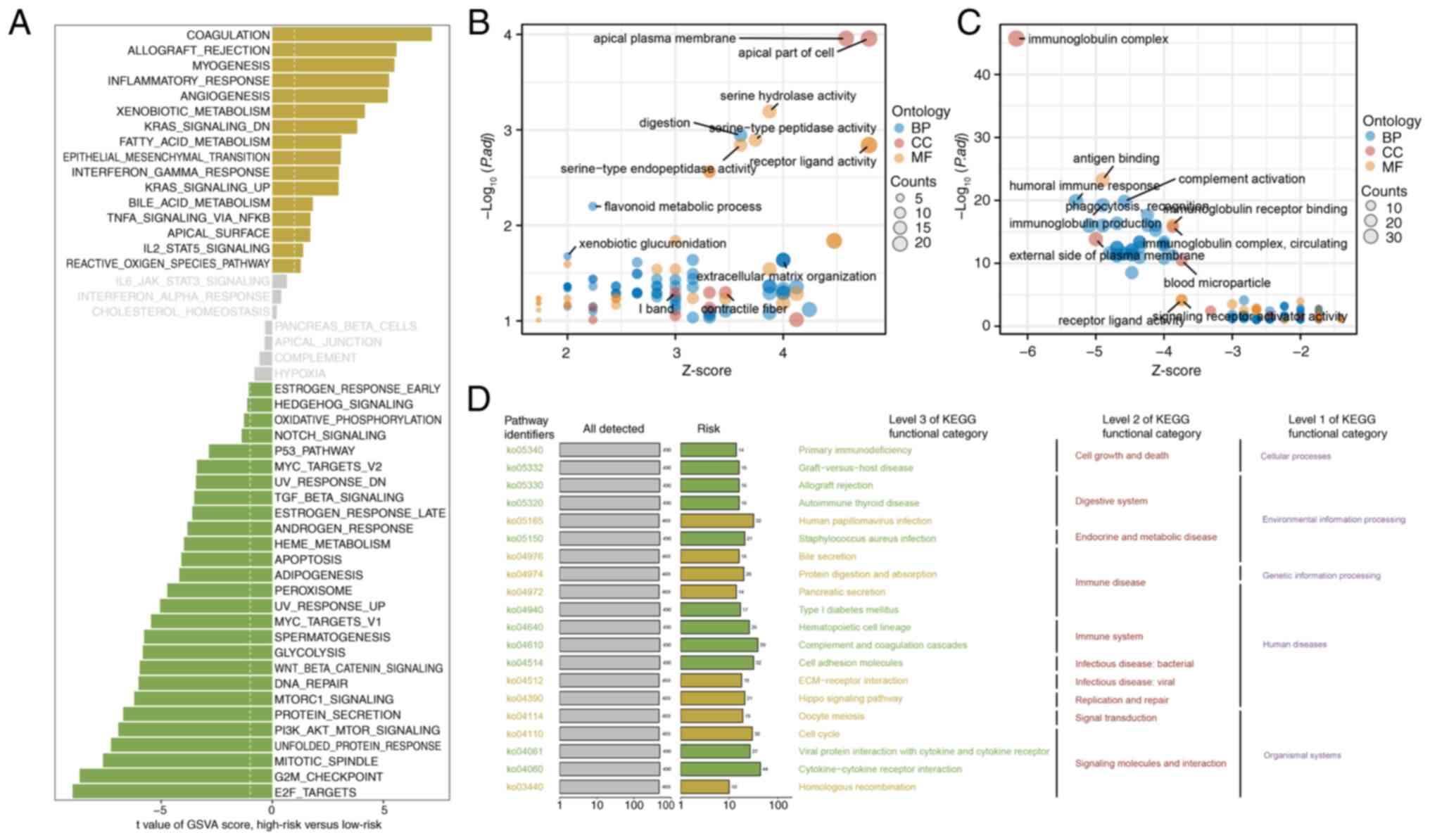
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:12–49.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zheng Z, Mei J, Guan R, Zhang J, Xiong X,
Gan J, Li S and Guo R: A novel liver-function-indicators-based
prognosis signature for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
treated with anti-programmed cell death-1 therapy. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 73:1582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Antonius Y, Kharisma VD, Widyananda MH,
Ansori ANM, Trinugroho JP, Ullah Md E, Naw SW, Jakhmola V and
Wahjudi M: Prediction of aflatoxin-B1 (AFB1) molecular mechanism
network and interaction to oncoproteins growth factor in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pure Appl Microbiol. 16:1844–1854.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jia G, He P, Dai T, Goh D, Wang J, Sun M,
Wee F, Li F, Lim JCT, Hao S, et al: Spatial immune scoring system
predicts hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. Nature.
640:1031–1041. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu B and Ma W: Biomarker discovery in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) for personalized treatment and
enhanced prognosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 79:29–38. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li M, Yang Y, Xiong L, Jiang P, Wang J and
Li C: Metabolism, metabolites, and macrophages in cancer. J Hematol
Oncol. 16:802023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brockmann L, Tran A, Huang Y, Edwards M,
Ronda C, Wang HH and Ivanov II: Intestinal microbiota-specific Th17
cells possess regulatory properties and suppress effector T cells
via c-MAF and IL-10. Immunity. 56:2719–2735.e7. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pascual-García M, Bonfill-Teixidor E,
Planas-Rigol E, Rubio-Perez C, Iurlaro R, Arias A, Cuartas I,
Sala-Hojman A, Escudero L, Martínez-Ricarte F, et al: LIF regulates
CXCL9 in tumor-associated macrophages and prevents CD8+ T cell
tumor-infiltration impairing anti-PD1 therapy. Nat Commun.
10:24162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han S, Bao X, Zou Y, Wang L, Li Y, Yang L,
Liao A, Zhang X, Jiang X, Liang D, et al: d-lactate modulates M2
tumor-associated macrophages and remodels immunosuppressive tumor
microenvironment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Adv.
9:eadg26972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li D, Zhang T, Guo Y, Bi C, Liu M and Wang
G: Biological impact and therapeutic implication of
tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell
Death Dis. 15:4982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Han G, Gu J, Chen Z and Wu J:
Role of tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma:
impact, mechanism, and therapy. Front Immunol. 15:14298122024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun Y, Zhao M, Cheng L, He X, Shen S, Lv
J, Zhang J, Shao Q, Yin W, Zhao F, et al: Reduction of alternative
polarization of macrophages by short-term activated hepatic
stellate cell-derived small extracellular vesicles. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 44:1172025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Du Y, Wu S, Xi S, Xu W, Sun L, Yan J, Gao
H, Wang Y, Zheng J, Wang F, et al: ASH1L in hepatoma cells and
hepatic stellate cells promotes fibrosis-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma by modulating tumor-associated macrophages. Adv Sci
(Weinh). 11:e24047562024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jeong JM, Choi SE, Shim YR, Kim HH, Lee
YS, Yang K, Kim K, Kim MJ, Chung KPS, Kim SH, et al: CX 3 CR1 +
macrophages interact with HSCs to promote HCC through CD8 + T-cell
suppression. Hepatology. 82:655–668. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai J, Song L, Zhang F, Wu S, Zhu G, Zhang
P, Chen S, Du J, Wang B, Cai Y, et al: Targeting SRSF10 might
inhibit M2 macrophage polarization and potentiate anti-PD-1 therapy
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Commun (Lond). 44:1231–1260.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ,
Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M and Alizadeh AA: Robust enumeration
of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods.
12:453–457. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aran D, Hu Z and Butte AJ: xCell:
Digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape.
Genome Biol. 18:2202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mellman I, Chen DS, Powles T and Turley
SJ: The cancer-immunity cycle: Indication, genotype, and
immunotype. Immunity. 56:2188–2205. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Finotello F, Mayer C, Plattner C,
Laschober G, Rieder D, Hackl H, Krogsdam A, Loncova Z, Posch W,
Wilflingseder D, et al: Molecular and pharmacological modulators of
the tumor immune contexture revealed by deconvolution of RNA-seq
data. Genome Med. 11:342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Racle J, de Jonge K, Baumgaertner P,
Speiser DE and Gfeller D: Simultaneous enumeration of cancer and
immune cell types from bulk tumor gene expression data. Elife.
6:e264762017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Becht E, Giraldo NA, Lacroix L, Buttard B,
Elarouci N, Petitprez F, Selves J, Laurent-Puig P, Sautès-Fridman
C, Fridman WH and de Reyniès A: Estimating the population abundance
of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using
gene expression. Genome Biol. 17:2182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R and Guinney J:
GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data.
BMC Bioinformatics. 14:72013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang G, Liu T and He WT: Visualization
analysis of research hotspots and trends on gastrointestinal tumor
organoids. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 16:2826–2841. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang P, Gu S, Pan D, Fu J, Sahu A, Hu X,
Li Z, Traugh N, Bu X, Li B, et al: Signatures of T cell dysfunction
and exclusion predict cancer immunotherapy response. Nat Med.
24:1550–1558. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kalhor K, Chen CJ, Lee HS, Cai M, Nafisi
M, Que R, Palmer CR, Yuan Y, Zhang Y, Li X, et al: Mapping human
tissues with highly multiplexed RNA in situ hybridization. Nat
Commun. 15:25112024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Han Y, Wang Y, Dong X, Sun D, Liu Z, Yue
J, Wang H, Li T and Wang C: TISCH2: expanded datasets and new tools
for single-cell transcriptome analyses of the tumor
microenvironment. Nucleic Acids Res. 51:D1425–D1431. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang X, Yang C, Zhang S, Geng H, Zhu AX,
Bernards R, Qin W, Fan J, Wang C and Gao Q: Precision treatment in
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 42:180–197. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ruf B, Bruhns M, Babaei S, Kedei N, Ma L,
Revsine M, Benmebarek MR, Ma C, Heinrich B, Subramanyam V, et al:
Tumor-associated macrophages trigger MAIT cell dysfunction at the
HCC invasive margin. Cell. 186:3686–3705.e32. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jin R, Neufeld L and McGaha TL: Linking
macrophage metabolism to function in the tumor microenvironment.
Nat Cancer. 6:239–252. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeng W, Li F, Jin S, Ho PC, Liu PS and Xie
X: Functional polarization of tumor-associated macrophages dictated
by metabolic reprogramming. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 42:2452023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang D, Zhao K, Han T, Zhang X, Xu X, Liu
Z, Ren X, Zhang X, Lu Z and Qin C: Bisphenol A promote the cell
proliferation and invasion ability of prostate cancer cells via
regulating the androgen receptor. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf.
269:1158182024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cai J, Chen T, Jiang Z, Yan J, Ye Z, Ruan
Y, Tao L, Shen Z, Liang X, Wang Y, et al: Bulk and single-cell
transcriptome profiling reveal extracellular matrix mechanical
regulation of lipid metabolism reprograming through YAP/TEAD4/ACADL
axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci. 19:2114–2131.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qu X, Zhao X, Lin K, Wang N, Li X, Li S,
Zhang L and Shi Y: M2-like tumor-associated macrophage-related
biomarkers to construct a novel prognostic signature, reveal the
immune landscape, and screen drugs in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Front Immunol. 13:9940192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen S, Zhang P, Zhu G, Wang B, Cai J,
Song L, Wan J, Yang Y, Du J, Cai Y, et al: Targeting GSDME-mediated
macrophage polarization for enhanced antitumor immunity in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Mol Immunol. 21:1505–1521. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vizcaino Castro A, Daemen T and Oyarce C:
Strategies to reprogram anti-inflammatory macrophages towards
pro-inflammatory macrophages to support cancer immunotherapies.
Immunol Lett. 267:1068642024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mace EM: Human natural killer cells: Form,
function, and development. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 151:371–385.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang G, Xiao S, Jiang Z, Zhou X, Chen L,
Long L, Zhang S, Xu K, Chen J and Jiang B: Machine learning
immune-related gene based on KLRB1 model for predicting the
prognosis and immune cell infiltration of breast cancer. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 14:11857992023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|