|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–48.
2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
National Lung Screening Trial Research
Team, . Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, Black WC, Clapp JD,
Fagerstrom RM, Gareen IF, Gatsonis C, Marcus PM and Sicks JD:
Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic
screening. N Engl J Med. 365:395–409. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, Michalski
J, Straube W, Bradley J, Fakiris A, Bezjak A, Videtic G, Johnstone
D, et al: Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early
stage lung cancer. JAMA. 303:1070–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun B, Brooks ED, Komaki R, Liao Z, Jeter
M, McAleer M, Balter PA, Welsh JD, O'Reilly M, Gomez D, et al:
Long-term outcomes of salvage stereotactic ablative radiotherapy
for isolated lung recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer: A phase
II clinical trial. J Thorac Oncol. 12:983–992. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG,
Hui R, Csőszi T, Fülöp A, Gottfried M, Peled N, Tafreshi A, Cuffe
S, et al: Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive
non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 375:1823–1833. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, Seto T, Crinó
L, Ahn MJ, De Pas T, Besse B, Solomon BJ, Blackhall F, et al:
Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 368:2385–2394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Riely GJ, Wood DE, Ettinger DS, Aisner DL,
Akerley W, Bauman JR, Bharat A, Bruno DS, Chang JY, Chirieac LR, et
al: Non-Small cell lung cancer, version 4.2024, NCCN clinical
practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
22:249–274. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Filipowska J, Kondegowda NG, Leon-Rivera
N, Dhawan S and Vasavada RC: LGR4, a G protein-coupled receptor
with a systemic role: From development to metabolic regulation.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:8670012022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ordaz-Ramos A, Rosales-Gallegos VH,
Melendez-Zajgla J, Maldonado V and Vazquez-Santillan K: The role of
LGR4 (GPR48) in normal and cancer processes. Int J Mol Sci.
22:46902021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zheng H, Liu J, Cheng Q, Zhang Q, Zhang Y,
Jiang L, Huang Y, Li W, Zhao Y, Chen G, et al: Targeted activation
of ferroptosis in colorectal cancer via LGR4 targeting overcomes
acquired drug resistance. Nat Cancer. 5:572–589. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yue Z, Yuan Z, Zeng L, Wang Y, Lai L, Li
J, Sun P, Xue X, Qi J, Yang Z, et al: LGR4 modulates breast cancer
initiation, metastasis, and cancer stem cells. FASEB J.
32:2422–2437. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liang F, Zhang H, Cheng D, Gao H, Wang J,
Yue J, Zhang N, Wang J, Wang Z and Zhao B: Ablation of LGR4
signaling enhances radiation sensitivity of prostate cancer cells.
Life Sci. 265:1187372021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Annunziato S, Sun T and Tchorz JS: The
RSPO-LGR4/5-ZNRF3/RNF43 module in liver homeostasis, regeneration,
and disease. Hepatology. 76:888–899. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Planas-Paz L, Orsini V, Boulter L,
Calabrese D, Pikiolek M, Nigsch F, Xie Y, Roma G, Donovan A, Marti
P, et al: The RSPO-LGR4/5-ZNRF3/RNF43 module controls liver
zonation and size. Nat Cell Biol. 18:467–479. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yue F, Jiang W, Ku AT, Young AIJ, Zhang W,
Souto EP, Gao Y, Yu Z, Wang Y, Creighton CJ, et al: A
Wnt-independent LGR4-egfr signaling axis in cancer metastasis.
Cancer Res. 81:4441–4454. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC,
Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, Meyer L, Gress DM, Byrd DR and
Winchester DP: The eighth edition AJCC cancer staging manual:
Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more
‘personalized’ approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin.
67:93–99. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dorsam RT and Gutkind JS:
G-protein-coupled receptors and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:79–94.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fang Q, Ye L, Han L, Yao S, Cheng Q, Wei
X, Zhang Y, Huang J, Ning G, Wang J, et al: LGR4 is a key regulator
of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med. 229:183–194. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang YY, Zhou YM, Xu JZ, Sun LH, Tao B,
Wang WQ, Wang JQ, Zhao HY and Liu JM: Lgr4 promotes aerobic
glycolysis and differentiation in osteoblasts via the canonical
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 36:1605–1620. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang L, Wang J, Gong X, Fan Q, Yang X, Cui
Y, Gao X, Li L, Sun X, Li Y and Wang Y: Emerging roles for LGR4 in
organ development, energy metabolism and carcinogenesis. Front
Genet. 12:7288272022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Steffen JS, Simon E, Warneke V, Balschun
K, Ebert M and Röcken C: LGR4 and LGR6 are differentially expressed
and of putative tumor biological significance in gastric carcinoma.
Virchows Arch. 461:355–365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cui J, Toh Y, Park S, Yu W, Tu J, Wu L, Li
L, Jacob J, Pan S, Carmon KS and Liu QJ: Drug conjugates of
antagonistic R-spondin 4 mutant for simultaneous targeting of
leucine-rich repeat-containing g protein-coupled receptors 4/5/6
for cancer treatment. J Med Chem. 64:12572–12581. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yue Z, Niu X, Yuan Z, Qin Q, Jiang W, He
L, Gao J, Ding Y, Liu Y, Xu Z, et al: RSPO2 and RANKL signal
through LGR4 to regulate osteoclastic premetastatic niche formation
and bone metastasis. J Clin Invest. 132:e1445792022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang D, Li JS, Xu QY, Xia T and Xia JH:
Inhibitory effect of MiR-449b on cancer cell growth and invasion
through LGR4 in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Curr Med Sci.
38:582–589. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
de Lau W, Barker N, Low TY, Koo BK, Li VS,
Teunissen H, Kujala P, Haegebarth A, Peters PJ, van de Wetering M,
et al: Lgr5 homologues associate with Wnt receptors and mediate
R-spondin signalling. Nature. 476:293–297. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luo J, Yang Z, Ma Y, Yue Z, Lin H, Qu G,
Huang J, Dai W, Li C, Zheng C, et al: LGR4 is a receptor for RANKL
and negatively regulates osteoclast differentiation and bone
resorption. Nat Med. 22:539–546. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
de Lau W, Peng WC, Gros P and Clevers H:
The R-spondin/Lgr5/Rnf43 module: Regulator of Wnt signal strength.
Genes Dev. 28:305–316. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Han XH, Jin YR, Tan L, Kosciuk T, Lee JS
and Yoon JK: Regulation of the follistatin gene by RSPO-LGR4
signaling via activation of the WNT/β-catenin pathway in skeletal
myogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 34:752–764. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yi Z, Ma T, Liu J, Tie W, Li Y, Bai J, Li
L and Zhang L: LGR4 promotes tumorigenesis by activating
TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway in multiple myeloma. Cell Signal.
110:1108142023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liang F, Yue J, Wang J, Zhang L, Fan R,
Zhang H and Zhang Q: GPCR48/LGR4 promotes tumorigenesis of prostate
cancer via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Med Oncol. 32:492015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|















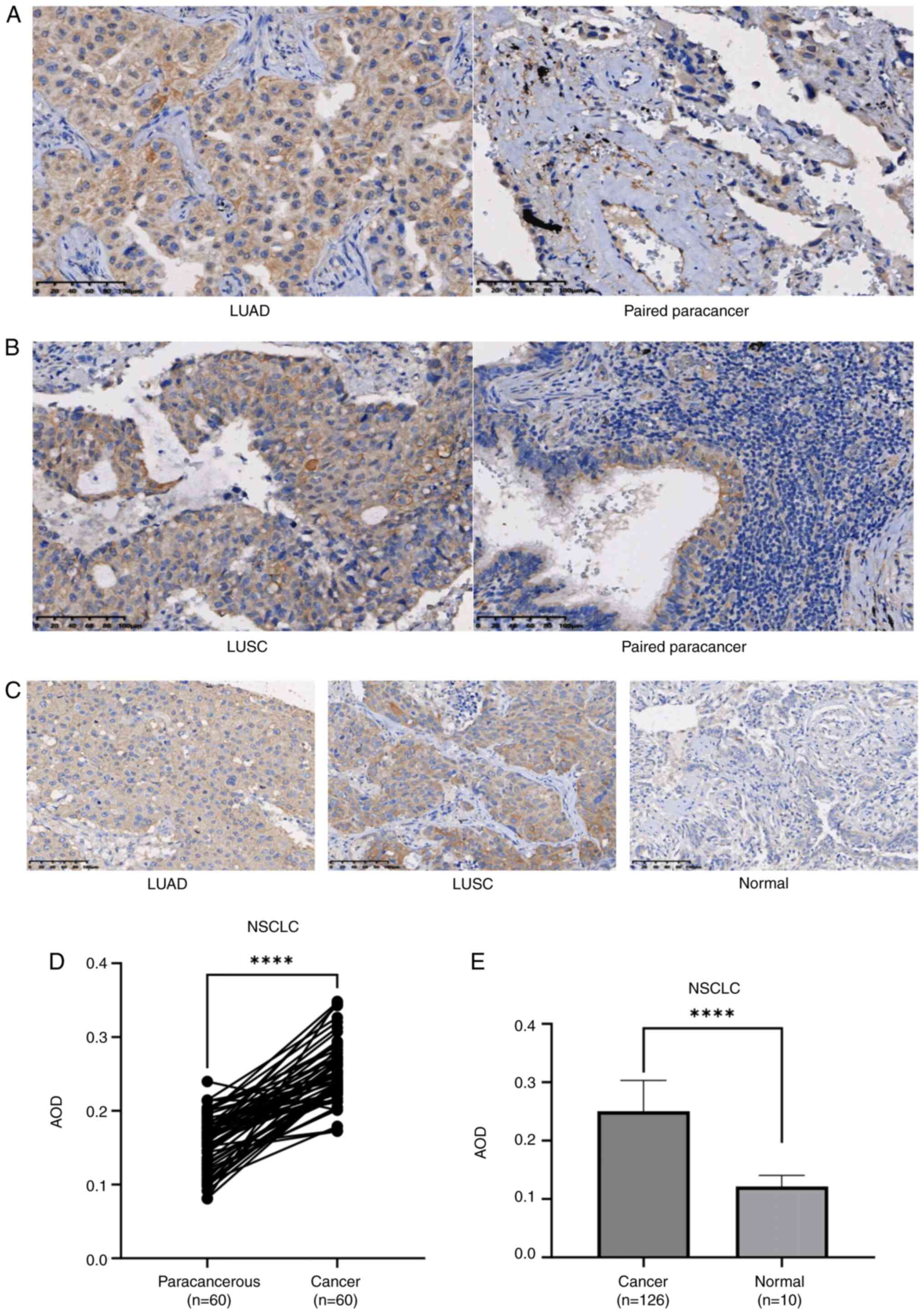
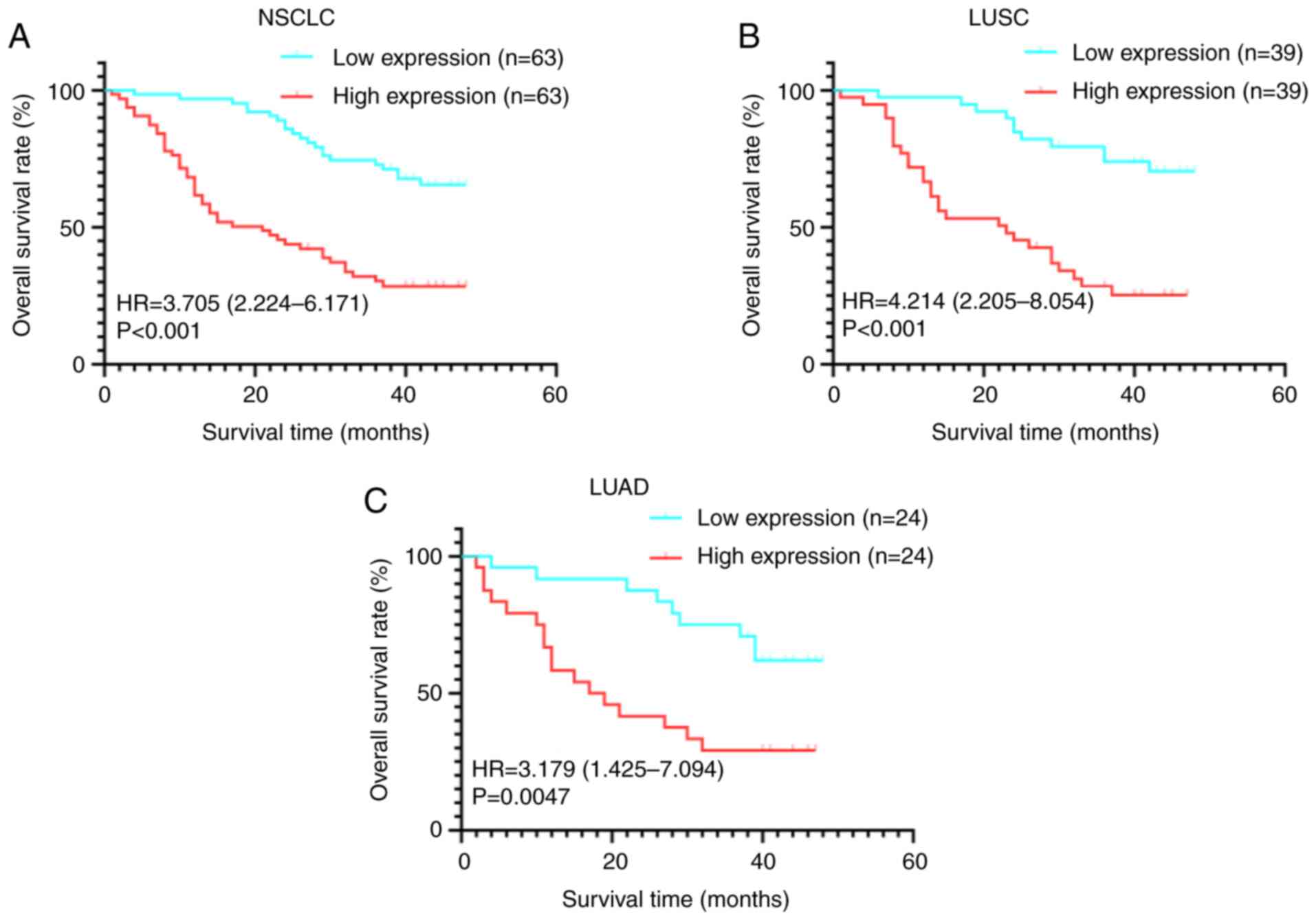
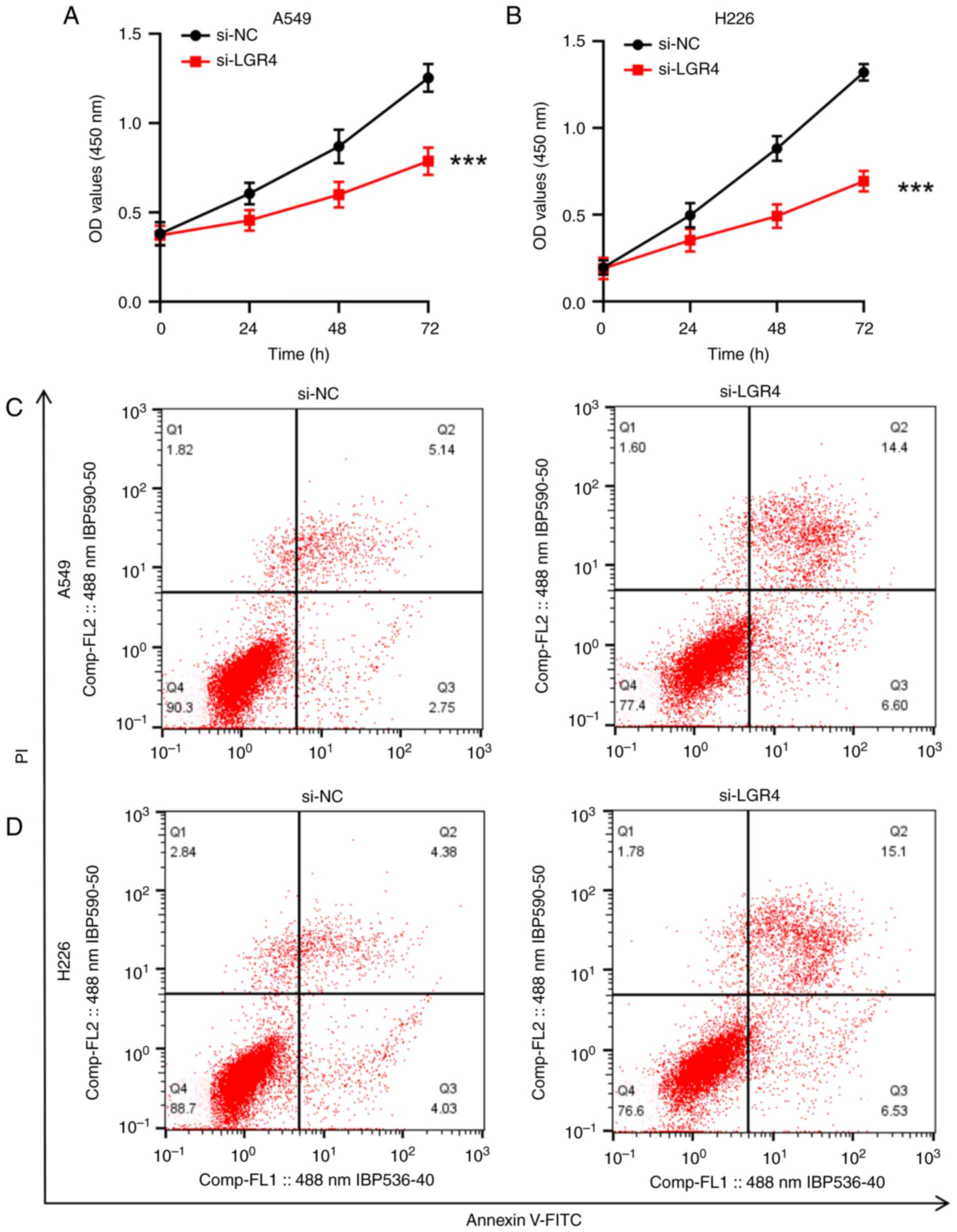
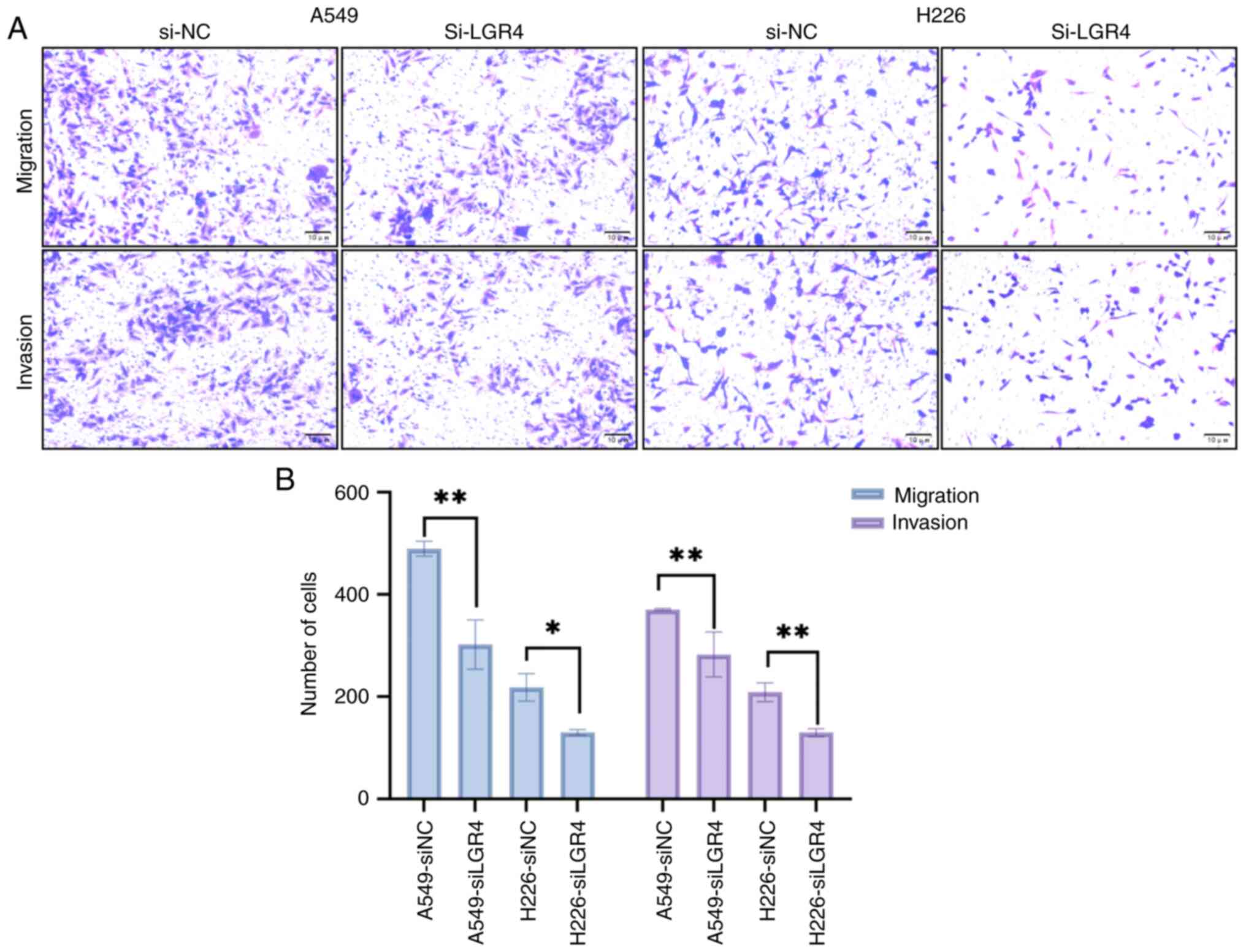
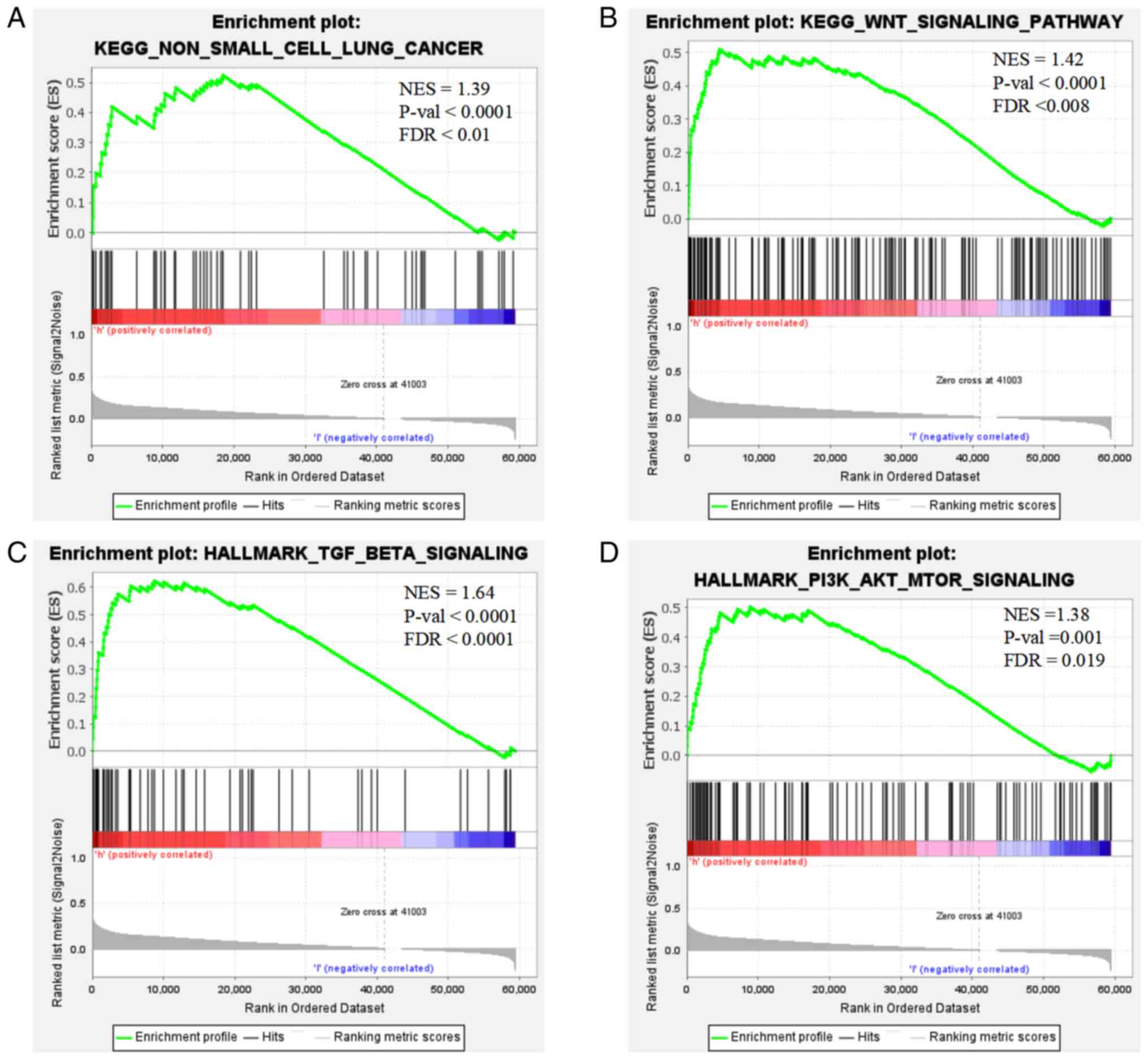
![LGR4 is highly expressed in NSCLC. (A)
Unpaired analysis. TCGA [NSCLC (n=1,043) vs. healthy tissues
(n=110); unpaired Student's t-test]. (B) High LGR4 expression is
associated with a poor prognosis in patients with NSCLC (data
fromTCGA). (C) Western blot analysis showed the expression level of
LGR4 protein in NSCLC cell lines. *P<0.05, **P<0.01,
***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001. (D) RT-qPCR analysis showed the
expression level of LGR4 mRNA in NSCLC cell lines (one-way ANOVA
followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test). (E) RT-qPCR
analysis showed that si-LGR4 transfection significantly reduced
LGR4 expression in A549 and H226 cells compared with the si-NC
group (one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison
test). LGR4, leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled
receptor 4; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; TCGA, The Cancer
Genome Atlas; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR;
si-NC, small-interfering RNA negative control.](/article_images/ol/30/6/ol-30-06-15304-g00.jpg)