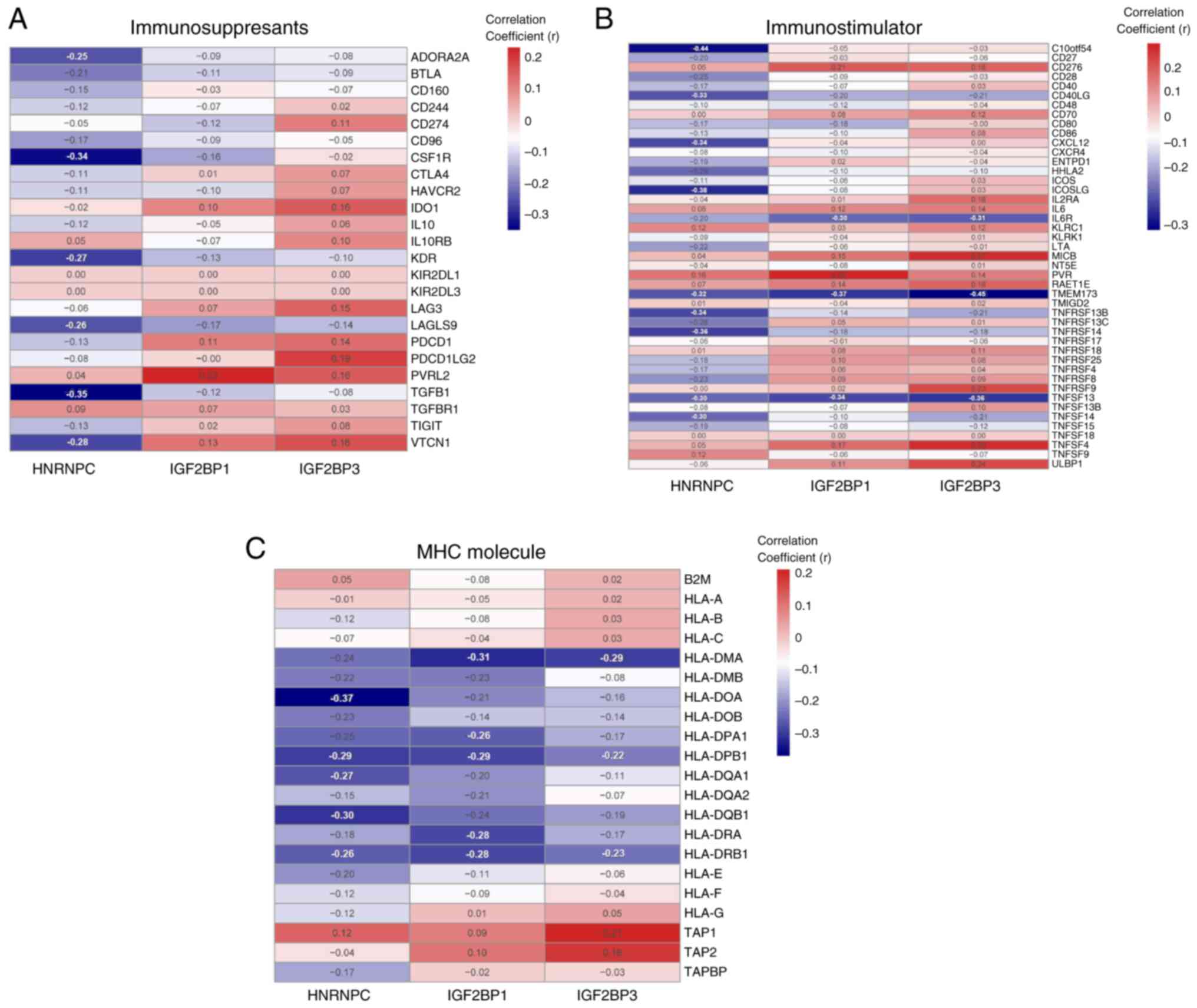
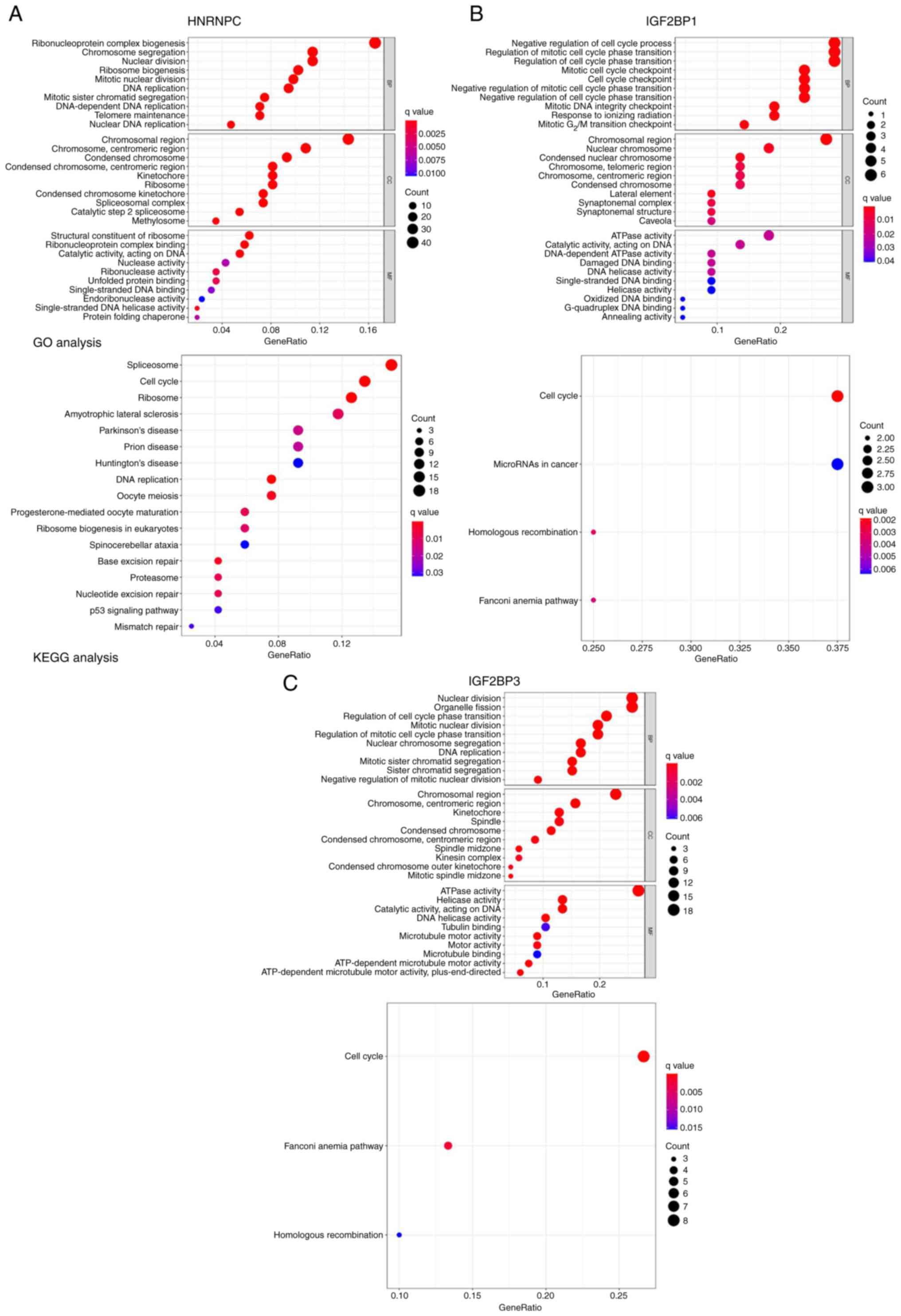
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M and Sung H: Global
cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and
mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J
Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen D, Wang R, Yu C, Cao F, Zhang X, Yan
F, Chen L, Zhu H, Yu Z and Feng J: FOX-A1 contributes to
acquisition of chemoresistance in human lung adenocarcinoma via
transactivation of SOX5. EBioMedicine. 44:150–161. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rizzo A: Identifying optimal first-line
treatment for advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma with high
PD-L1 expression: A matter of debate. Br J Cancer. 127:1381–1382.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sahin TK, Ayasun R, Rizzo A and Guven DC:
Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-eosinophil ratio (NER) in cancer:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel).
16:36892024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bas O, Sahin TK, Karahan L, Rizzo A and
Guven DC: Prognostic significance of the cachexia index (CXI) in
patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin
Nutr ESPEN. 68:240–247. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lamberti G, Andrini E, Sisi M, Rizzo A,
Parisi C, Di Federico A, Gelsomino F and Ardizzoni A: Beyond EGFR,
ALK and ROS1: Current evidence and future perspectives on newly
targetable oncogenic drivers in lung adenocarcinoma. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 156:1031192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu F, Hu C, He Y, Sun Y, Han C, Zhang X,
Yu L, Shi D, Sun Y, Zhang J, et al: TLR7: A key prognostic
biomarker and immunotherapeutic target in lung adenocarcinoma.
Biomedicines. 13:1512025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang H and Lin J: Comprehensive analysis
of co-expressed genes with TDP-43: Prognostic and therapeutic
potential in lung adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
150:442024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kwok CT, Marshall AD, Rasko JE and Wong
JJ: Genetic alterations of m(6)A regulators predict poorer survival
in acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 10:392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Adamopoulos PG, Athanasopoulou K, Daneva
GN and Scorilas A: The repertoire of RNA modifications orchestrates
a plethora of cellular responses. Int J Mol Sci. 24:23872023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Balacco DL, Hewitt BJ, Bardhan A, Shriane
LM, Hunjan M, Hickerson R, Heagerty AHM and Chapple IL: Unlocking
the potential: m6A-RNA methylation in severe epidermolysis bullosa
simplex. Biosci Rep. 45:429–438. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bai R, Sun M, Chen Y, Zhuo S, Song G, Wang
T and Zhang Z: H19 recruited N 6-methyladenosine (m 6 A) reader
YTHDF1 to promote SCARB1 translation and facilitate angiogenesis in
gastric cancer. Chin Med J. 136:1719–1731. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen J, Zhang YC, Huang C, Shen H, Sun B,
Cheng X, Zhang YJ, Yang YG, Shu Q, Yang Y and Li X: m6A
regulates neurogenesis and neuronal development by modulating
histone methyltransferase Ezh2. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics.
17:154–168. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Athanasopoulou K and Adamopoulos PG: New
insights into the dynamics of m6A epitranscriptome: Hybrid-seq
identifies novel mRNAs of the m6A writers METTL3/14. Epigenomics.
16:1159–1174. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Alarcón CR, Goodarzi H, Lee H, Liu X,
Tavazoie S and Tavazoie SF: HNRNPA2B1 is a mediator of
m(6)A-dependent nuclear RNA processing events. Cell. 162:1299–1308.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rong ZX, Li Z, He JJ, Liu LY, Ren XX, Gao
J, Mu Y, Guan YD, Duan YM, Zhang XP, et al: Downregulation of fat
mass and obesity associated (FTO) promotes the progression of
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 9:3692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen XY, Zhang J and Zhu JS: The role of
m6A RNA methylation in human cancer. Mol Cancer.
18:1032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Y, Li Y, Yue M, Wang J, Kumar S,
Wechsler-Reya RJ, Zhang Z, Ogawa Y, Kellis M, Duester G and Zhao
JC: N(6)-methyladenosine RNA modification regulates embryonic
neural stem cell self-renewal through histone modifications. Nat
Neurosci. 21:195–206. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jung H, Kim HS, Kim JY, Sun JM, Ahn JS,
Ahn MJ, Park K, Esteller M, Lee SH and Choi JK: DNA methylation
loss promotes immune evasion of tumours with high mutation and copy
number load. Nat Commun. 10:42782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cho JW, Hong MH, Ha SJ, Kim YJ, Cho BC,
Lee I and Kim HR: Genome-wide identification of differentially
methylated promoters and enhancers associated with response to
anti-PD-1 therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Exp Mol Med.
52:1550–1563. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chenard S, Jackson C, Vidotto T, Chen L,
Hardy C, Jamaspishvilli T, Berman D, Siemens DR and Koti M: Sexual
Dimorphism in outcomes of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A
role of CD163+ macrophages, B cells, and PD-L1 immune checkpoint.
Eur Urol Open Sci. 29:50–58. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yuan K, Zhao S, Ye B, Wang Q, Liu Y, Zhang
P, Xie J, Chi H, Chen Y, Cheng C and Liu J: A novel T-cell
exhaustion-related feature can accurately predict the prognosis of
OC patients. Front Pharmacol. 14:11927772023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim JY, Choi JK and Jung H: Genome-wide
methylation patterns predict clinical benefit of immunotherapy in
lung cancer. Clin Epigenetics. 12:1192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu R, Lee YJ, Kim CH, Min GH, Kim YB, Park
JW, Kim DH, Kim JH and Yim H: Invasive FoxM1 phosphorylated by PLK1
induces the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages to promote
immune escape and metastasis, amplified by IFITM1. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 42:3022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Olawaiye AB, Baker TP, Washington MK and
Mutch DG: The new (Version 9) American Joint Committee on Cancer
tumor, node, metastasis staging for cervical cancer. CA Cancer J
Clin. 71:287–298. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono
H and Kanehisa M: KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.
Nucleic Acids Res. 27:29–34. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kanehisa M: Toward understanding the
origin and evolution of cellular organisms. Protein Sci.
28:1947–1951. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Sato Y, Kawashima
M and Ishiguro-Watanabe M: KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of
pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 51:D587–D592. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Y, Yuan Y, Li Y, Zhang P, Chen P and
Sun S: An inverse interaction between HOXA11 and HOXA11-AS is
associated with cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma.
Epigenetics. 14:949–960. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kanda M, Sugimoto H and Kodera Y: Genetic
and epigenetic aspects of initiation and progression of
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 21:10584–10597.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu M, Chen X, Lin K, Zeng K, Liu X, Pan B,
Xu X, Xu T, Hu X, Sun L, et al: The long noncoding RNA SNHG1
regulates colorectal cancer cell growth through interactions with
EZH2 and miR-154-5p. Mol Cancer. 17:1412018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou J, Wang J, Hong B, Ma K, Xie H, Li L,
Zhang K, Zhou B, Cai L and Gong K: Gene signatures and prognostic
values of m6A regulators in clear cell renal cell carcinoma-a
retrospective study using TCGA database. Aging (Albany NY).
11:1633–1647. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lin S, Liu J, Jiang W, Wang P, Sun C, Wang
X, Chen Y and Wang H: METTL3 promotes the proliferation and
mobility of gastric cancer cells. Open Med (Wars). 14:25–31. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Luo Y, Zeng C, Ouyang Z, Zhu W, Wang J,
Chen Z, Xiao C, Wu G, Li L, Qian Y, et al: YTH domain family
protein 3 accelerates non-small cell lung cancer immune evasion
through targeting CD8(+) T lymphocytes. Cell Death Discov.
10:3202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yuan S, Xi S, Weng H, Guo MM, Zhang JH, Yu
ZP, Zhang H, Yu Z, Xing Z, Liu MY, et al: YTHDC1 as a tumor
progression suppressor through modulating FSP1-dependent
ferroptosis suppression in lung cancer. Cell Death Differ.
30:2477–2490. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang X, Hu Y, Li X, Zhu C and Chen F:
YTHDC2-mediated m6A mRNA modification of Id3 suppresses cisplatin
resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis.
15:1247–1257. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fang H, Sun Q, Zhou J, Zhang H, Song Q,
Zhang H, Yu G, Guo Y, Huang C, Mou Y, et al: m(6)A methylation
reader IGF2BP2 activates endothelial cells to promote angiogenesis
and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 22:992023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun S, Fei K, Zhang G, Wang J, Yang Y, Guo
W, Yang Z, Wang J, Xue Q, Gao Y and He J: Construction and
comprehensive analyses of a METTL5-associated prognostic signature
with immune implication in lung adenocarcinomas. Front Genet.
11:6171742020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liao M, Li C, Yang R, Li J, Wu K, Zhang J,
Zhu Q, Shi Y and Zhang X: HNRNPC promotes progression of non-small
cell lung cancer by maintaining TFAP2A mRNA stability. Cancer Cell
Int. 25:852025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hu S, Yan X, Bian W and Ni B: The m6A
reader IGF2BP1 manipulates BUB1B expression to affect malignant
behaviors, stem cell properties, and immune resistance of
non-small-cell lung cancer stem cells. Cytotechnology. 75:517–532.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fujiwara Y, Takahashi RU, Saito M,
Umakoshi M, Shimada Y, Koyama K, Yatabe Y, Watanabe SI, Koyota S,
Minamiya Y, et al: Oncofetal IGF2BP3-mediated control of microRNA
structural diversity in the malignancy of early-stage lung
adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 121:e24070161212024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Song H, Feng X, Zhang H, Luo Y, Huang J,
Lin M, Jin J, Ding X, Wu S, Huang H, et al: METTL3 and ALKBH5
oppositely regulate m6A modification of TFEB mRNA, which
dictates the fate of hypoxia/reoxygenation-treated cardiomyocytes.
Autophagy. 15:1419–1437. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lan Q, Liu PY, Haase J, Bell JL,
Hüttelmaier S and Liu T: The critical role of RNA m6A
methylation in cancer. Cancer Res. 79:1285–1292. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Deng X, Su R, Weng H, Huang H, Li Z and
Chen J: RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in cancers:
current status and perspectives. Cell Res. 28:507–517. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|