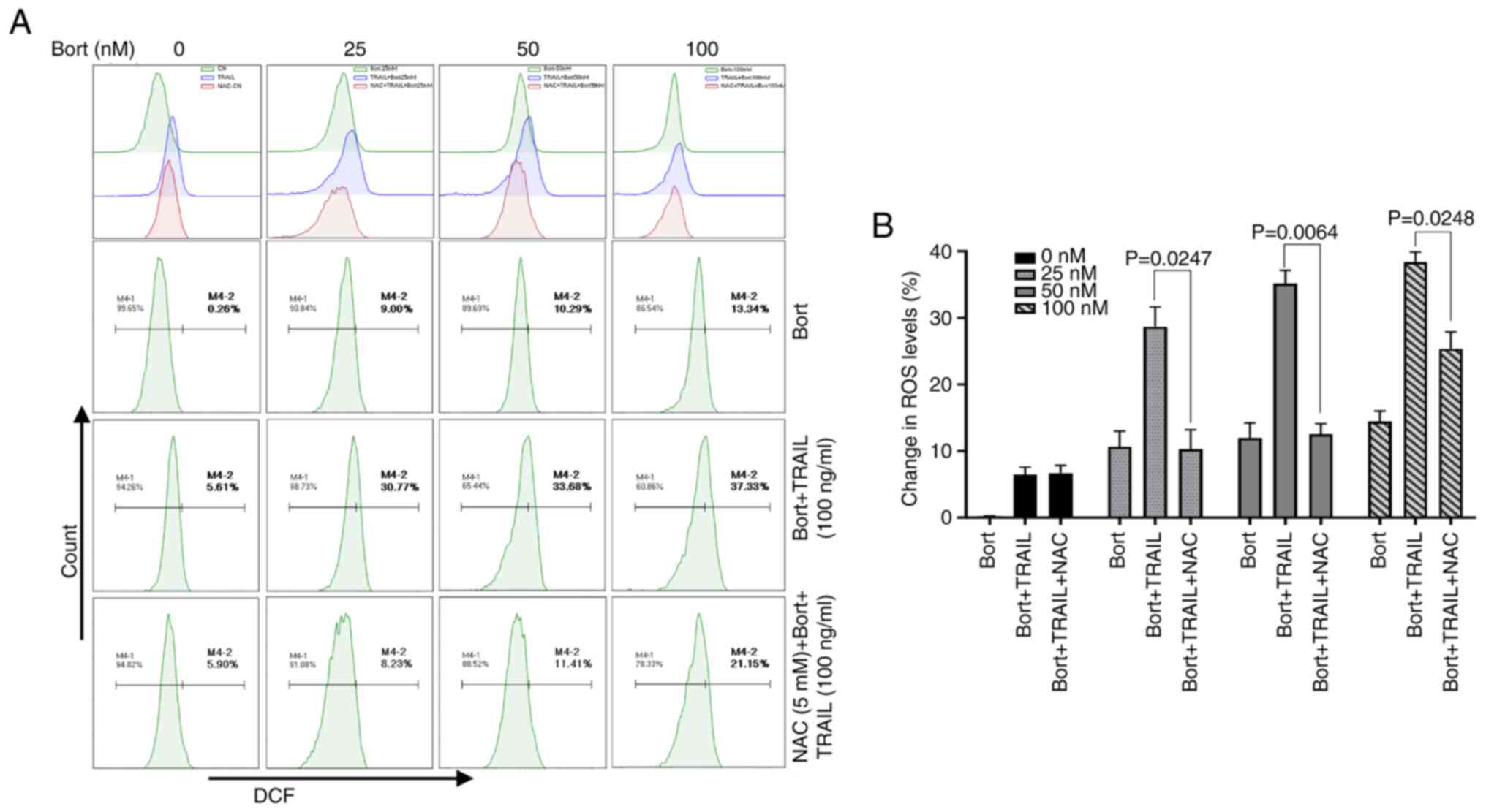
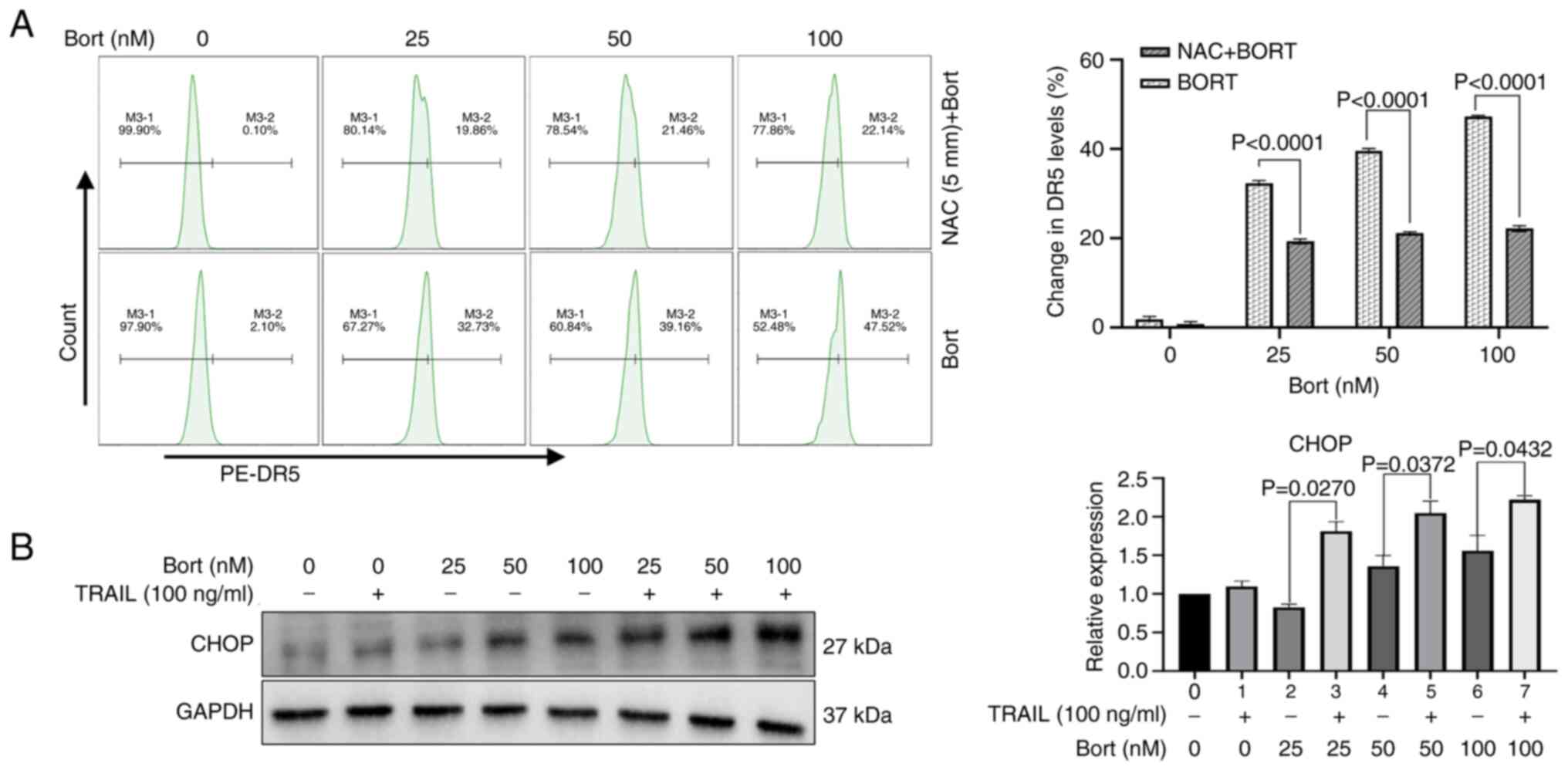
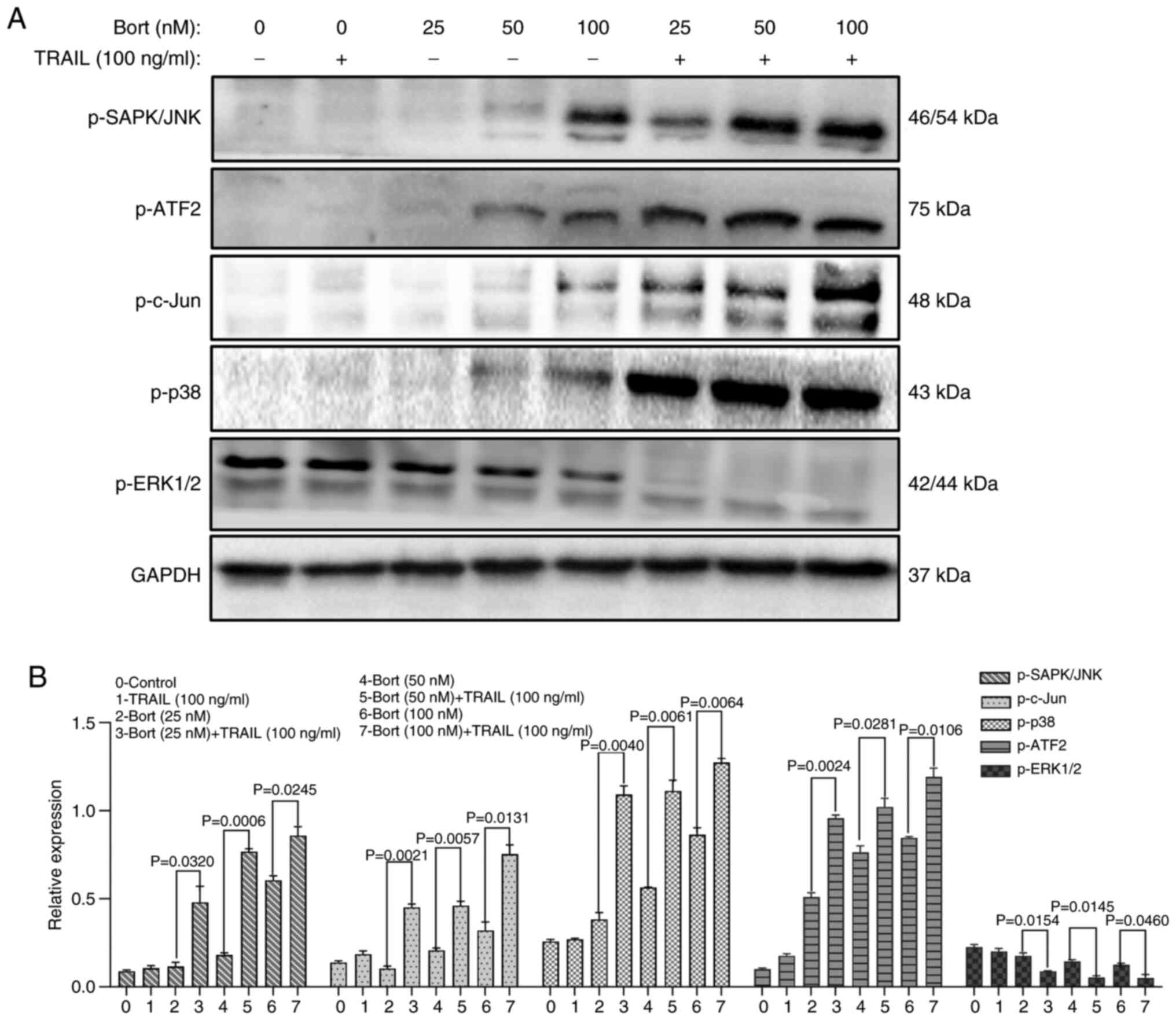
|
1
|
Saleh K, Michot JM, Camara-Clayette V,
Vassetsky Y and Ribrag V: Burkitt and burkitt-like lymphomas: A
systematic review. Curr Oncol Rep. 22:332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sun K, Wu H, Zhu Q, Gu K, Wei H, Wang S,
Li L, Wu C, Chen R, Pang Y, et al: Global landscape and trends in
lifetime risks of haematologic malignancies in 185 countries:
Population-based estimates from GLOBOCAN 2022. EClinicalMedicine.
83:1031932025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chu Y, Liu Y, Fang X, Jiang Y, Ding M, Ge
X, Yuan D, Lu K, Li P, Li Y, et al: The epidemiological patterns of
non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Global estimates of disease burden, risk
factors, and temporal trends. Front Oncol. 13:10599142023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Molyneux EM, Rochford R, Griffin B, Newton
R, Jackson G, Menon G, Harrison CJ, Israels T and Bailey S:
Burkitt's lymphoma. Lancet. 379:1234–1244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Holmes M, Scott GB, Heaton S, Barr T,
Askar B, Müller LME, Jennings VA, Ralph C, Burton C, Melcher A, et
al: Efficacy of coxsackievirus A21 against drug-resistant
neoplastic B cells. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 29:17–29. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jacobson C and LaCasce A: How I treat
Burkitt lymphoma in adults. Blood. 124:2913–2920. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Naimi A, Movassaghpour AA, Hagh MF, Talebi
M, Entezari A, Jadidi-Niaragh F and Solali S: TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) as the potential therapeutic
target in hematological malignancies. Biomed Pharmacother.
98:566–576. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lemke J, von Karstedt S, Zinngrebe J and
Walczak H: Getting TRAIL back on track for cancer therapy. Cell
Death Differ. 21:1350–1364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu FT, Agrawal SG, Gribben JG, Ye H, Du
MQ, Newland AC and Jia L: Bortezomib blocks bax degradation in
malignant B cells during treatment with TRAIL. Blood.
111:2797–2805. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Deng L, Zhai X, Liang P and Cui H:
Overcoming TRAIL resistance for glioblastoma treatment.
Biomolecules. 11:5722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Quiroz-Reyes AG, Delgado-Gonzalez P, Islas
JF, Gallegos JLD, Garza JH and Garza-Trevino EN: Behind the
adaptive and resistance mechanisms of cancer stem cells to TRAIL.
Pharmaceutics. 13:10622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yagolovich AV, Gasparian ME, Isakova AA,
Artykov AA, Dolgikh DA and Kirpichnikov MP: Cytokine TRAIL death
receptor agonists: Design strategies and clinical prospects.
Russian Chemical Reviews. 94:RCR51542025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kundu M, Greer YE, Dine JL and Lipkowitz
S: Targeting TRAIL death receptors in triple-negative breast
cancers: Challenges and strategies for cancer therapy. Cells.
11:37172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thorburn A, Behbakht K and Ford H: TRAIL
receptor-targeted therapeutics: Resistance mechanisms and
strategies to avoid them. Drug Resist Updat. 11:17–24. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cingoz A, Ozyerli-Goknar E, Morova T,
Seker-Polat F, Selvan ME, Gümüş ZH, Bhere D, Shah K, Solaroglu I
and Bagci-Onder T: Generation of TRAIL-resistant cell line models
reveals distinct adaptive mechanisms for acquired resistance and
re-sensitization. Oncogene. 40:3201–3216. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Robak P and Robak T: Bortezomib for the
treatment of hematologic malignancies: 15 years later. Drugs R D.
19:73–92. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bui HTT, Le NH, Le QA, Kim SE, Lee S and
Kang D: Synergistic apoptosis of human gastric cancer cells by
bortezomib and TRAIL. Int J Med Sci. 16:1412–1423. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ryu S, Ahn YJ, Yoon C, Chang JH, Park Y,
Kim TH, Howland AR, Armstrong CA, Song PI and Moon AR: The
regulation of combined treatment-induced cell death with
recombinant TRAIL and bortezomib through TRAIL signaling in
TRAIL-resistant cells. BMC Cancer. 18:4322018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kabore AF, Sun J, Hu X, McCrea K, Johnston
JB and Gibson SB: The TRAIL apoptotic pathway mediates proteasome
inhibitor induced apoptosis in primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia
cells. Apoptosis. 11:1175–1193. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qin X, Chen Z and Chen Y: Sensitivity of
tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligands in B
lymphoma cell lines and mechanisms of apoptosis induction. J
Chengdu Med Coll. 11:413–442. 2016.
|
|
21
|
Pedre B, Barayeu U, Ezeriņa D and Dick TP:
The mechanism of action of N-acetylcysteine (NAC): The emerging
role of H(2)S and sulfane sulfur species. Pharmacol Ther.
228:1079162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang X, Qiao X, Shang Y, Zhang S, Li Y, He
H and Chen SZ: RGD and NGR modified TRAIL protein exhibited potent
anti-metastasis effects on TRAIL-insensitive cancer cells in vitro
and in vivo. Amino Acids. 49:931–941. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chou TC: Drug combination studies and
their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer
Res. 70:440–446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A and Levi-Schaffer F:
Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction.
Apoptosis. 5:415–418. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu M, Wu X, Cui Y, Liu P, Xiao B, Zhang
X, Zhang J, Sun Z, Song M, Shao B and Li Y: Mitophagy and apoptosis
mediated by ROS participate in AlCl(3)-induced MC3T3-E1 cell
dysfunction. Food Chem Toxicol. 155:1123882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim BR, Park SH, Jeong YA, Na YJ, Kim JL,
Jo MJ, Jeong S, Yun HK, Oh SC and Lee DH: RUNX3 enhances
TRAIL-induced apoptosis by upregulating DR5 in colorectal cancer.
Oncogene. 38:3903–3918. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yamaguchi H and Wang HG: CHOP is involved
in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis by enhancing DR5
expression in human carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 279:45495–45502.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Han SH, Lee JH, Woo JS, Jung GH, Jung SH,
Han EJ, Park YS, Kim BS, Kim SK, Park BK, et al: Myricetin induces
apoptosis through the MAPK pathway and regulates JNK-mediated
autophagy in SK-BR-3 cells. Int J Mol Med. 49:542022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
De Wilt L, Sobocki BK, Jansen G, Tabeian
H, de Jong S, Peters GJ and Kruyt F: Mechanisms underlying reversed
TRAIL sensitivity in acquired bortezomib-resistant non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Cancer Drug Resist. 7:122024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xi H, Wang S, Wang B, Hong X, Liu X, Li M,
Shen R and Dong Q: The role of interaction between autophagy and
apoptosis in tumorigenesis (Review). Oncol Rep. 48:2082022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim HJ, Kang S, Kim DY, You S, Park D, Oh
SC and Lee DH: Diallyl disulfide (DADS) boosts TRAIL-Mediated
apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting Bcl-2. Food Chem
Toxicol. 125:354–360. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fresquet V, Rieger M, Carolis C,
Garcia-Barchino MJ and Martinez-Climent JA: Acquired mutations in
BCL2 family proteins conferring resistance to the BH3 mimetic
ABT-199 in lymphoma. Blood. 123:4111–4119. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim R: Unknotting the roles of Bcl-2 and
Bcl-xL in cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 333:336–343.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Waltz F, Salinas-Giege T, Englmeier R,
Meichel H, Soufari H, Kuhn L, Pfeffer S, Förster F, Engel BD, Giegé
P, et al: How to build a ribosome from RNA fragments in
Chlamydomonas mitochondria. Nat Commun. 12:71762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lan Q, Lim U, Liu CS, Weinstein SJ,
Chanock S, Bonner MR, Virtamo J, Albanes D and Rothman N: A
prospective study of mitochondrial DNA copy number and risk of
non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 112:4247–4249. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jin CY, Molagoda IMN, Karunarathne W, Kang
SH, Park C, Kim GY and Choi YH: TRAIL attenuates
sulforaphane-mediated Nrf2 and sustains ROS generation, leading to
apoptosis of TRAIL-resistant human bladder cancer cells. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 352:132–141. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jeong S, Farag AK, Yun HK, Jeong YA, Kim
DY, Jo MJ, Park SH, Kim BR, Kim JL, Kim BG, et al: AF8c, a
multi-kinase inhibitor induces apoptosis by activating DR5/Nrf2 via
ROS in colorectal cancer cells. Cancers (Basel). 14:30432022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lv Z, Hu J, Su H, Yu Q, Lang Y, Yang M,
Fan X, Liu Y, Liu B, Zhao Y, et al: TRAIL induces podocyte
PANoptosis via death receptor 5 in diabetic kidney disease. Kidney
Int. 107:317–331. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim HH, Lee SY and Lee DH: Apoptosis of
pancreatic cancer cells after co-treatment with eugenol and tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Cancers (Basel).
16:30922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liao H, Li X, Zhang H, Yin S, Hong Y, Chen
R, Gui F, Yang L, Yang J and Zhang J: The ototoxicity of
chlorinated paraffins via inducing apoptosis, oxidative stress and
endoplasmic reticulum stress in cochlea hair cells. Ecotoxicol
Environ Saf. 284:1169362024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu M, Yao Y, Chen R, Fu B, Sun Y, Yu Y,
Liu Y, Feng H, Guo S, Yang Y and Zhang C: Effects of melatonin and
3,5,3′-Triiodothyronine on the development of rat granulosa cells.
Nutrients. 16:30852024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rezatabar S, Karimian A, Rameshknia V,
Parsian H, Majidinia M, Kopi TA, Bishayee A, Sadeghinia A, Yousefi
M, Monirialamdari M and Yousefi B: RAS/MAPK signaling functions in
oxidative stress, DNA damage response and cancer progression. J
Cell Physiol. 234:14951–14965. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lewis TS, Shapiro PS and Ahn NG: Signal
transduction through MAP kinase cascades. Adv Cancer Res.
74:49–139. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li HC, Li JY, Wang XC, Zeng M, Wu YK, Chen
YL, Kong CH, Chen KL, Wu JR, Mo ZX, et al: Network pharmacology,
experimental validation and pharmacokinetics integrated strategy to
reveal pharmacological mechanism of goutengsan on methamphetamine
dependence. Front Pharmacol. 15:14805622024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ju Z, Bi Y, Gao M, Yin Y, Xu T and Xu S:
Emamectin benzoate and nanoplastics induce PANoptosis of common
carp (Cyprinus carpio) gill through MAPK pathway. Pestic Biochem
Physiol. 206:1062022024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kciuk M, Gielecinska A, Budzinska A,
Mojzych M and Kontek R: Metastasis and MAPK pathways. Int J Mol
Sci. 23:38472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|