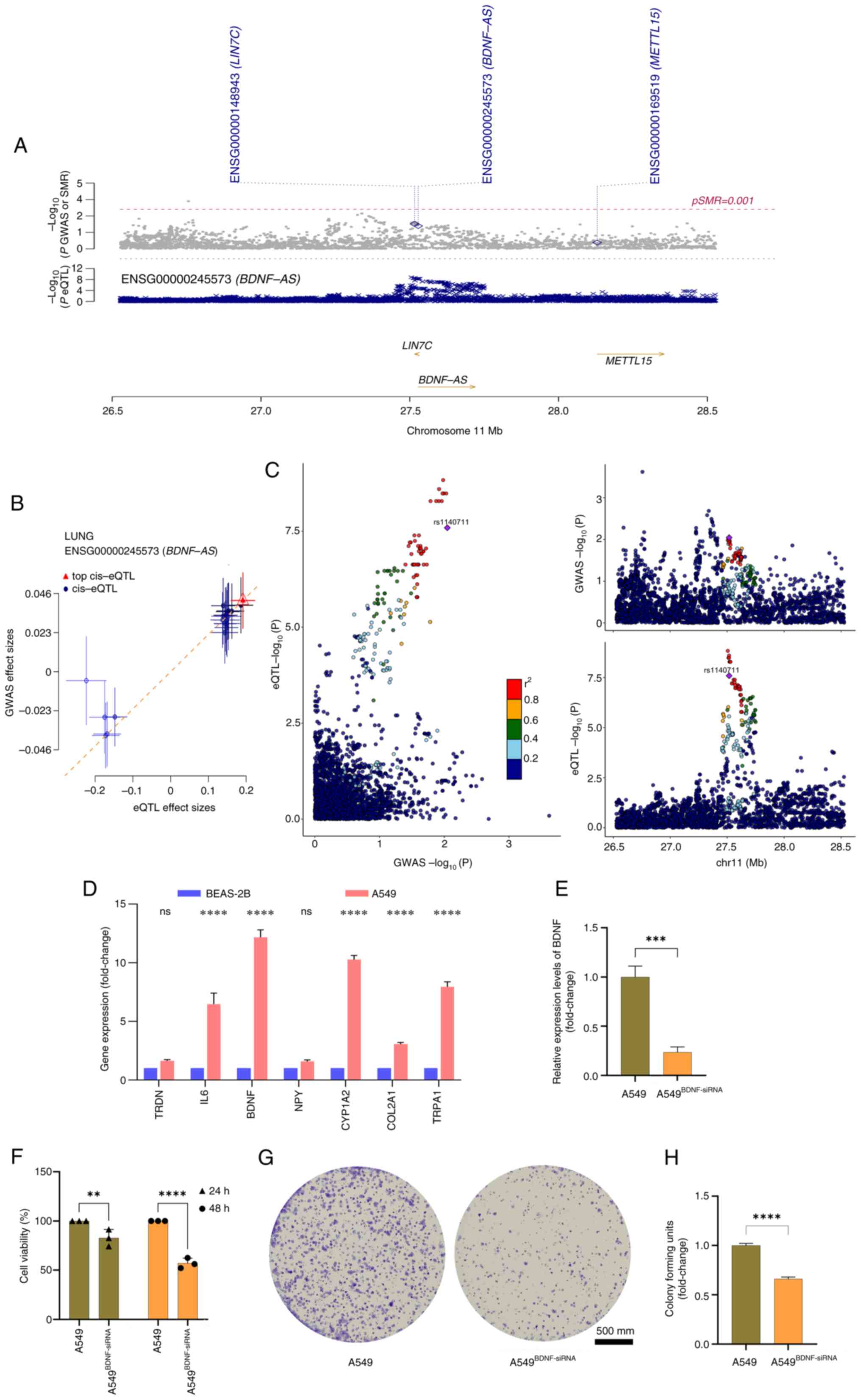
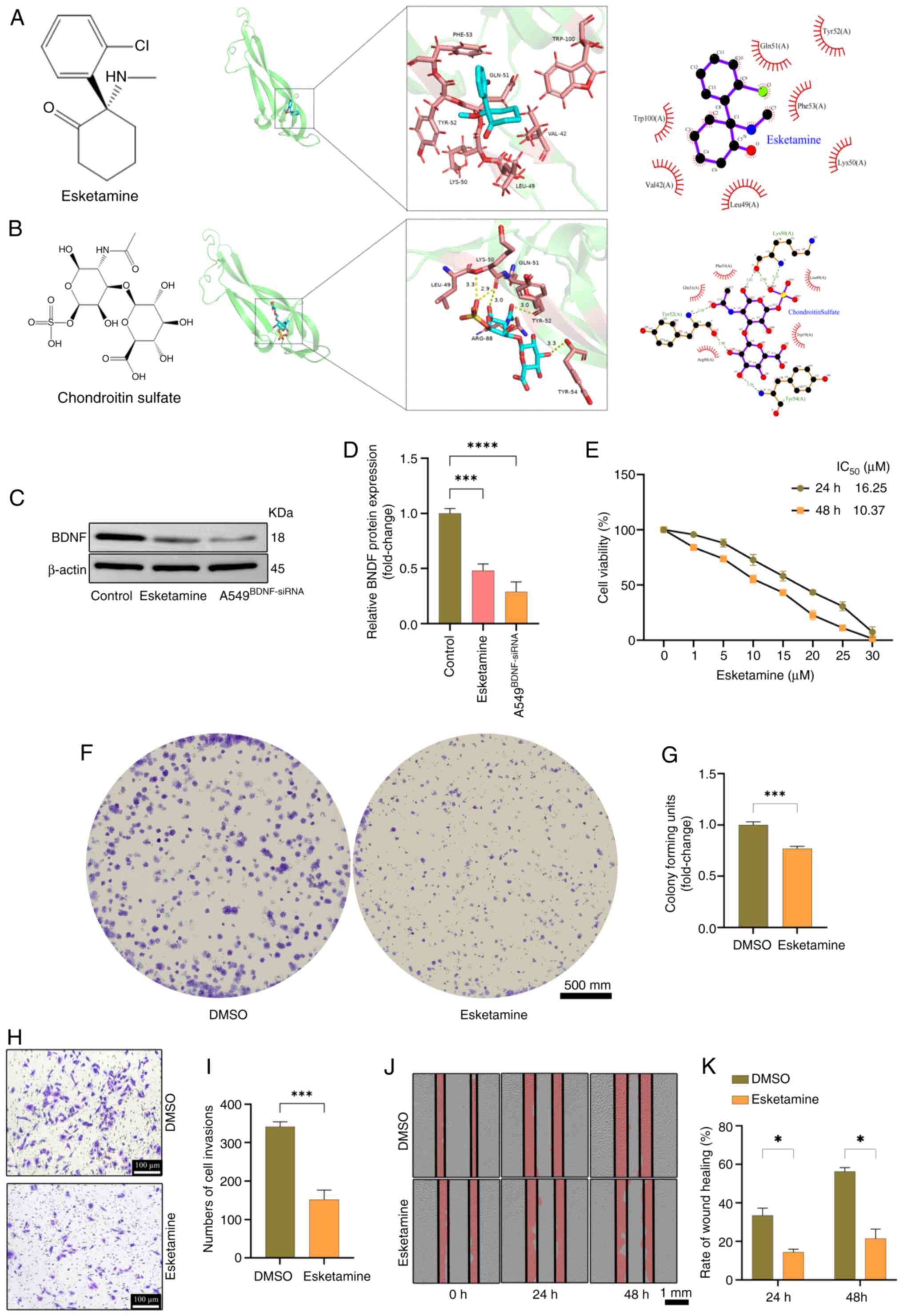
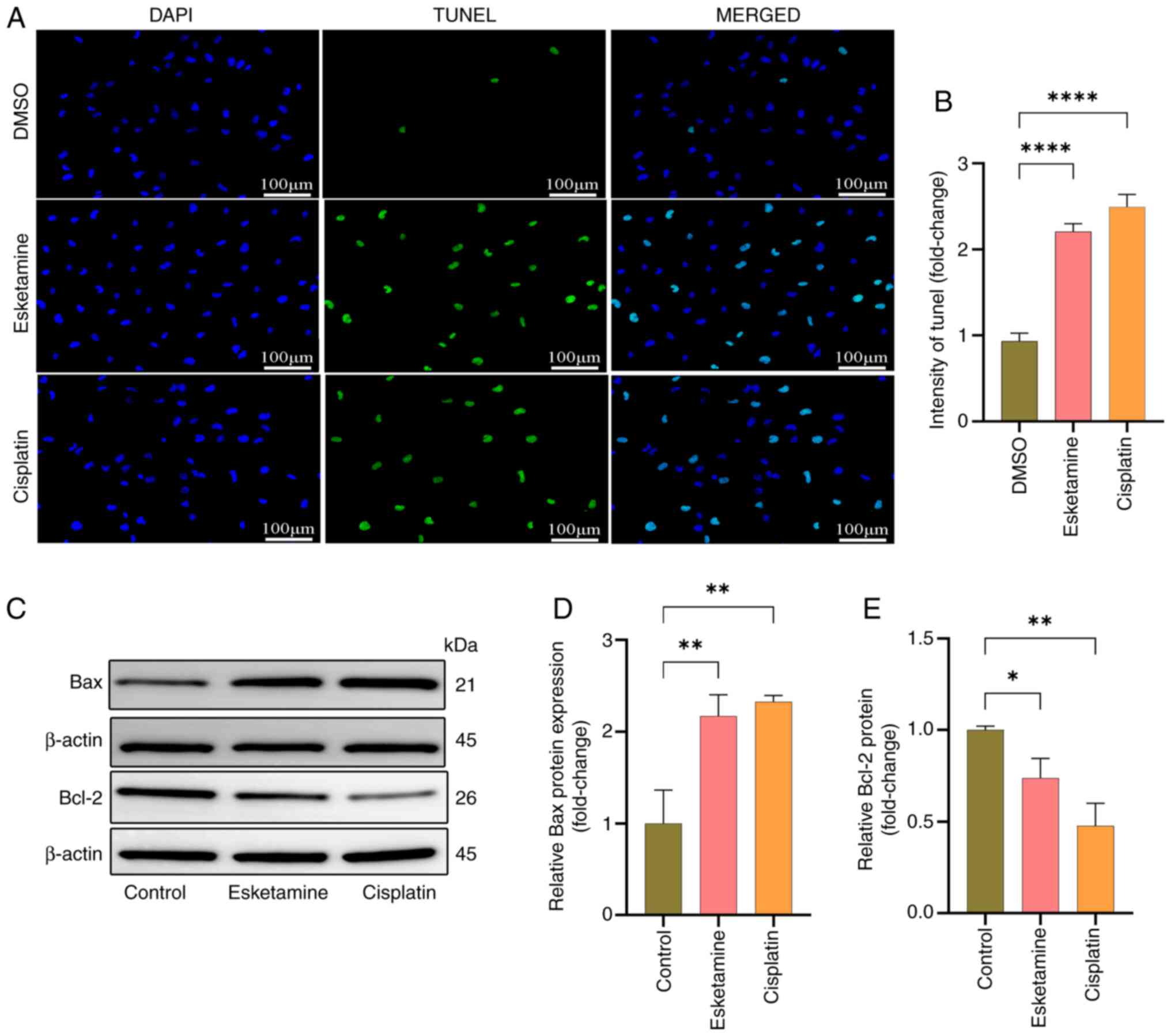
|
1
|
Thai AA, Solomon BJ, Sequist LV, Gainor JF
and Heist RS: Lung cancer. Lancet. 398:535–554. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang Y, Vaccarella S, Morgan E, Li M,
Etxeberria J, Chokunonga E, Manraj SS, Kamate B, Omonisi A and Bray
F: Global variations in lung cancer incidence by histological
subtype in 2020: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol.
24:1206–1218. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bi KW, Wei XG, Qin XX and Li B: BTK Has
potential to be a prognostic factor for lung adenocarcinoma and an
indicator for tumor microenvironment remodeling: A study based on
TCGA data mining. Front Oncol. 10:4242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Succony L, Rassl DM, Barker AP, McCaughan
FM and Rintoul RC: Adenocarcinoma spectrum lesions of the lung:
Detection, pathology and treatment strategies. Cancer Treat Rev.
99:1022372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu J, Zhang Y, Li M, Shao Z, Dong Y, Li Q,
Bai H, Duan J, Zhong J, Wan R, et al: A single-cell characterised
signature integrating heterogeneity and microenvironment of lung
adenocarcinoma for prognostic stratification. EBioMedicine.
102:1050922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun R, Hou Z, Zhang Y and Jiang B: Drug
resistance mechanisms and progress in the treatment of EGFR-mutated
lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett. 24:4082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Y, Liu B, Min Q, Yang X, Yan S, Ma Y,
Li S, Fan J, Wang Y, Dong B, et al: Spatial transcriptomics
delineates molecular features and cellular plasticity in lung
adenocarcinoma progression. Cell Discov. 9:962023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McLaughlin M and Vandenbroeck K: The
endoplasmic reticulum protein folding factory and its chaperones:
New targets for drug discovery? Br J Pharmacol. 162:328–345. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Saaoud F, Lu Y, Xu K, Shao Y, Praticò D,
Vazquez-Padron RI, Wang H and Yang X: Protein-rich foods, sea
foods, and gut microbiota amplify immune responses in chronic
diseases and cancers-targeting PERK as a novel therapeutic strategy
for chronic inflammatory diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and
cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 255:1086042024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Oakes SA: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
signaling in cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 190:934–946. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin L, Lin G, Lin H, Chen L, Chen X, Lin
Q, Xu Y and Zeng Y: Integrated profiling of endoplasmic reticulum
stress-related DERL3 in the prognostic and immune features of lung
adenocarcinoma. Front Immunol. 13:9064202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen X and Cubillos-Ruiz JR: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress signals in the tumour and its microenvironment.
Nat Rev Cancer. 21:71–88. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Bettigole SE and
Glimcher LH: Tumorigenic and immunosuppressive effects of
endoplasmic reticulum stress in cancer. Cell. 168:692–706. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cao T, Zhang W, Wang Q, Wang C, Ma W,
Zhang C, Ge M, Tian M, Yu J, Jiao A, et al: Cancer SLC6A6-mediated
taurine uptake transactivates immune checkpoint genes and induces
exhaustion in CD8+ T cells. Cell. 187:2288–2304.e27.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fan C, Yang Y, Liu Y, Jiang S, Di S, Hu W,
Ma Z, Li T, Zhu Y, Xin Z, et al: Icariin displays anticancer
activity against human esophageal cancer cells via regulating
endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptotic signaling. Sci Rep.
6:211452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Xiong Y, Zhang J, Feng Y and Xu
A: Systematic proteome-wide Mendelian randomization using the human
plasma proteome to identify therapeutic targets for lung
adenocarcinoma. J Transl Med. 22:3302024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Deng B, Liao F, Liu Y, He P, Wei S, Liu C
and Dong W: Comprehensive analysis of endoplasmic reticulum
stress-associated genes signature of ulcerative colitis. Front
Immunol. 14:11586482023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qiu WR, Qi BB, Lin WZ, Zhang SH, Yu WK and
Huang SF: Predicting the lung adenocarcinoma and its biomarkers by
integrating gene expression and DNA methylation data. Front Genet.
13:9269272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang S, Xiong Y, Zhao L, Gu K, Li Y, Zhao
F, Li J, Wang M, Wang H, Tao Z, et al: UCSCXenaShiny: an R/CRAN
package for interactive analysis of UCSC Xena data. Bioinformatics.
38:527–529. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Z, Wang Y, Chang M, Wang Y, Liu P, Wu
J, Wang G, Tang X, Hui X, Liu P, et al: Single-cell transcriptomic
analyses provide insights into the cellular origins and drivers of
brain metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma. Neuro Oncol.
25:1262–1274. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang J, Zhang J, Zhang F, Lu S, Guo S,
Shi R, Zhai Y, Gao Y, Tao X, Jin Z, et al: Identification of a
disulfidptosis-related genes signature for prognostic implication
in lung adenocarcinoma. Comput Biol Med. 165:1074022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu F, Cai J, Wen C and Tan H: Co-sparse
non-negative matrix factorization. Front Neurosci. 15:8045542022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu S, Zheng Z, Hu W and Lei C:
Conditional cancer-specific survival for inflammatory breast
cancer: Analysis of SEER, 2010 to 2016. Clin Breast Cancer.
23:628–639.e2. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qin Y, Liu Y, Xiang X, Long X, Chen Z,
Huang X, Yang J and Li W: Cuproptosis correlates with
immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment based on pan-cancer
multiomics and single-cell sequencing analysis. Mol Cancer.
22:592023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Q, Qiao W, Zhang H, Liu B, Li J, Zang
C, Mei T, Zheng J and Zhang Y: Nomogram established on account of
Lasso-Cox regression for predicting recurrence in patients with
early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Immunol.
13:10196382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song M, Zhang Q, Song C, Liu T, Zhang X,
Ruan G, Tang M, Xie H, Zhang H, Ge Y, et al: The advanced lung
cancer inflammation index is the optimal inflammatory biomarker of
overall survival in patients with lung cancer. J Cachexia
Sarcopenia Muscle. 13:2504–2514. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhai T: Druggable genome-wide Mendelian
randomization for identifying the role of integrated stress
response in therapeutic targets of bipolar disorder. J Affect
Disord. 362:843–852. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shao Y, Wang Z, Wu J, Lu Y, Chen Y, Zhang
H, Huang C, Shen H, Xu L and Fu Z: Unveiling immunogenic cell
death-related genes in colorectal cancer: an integrated study
incorporating transcriptome and Mendelian randomization analyses.
Funct Integr Genomics. 23:3162023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bisht A, Tewari D, Kumar S and Chandra S:
Network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics
simulation to elucidate the mechanism of anti-aging action of
Tinospora cordifolia. Mol Divers. 28:1743–1763. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jaganathan R and Kumaradhas P: Binding
mechanism of anacardic acid, carnosol and garcinol with PCAF: A
comprehensive study using molecular docking and molecular dynamics
simulations and binding free energy analysis. J Cell Biochem.
124:731–742. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu Y, Zhang C and Zhao D, Li W, Zhao Z,
Yao S and Zhao D: BDNF Acts as a prognostic factor associated with
tumor-infiltrating Th2 cells in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Dis
Markers. 2021:78420352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu L, Zhou S, Hong W, Lin N, Wang Q and
Liang P: Characterization of an endoplasmic reticulum
stress-associated lncRNA prognostic signature and the
tumor-suppressive role of RP11-295G20.2 knockdown in lung
adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. 14:122832024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang T, Weng H, Zhou H, Yang Z, Tian Z, Xi
B and Li Y: Esketamine alleviates postoperative depression-like
behavior through anti-inflammatory actions in mouse prefrontal
cortex. J Affect Disord. 307:97–107. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Siebert JR and Osterhout DJ: Select
neurotrophins promote oligodendrocyte progenitor cell process
outgrowth in the presence of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans. J
Neurosci Res. 99:1009–1023. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nakagawa K, Garon EB, Seto T, Nishio M,
Ponce Aix S, Paz-Ares L, Chiu CH, Park K, Novello S, Nadal E, et
al: Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated,
EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): A
randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 20:1655–1669. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Salvagno C, Mandula JK, Rodriguez PC and
Cubillos-Ruiz JR: Decoding endoplasmic reticulum stress signals in
cancer cells and antitumor immunity. Trends Cancer. 8:930–943.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Qiao L, Shao X, Gao S, Ming Z, Fu X and
Wei Q: Research on endoplasmic reticulum-targeting fluorescent
probes and endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated nanoanticancer
strategies: A review. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.
208:1120462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cao LL and Kagan JC: Targeting innate
immune pathways for cancer immunotherapy. Immunity. 56:2206–2217.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang H, Li Z, Tao Y, Ou S, Ye J, Ran S,
Luo K, Guan Z, Xiang J, Yan G, et al: Characterization of
endoplasmic reticulum stress unveils ZNF703 as a promising target
for colorectal cancer immunotherapy. J Transl Med. 21:7132023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang YH, Huo BL, Li C, Ma G and Cao W:
Knockdown of long noncoding RNA SNHG7 inhibits the proliferation
and promotes apoptosis of thyroid cancer cells by downregulating
BDNF. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:4815–4821. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu Y, Jiang WG, Wang HC, Martin T, Zeng
YX, Zhang J and Qi YS: BDNF activates TrkB/PLCγ1 signaling pathway
to promote proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells
through inhibition of apoptosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:5093–5100. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|