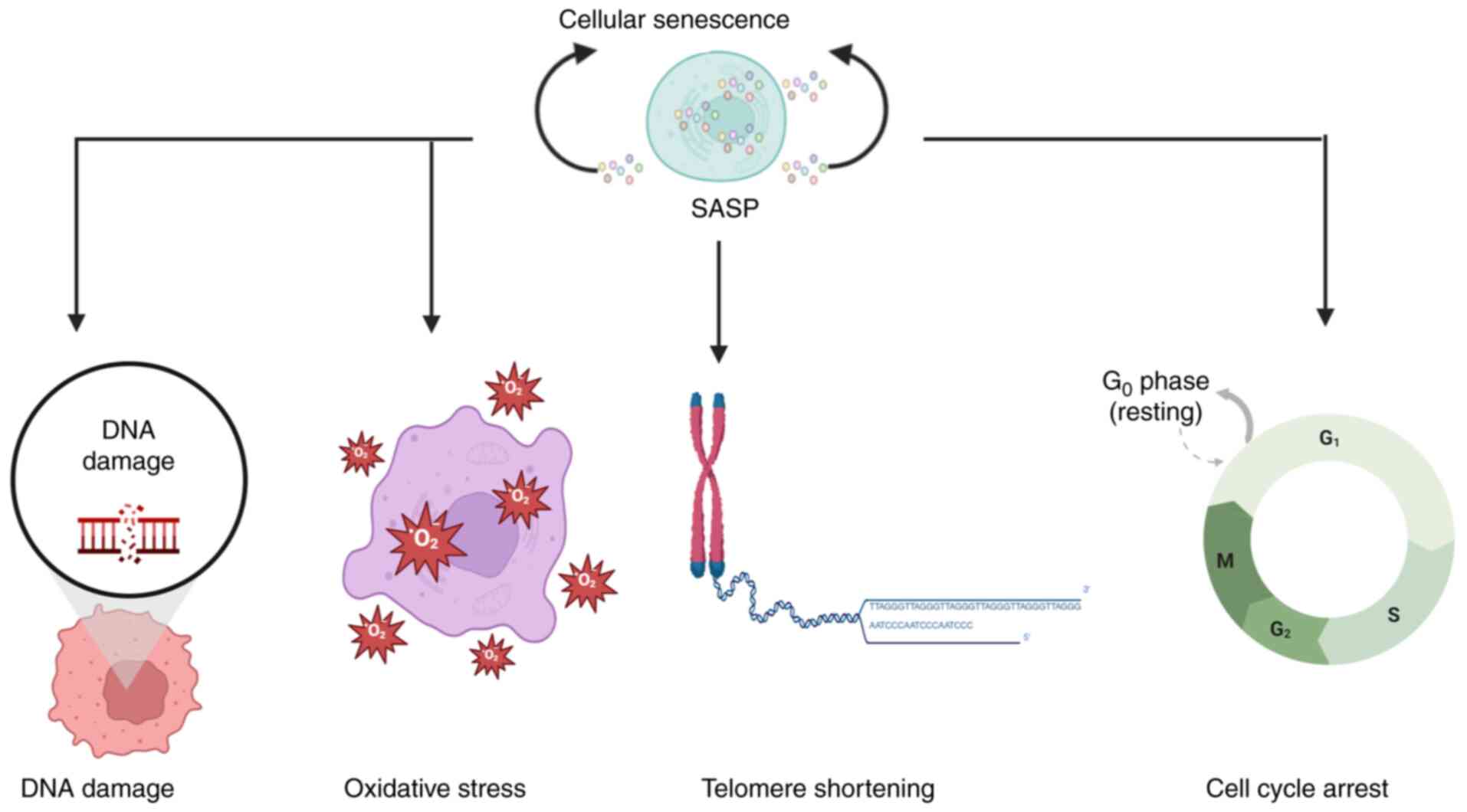
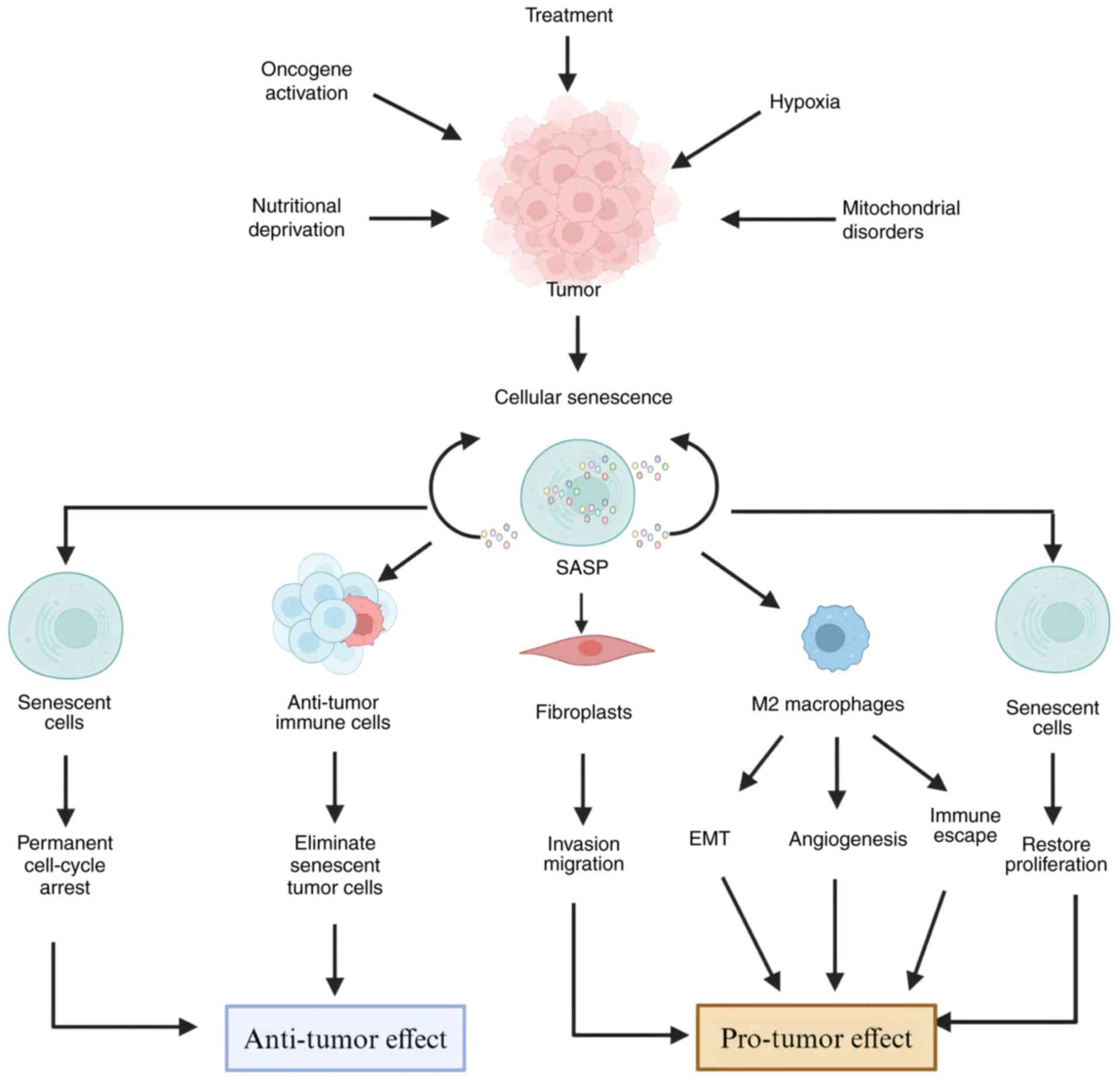
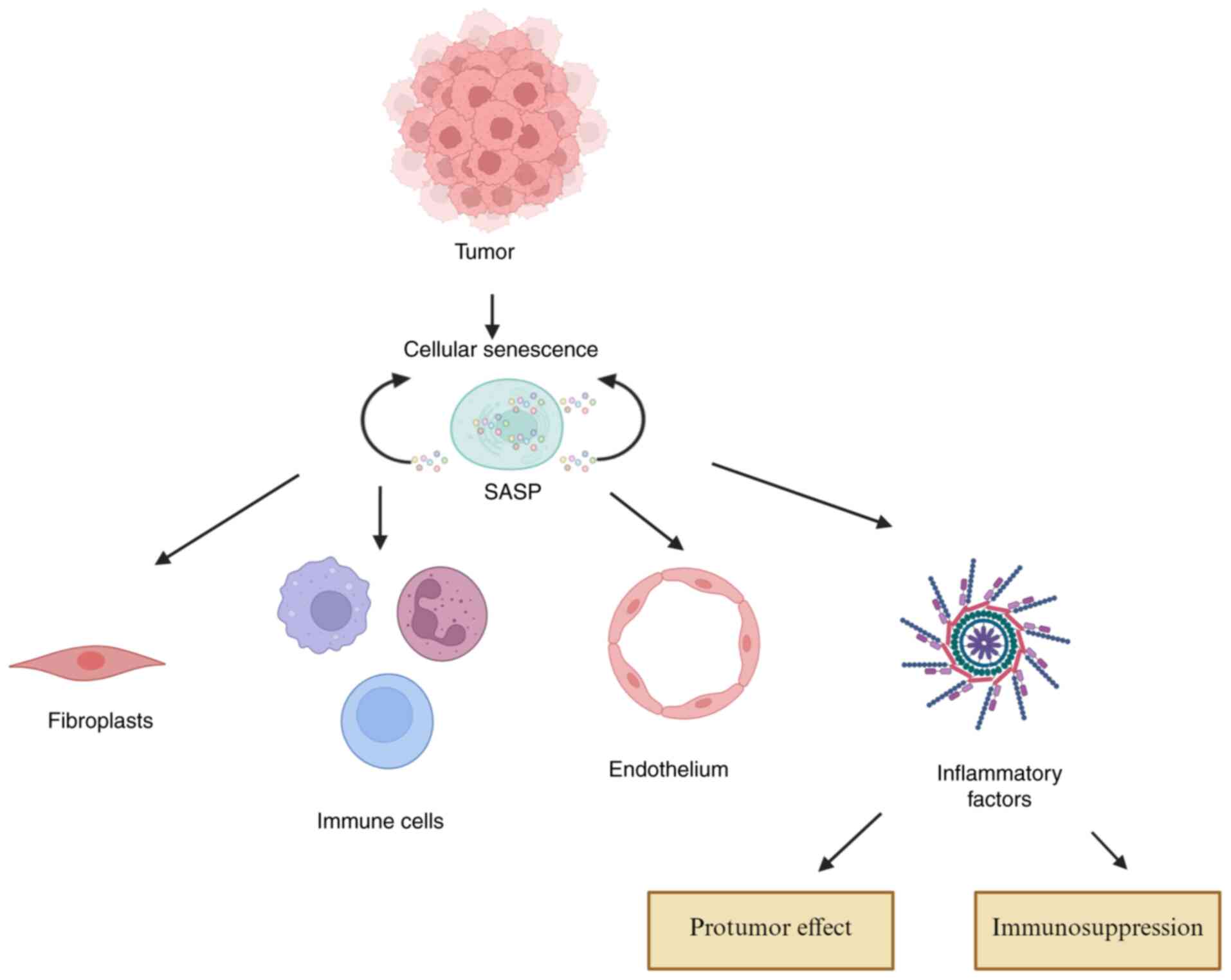
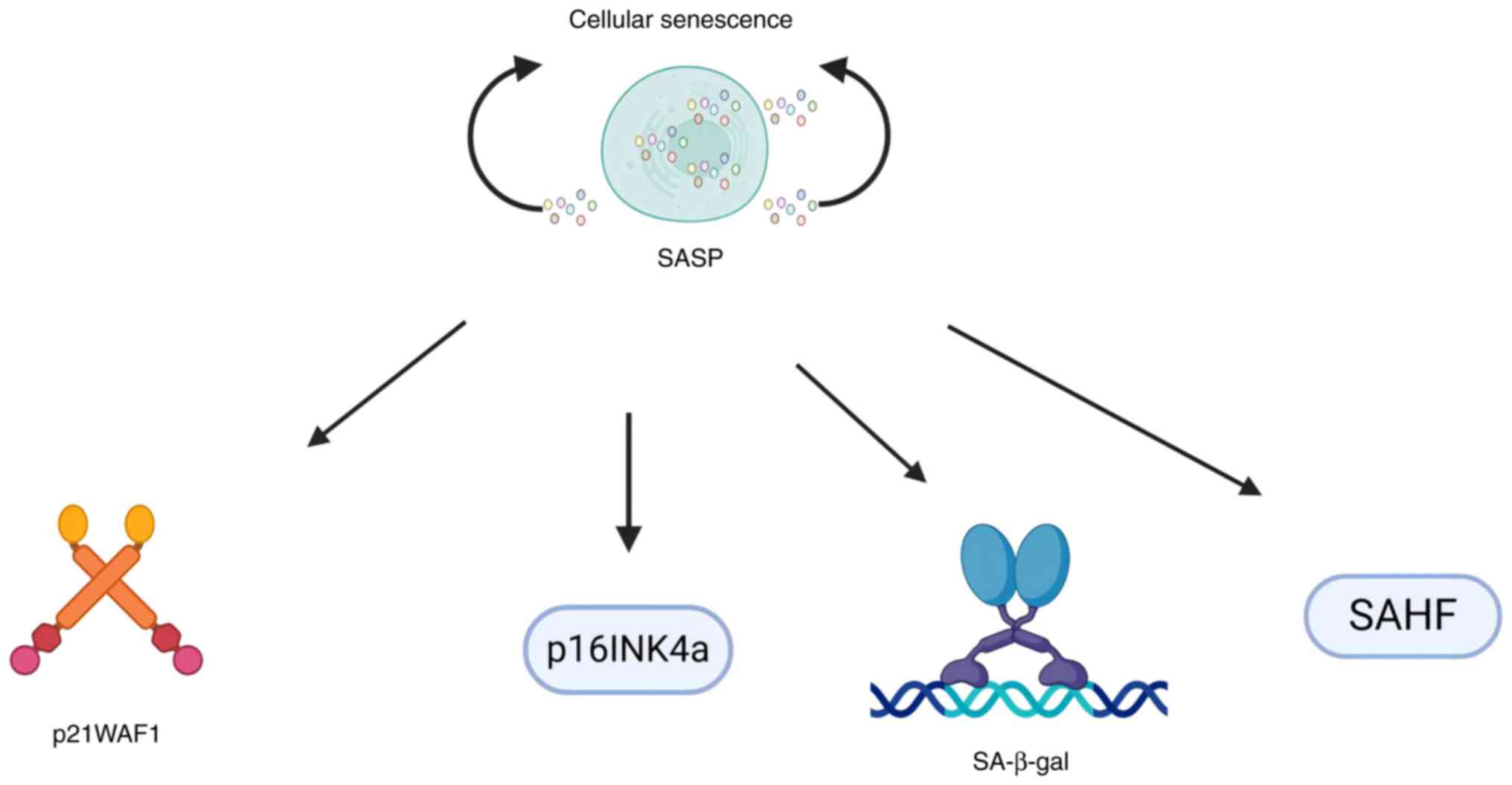
|
1
|
Campisi J and d'Adda di Fagagna F:
Cellular senescence: When bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 8:729–740. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schosserer M, Grillari J and Breitenbach
M: The dual role of cellular senescence in developing tumors and
their response to cancer therapy. Front Oncol. 7:2782017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nacarelli T, Liu P and Zhang R: Epigenetic
basis of cellular senescence and its implications in aging. Genes
(Basel). 8:3432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lai P, Liu L, Bancaro N, Troiani M, Calì
B, Li Y, Chen J, Singh PK, Arzola RA, Attanasio G, et al:
Mitochondrial DNA released by senescent tumor cells enhances
PMN-MDSC-driven immunosuppression through the cGAS-STING pathway.
Immunity. 58:811–825.e7. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen D, Wang J, Li Y, Xu C, Fanzheng M,
Zhang P and Liu L: LncRNA NEAT1 suppresses cellular senescence in
hepatocellular carcinoma via KIF11-dependent repression of CDKN2A.
Clin Transl Med. 13:e14182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu N, Wu J, Deng E, Zhong J, Wei B, Cai
T, Xie Z, Duan X, Fu S, Osei-Hwedieh DO, et al: Immunotherapy and
senolytics in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Phase 2 trial
results. Nat Med. 31:3047–3061. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zandi M, Behboudi E, Shojaei MR, Soltani S
and Karami H: Letter to the editor regarding ‘An overview on
serology and molecular tests for COVID-19: An important challenge
of the current century (doi: 10.22034/iji.2021.88660.1894.)’. Iran
J Immunol. 19:3372022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Khosravi M, Behboudi E, Razavi-Nikoo H and
Tabarraei A: Hepatitis B virus X protein induces expression changes
of miR-21, miR-22, miR-122, miR-132, and miR-222 in Huh-7 cell
line. Arch Razi Inst. 79:111–119. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Edalat F, Gholamzad A, Ghoreshi ZA,
Dalfardi M, Golkar A, Behboudi E and Arefinia N: Prevalence and
genetic diversity of HTLV-1 among blood donors in Jiroft, Iran: A
comprehensive study. Virus Genes. 61:424–431. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hao X, Billings SD, Wu F, Stultz TW,
Procop GW, Mirkin G and Vidimos AT: Dermatofibrosarcoma
protuberans: Update on the diagnosis and treatment. J Clin Med.
9:17522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Molina-Peña R, Tudon-Martinez JC and
Aquines-Gutiérrez O: A mathematical model of average dynamics in a
stem cell hierarchy suggests the combinatorial targeting of cancer
stem cells and progenitor cells as a potential strategy against
tumor growth. Cancers (Basel). 12:25902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu L, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhai J, Ren L and
Zhu G: Radiation-induced osteocyte senescence alters bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cell differentiation potential via paracrine
signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 22:93232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Childs BG, Baker DJ, Kirkland JL, Campisi
J and van Deursen JM: Senescence and apoptosis: Dueling or
complementary cell fates? EMBO Rep. 15:1139–1153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rhinn M, Ritschka B and Keyes WM: Cellular
senescence in development, regeneration and disease. Development.
146:dev1518372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gorgoulis V, Adams PD, Alimonti A, Bennett
DC, Bischof O, Bishop C, Campisi J, Collado M, Evangelou K,
Ferbeyre G, et al: Cellular senescence: Defining a path forward.
Cell. 179:813–827. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Olivieri F, Prattichizzo F, Grillari J and
Balistreri CR: Cellular senescence and inflammaging in Age-related
diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2018:90764852018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Di Micco R, Krizhanovsky V, Baker D and
d'Adda di Fagagna F: Cellular senescence in ageing: From mechanisms
to therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 22:75–95.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mikuła-Pietrasik J, Niklas A, Uruski P,
Tykarski A and Książek K: Mechanisms and significance of
therapy-induced and spontaneous senescence of cancer cells. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 77:213–229. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ou HL, Hoffmann R, González-López C,
Doherty GJ, Korkola JE and Muñoz-Espín D: Cellular senescence in
cancer: From mechanisms to detection. Mol Oncol. 15:2634–2671.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Di Mitri D and Alimonti A:
Non-Cell-Autonomous regulation of cellular senescence in cancer.
Trends Cell Biol. 26:215–226. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park SS, Choi YW, Kim JH, Kim HS and Park
TJ: Senescent tumor cells: An overlooked adversary in the battle
against cancer. Exp Mol Med. 53:1834–1841. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saleh T, Tyutynuk-Massey L, Cudjoe EK Jr,
Idowu MO, Landry JW and Gewirtz DA: Non-cell autonomous effects of
the Senescence-associated secretory phenotype in cancer therapy.
Front Oncol. 8:1642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Herranz N and Gil J: Mechanisms and
functions of cellular senescence. J Clin Invest. 128:1238–1246.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rao SG and Jackson JG: SASP: Tumor
suppressor or promoter? Yes! Trends Cancer. 2:676–687. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
He Y, Long K, Du B, Liao W, Zou R, Su J,
Luo J, Shi Z and Wang L: The cellular senescence score (CSS) is a
comprehensive biomarker to predict prognosis and assess senescence
and immune characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 739:1505762024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ru K, Cui L, Wu C, Tan XX, An WT, Wu Q, Ma
YT, Hao Y, Xiao X, Bai J, et al: Exploring the molecular and immune
landscape of cellular senescence in lung adenocarcinoma. Front
Immunol. 15:13477702024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Geng H, Huang C, Xu L, Zhou Y, Dong Z,
Zhong Y, Li Q, Yang C, Huang S, Liao W, et al: Targeting cellular
senescence as a therapeutic vulnerability in gastric cancer. Life
Sci. 346:1226320241
|
|
28
|
Liu H, Zhao H and Sun Y: Tumor
microenvironment and cellular senescence: Understanding therapeutic
resistance and harnessing strategies. Semin Cancer Biol.
86:769–781. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Higashiguchi M, Murakami H, Akita H,
Kobayashi S, Takahama S, Iwagami Y, Yamada D, Tomimaru Y, Noda T,
Gotoh K, et al: The impact of cellular senescence and
senescence-associated secretory phenotype in cancer-associated
fibroblasts on the malignancy of pancreatic cancer. Oncol Rep.
49:982023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu H, Lv R, Song F, Yang Y, Zhang F, Xin
L, Zhang P, Zhang Q and Ding C: A near-IR ratiometric fluorescent
probe for the precise tracking of senescence: A multidimensional
sensing assay of biomarkers in cell senescence pathways. Chem Sci.
15:5681–5693. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin W, Wang X, Wang Z, Shao F, Yang Y, Cao
Z, Feng X, Gao Y and He J: Comprehensive analysis uncovers
prognostic and immunogenic characteristics of cellular senescence
for lung adenocarcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7804612021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang W, Li Y, Lyu J, Shi F, Kong Y, Sheng
C, Wang S and Wang Q: An aging-related signature predicts favorable
outcome and immunogenicity in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci.
113:891–903. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pérez-Mancera PA, Young AR and Narita M:
Inside and out: The activities of senescence in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 14:547–558. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang Y, Cai Q, Zhu M, Rong J, Feng X and
Wang K: Exploring the Double-edged role of cellular senescence in
chronic liver disease for new treatment approaches. Life Sci.
373:1236782025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wyld L, Bellantuono I, Tchkonia T, Morgan
J, Turner O, Foss F, George J, Danson S and Kirkland JL: Senescence
and cancer: A review of clinical implications of senescence and
senotherapies. Cancers (Basel). 12:21342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gu Y, Xu T, Fang Y, Shao J, Hu T, Wu X,
Shen H, Xu Y, Zhang J, Song Y, et al: CBX4 counteracts cellular
senescence to desensitize gastric cancer cells to chemotherapy by
inducing YAP1 SUMOylation. Drug Resist Updat. 77:1011362024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liang X, Lin X, Lin Z, Lin W, Peng Z and
Wei S: Genes associated with cellular senescence favor melanoma
prognosis by stimulating immune responses in tumor
microenvironment. Comput Biol Med. 158:1068502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao Q, Hu W, Xu J, Zeng S, Xi X, Chen J,
Wu X, Hu S and Zhong T: Comprehensive Pan-cancer analysis of
senescence with cancer prognosis and immunotherapy. Front Mol
Biosci. 9:9192742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fan Y, Gao Z, Li X, Wei S and Yuan K: Gene
expression and prognosis of x-ray repair cross-complementing family
members in non-small cell lung cancer. Bioengineered. 12:6210–6228.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mavrogonatou E, Pratsinis H and Kletsas D:
The role of senescence in cancer development. Semin Cancer Biol.
62:182–191. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu H, Xu Q, Wufuer H, Li Z, Sun R, Jiang
Z, Dou X, Fu Q, Campisi J and Sun Y: Rutin is a potent senomorphic
agent to target senescent cells and can improve chemotherapeutic
efficacy. Aging Cell. 23:e139212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sun Y, Coppé JP and Lam EW: Cellular
senescence: The sought or the unwanted? Trends Mol Med. 24:871–885.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen Y, Zhou T, Zhou R, Sun W, Li Y, Zhou
Q, Xu D, Zhao Y, Hu P, Liang J, et al: TRAF7 knockdown induces
cellular senescence and synergizes with lomustine to inhibit glioma
progression and recurrence. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 44:1122025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Calcinotto A, Kohli J, Zagato E,
Pellegrini L, Demaria M and Alimonti A: Cellular senescence: Aging,
cancer, and injury. Physiol Rev. 99:1047–1078. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kamal M, Shanmuganathan M, Kroezen Z,
Joanisse S, Britz-McKibbin P and Parise G: Senescent myoblasts
exhibit an altered exometabolome that is linked to
senescence-associated secretory phenotype signaling. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 328:C440–C451. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lecot P, Alimirah F, Desprez PY, Campisi J
and Wiley C: Context-dependent effects of cellular senescence in
cancer development. Br J Cancer. 114:1180–1184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lian J, Yue Y, Yu W and Zhang Y:
Immunosenescence: A key player in cancer development. J Hematol
Oncol. 13:1512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ruhland MK and Alspach E: Senescence and
immunoregulation in the tumor microenvironment. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9:7540692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lau L and David G: Pro- and
anti-tumorigenic functions of the senescence-associated secretory
phenotype. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 23:1041–1051. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gonzalez-Meljem JM, Apps JR, Fraser HC and
Martinez-Barbera JP: Paracrine roles of cellular senescence in
promoting tumourigenesis. Br J Cancer. 118:1283–1288. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang G, Cheng X, Zhang J, Liao Y, Jia Y
and Qing C: Possibility of inducing tumor cell senescence during
therapy. Oncol Lett. 22:4962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Maggiorani D, Le O, Lisi V, Landais S,
Moquin-Beaudry G, Lavallée VP, Decaluwe H and Beauséjour C:
Senescence drives immunotherapy resistance by inducing an
immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Nat Commun. 15:24352024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lasry A and Ben-Neriah Y:
Senescence-associated inflammatory responses: Aging and cancer
perspectives. Trends Immunol. 36:217–228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Murray KO, Mahoney SA, Ludwig KR,
Miyamoto-Ditmon JH, VanDongen NS, Banskota N, Herman AB, Seals DR,
Mankowski RT, Rossman MJ and Clayton ZS: Intermittent
supplementation with fisetin improves physical function and
decreases cellular senescence in skeletal muscle with aging: A
comparison to genetic clearance of senescent cells and synthetic
senolytic approaches. Aging Cell. 24:e701142025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ayoub M, Abou Jaoude C, Ayoub M, Hamade A
and Rima M: The immune system and cellular senescence: A complex
interplay in aging and disease. Immunology. Sep 12–2025.doi:
10.1111/imm.70036 (Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang W, Zhang K, Shi J, Qiu H, Kan C, Ma
Y, Hou N, Han F and Sun X: The impact of the senescent
microenvironment on tumorigenesis: Insights for cancer therapy.
Aging Cell. 23:e141822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kirkland JL: Tumor dormancy and disease
recurrence. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 42:9–12. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
de Paula B, Kieran R, Koh SSY, Crocamo S,
Abdelhay E and Muñoz-Espín D: Targeting senescence as a therapeutic
opportunity for Triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
22:583–598. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lee S and Lee JS: Cellular senescence: A
promising strategy for cancer therapy. BMB Rep. 52:35–41. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang C, Hao X and Zhang R: Targeting
cellular senescence to combat cancer and ageing. Mol Oncol.
16:3319–3332. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Battram AM, Bachiller M and Martín-Antonio
B: Senescence in the development and response to cancer with
immunotherapy: A Double-edged sword. Int J Mol Sci. 21:43462020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fan DN and Schmitt CA: Detecting markers
of Therapy-induced senescence in cancer cells. Methods Mol Biol.
1534:41–52. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ruhland MK, Coussens LM and Stewart SA:
Senescence and cancer: An evolving inflammatory paradox. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1865:14–22. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Song S, Lam EW, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL
and Sun Y: Senescent cells: Emerging targets for human aging and
Age-related diseases. Trends Biochem Sci. 45:578–592. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Paleari L: Personalized assessment for
cancer prevention, detection, and treatment. Int J Mol Sci.
25:81402024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ohtani N: The roles and mechanisms of
senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP): Can it be
controlled by senolysis? Inflamm Regen. 42:112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kaur J and Farr JN: Cellular senescence in
Age-related disorders. Transl Res. 226:96–104. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Hughes BK, Davis A, Milligan D, Wallis R,
Mossa F, Philpott MP, Wainwright LJ, Gunn DA and Bishop CL:
SenPred: A single-cell RNA sequencing-based machine learning
pipeline to classify deeply senescent dermal fibroblast cells for
the detection of an in vivo senescent cell burden. Genome Med.
17:22025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Uyar B, Palmer D, Kowald A, Murua Escobar
H, Barrantes I, Möller S, Akalin A and Fuellen G: Single-cell
analyses of aging, inflammation and senescence. Ageing Res Rev.
64:1011562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Sprenger HG, MacVicar T, Bahat A, Fiedler
KU, Hermans S, Ehrentraut D, Ried K, Milenkovic D, Bonekamp N,
Larsson NG, et al: Cellular pyrimidine imbalance triggers
mitochondrial DNA-dependent innate immunity. Nat Metab. 3:636–650.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liang A, Kong Y, Chen Z, Qiu Y, Wu Y, Zhu
X and Li Z: Advancements and applications of single-cell
multi-omics techniques in cancer research: Unveiling heterogeneity
and paving the way for precision therapeutics. Biochem Biophys Rep.
37:1015892023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Avelar RA, Ortega JG, Tacutu R, Tyler EJ,
Bennett D, Binetti P, Budovsky A, Chatsirisupachai K, Johnson E,
Murray A, et al: A multidimensional systems biology analysis of
cellular senescence in aging and disease. Genome Biol. 21:912020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wu L, Xie X, Liang T, Ma J, Yang L, Yang
J, Li L, Xi Y, Li H, Zhang J, et al: Integrated Multi-omics for
novel aging biomarkers and antiaging targets. Biomolecules.
12:392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Aird KM and Zhang R: Nucleotide
metabolism, oncogene-induced senescence and cancer. Cancer Lett.
356:204–210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yang K, Li X and Xie K: Senescence program
and its reprogramming in pancreatic premalignancy. Cell Death Dis.
14:5282023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hwang HJ, Jung SH, Lee HC, Han NK, Bae IH,
Lee M, Han YH, Kang YS, Lee SJ, Park HJ, et al: Identification of
novel therapeutic targets in the secretome of ionizing
radiation-induced senescent tumor cells. Oncol Rep. 35:841–850.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Matjusaitis M, Chin G, Sarnoski EA and
Stolzing A: Biomarkers to identify and isolate senescent cells.
Ageing Res Rev. 29:1–12. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ziglari T, Calistri NL, Finan JM, Derrick
DS, Nakayasu ES, Burnet MC, Kyle JE, Hoare M, Heiser LM and Pucci
F: Senescent Cell-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit cancer
recurrence by coordinating immune surveillance. Cancer Res.
85:859–874. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Davalli P, Mitic T, Caporali A, Lauriola A
and D'Arca D: ROS, cell senescence, and novel molecular mechanisms
in aging and Age-related diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:35651272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Amor C, Fernández-Maestre I, Chowdhury S,
Ho YJ, Nadella S, Graham C, Carrasco SE, Nnuji-John E, Feucht J,
Hinterleitner C, et al: Prophylactic and Long-lasting efficacy of
senolytic CAR T cells against Age-related metabolic dysfunction.
Nat Aging. 4:336–349. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Alqahtani S, Alqahtani T, Venkatesan K,
Sivadasan D, Ahmed R, Sirag N, Elfadil H, Abdullah Mohamed H, T A
H, Elsayed Ahmed R, et al: SASP modulation for cellular
rejuvenation and tissue homeostasis: Therapeutic strategies and
molecular insights. Cells. 14:6082025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Schmitt CA, Fridman JS, Yang M, Lee S,
Baranov E, Hoffman RM and Lowe SW: A senescence program controlled
by p53 and p16INK4a contributes to the outcome of cancer therapy.
Cell. 109:335–346. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wang S, Xing Y, Wang R and Jin Z: Jianpi
Huayu Decoction suppresses cellular senescence in colorectal cancer
via p53-p21-Rb pathway: Network pharmacology and in vivo
validation. J Ethnopharmacol. 319:1173472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Wu M, Wu B, Huang X, Wang Z, Zhu M, Zhu Y,
Yu L and Liu J: Inhibition of the FEN1-PBX1 axis elicits cellular
senescence in breast cancer via the increased intracellular
reactive oxygen species levels. J Transl Med. 23:2482025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Wang K, Jiang X, Jiang Y, Liu J, Du Y,
Zhang Z, Li Y, Zhao X, Li J and Zhang R: EZH2-H3K27me3-mediated
silencing of mir-139-5p inhibits cellular senescence in
hepatocellular carcinoma by activating TOP2A. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 42:3202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Yuan W, Xu Y, Wu Z, Huang Y, Meng L, Dai
S, Ying S, Chen Z and Xu A: Cellular senescence-related genes:
Predicting prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer.
23:10012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhang C, Wang X and Zhang C: Icaritin
inhibits CDK2 expression and activity to interfere with tumor
progression. iScience. 25:1049912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Sieben CJ, Sturmlechner I, van de Sluis B
and van Deursen JM: Two-Step senescence-focused cancer therapies.
Trends Cell Biol. 28:723–737. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Sikora E, Bielak-Zmijewska A and Mosieniak
G: Targeting normal and cancer senescent cells as a strategy of
senotherapy. Ageing Res Rev. 55:1009412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Short S, Fielder E, Miwa S and von
Zglinicki T: Senolytics and senostatics as adjuvant tumour therapy.
EBioMedicine. 41:683–692. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Yang N and Sen P: The senescent cell
epigenome. Aging (Albany NY). 10:3590–3609. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Choi YW, Kim YH, Oh SY, Suh KW, Kim YS,
Lee GY, Yoon JE, Park SS, Lee YK, Park YJ, et al: Senescent tumor
cells build a cytokine shield in colorectal cancer. Adv Sci
(Weinh). 8:20024972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Vilgelm AE, Johnson CA, Prasad N, Yang J,
Chen SC, Ayers GD, Pawlikowski JS, Raman D, Sosman JA, Kelley M, et
al: Connecting the dots: Therapy-induced senescence and a
Tumor-suppressive immune microenvironment. J Natl Cancer Inst.
108:djv4062015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Aimono Y, Endo K and Sekiya I: Cellular
senescence contributes to spontaneous repair of the rat meniscus.
Aging Cell. 24:e143852025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Ohtani N: The role of SASP in tumor
microenvironment. Clin Calcium. 27:835–843. 2017.(In Japanese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hatzikirou H, Alfonso JC, Mühle S, Stern
C, Weiss S and Meyer-Hermann M: Cancer therapeutic potential of
combinatorial immuno- and vasomodulatory interventions. J R Soc
Interface. 12:201504392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Rebbaa A: Targeting senescence pathways to
reverse drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Lett. 219:1–13. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Cuollo L, Antonangeli F, Santoni A and
Soriani A: The Senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) in
the challenging future of cancer therapy and Age-related diseases.
Biology (Basel). 9:4852020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Chen J, Wang J, Lucas M, Liu H, Wheeler C,
Johnson K, Woodard K, Chang C, Frey G, Boyle WJ and Short JM:
Abstract B022: Targeting senescence cells in cancer and aging by
conditionally active biologic therapeutics In: Proceedings of the
AACR Special Conference: Aging and Cancer; 2022 Nov 17–20, San
Diego, CA, AACR, Philadelphia, PA. Cancer Res. 83 (2
Suppl_1):Abstract nr B022. 2022.
|
|
100
|
Butt AQ and Mills KH: Immunosuppressive
networks and checkpoints controlling antitumor immunity and their
blockade in the development of cancer immunotherapeutics and
vaccines. Oncogene. 33:4623–4631. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Ivey JW, Bonakdar M, Kanitkar A, Davalos
RV and Verbridge SS: Improving cancer therapies by targeting the
physical and chemical hallmarks of the tumor microenvironment.
Cancer Lett. 380:330–339. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Papismadov N, Gal H and Krizhanovsky V:
The anti-aging promise of p21. Cell Cycle. 16:1997–1998. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Gonzalez-Meljem JM and Martinez-Barbera
JP: Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma as a model to understand
paracrine and Senescence-induced tumourigenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
78:4521–4544. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
He S and Sharpless NE: Senescence in
health and disease. Cell. 169:1000–1011. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Janelle V, Neault M, Lebel MÈ, De Sousa
DM, Boulet S, Durrieu L, Carli C, Muzac C, Lemieux S, Labrecque N,
et al: p16INK4a regulates cellular senescence in PD-1-expressing
human T cells. Front Immunol. 12:6985652021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Park SS, Lee YK, Kim YH, Park SH, Kang HY,
Kim JC, Kim DJ, Lim SB, Yoon G, Kim JH, et al: Distribution and
impact of p16INK4A+ senescent cells in elderly tissues: A focus on
senescent immune cell and epithelial dysfunction. Exp Mol Med.
56:2631–2641. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Baker DJ, Childs BG, Durik M, Wijers ME,
Sieben CJ, Zhong J, Saltness RA, Jeganathan KB, Verzosa GC,
Pezeshki A, et al: Naturally occurring p16(Ink4a)-positive cells
shorten healthy lifespan. Nature. 530:184–189. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Courtois-Cox S, Jones SL and Cichowski K:
Many roads lead to Oncogene-induced senescence. Oncogene.
27:2801–2809. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Angelini PD, Zacarias Fluck MF, Pedersen
K, Parra-Palau JL, Guiu M, Bernadó Morales C, Vicario R,
Luque-García A, Navalpotro NP, Giralt J, et al: Constitutive HER2
signaling promotes breast cancer metastasis through cellular
senescence. Cancer Res. 73:450–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Zhang B, Lam EW and Sun Y: Senescent
cells: A new Achilles' heel to exploit for cancer medicine? Aging
Cell. 18:e128752019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Du PY, Gandhi A, Bawa M and Gromala J: The
ageing immune system as a potential target of senolytics. Oxf Open
Immunol. 4:iqad0042023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Saleh T, Tyutyunyk-Massey L and Gewirtz
DA: Tumor cell escape from Therapy-induced senescence as a model of
disease recurrence after dormancy. Cancer Res. 79:1044–1046. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Salam R, Saliou A, Bielle F, Bertrand M,
Antoniewski C, Carpentier C, Alentorn A, Capelle L, Sanson M,
Huillard E, et al: Cellular senescence in malignant cells promotes
tumor progression in mouse and patient Glioblastoma. Nat Commun.
14:4412023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Zheng J, Liu Y, Lau YL and Tu W: γδ-T
cells: An unpolished sword in human Anti-infection immunity. Cell
Mol Immunol. 10:50–57. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Wang W, Luo HS and Yu BP: Expression of
NF-kappaB and human telomerase reverse transcriptase in gastric
cancer and precancerous lesions. World J Gastroenterol. 10:177–181.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Meyerson M, Counter CM, Eaton EN, Ellisen
LW, Steiner P, Caddle SD, Ziaugra L, Beijersbergen RL, Davidoff MJ,
Liu Q, et al: hEST2, the putative human telomerase catalytic
subunit gene, is up-regulated in tumor cells and during
immortalization. Cell. 90:785–795. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Saleh S, Lam AK and Ho YH: Real-time PCR
quantification of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) in
colorectal cancer. Pathology. 40:25–30. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Eastley N, Ottolini B, Garrido C, Shaw JA,
McCulloch TA, Ashford RU and Royle NJ: Telomere maintenance in soft
tissue sarcomas. J Clin Pathol. 70:371–377. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Bojko A, Czarnecka-Herok J, Charzynska A,
Dabrowski M and Sikora E: Diversity of the senescence phenotype of
cancer cells treated with chemotherapeutic agents. Cells.
8:15012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Ganesan K and Xu B: Telomerase inhibitors
from natural products and their anticancer potential. Int J Mol
Sci. 19:132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Banik K, Khatoon E, Harsha C, Rana V,
Parama D, Thakur KK, Bishayee A and Kunnumakkara AB: Wogonin and
its analogs for the prevention and treatment of cancer: A
systematic review. Phytother Res. 36:1854–1883. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Shay JW and Wright WE: Telomeres and
telomerase: Three decades of progress. Nat Rev Genet. 20:299–309.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Saretzki G: Role of telomeres and
telomerase in cancer and aging. Int J Mol Sci. 24:99322023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Bollmann FM: Targeting ALT: The role of
alternative lengthening of telomeres in pathogenesis and prevention
of cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 33:704–709. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|