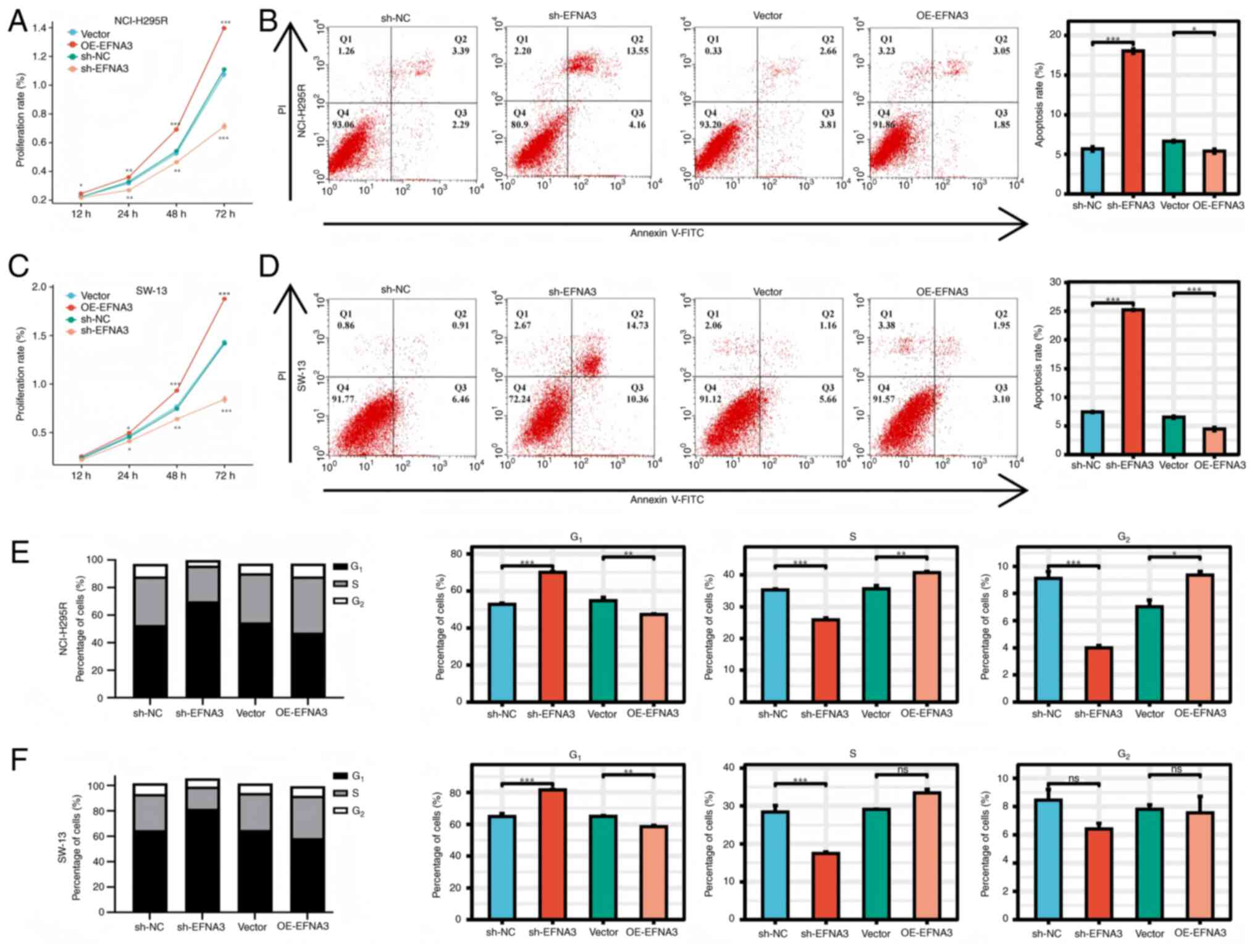
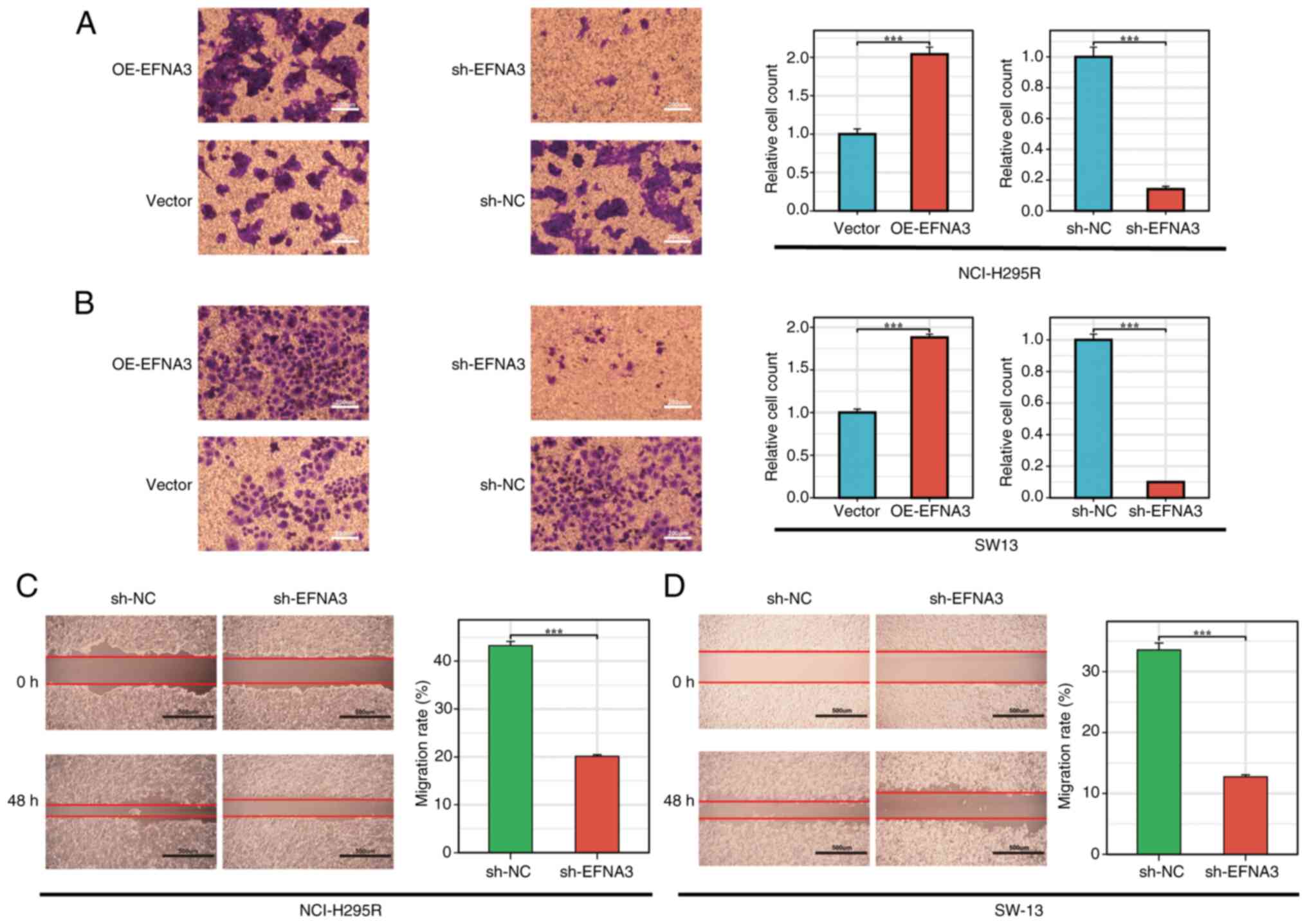
|
1
|
Else T, Kim AC, Sabolch A, Raymond VM,
Kandathil A, Caoili EM, Jolly S, Miller BS, Giordano TJ and Hammer
GD: Adrenocortical carcinoma. Endocr Rev. 35:282–326. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sinclair TJ, Gillis A, Alobuia WM, Wild H
and Kebebew E: Surgery for adrenocortical carcinoma: When and how?
Best Pract Res Clin En. 34:1014082020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Del Rivero J, Else T, Hallanger-Johnson J,
Kiseljak-Vassiliades K, Raj N, Reidy-Lagunes D, Srinivas S, Gilbert
J, Vaidya A, Aboujaoude E, et al: A review of mitotane in the
management of adrenocortical cancer. Oncologist. 29:747–760. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fassnacht M, Dekkers O, Else T, Baudin E,
Berruti A, de Krijger R, Haak H, Mihai R, Assie G and Terzolo M:
European society of endocrinology clinical practice guidelines on
the management of adrenocortical carcinoma in adults, in
collaboration with the European network for the study of adrenal
tumors. Eur J Endocrinol. 179:G1–G46. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen L, Huang L, Gu Y, Cang W, Sun P and
Xiang Y: Lactate-Lactylation hands between metabolic reprogramming
and immunosuppression. Int J Mol Sci. 23:119432022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ganapathy-Kanniappan S and Geschwind JH:
Tumor glycolysis as a target for cancer therapy: Progress and
prospects. Mol Cancer. 12:1522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boedtkjer E and Pedersen SF: The acidic
tumor microenvironment as a driver of cancer. Annu Rev Physiol.
82:103–126. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu S, Shen G, Zhou X, Sun L, Yu L, Cao Y,
Shu X and Ran Y: Hsp90 promotes gastric cancer cell metastasis and
stemness by regulating the regional distribution of
glycolysis-related metabolic enzymes in the cytoplasm. Adv Sci.
11:e23101092024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nievergall E, Lackmann M and Janes PW:
Eph-dependent cell-cell adhesion and segregation in development and
cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:1813–1842. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Himanen J, Saha N and Nikolov DB:
Cell-cell signaling via Eph receptors and ephrins. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 19:534–542. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kou CJ and Kandpal RP: Differential
expression patterns of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands in human
cancers. Biomed Res Int. 2018:73901042018.
|
|
12
|
Stewen J, Kruse K, Godoi-Filip AT, Zenia
Jeong H, Adams S, Berkenfeld F, Stehling M, Red-Horse K, Adams RH
and Pitulescu ME: Eph-ephrin signaling couples endothelial cell
sorting and arterial specification. Nat Commun. 15:25392024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pasquale EB: Eph receptors and ephrins in
cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 24:5–27. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deng M, Tong R, Zhang Z, Wang T, Liang C,
Zhou X and Hou G: EFNA3 as a predictor of clinical prognosis and
immune checkpoint therapy efficacy in patients with lung
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 21:5352021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hao Y and Li G: Role of EFNA1 in
tumorigenesis and prospects for cancer therapy. Biomed
Pharmacother. 130:1105672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yamashita T, Ohneda K, Nagano M, Miyoshi
C, Kaneko N, Miwa Y, Yamamoto M, Ohneda O and Fujii-Kuriyama Y:
Hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-2alpha in endothelial cells
regulates tumor neovascularization through activation of ephrin A1.
J Biol Chem. 283:18926–18936. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakamura R, Kataoka H, Sato N, Kanamori M,
Ihara M, Igarashi H, Ravshanov S, Wang Y, Li Z, Shimamura T, et al:
EPHA2/EFNA1 expression in human gastric cancer. Cancer Sci.
96:42–47. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cui Y, Chang Y, Ma X, Sun M, Huang Y, Yang
F, Li S, Zhuo W, Liu W, Yang B, et al: Ephrin A1 stimulates CCL2
secretion to facilitate pre-metastatic niche formation and promote
gastric cancer liver metastasis. Cancer Res. 85:263–276. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wilson K, Shiuan E and Brantley-Sieders
DM: Oncogenic functions and therapeutic targeting of EphA2 in
cancer. Oncogene. 40:2483–2495. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mao L, Yuan W, Cai K, Lai C, Huang C, Xu
Y, Zhong S, Yang C, Wang R, Zeng P, et al: EphA2-YES1-ANXA2 pathway
promotes gastric cancer progression and metastasis. Oncogene.
40:3610–3623. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Y, Peng Q and Wang L: EphA2 as a phase
separation protein associated with ferroptosis and immune cell
infiltration in colorectal cancer. Aging (Albany NY).
15:12952–12965. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pei J, Zhang C, Yusupu M, Zhang C and Dai
DQ: Screening and validation of the hypoxia-related signature of
evaluating tumor immune microenvironment and predicting prognosis
in gastric cancer. Front Immunol. 12:7055112021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xie R, Yuan M and Jiang Y: The pan-cancer
crosstalk between the EFNA family and tumor microenvironment for
prognosis and immunotherapy of gastric cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol.
10:7909472022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bhatia S, Oweida A, Lennon S, Darragh LB,
Milner D, Phan AV, Mueller AC, Van Court B, Raben D, Serkova NJ, et
al: Inhibition of EphB4-Ephrin-B2 signaling reprograms the tumor
immune microenvironment in head and neck cancers. Cancer Res.
79:2722–2735. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Janes PW, Vail ME, Ernst M and Scott AM:
Eph receptors in the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.
Cancer Res. 81:801–805. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma W, Zhu M, Wang B, Gong Z, Du X, Yang T,
Shi X, Dai B, Zhan Y, Zhang D, et al: Vandetanib drives growth
arrest and promotes sensitivity to imatinib in chronic myeloid
leukemia by targeting ephrin type-B receptor 4. Mol Oncol.
16:2747–2765. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen B, Khodadoust MS, Liu CL, Newman AM
and Alizadeh AA: Profiling tumor infiltrating immune cells with
CIBERSORT. Methods Mol Biol. 1711:243–259. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kuang L, Pang Y and Fang Q: TMEM101
expression and its impact on immune cell infiltration and prognosis
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. 14:318472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu Q, Li P, Tao X, Lin N, Mao B and Xie X:
A novel super-enhancer-related risk model for predicting prognosis
and guiding personalized treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC
Cancer. 24:10872024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lin P and Yang H: EFNA3 is a prognostic
biomarker for the overall survival of patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatol. 77:879–880. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang L, Song Y, Wang H, Liu K, Shao Z and
Shang Z: MiR-210-3p-EphrinA3-PI3K/AKT axis regulates the
progression of oral cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 24:4011–4022. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chatzikyriakou P, Brempou D, Quinn M,
Fishbein L, Noberini R, Anastopoulos IN, Tufton N, Lim ES, Obholzer
R, Hubbard JG, et al: A comprehensive characterisation of
phaeochromocytoma and paraganglioma tumours through histone protein
profiling, DNA methylation and transcriptomic analysis genome wide.
Clin Epigenetics. 15:1962023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Husain A, Chiu Y, Sze KM, Ho DW, Tsui Y,
Suarez EMS, Zhang VX, Chan L, Lee E, Lee JM, et al: Ephrin-A3/EphA2
axis regulates cellular metabolic plasticity to enhance cancer
stemness in hypoxic hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol.
77:383–396. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yiminniyaze R, Zhang X, Zhu N, Wang J, Li
C, Wumaier G, Zhou D, Li J, Xia J, Zhang Y, et al: EphrinA3 is a
key regulator of malignant behaviors and a potential prognostic
factor in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med. 12:1630–1642. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Peng Q and Wang L: EphA2 as a phase
separation protein associated with ferroptosis and immune cell
infiltration in colorectal cancer. Aging (Albany NY).
15:12952–12965. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pei J, Zhang C, Yusupu M, Zhang C and Dai
D: Screening and validation of the hypoxia-related signature of
evaluating tumor immune microenvironment and predicting prognosis
in gastric cancer. Front Immunol. 12:7055112021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Deng M, Tong R, Zhang Z, Wang T, Liang C,
Zhou X and Hou G: EFNA3 as a predictor of clinical prognosis and
immune checkpoint therapy efficacy in patients with lung
adenocarcinoma. Cancer cell Int. 21:5352021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kiri S and Ryba T: Cancer, metastasis, and
the epigenome. Mol Cancer. 23:1542024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zheng S, Cherniack AD, Dewal N, Moffitt
RA, Danilova L, Murray BA, Lerario AM, Else T, Knijnenburg TA,
Ciriello G, et al: Comprehensive pan-genomic characterization of
adrenocortical carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 29:723–736. 2016.
|
|
42
|
Sun-Zhang A, Juhlin CC, Carling T, Scholl
U, Schott M, Larsson C and Bajalica-Lagercrantz S: Comprehensive
genomic analysis of adrenocortical carcinoma reveals genetic
profiles associated with patient survival. ESMO Open. 9:1036172024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sun L, Zhang H and Gao P: Metabolic
reprogramming and epigenetic modifications on the path to cancer.
Protein Cell. 13:877–919. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Orsolic I, Carrier A and Esteller M:
Genetic and epigenetic defects of the RNA modification machinery in
cancer. Trends Genet. 39:74–88. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Clay MR, Pinto EM, Cline C, Tran QT, Lin
T, Dyer MA, Shi L, Wu H, Pounds SB, Zambetti GP, et al: DNA
methylation profiling reveals prognostically significant groups in
pediatric adrenocortical tumors: A report from the international
pediatric adrenocortical tumor registry. JCO Precis Oncol.
3:PO.19.00163. 2019.
|
|
46
|
Mohan DR, Lerario AM, Else T, Mukherjee B,
Almeida MQ, Vinco M, Rege J, Mariani BMP, Zerbini MCN, Mendonca BB,
et al: Targeted assessment of G0S2 methylation identifies a rapidly
recurrent, routinely fatal molecular subtype of adrenocortical
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 25:3276–3288. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li C, Tang Y, Li Q, Liu H, Ma X, He L and
Shi H: The prognostic and immune significance of C15orf48 in
pan-cancer and its relationship with proliferation and apoptosis of
thyroid carcinoma. Front Immunol. 14:11318702023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Oliver J, Garcia-Aranda M, Chaves P, Alba
E, Cobo-Dols M, Onieva JL and Barragan I: Emerging noninvasive
methylation biomarkers of cancer prognosis and drug response
prediction. Semin Cancer Biol. 83:584–595. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Suh I, Weng J, Fernandez-Ranvier G, Shen
WT, Duh Q, Clark OH and Kebebew E: Antineoplastic effects of
decitabine, an inhibitor of DNA promoter methylation, in
adrenocortical carcinoma cells. Arch Surg. 145:226–232. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Endo A, Ly T, Pippa R, Bensaddek D,
Nicolas A and Lamond AI: The chromatin assembly factor complex 1
(CAF1) and 5-Azacytidine (5-AzaC) affect cell motility in
src-transformed human epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 292:172–184.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li X, Li Y, Dong L, Chang Y, Zhang X, Wang
C, Chen M, Bo X, Chen H, Han W and Nie J: Decitabine priming
increases anti-PD-1 antitumor efficacy by promoting CD8+ progenitor
exhausted T cell expansion in tumor models. J Clin Invest.
133:e1656732023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Wang Y, Tong C, Dai H, Wu Z, Han X, Guo Y,
Chen D, Wei J, Ti D, Liu Z, et al: Low-dose decitabine priming
endows CAR T cells with enhanced and persistent antitumour
potential via epigenetic reprogramming. Nat Commun. 12:4092021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sarhadi VK and Armengol G: Molecular
biomarkers in cancer. Biomolecules. 12:10212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xu F, Guan Y, Ma Y, Xue L, Zhang P, Yang X
and Chong T: Bioinformatic analyses and experimental validation of
the role of m6A RNA methylation regulators in progression and
prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY).
13:11919–11941. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fu Y, Sun S, Bi J, Kong C and Yin L:
Expression patterns and prognostic value of m6A RNA methylation
regulators in adrenocortical carcinoma. Medicine (Baltimore).
100:e250312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S,
Lu Z, Chen Y, Sulman EP, Xie K, Bogler O, et al: m(6)A Demethylase
ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells by
sustaining FOXM1 expression and cell proliferation program. Cancer
Cell. 31:591–606. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Xiong J, He J, Zhu J, Pan J, Liao W, Ye H,
Wang H, Song Y, Du Y, Cui B, et al: Lactylation-driven
METTL3-mediated RNA m6A modification promotes
immunosuppression of tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells. Mol Cell.
82:1660–1677. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Wang L, Dou X, Chen S, Yu X, Huang X,
Zhang L, Chen Y, Wang J, Yang K, Bugno J, et al: YTHDF2 inhibition
potentiates radiotherapy antitumor efficacy. Cancer Cell.
41:1294–1308. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Barbari C, Fontaine T, Parajuli P,
Lamichhane N, Jakubski S, Lamichhane P and Deshmukh RR:
Immunotherapies and combination strategies for immuno-oncology. Int
J Mol Sci. 21:50092020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Rui R, Zhou L and He S: Cancer
immunotherapies: Advances and bottlenecks. Front Immunol.
14:12124762023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Wu T and Dai Y: Tumor microenvironment and
therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. 387:61–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Raj N, Zheng Y, Kelly V, Katz SS, Chou J,
Do RKG, Capanu M, Zamarin D, Saltz LB, Ariyan CE, et al: PD-1
blockade in advanced adrenocortical carcinoma. J Clin Oncol.
38:71–80. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Habra MA, Stephen B, Campbell M, Hess K,
Tapia C, Xu M, Ahnert JR, Jimenez C, Lee JE, Perrier ND, et al:
Phase II clinical trial of pembrolizumab efficacy and safety in
advanced adrenocortical carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. 7:2532019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Fassnacht M, Puglisi S, Kimpel O and
Terzolo M: Adrenocortical carcinoma: A practical guide for
clinicians. Lancet Diabetes Endo. 13:438–452. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Remde H, Schmidt-Pennington L, Reuter M,
Landwehr L, Jensen M, Lahner H, Kimpel O, Altieri B, Laubner K,
Schreiner J, et al: Outcome of immunotherapy in adrenocortical
carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study. Eur J Endocrinol.
188:485–493. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Khalafizadeh A, Hashemizadegan SD, Shokri
F, Bakhshinejad B, Jabbari K, Motavaf M and Babashah S: Competitive
endogenous RNA networks: Decoding the role of long non-coding RNAs
and circular RNAs in colorectal cancer chemoresistance. J Cell Mol
Med. 28:e181972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang L, Song Y, Wang H, Liu K, Shao Z and
Shang Z: MiR-210-3p-EphrinA3-PI3K/AKT axis regulates the
progression of oral cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 24:4011–4022. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang Z, Yin B, Wang B, Ma Z, Liu W and Lv
G: MicroRNA-210 promotes proliferation and invasion of peripheral
nerve sheath tumor cells targeting EFNA3. Oncol Res. 21:145–154.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gomez-Maldonado L, Tiana M, Roche O,
Prado-Cabrero A, Jensen L, Fernandez-Barral A, Guijarro-Munoz I,
Favaro E, Moreno-Bueno G, Sanz L, et al: EFNA3 long noncoding RNAs
induced by hypoxia promote metastatic dissemination. Oncogene.
34:2609–2620. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Long B, Yang X, Xu X, Li X, Xu X, Zhang X
and Zhang S: Long noncoding RNA ASB16-AS1 inhibits adrenocortical
carcinoma cell growth by promoting ubiquitination of RNA-binding
protein HuR. Cell Death Dis. 11:9952020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Li S, Monazzam A, Razmara M, Chu X,
Stalberg P and Skogseid B: MiR-486-3p was downregulated at microRNA
profiling of adrenals of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 mice,
and inhibited human adrenocortical carcinoma cell lines. Sci Rep.
11:147722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Subramanian C, McNamara K, Croslow SW, Tan
Y, Hess D, Kiseljak-Vassiliades K, Wierman ME, Sweedler JV and
Cohen MS: Novel repurposing of sulfasalazine for the treatment of
adrenocortical carcinomas, probably through the
SLC7A11/xCT-hsa-miR-92a-3p-OIP5-AS1 network pathway. Surgery.
177:1088322025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Gouirand V, Gicquel T, Lien EC, Jaune-Pons
E, Da Costa Q, Finetti P, Metay E, Duluc C, Mayers JR, Audebert S,
et al: Ketogenic HMG-CoA lyase and its product beta-hydroxybutyrate
promote pancreatic cancer progression. EMBO J. 41:e1104662022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Yarmolinsky J, Bull CJ, Vincent EE,
Robinson J, Walther A, Smith GD, Lewis SJ, Relton CL and Martin RM:
Association between genetically proxied inhibition of HMG-CoA
reductase and epithelial ovarian cancer. JAMA. 323:646–655. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Jiang W, Hu J and He X, Jin W and He X:
Statins: A repurposed drug to fight cancer. J Exp Clin Canc Res.
40:2412021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Dorsch M, Kowalczyk M, Planque M, Heilmann
G, Urban S, Dujardin P, Forster J, Ueffing K, Nothdurft S, Oeck S,
et al: Statins affect cancer cell plasticity with distinct
consequences for tumor progression and metastasis. Cell Rep.
37:1100562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Feng J, Dai W, Mao Y, Wu L, Li J, Chen K,
Yu Q, Kong R, Li S, Zhang J, et al: Simvastatin re-sensitizes
hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib by inhibiting
HIF-1alpha/PPAR-gamma/PKM2-mediated glycolysis. J Exp Clin Canc
Res. 39:242020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Yao X, Xie R, Cao Y, Tang J, Men Y, Peng H
and Yang W: Simvastatin induced ferroptosis for triple-negative
breast cancer therapy. J Nanobiotechnol. 19:3112021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Ma W, Wei S, Li Q, Zeng J, Xiao W, Zhou C,
Yoneda KY, Zeki AA and Li T: Simvastatin overcomes resistance to
tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patient-derived, oncogene-driven lung
adenocarcinoma models. Mol Cancer Ther. 23:700–710. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Xie W, Peng M, Liu Y, Zhang B, Yi L and
Long Y: Simvastatin induces pyroptosis via ROS/caspase-1/GSDMD
pathway in colon cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 21:3292023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Budillon A, Leone A, Passaro E, Silvestro
L, Foschini F, Iannelli F, Roca MS, Macchini M, Bruzzese F, Bermejo
ML, et al: Randomized phase 2 study of valproic acid combined with
simvastatin and gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel-based regimens in
untreated metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients: The VESPA
trial study protocol. BMC Cancer. 24:11672024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jing Z, Yuan W, Wang J, Ni R, Qin Y, Mao
Z, Wei F, Song C, Zheng Y, Cai H and Liu Z:
Simvastatin/hydrogel-loaded 3D-printed titanium alloy scaffolds
suppress osteosarcoma via TF/NOX2-associated ferroptosis while
repairing bone defects. Bioact Mater. 33:223–241. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Lee YG, Chou F, Tung S, Chou H, Ko T, Fann
YC and Juan S: Tumoricidal activity of simvastatin in synergy with
rhoa inactivation in antimigration of clear cell renal cell
carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Sci. 24:97382023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Okubo K, Miyai K, Kato K, Asano T and Sato
A: Simvastatin-romidepsin combination kills bladder cancer cells
synergistically. Transl Oncol. 14:1011542021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Fuentes-Fayos AC, G-Garcia ME, Perez-Gomez
JM, Montero-Hidalgo AJ, Martin-Colom J, Doval-Rosa C,
Blanco-Acevedo C, Torres E, Toledano-Delgado A, Sanchez-Sanchez R,
et al: Metformin and simvastatin exert additive antitumour effects
in glioblastoma via senescence-state: Clinical and translational
evidence. Ebiomedicine. 90:1044842023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Dong G, Huang X, Jiang S, Ni L and Chen S:
Simvastatin mitigates apoptosis and transforming growth factor-beta
upregulation in stretch-induced endothelial cells. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2019:60260512019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wang S, Ho HJ, Lin J, Shieh J and Wu C:
Simvastatin-induced cell cycle arrest through inhibition of
STAT3/SKP2 axis and activation of AMPK to promote p27 and p21
accumulation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis.
8:e26262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Stine JE, Guo H, Sheng X, Han X,
Schointuch MN, Gilliam TP, Gehrig PA, Zhou C and Bae-Jump VL: The
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, simvastatin, exhibits anti-metastatic
and anti-tumorigenic effects in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget.
7:946–960. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Afshordel S, Kern B, Clasohm J, Konig H,
Priester M, Weissenberger J, Kogel D and Eckert GP: Lovastatin and
perillyl alcohol inhibit glioma cell invasion, migration, and
proliferation-impact of Ras-/Rho-prenylation. Pharmacol Res.
91:69–77. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Conde J, Fernandez-Pisonero I,
Lorenzo-Martin LF, Garcia-Gomez R, Casar B, Crespo P and Bustelo
XR: The mevalonate pathway contributes to breast primary
tumorigenesis and lung metastasis. Mol Oncol. 19:56–80. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Tai Y and Shang J: Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway in the tumor progression of adrenocortical carcinoma. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 14:12607012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Rubin B, Pilon C, Pezzani R, Rebellato A
and Fallo F: The effects of mitotane and 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin
D3 on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in human adrenocortical
carcinoma cells. J Endocrinol Invest. 43:357–367. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Batlle E, Henderson JT, Beghtel H, van den
Born MMW, Sancho E, Huls G, Meeldijk J, Robertson J, van de
Wetering M, Pawson T, et al: Beta-catenin and TCF mediate cell
positioning in the intestinal epithelium by controlling the
expression of EphB/ephrinB. Cell. 111:251–263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Zhang C, Liu L, Li W, Li M, Zhang X, Zhang
C, Yang H, Xie J, Pan W, Guo X, et al: Upregulation of FAM83F by
c-Myc promotes cervical cancer growth and aerobic glycolysis via
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling activation. Cell Death Dis. 14:8372023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Yang H, Shen J, Wang Y, Liu Y, Shen D and
Quan S: Tankyrase promotes aerobic glycolysis and proliferation of
ovarian cancer through activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.
Biomed Res Int. 2019:26863402019.
|
|
96
|
Sprowl-Tanio S, Habowski AN, Pate KT,
McQuade MM, Wang K, Edwards RA, Grun F, Lyou Y and Waterman ML:
Lactate/pyruvate transporter MCT-1 is a direct Wnt target that
confers sensitivity to 3-bromopyruvate in colon cancer. Cancer
Metab. 4:202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Du Y, Jiang Y, Hou Y and Shi Y: Complement
factor I knockdown inhibits colon cancer development by affecting
Wnt/beta-catenin/c-Myc signaling pathway and glycolysis. World J
Gastrointest Oncol. 16:2646–2662. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Vergara D, Stanca E, Guerra F, Priore P,
Gaballo A, Franck J, Simeone P, Trerotola M, De Domenico S,
Fournier I, et al: beta-catenin knockdown affects mitochondrial
biogenesis and lipid metabolism in breast cancer cells. Front
Physiol. 8:5442017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Halma MTJ, Tuszynski JA and Marik PE:
Cancer metabolism as a therapeutic target and review of
interventions. Nutrients. 15:5442023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Sun W, Jia M, Feng Y and Cheng X: Lactate
is a bridge linking glycolysis and autophagy through lactylation.
Autophagy. 19:3240–3241. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Williams JL, Smith C, Hall C, Khaled Z,
Maharaj A, Kwong R, Pittaway J, Casas J, Parvanta L, Abdel-Aziz TE,
et al: Elevated sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase leads to increased
metabolism and reduced survival in adrenocortical carcinoma. Eur J
Endocrinol. 188:lvac0072023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Krishnamurthy N and Kurzrock R: Targeting
the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: Update on effectors and
inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev. 62:50–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|