|
1
|
Schadendorf D, van Akkooi ACJ, Berking C,
Griewank KG, Gutzmer R, Hauschild A, Stang A, Roesch A and Ugurel
S: Melanoma. Lancet. 392:971–984. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gershenwald JE, Scolyer RA, Hess KR,
Sondak VK, Long GV, Ross MI, Lazar AJ, Faries MB, Kirkwood JM,
McArthur GA, et al: Melanoma staging: Evidence-Based changes in the
American joint committee on cancer eighth edition cancer staging
manual. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:472–492. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Slominski RM, Kim TK, Janjetovic Z,
Brożyna AA, Podgorska E, Dixon KM, Mason RS, Tuckey RC, Sharma R,
Crossman DK, et al: Malignant melanoma: An overview, new
perspectives, and vitamin D signaling. Cancers (Basel).
16:22622024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Slominski RM, Raman C, Jetten AM and
Slominski AT: Neuro-immuno-endocrinology of the skin: How
environment regulates body homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
21:495–509. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
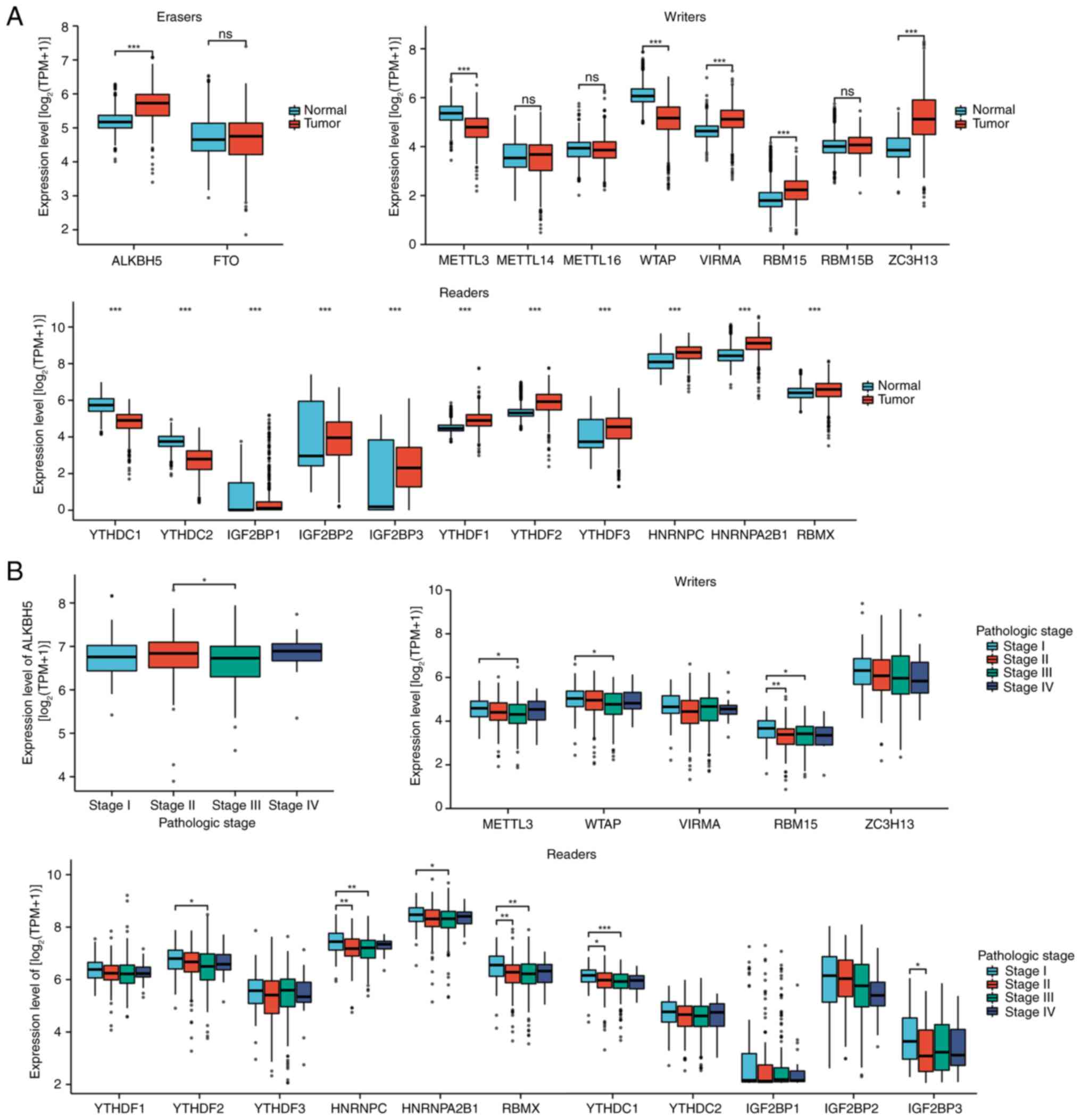
6
|
Slominski RM, Chen JY, Raman C and
Slominski AT: Photo-neuro-immuno-endocrinology: How the ultraviolet
radiation regulates the body, brain, and immune system. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 121:e23083741212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
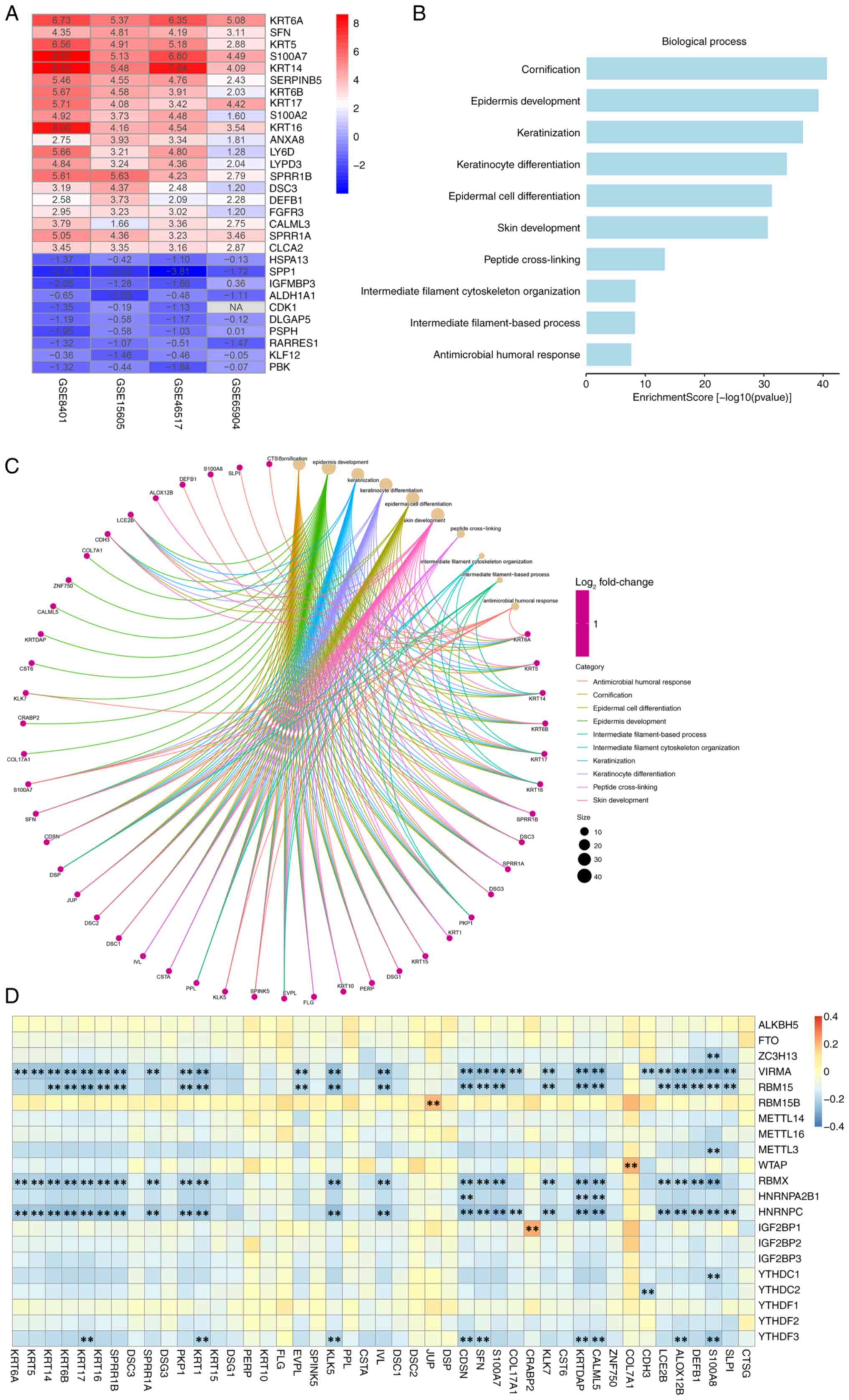
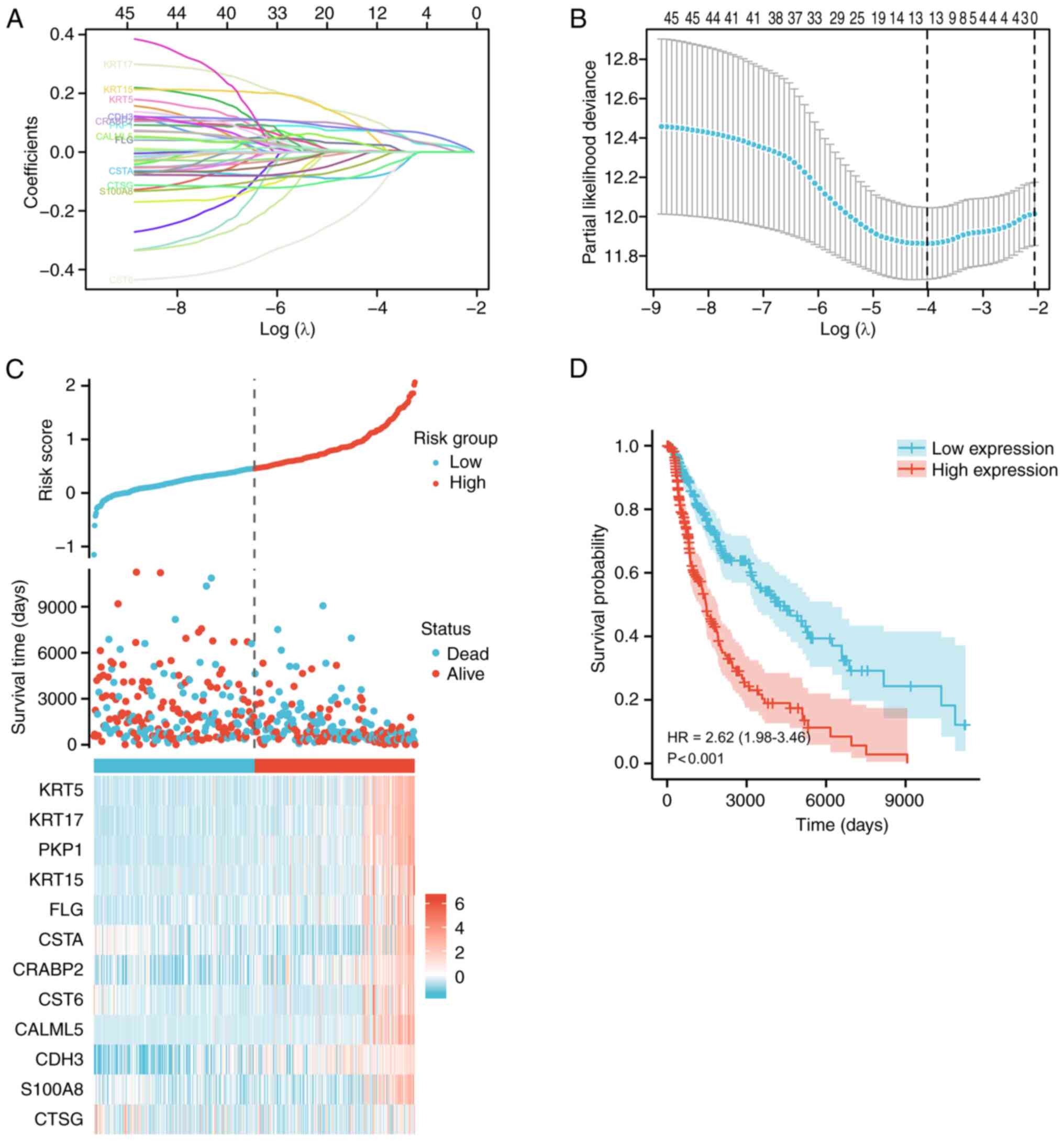
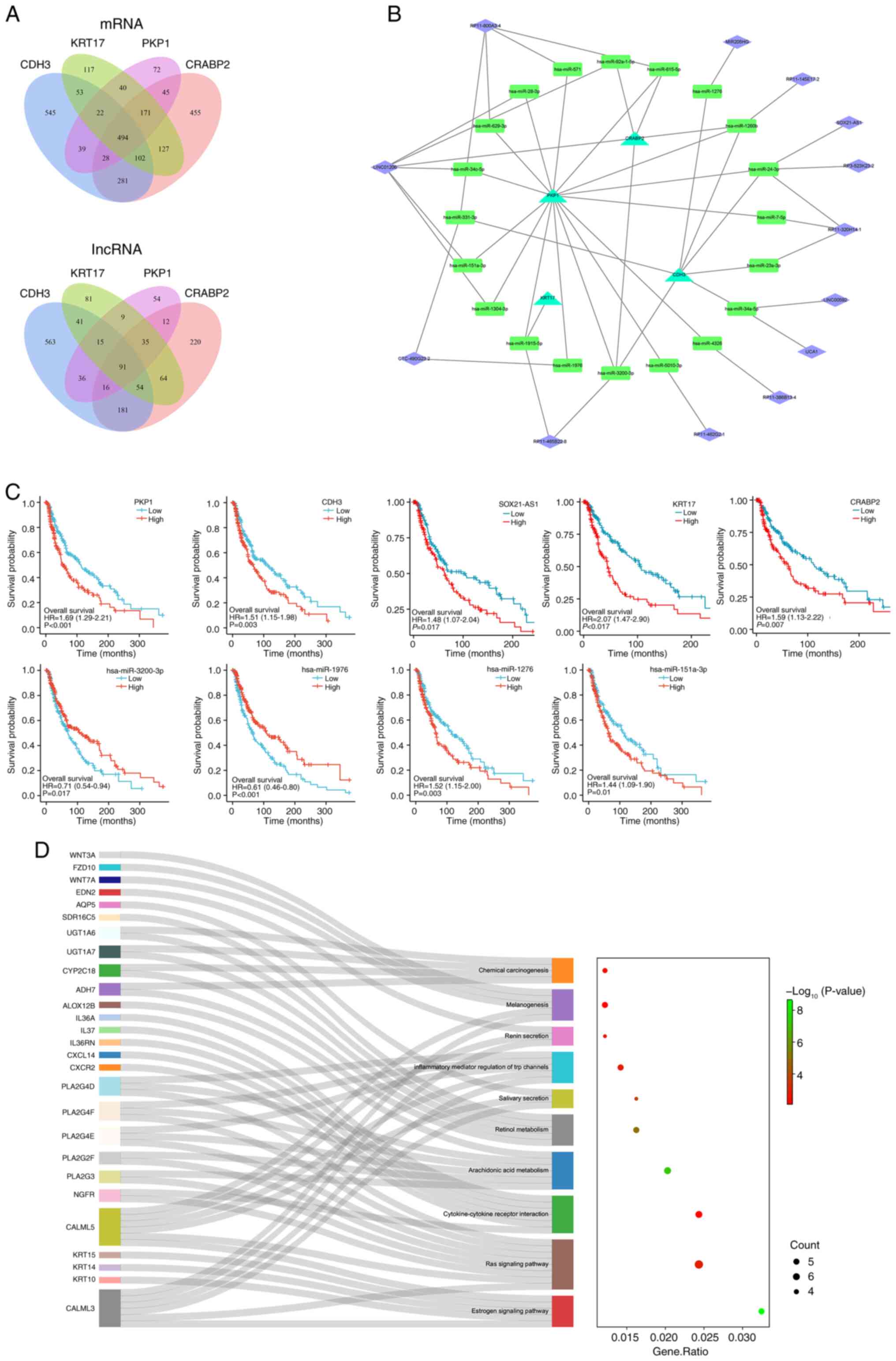
7
|
Tan B, Liu H, Zhang S, da Silva SR, Zhang
L, Meng J, Cui X, Yuan H, Sorel O, Zhang SW, et al: Viral and
cellular N6-Methyladenosine and
N6,2′-O-Dimethyladenosine epitranscriptomes in the KSHV
life cycle. Nat Microbiol. 3:108–120. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Pfeifer GP: Defining driver DNA
methylation changes in human cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 19:11662018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Li Y, Toth JI, Petroski MD, Zhang
Z and Zhao JC: N6-Methyladenosine modification destabilizes
developmental regulators in embryonic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol.
16:191–198. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Alarcón CR, Lee H, Goodarzi H, Halberg N
and Tavazoie SF: N6-Methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for
processing. Nature. 519:482–485. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang H, Weng H and Chen J: m6A
modification in coding and non-coding RNAs: Roles and therapeutic
implications in cancer. Cancer Cell. 37:270–288. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Huang H, Weng H and Chen J: The biogenesis
and precise control of RNA m6A methylation. Trends
Genet. 36:44–52. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Huang H, Weng H, Deng X and Chen J: RNA
modifications in cancer: Functions, mechanisms, and therapeutic
implications. Annu Rev Cancer Biol. 4:221–240. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Weng H, Huang H, Wu H, Qin X, Zhao BS,
Dong L, Shi H, Skibbe J, Shen C, Hu C, et al: METTL14 inhibits
hematopoietic stem/progenitor differentiation and promotes
leukemogenesis via mRNA m6A modification. Cell Stem
Cell. 22:191–205. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang C, Chen Y, Sun B, Wang L, Yang Y, Ma
D, Lv J, Heng J, Ding Y, Xue Y, et al: m6A modulates
haematopoietic stem and progenitor cell specification. Nature.
549:273–276. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Z, Weng H, Su R, Weng X, Zuo Z, Li C,
Huang H, Nachtergaele S, Dong L, Hu C, et al: FTO plays an
oncogenic role in acute myeloid leukemia as a
N6-methyladenosine RNA demethylase. Cancer Cell.
31:127–141. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S,
Lu Z, Chen Y, Sulman EP, Xie K, Bögler O, et al: m6A demethylase
ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells by
Sustaining FOXM1 expression and cell proliferation program. Cancer
Cell. 31:591–606.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang C, Samanta D, Lu H, Bullen JW, Zhang
H, Chen I, He X and Semenza GL: Hypoxia induces the breast cancer
stem cell phenotype by HIF-dependent and ALKBH5-mediated
m6A-demethylation of NANOG mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E2047–E2056. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He F, Yu J, Yang J, Wang S, Zhuang A, Shi
H, Gu X, Xu X, Chai P and Jia R: m6A RNA
hypermethylation-induced BACE2 boosts intracellular calcium release
and accelerates tumorigenesis of ocular melanoma. Mol Ther.
29:2121–2133. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dahal U, Le K and Gupta M: RNA m6A
methyltransferase METTL3 regulates invasiveness of melanoma cells
by matrix metallopeptidase 2. Melanoma Res. 29:382–389. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu L, Shen SS, Hoshida Y, Subramanian A,
Ross K, Brunet JP, Wagner SN, Ramaswamy S, Mesirov JP and Hynes RO:
Gene expression changes in an animal melanoma model correlate with
aggressiveness of human melanoma metastases. Mol Cancer Res.
6:760–769. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cabrita R, Lauss M, Sanna A, Donia M,
Larsen MS, Mitra S, Johansson I, Phung B, Harbst K,
Vallon-Christersson J, et al: Tertiary lymphoid structures improve
immunotherapy and survival in melanoma. Nature. 577:561–565. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singh MP, Sethuraman SN, Ritchey J,
Fiering S, Guha C, Malayer J and Ranjan A: In-situ vaccination
using focused ultrasound heating and anti-CD-40 agonistic antibody
enhances T-cell mediated local and abscopal effects in murine
melanoma. Int J Hyperthermia. 36:64–73. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Raskin L, Fullen DR, Giordano TJ, Thomas
DG, Frohm ML, Cha KB, Ahn J, Mukherjee B, Johnson TM and Gruber SB:
Transcriptome profiling identifies HMGA2 as a biomarker of melanoma
progression and prognosis. J Invest Dermatol. 133:2585–2592. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xu F, Lin H, He P, He L, Chen J, Lin L and
Chen Y: A TP53-associated gene signature for prediction of
prognosis and therapeutic responses in lung squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncoimmunology. 9:17319432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li H, Han D, Hou Y, Chen H and Chen Z:
Statistical inference methods for two crossing survival curves: A
comparison of methods. PLoS One. 10:e01167742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-Seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kolde R, Laur S, Adler P and Vilo J:
Robust rank aggregation for gene list integration and
meta-analysis. Bioinformatics. 28:573–580. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M,
Khodabakhshi A.H, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C and Chanda SK: Metascape
provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of
systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 10:15232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zaccara S, Ries RJ and Jaffrey SR:
Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 20:608–624. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: MicroRNA targets in drosophila. Genome Biol.
5:R12003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R and Guinney
J.GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-Seq
data. BMC Bioinformatics. 14:72013.
|
|
35
|
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Tosolini M,
Kirilovsky A, Waldner M, Obenauf AC, Angell H, Fredriksen T,
Lafontaine L, Berger A, et al: Spatiotemporal dynamics of
intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human
cancer. Immunity. 39:782–795. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The rosetta stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Markovic SN, Erickson LA, Rao RD, Weenig
RH, Pockaj BA, Bardia A, Vachon CM, Schild SE, McWilliams RR, Hand
JL, et al: Malignant melanoma in the 21st century, part 1:
Epidemiology, risk factors, screening, prevention, and diagnosis.
Mayo Clin Proc. 82:364–380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Osipov M and Sokolnikov M: Previous
malignancy as a risk factor for the second solid cancer in a cohort
of nuclear workers. SciMedicine J. 3:8–15. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Jiang X, Liu B, Nie Z, Duan L, Xiong Q,
Jin Z, Yang C and Chen Y: The role of m6A modification in the
biological functions and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
6:742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang X, Li Z, Kong B, Song C, Cong J, Hou
J and Wang S: Reduced m6A mRNA methylation is correlated
with the progression of human cervical cancer. Oncotarget.
8:98918–98930. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kwok CT, Marshall AD, Rasko JEJ and Wong
JJL: Genetic alterations of m6A regulators predict
poorer survival in acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol.
10:392017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Cho SH, Ha M, Cho YH, Ryu JH, Yang K, Lee
KH, Han ME, Oh SO and Kim YH: ALKBH5 gene is a novel biomarker that
predicts the prognosis of pancreatic cancer: A retrospective
multicohort study. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 22:305–309.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhao X, Chen Y, Mao Q, Jiang X, Jiang W,
Chen J, Xu W, Zhong L and Sun X: Overexpression of YTHDF1 is
associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Biomarkers. 21:859–868. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Slebos RJC, Jehmlich N, Brown B, Yin Z,
Chung CH, Yarbrough WG and Liebler DC: Proteomic analysis of
oropharyngeal carcinomas reveals novel HPV-associated biological
pathways. Int J Cancer. 132:568–579. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Deng X, Su R, Feng X, Wei M and Chen J:
Role of N6-methyladenosine modification in cancer. Curr
Opin Genet Dev. 48:1–7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Slominski RM, Sarna T, Płonka PM, Raman C,
Brożyna AA and Slominski AT: Melanoma, melanin, and melanogenesis:
The yin and yang relationship. Front Oncol. 12:8424962022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Han W, Hu C, Fan ZJ and Shen GL:
Transcript levels of keratin 1/5/6/14/15/16/17 as potential
prognostic indicators in melanoma patients. Sci Rep. 11:10232021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Han Y, Li X, Yan J, Ma C, Wang X, Pan H,
Zheng X, Zhang Z, Gao B and Ji XY: Bioinformatic analysis
identifies potential key genes in the pathogenesis of melanoma.
Front Oncol. 10:5819852020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kodet O, Lacina L, Krejčí E, Dvořánková B,
Grim M, Štork J, Kodetová D, Vlček Č, Šáchová J, Kolář M, et al:
Melanoma cells influence the differentiation pattern of human
epidermal keratinocytes. Mol Cancer. 14:12015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
van de Rijn M, Perou CM, Tibshirani R,
Haas P, Kallioniemi O, Kononen J, Torhorst J, Sauter G, Zuber M,
Köchli OR, et al: Expression of cytokeratins 17 and 5 identifies a
group of breast carcinomas with poor clinical outcome. Am J Pathol.
161:1991–1996. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Wang YF, Lang HY, Yuan J, Wang J, Wang R,
Zhang XH, Zhang J, Zhao T, Li YR, Liu JY, et al: Overexpression of
keratin 17 is associated with poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian
cancer. Tumour Biol. 34:1685–1689. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Escobar-Hoyos LF, Yang J, Zhu J, Cavallo
JA, Zhai H, Burke S, Koller A, Chen EI and Shroyer KR: Keratin 17
in premalignant and malignant squamous lesions of the cervix:
Proteomic discovery and immunohistochemical validation as a
diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. Mod Pathol. 27:621–630. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Chivu-Economescu M, Dragu DL, Necula LG,
Matei L, Enciu AM, Bleotu C and Diaconu CC: Knockdown of KRT17 by
siRNA induces antitumoral effects on gastric cancer cells. Gastric
Cancer. 20:948–959. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Harris TM, Du P, Kawachi N, Belbin TJ,
Wang Y, Schlecht NF, Ow TJ, Keller CE, Childs GJ, Smith RV, et al:
Proteomic analysis of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma specimens
identifies patient outcome-associated proteins. Arch Pathol Lab
Med. 139:494–507. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kaz AM, Luo Y, Dzieciatkowski S, Chak A,
Willis JE, Upton MP, Leidner RS and Grady WM: Aberrantly methylated
PKP1 in the progression of Barrett's esophagus to esophageal
adenocarcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 51:384–393. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Haase D, Cui T, Yang L, Ma Y, Liu H, Theis
B, Petersen I and Chen Y: Plakophilin 1 is methylated and has a
tumor suppressive activity in human lung cancer. Exp Mol Pathol.
108:73–79. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Xu Y, Zhao J, Dai X, Xie Y and Dong M:
High expression of CDH3 predicts a good prognosis for colon
adenocarcinoma patients. Exp Ther Med. 18:841–847. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhai J, Li S, Sen S, Opoku-Anane J, Du Y,
Chen ZJ and Giudice LC: m6A RNA methylation regulators
contribute to eutopic endometrium and myometrium dysfunction in
adenomyosis. Front Genet. 11:71620202020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Yan J, Wu X, Yu J, Zhu Y and Cang S:
Prognostic role of tumor mutation burden combined with immune
infiltrates in skin cutaneous melanoma based on multi-omics
analysis. Front Oncol. 10:5706542020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zhang C, Zhi WI, Lu H, Samanta D, Chen I,
Gabrielson E and Semenza GL: Hypoxia-Inducible factors regulate
pluripotency factor expression by ZNF217- and ALKBH5-mediated
modulation of RNA methylation in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget.
7:64527–64542. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Chao Y, Shang J and Ji W:
ALKBH5-m6A-FOXM1 signaling axis promotes proliferation
and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells under intermittent
hypoxia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 521:499–506. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Schöller E, Weichmann F, Treiber T, Ringle
S, Treiber N, Flatley A, Feederle R, Bruckmann A and Meister G:
Interactions, localization, and phosphorylation of the
m6A generating METTL3-METTL14-WTAP complex. RNA.
24:499–512. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Chen Y, Peng C, Chen J, Chen D, Yang B, He
B, Hu W, Zhang Y, Liu H, Dai L, et al: WTAP facilitates progression
of hepatocellular carcinoma via m6A-HuR-dependent epigenetic
silencing of ETS1. Mol Cancer. 18:1272019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ma JZ, Yang F, Zhou CC, Liu F, Yuan JH,
Wang F, Wang TT, Xu QG, Zhou WP and Sun SH: METTL14 suppresses the
metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating
N6-methyladenosine-dependent primary MicroRNA
processing. Hepatology. 65:529–543. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chen M, Wei L, Law CT, Tsang FHC, Shen J,
Cheng CLH, Tsang LH, Ho DWH, Chiu DKC, Lee JMF, et al: RNA
N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer
progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing
of SOCS2. Hepatology. 67:2254–2270. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Georganaki M, Ramachandran M, Tuit S,
Núñez NG, Karampatzakis A, Fotaki G, van Hooren L, Huang H, Lugano
R, Ulas T, et al: Tumor endothelial cell up-regulation of IDO1 is
an immunosuppressive feed-back mechanism that reduces the response
to CD40-stimulating immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology. 9:17305382020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Slominski RM, Raman C, Chen JY and
Slominski AT: How cancer hijacks the body's homeostasis through the
neuroendocrine system. Trends Neurosci. 46:263–275. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|