|
1
|
Siegel RL, Kratzer TB, Giaquinto AN, Sung
H and Jemal A: Cancer statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J Clin. 75:10–45.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xiong Q, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Yang Y, Zhang Z,
Zhou Y, Zhang S, Zhou L, Wan X, Yang X, et al: tiRNA-Val-CAC-2
interacts with FUBP1 to promote pancreatic cancer metastasis by
activating c-MYC transcription. Oncogene. 43:1274–1287. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Munigala S, Almaskeen S, Subramaniam DS,
Bandi S, Bowe B, Xian H, Sheth SG, Burroughs TE and Agarwal B:
Acute pancreatitis recurrences augment long-term pancreatic cancer
risk. Am J Gastroenterol. 118:727–737. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Topal H, Aerts R, Laenen A, Collignon A,
Jaekers J, Geers J and Topal B: Survival after minimally invasive
vs open surgery for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. JAMA Netw Open.
5:e22481472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Padrón LJ, Maurer DM, O'Hara MH, O'Reilly
EM, Wolff RA, Wainberg ZA, Ko AH, Fisher G, Rahma O, Lyman JP, et
al: Sotigalimab and/or nivolumab with chemotherapy in first-line
metastatic pancreatic cancer: Clinical and immunologic analyses
from the randomized phase 2 PRINCE trial. Nat Med. 28:1167–1177.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li K, Tandurella JA, Gai J, Zhu Q, Lim SJ,
Thomas DL II, Xia T, Mo G, Mitchell JT, Montagne J, et al:
Multi-omic analyses of changes in the tumor microenvironment of
pancreatic adenocarcinoma following neoadjuvant treatment with
anti-PD-1 therapy. Cancer Cell. 40:1374–1391. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Guo X, Xu P, Song Y, Huang J, Chen
X, Zhu W, Hao J and Gao S: Clinical outcomes of second-line
chemotherapy in patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A
real-world study. Cancer Biol Med. 21:799–812. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Beutel AK and Halbrook CJ: Barriers and
opportunities for gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer therapy. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 324:C540–C552. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Patzak MS, Kari V, Patil S, Hamdan FH,
Goetze RG, Brunner M, Gaedcke J, Kitz J, Jodrell DI, Richards FM,
et al: Cytosolic 5′-nucleotidase 1A is overexpressed in pancreatic
cancer and mediates gemcitabine resistance by reducing
intracellular gemcitabine metabolites. EBioMedicine. 40:394–405.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Neoptolemos JP, Palmer DH, Ghaneh P,
Psarelli EE, Valle JW, Halloran CM, Faluyi O, O'Reilly DA,
Cunningham D, Wadsley J, et al: Comparison of adjuvant gemcitabine
and capecitabine with gemcitabine monotherapy in patients with
resected pancreatic cancer (ESPAC-4): A multicentre, open-label,
randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 389:1011–1024. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hosein AN, Brekken RA and Maitra A:
Pancreatic cancer stroma: An update on therapeutic targeting
strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:487–505. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wicks EE and Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible
factors: Cancer progression and clinical translation. J Clin
Invest. 132:e1598392022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mao Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Fu Z, Dong L and
Liu J: Hypoxia induced exosomal Circ-ZNF609 promotes pre-metastatic
niche formation and cancer progression via miR-150-5p/VEGFA and
HuR/ZO-1 axes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death
Discov. 10:1332024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song H, Qiu Z, Wang Y, Xi C, Zhang G, Sun
Z, Luo Q and Shen C: HIF-1α/YAP signaling rewrites glucose/iodine
metabolism program to promote papillary thyroid cancer progression.
Int J Biol Sci. 19:225–241. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang Q, Xiong L, Wei T, Liu Q, Yan L,
Chen J, Dai L, Shi L, Zhang W, Yang J, et al: Hypoxia-responsive
PPARGC1A/BAMBI/ACSL5 axis promotes progression and resistance to
lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 42:1509–1523.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ye M, Lu F, Gu D, Xue B, Xu L, Hu C, Chen
J, Yu P, Zheng H, Gao Y, et al: Hypoxia exosome derived CEACAM5
promotes tumor-associated macrophages M2 polarization to accelerate
pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors metastasis via MMP9. FASEB J.
38:e237622024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hou SM, Lin CY, Fong YC and Tang CH:
Hypoxia-regulated exosomes mediate M2 macrophage polarization and
promote metastasis in chondrosarcoma. Aging (Albany NY).
15:13163–13175. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu W, Li L, Rong Y, Qian D, Chen J, Zhou
Z, Luo Y, Jiang D, Cheng L, Zhao S, et al: Hypoxic mesenchymal stem
cell-derived exosomes promote bone fracture healing by the transfer
of miR-126. Acta Biomater. 103:196–212. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang M, Zheng Y, Hao Q, Mao G, Dai Z, Zhai
Z, Lin S, Liang B, Kang H and Ma X: Hypoxic BMSC-derived exosomal
miR-210-3p promotes progression of triple-negative breast cancer
cells via NFIX-Wnt/β-catenin signaling axis. J Transl Med.
23:392025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jia Y, Zhao J, Yang J, Shao J and Cai Z:
miR-301 regulates the SIRT1/SOX2 pathway via CPEB1 in the breast
cancer progression. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 22:13–26. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xia X, Wang S, Ni B, Xing S, Cao H, Zhang
Z, Yu F, Zhao E and Zhao G: Hypoxic gastric cancer-derived exosomes
promote progression and metastasis via MiR-301a-3p/PHD3/HIF-1α
positive feedback loop. Oncogene. 39:6231–6244. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alves Â, Ferreira M, Eiras M, Lima L,
Medeiros R, Teixeira AL and Dias F: Exosome-derived
hsa-miR-200c-3p, hsa-miR-25-3p and hsa-miR-301a-3p as potential
biomarkers and therapeutic targets for restoration of PTEN
expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J Biol Macromol.
302:1406072025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhong M, Huang Z, Wang L, Lin Z, Cao Z, Li
X, Zhang F, Wang H, Li Y and Ma X: Malignant transformation of
human bronchial epithelial cells induced by arsenic through
STAT3/miR-301a/SMAD4 loop. Sci Rep. 8:132912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang X, Luo G, Zhang K, Cao J, Huang C,
Jiang T, Liu B, Su L and Qiu Z: Hypoxic tumor-derived exosomal
miR-301a mediates M2 macrophage polarization via PTEN/PI3K gamma to
promote pancreatic cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 78:4586–4598.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luo G, Xia X, Wang X, Zhang K, Cao J,
Jiang T, Zhao Q and Qiu Z: miR-301a plays a pivotal role in
hypoxia-induced gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer. Exp
Cell Res. 369:120–128. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ding K, Liu C, Li L, Yang M, Jiang N, Luo
S and Sun L: Acyl-CoA synthase ACSL4: An essential target in
ferroptosis and fatty acid metabolism. Chin Med J (Engl).
136:2521–2537. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qiu Y, Wang X, Sun Y, Jin T, Tang R, Zhou
X, Xu M, Gan Y, Wang R, Luo H, et al: ACSL4-mediated membrane
phospholipid remodeling induces integrin β1 activation to
facilitate triple-negative breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res.
84:1856–1871. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen J, Ding C, Chen Y, Hu W, Yu C, Peng
C, Feng X, Cheng Q, Wu W, Lu Y, et al: ACSL4 reprograms fatty acid
metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma via c-Myc/SREBP1 pathway.
Cancer Lett. 502:154–165. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Grube J, Woitok MM, Mohs A, Erschfeld S,
Lynen C, Trautwein C and Otto T: ACSL4-dependent ferroptosis does
not represent a tumor-suppressive mechanism but ACSL4 rather
promotes liver cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. 13:7042022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lu Y, Chan YT, Tan HY, Zhang C, Guo W, Xu
Y, Sharma R, Chen ZS, Zheng YC, Wang N and Feng Y: Epigenetic
regulation of ferroptosis via ETS1/miR-23a-3p/ACSL4 axis mediates
sorafenib resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 41:32022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shi L, Song Z, Li Y, Huang J, Zhao F, Luo
Y, Wang J, Deng F, Shadekejiang H, Zhang M, et al: MiR-20a-5p
alleviates kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting
ACSL4-dependent ferroptosis. Am J Transplant. 23:11–25. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Qi R, Bai Y, Li K, Liu N, Xu Y, Dal E,
Wang Y, Lin R, Wang H, Liu Z, et al: Cancer-associated fibroblasts
suppress ferroptosis and induce gemcitabine resistance in
pancreatic cancer cells by secreting exosome-derived
ACSL4-targeting miRNAs. Drug Resist Updat. 68:1009602023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Deer EL, González-Hernández J, Coursen JD,
Shea JE, Ngatia J, Scaife CL, Firpo MA and Mulvihill SJ: Phenotype
and genotype of pancreatic cancer cell lines. Pancreas. 39:425–435.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li W, Zhou C, Yu L, Hou Z, Liu H, Kong L,
Xu Y, He J, Lan J, Ou Q, et al: Tumor-derived lactate promotes
resistance to bevacizumab treatment by facilitating autophagy
enhancer protein RUBCNL expression through histone H3 lysine 18
lactylation (H3K18la) in colorectal cancer. Autophagy. 20:114–130.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:12–49. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang L, Zhao S, Liu X, Zhang Y, Zhao S,
Fang X and Zhang J: Hypoxic cancer-associated fibroblast exosomal
circSTAT3 drives triple negative breast cancer stemness via
miR-671-5p/NOTCH1 signaling. J Transl Med. 23:8142025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shukla SK, Purohit V, Mehla K, Gunda V,
Chaika NV, Vernucci E, King RJ, Abrego J, Goode GD, Dasgupta A, et
al: MUC1 and HIF-1alpha signaling crosstalk induces anabolic
glucose metabolism to impart gemcitabine resistance to pancreatic
cancer. Cancer Cell. 32:71–87. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yoo HC, Park SJ, Nam M, Kang J, Kim K, Yeo
JH, Kim JK, Heo Y, Lee HS, Lee MY, et al: A variant of SLC1A5 is a
mitochondrial glutamine transporter for metabolic reprogramming in
cancer cells. Cell Metab. 31:267–283. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ding J, Xie Y, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Ni B, Yan
J, Zhou T and Hao J: Hypoxic and acidic tumor
microenvironment-driven AVL9 promotes chemoresistance of pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma via the AVL9-IκBα-SKP1 complex.
Gastroenterology. 168:539–555. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cheng C, Zhang Z, Cheng F and Shao Z:
Exosomal lncRNA RAMP2-AS1 derived from chondrosarcoma cells
promotes angiogenesis through miR-2355-5p/VEGFR2 axis. Onco Targets
Ther. 13:3291–3301. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Organization NP, . Nobel Prize in
Physiology or Medicine. 2024.https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/2024/press–release/January
5–2025
|
|
44
|
Zhao S, Mi Y, Guan B, Zheng B, Wei P, Gu
Y, Zhang Z, Cai S, Xu Y, Li X, et al: Tumor-derived exosomal
miR-934 induces macrophage M2 polarization to promote liver
metastasis of colorectal cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 13:1562020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhang H, Deng T, Liu R, Ning T, Yang H,
Liu D, Zhang Q, Lin D, Ge S, Bai M, et al: CAF secreted miR-522
suppresses ferroptosis and promotes acquired chemo-resistance in
gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 19:432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li X, Li J, Cai Y, Peng S, Wang J, Xiao Z,
Wang Y, Tao Y, Li J, Leng Q, et al: Hyperglycaemia-induced miR-301a
promotes cell proliferation by repressing p21 and Smad4 in prostate
cancer. Cancer Lett. 418:211–220. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Qi B, Wang Y, Zhu X, Gong Y, Jin J, Wu H,
Man X, Liu F, Yao W and Gao J: miR-301a-mediated crosstalk between
the Hedgehog and HIPPO/YAP signaling pathways promotes pancreatic
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 26:24577612025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang KD, Hu B, Cen G, Yang YH, Chen WW,
Guo ZY, Wang XF, Zhao Q and Qiu ZJ: MiR-301a transcriptionally
activated by HIF-2α promotes hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition by targeting TP63 in pancreatic cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 26:2349–2373. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Li J, Ma C, Cao P, Guo W, Wang P, Yang Y,
Ding B, Yin F, Li Z, Wang Y, et al: A CD147-targeted small-molecule
inhibitor potentiates gemcitabine efficacy by triggering
ferroptosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Rep Med.
6:1022922025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|















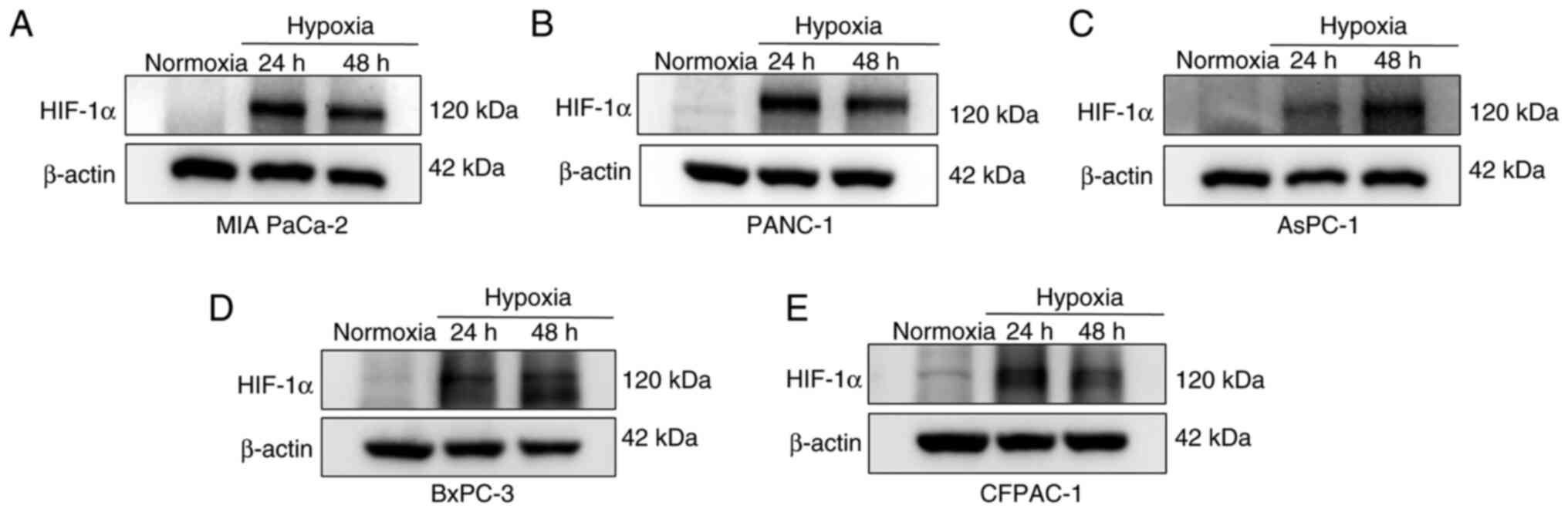
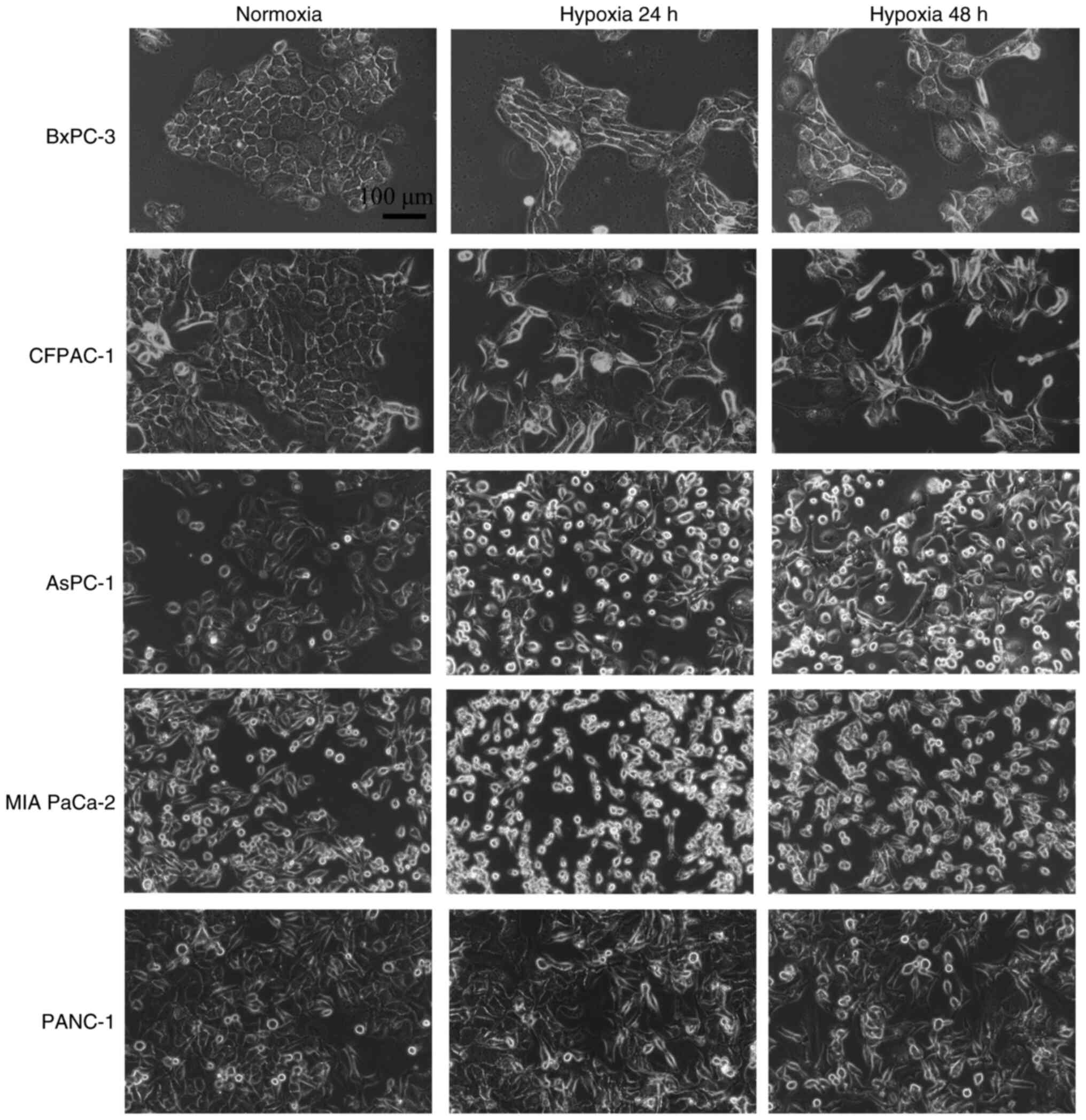
![Hypoxia upregulates the expression
levels of miR-301a and enhances GEM resistance in PC cells. (A-E)
Relative expression levels of miR-301a in PC cell lines [(A) MIA
PaCa-2, (B) PANC-1, (C) AsPC-1, (D) BxPC-3 and (E) CFPAC-1] were
detected using RT-qPCR following culture under normoxia conditions
and hypoxic conditions for 24 and 48 h. (F-J) Cell viability of PC
cells [(F) MIA PaCa-2, (G) PANC-1, (H) BxPC-3, (I) AsPC-1 and (J)
CFPAC-1] in both hypoxic and normoxic treatment groups was measured
using CCK-8 cytotoxicity assays upon exposure to various
concentrations of GEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and
****P<0.0001. NO, normoxic; HO, hypoxic; PC, pancreatic cancer;
miR, microRNA; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR;
CCK-8, Cell Counting Kit-8; GEM, gemcitabine; CFPAC-1, cystic
fibrosis pancreatic adenocarcinoma; AsPC-1, ascites pancreatic
cancer 1; MIA PaCa-2, malignant inflammatory adenocarcinoma
pancreatic carcinoma-2.](/article_images/ol/30/6/ol-30-06-15352-g02.jpg)