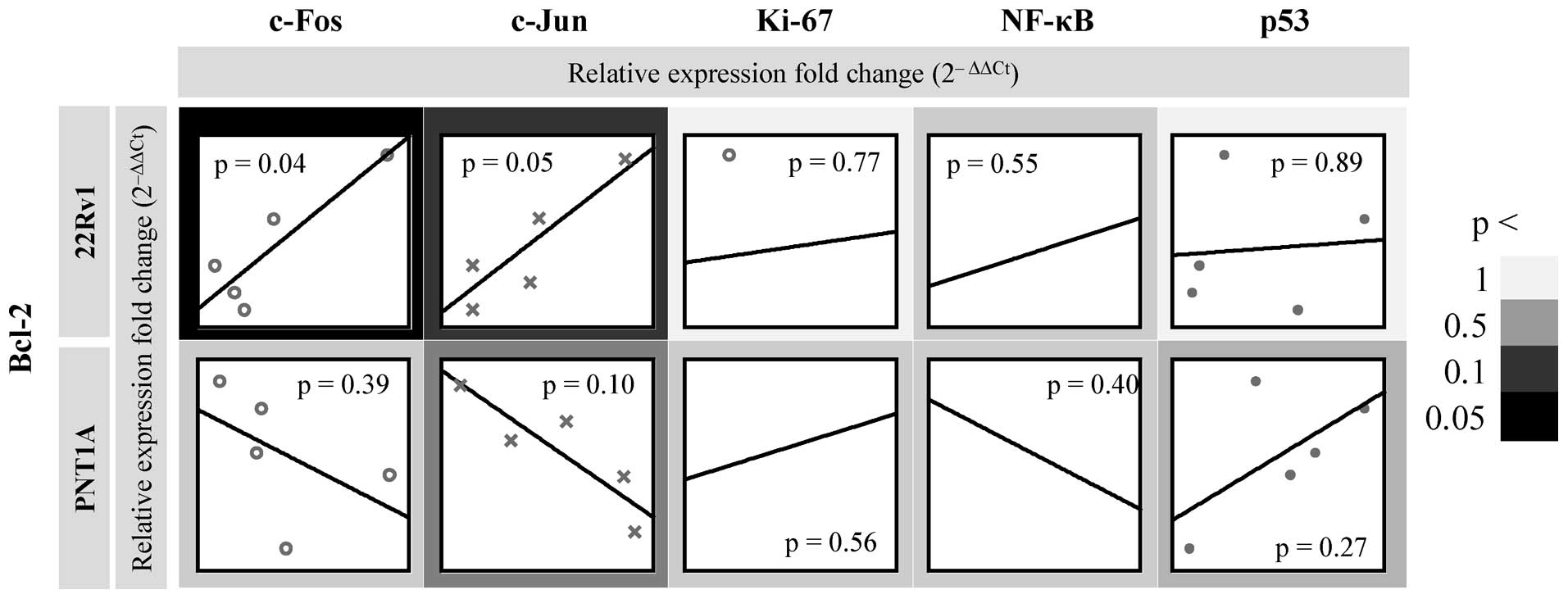
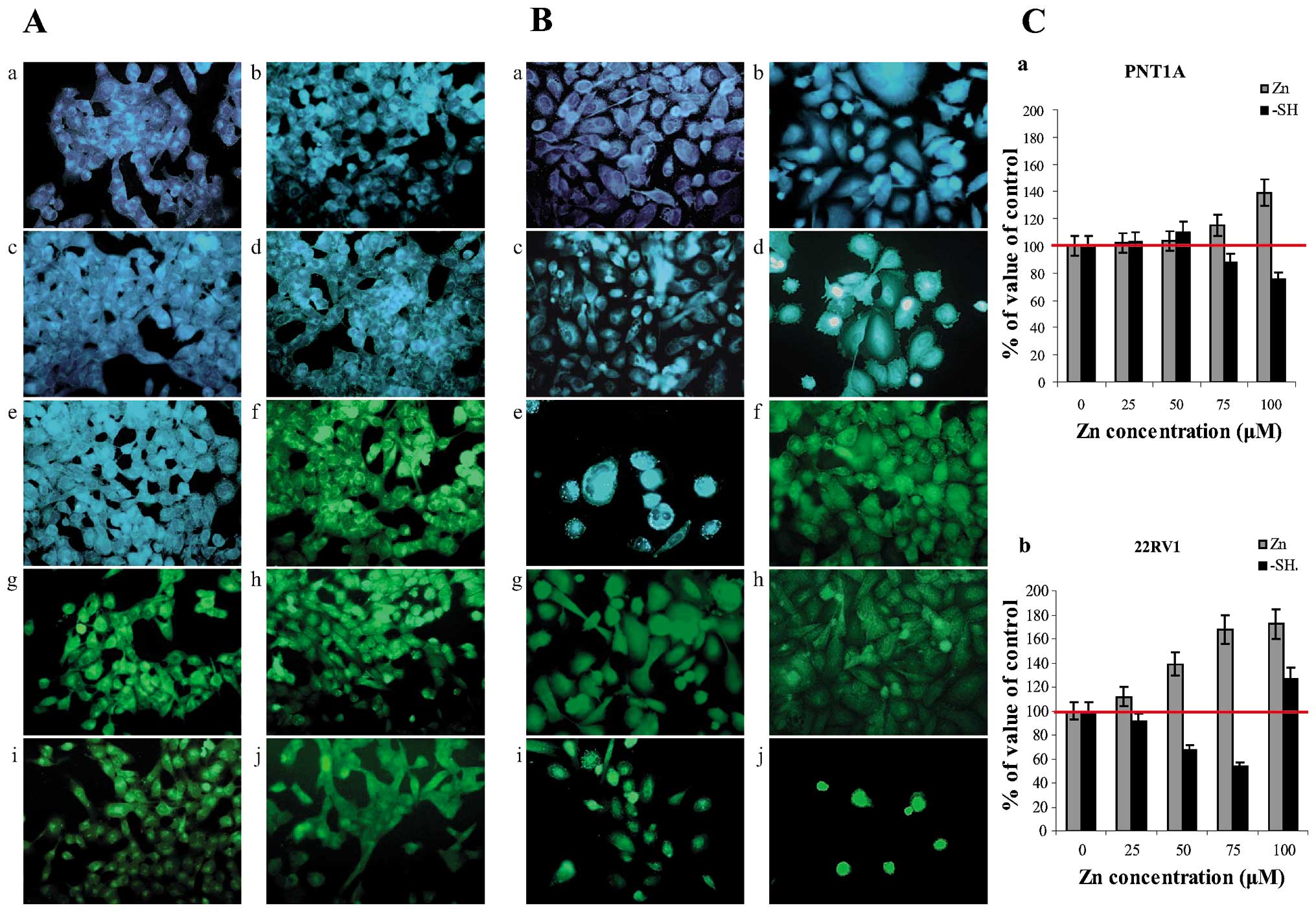
|
1
|
Bray F, Lortet-Tieulent J, Ferlay J,
Forman D and Auvinen A: Prostate cancer incidence and mortality
trends in 37 European countries: an overview. Eur J Cancer.
46:3040–3052. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ghoneum M and Gollapudi S: Susceptibility
of the human LNCaP prostate cancer cells to the apoptotic effect of
marina crystal minerals (MCM) in vitro. Oncol Rep.
22:155–159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zaichick VY, Sviridova TV and Zaichick SV:
Zinc in human prostate gland: normal, hyperplastic and cancerous. J
Radioanal Nucl Chem. 217:157–161. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Costello LC and Franklin RB: Zinc is
decreased in prostate cancer: an established relationship of
prostate cancer! J Biol Inorg Chem. 16:3–8. 2011.
|
|
5
|
Krizkova S, Blahova P, Nakielna J, et al:
Comparison of metallothionein detection by using of Brdicka
reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay employing chicken
yolk antibodies. Electroanalysis. 21:2575–2583. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Krizkova S, Ryvolova M, Gumulec J, et al:
Electrophoretic fingerprint metallothionein analysis as a potential
prostate cancer biomarker. Electrophoresis. 32:1952–1961. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Krizkova S, Masarik M, Eckschlager T, Adam
V and Kizek R: Effects of redox conditions and zinc(II) ions on
metallothionein aggregation revealed by chip capillary
electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A. 1217:7966–7971. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bataineh ZM, Hani IHB and Al-Alami JR:
Zinc in normal and pathological human prostate gland. Saudi Med J.
23:218–220. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cory S, Huang DCS and Adams JM: The Bcl-2
family: roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene.
22:8590–8607. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bruckheimer EM, Cho S, Brisbay S, et al:
The impact of bcl-2 expression and bax deficiency on prostate
homeostasis in vivo. Oncogene. 19:2404–2412. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gastman BR: Apoptosis and its clinical
impact. Head Neck-J Sci Spec Head Neck. 23:409–425. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anai S, Goodison S, Shiverick K, Hirao Y,
Brown BD and Rosser CJ: Knock-down of Bcl-2 by antisense
oligodeoxynucleotides induces radiosensitization and inhibition of
angiogenesis in human PC-3 prostate tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer
Ther. 6:101–111. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu L, Yang DJ, Wang SM, et al:
(-)-gossypol enhances response to radiation therapy and results in
tumor regression of human prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
4:197–205. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nomura T, Yamasaki M, Nomura Y and Mimata
H: Expression of the inhibitors of apoptosis proteins in
cisplatin-resistant prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 14:993–997.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Concato J, Jain D, Uchio E, Risch H, Li WW
and Wells CK: Molecular markers and death from prostate cancer. Ann
Intern Med. 150:U595–U596. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Dachille G, Cai T, Ludovico GM, et al:
Prognostic role of cell apoptotic rate in prostate cancer: outcome
of a long-time follow-up study. Oncol Rep. 19:541–545.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Catz SD and Johnson JL: Bcl-2 in prostate
cancer: a minireview. Apoptosis. 8:29–37. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Masarik M, Gumulec J, Sztalmachova M, et
al: Isolation of metallothionein from cells derived from aggressive
form of high-grade prostate carcinoma using paramagnetic
antibody-modified microbeads off-line coupled with electrochemical
and electrophoretic analysis. Electrophoresis. 32:3576–3588. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Babula P, Kohoutkova V, Opatrilova R,
Dankova I, Masarik M and Kizek R: Pharmaceutical importance of zinc
and metallothionein in cell signalling. Chim Oggi-Chem Today.
28:18–21. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Krizkova S, Fabrik I, Adam V, Hrabeta J,
Eckschlager T and Kizek R: Metallothionein - a promising tool for
cancer diagnostics. Bratisl Med J-Bratisl Lek Listy. 110:93–97.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Eckschlager T, Adam V, Hrabeta J, Figova K
and Kizek R: Metallothioneins and cancer. Curr Protein Pept Sci.
10:360–375. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Adam V, Fabrik I, Eckschlager T, Stiborova
M, Trnkova L and Kizek R: Vertebrate metallothioneins as target
molecules for analytical techniques. TRAC-Trends Anal Chem.
29:409–418. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ryvolova M, Adam V and Kizek R: Analysis
of metallothionein by capillary electrophoresis (review). J
Chromatogr A. 1226:31–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ryvolova M, Krizkova S, Adam V, et al:
Analytical methods for metallothionein detection. Curr Anal Chem.
7:243–261. 2011.
|
|
26
|
Costello LC, Liu YY, Franklin RB and
Kennedy MC: Zinc inhibition of mitochondrial aconitase and its
importance in citrate metabolism of prostate epithelial cells. J
Biol Chem. 272:28875–28881. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Beyersmann D and Haase H: Functions of
zinc in signaling, proliferation and differentiation of mammalian
cells. Biometals. 14:331–341. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Baranano DE, Ferris CD and Snyder SH:
Atypical neural messengers. Trends Neurosci. 24:99–106. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hogstrand C, Kille P, Nicholson RI and
Taylor KM: Zinc transporters and cancer: a potential role for ZIP7
as a hub for tyrosine kinase activation. Trends Mol Med.
15:101–111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Costello LC and Franklin RB: The
intermediary metabolism of the prostate: A key to understanding the
pathogenesis and progression of prostate malignancy. Oncology.
59:269–282. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gumulec J, Masarik M, Krizkova S, et al:
Insight to physiology and pathology of zinc(II) ions and their
actions in breast and prostate carcinoma. Curr Med Chem.
18:5041–5051. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Scott SL, Higdon R, Beckett L, et al:
Bcl-2 antisense reduces prostate cancer cell survival following
irradiation. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 17:647–656. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hess J, Angel P and Schorpp-Kistner M:
AP-1 subunits: quarrel and harmony among siblings. J Cell Sci.
117:5965–5973. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ameyar M, Wisniewska M and Weitzman JB: A
role for AP-1 in apoptosis: the case for and against. Biochimie.
85:747–752. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Leppa S and Bohmann D: Diverse functions
of JNK signaling and c-Jun in stress response and apoptosis.
Oncogene. 18:6158–6162. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wisdom R, Johnson RS and Moore C: c-Jun
regulates cell cycle progression and apoptosis by distinct
mechanisms. EMBO J. 18:188–197. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Charital YM, van Haasteren G, Massiha A,
Schlegel W and Fujita T: A functional NF-kappaB enhancer element in
the first intron contributes to the control of c-fos transcription.
Gene. 430:116–122. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang L, Kirschke CP and Zhang Y:
Decreased intracellular zinc in human tumorigenic prostate
epithelial cells: a possible role in prostate cancer progression.
Cancer Cell Int. 6:1–10. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Golovine K, Uzzo RG, Makhov P, Crispen PL,
Kunkle D and Kolenko VM: Depletion of intracellular zinc increases
expression of tumorigenic cytokines VEGF, IL-6 and IL-8 in prostate
cancer cells via NF-kappa B-dependent pathway. Prostate.
68:1443–1449. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Radhakrishnan SK and Kamalakaran S:
Pro-apoptotic role of NF-kappaB: implications for cancer therapy.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1766:53–62. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bohuslav J, Chen LF, Kwon H, Mu YJ and
Greene WC: p53 induces NF-kappa B activation by an I kappa B
kinase-independent mechanism involving phosphorylation of p65 by
ribosomal S6 kinase 1. J Biol Chem. 279:26115–26125. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Webster GA and Perkins ND: Transcriptional
cross talk between NF-kappaB and p53. Mol Cell Biol. 19:3485–3495.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chowdhury R, Chowdhury S, Roychoudhury P,
Mandal C and Chaudhuri K: Arsenic induced apoptosis in malignant
melanoma cells is enhanced by menadione through ROS generation, p38
signaling and p53 activation. Apoptosis. 14:108–123. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li ZS, Shi KJ, Guan LY, et al: ROS leads
to MnSOD upregulation through ERK2 translocation and p53 activation
in selenite-induced apoptosis of NB4 cells. FEBS Lett.
584:2291–2297. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bragado P, Armesilla A, Silva A and Porras
A: Apoptosis by cisplatin requires p53 mediated p38 alpha MAPK
activation through ROS generation. Apoptosis. 12:1733–1742. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bullwinkel J, Baron-Luhr B, Ludemann A,
Wohlenberg C, Gerdes J and Scholzen T: Ki-67 protein is associated
with ribosomal RNA transcription in quiescent and proliferating
cells. J Cell Physiol. 206:624–635. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rahmanzadeh R, Huttmann G, Gerdes J and
Scholzen T: Chromophore-assisted light inactivation of pKi-67 leads
to inhibition of ribosomal RNA synthesis. Cell Prolif. 40:422–430.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nariculam J, Freeman A, Bott S, et al:
Utility of tissue microarrays for profiling prognostic biomarkers
in clinically localized prostate cancer: the expression of Bcl-2,
E-cadherin, Ki-67 and p53 as predictors of biochemical failure
after radical prostatectomy with nested control for clinical and
pathological risk factors. Asian J Androl. 11:109–118. 2009.
|
|
49
|
Mitra AV, Jameson C, Barbachano Y, et al:
Elevated expression of Ki-67 identifies aggressive prostate cancers
but does not distinguish BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation carriers. Oncol
Rep. 23:299–305. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Khatami A, Hugosson J, Wang WZ and Damber
JE: Ki-67 in screen-detected, low-grade, low-stage prostate cancer,
relation to prostate-specific antigen doubling time, Gleason score
and prostate-specific antigen relapse after radical prostatectomy.
Scand J Urol Nephrol. 43:12–18. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Jhavar S, Bartlett J, Kovacs G, et al:
Biopsy tissue microarray study of Ki-67 expression in untreated,
localized prostate cancer managed by active surveillance. Prostate
Cancer Prostatic Dis. 12:143–147. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li RL, Heydon K, Hammond ME, et al: Ki-67
staining index predicts distant metastasis and survival in locally
advanced prostate cancer treated with radiotherapy: an analysis of
patients in radiation therapy oncology group protocol 86-10. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:4118–4124. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|