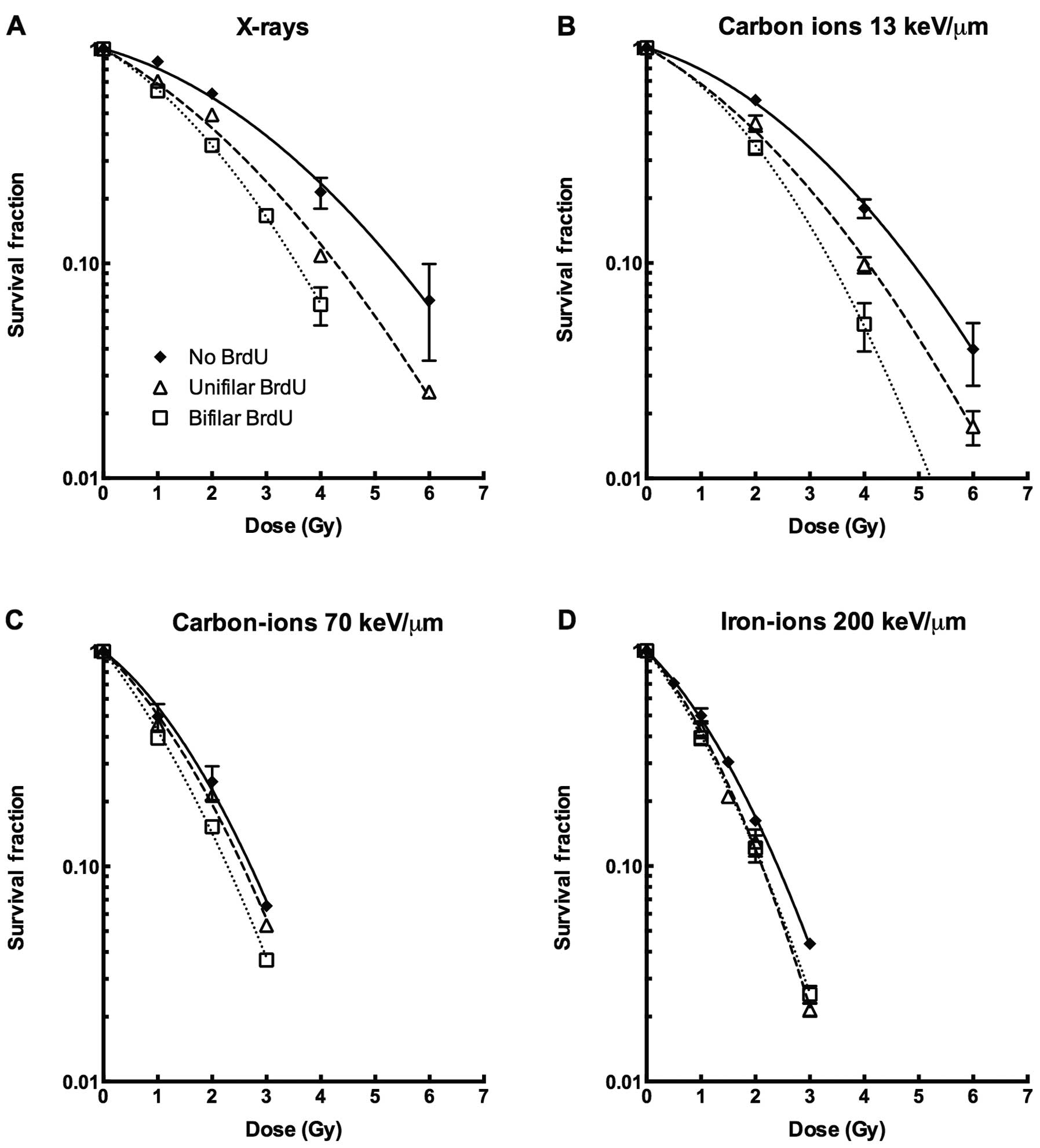
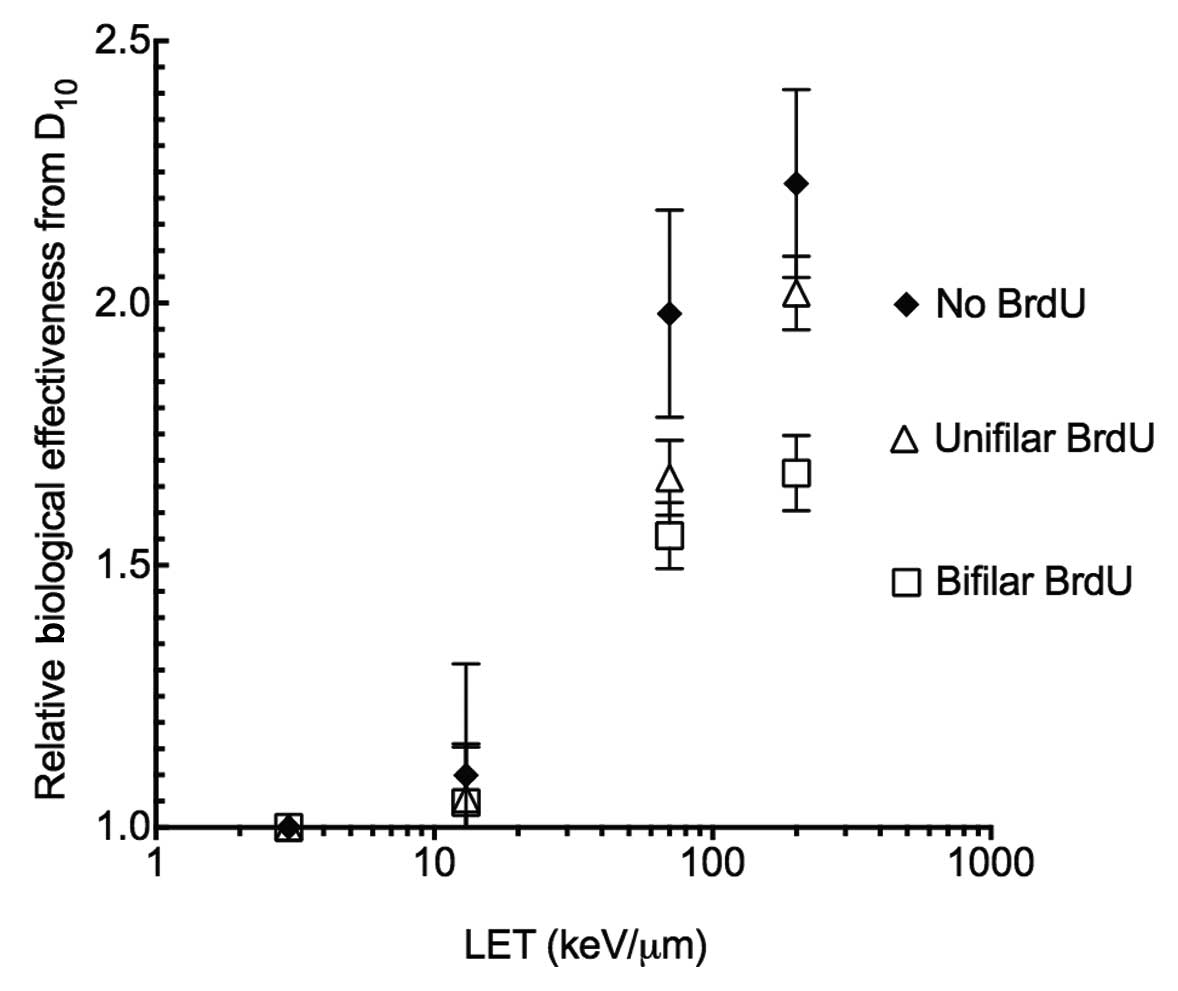
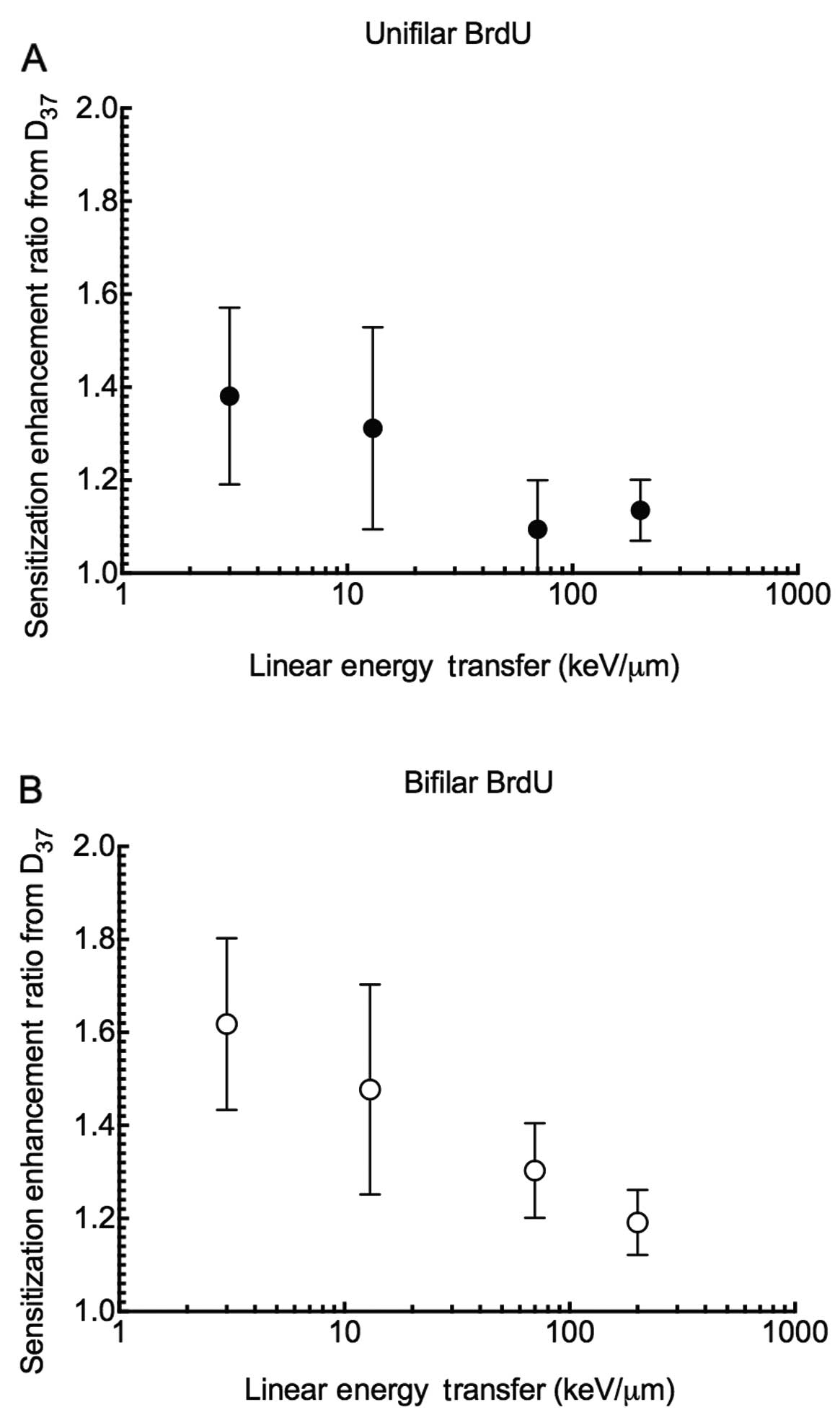
|
1
|
Mitchell JB, Russo A, Cook JA, Straus KL
and Glatstein E: Radiobiology and clinical application of
halogenated pyrimidine radiosensitizers. Int J Radiat Biol.
56:827–836. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Franken NA, Van Bree CV, Kipp JB and
Barendsen GW: Modification of potentially lethal damage in
irradiated Chinese hamster V79 cells after incorporation of
halogenated pyrimidines. Int J Radiat Biol. 72:101–109. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
McLaughlin PW, Lawrence TS, Seabury H, et
al: Bromodeoxyuridine-mediated radiosensitization in human glioma:
the effect of concentration, duration, and fluoropyrimidine
modulation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 30:601–607. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kinsella TJ, Dobson PP, Mitchell JB and
Fornace AJ Jr: Enhancement of X ray-induced DNA damage by
pre-treatment with halogenated pyrimidine analogs. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 13:733–739. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zeng Y and Wang Y: UVB-induced formation
of intrastrand cross-link products of DNA in MCF-7 cells treated
with 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine. Biochemistry. 46:8189–8195.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zeng Y and Wang Y: Sequence-dependent
formation of intrastrand crosslink products from the UVB
irradiation of duplex DNA containing a 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine or
5-bromo-2′-deoxycytidine. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:6521–6529.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Puck TT and Kao FT: Genetics of somatic
mammalian cells. V Treatment with 5-bromodeoxyuridine and visible
light for isolation of nutritionally deficient mutants. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 58:1227–1234. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Iliakis G, Pantelias G and Kurtzman S:
Mechanism of radiosensitization by halogenated pyrimidines: effect
of BrdU on cell killing and interphase chromosome breakage in
radiation-sensitive cells. Radiat Res. 125:56–64. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Webb CF, Jones GD, Ward JF, Moyer DJ,
Aguilera JA and Ling LL: Mechanisms of radiosensitization in
bromodeoxyuridine-substituted cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 64:695–705.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zimbrick JD, Ward JF and Myers LS Jr:
Studies on the chemical basis of cellular radiosensitization by
5-bromouracil substitution in DNA. I Pulse- and steady-state
radiolysis of 5-bromouracil and thymine. Int J Radiat Biol Relat
Stud Phys Chem Med. 16:505–523. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zimbrick JD, Ward JF and Myers LS Jr:
Studies on the chemical basis of cellular radiosensitization by
5-bromouracil substitution in DNA. II Pulse- and steady state
radiolysis of bromouracil-substituted and -unsubstituted DNA. Int J
Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 16:525–534. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Watanabe R and Nikjoo H: Modelling the
effect of incorporated halogenated pyrimidine on radiation-induced
DNA strand breaks. Int J Radiat Biol. 78:953–966. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jones GD, Ward JF, Limoli CL, Moyer DJ and
Aguilera JA: Mechanisms of radiosensitization in
iododeoxyuridine-substituted cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 67:647–653.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Iliakis G, Wang Y, Pantelias GE and
Metzger L: Mechanism of radiosensitization by halogenated
pyrimidines: effect of BrdU on repair of DNA breaks, interphase
chromatin breaks, and potentially lethal damage in plateau-phase
CHO cells. Radiat Res. 129:202–211. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Iliakis G, Kurtzman S, Pantelias G and
Okayasu R: Mechanism of radiosensitization by halogenated
pyrimidines: effect of BrdU on radiation induction of DNA and
chromosome damage and its correlation with cell killing. Radiat
Res. 119:286–304. 1989. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Iliakis G and Kurtzman S: Mechanism of
radiosensitization by halogenated pyrimidines: bromodeoxyuridine
and beta-arabinofuranosyladenine affect similar subsets of
radiation-induced potentially lethal lesions in plateau-phase
Chinese hamster ovary cells. Radiat Res. 127:45–51. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Blakely EA and Kronenberg A: Heavy-ion
radiobiology: new approaches to delineate mechanisms underlying
enhanced biological effectiveness. Radiat Res. 150:S126–S145. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Eguchi-Kasai K, Murakami M, Itsukaichi H,
et al: Repair of DNA double-strand breaks and cell killing by
charged particles. Adv Space Res. 22:543–549. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tsujii H, Mizoe JE, Kamada T, et al:
Overview of clinical experiences on carbon ion radiotherapy at
NIRS. Radiother Oncol. 73(Suppl 2): S41–S49. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jakel O: The relative biological
effectiveness of proton and ion beams. Z Med Phys. 18:276–285.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Prise KM, Pinto M, Newman HC and Michael
BD: A review of studies of ionizing radiation-induced double-strand
break clustering. Radiat Res. 156:572–576. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fakir H, Sachs RK, Stenerlow B and Hofmann
W: Clusters of DNA double-strand breaks induced by different doses
of nitrogen ions for various LETs: experimental measurements and
theoretical analyses. Radiat Res. 166:917–927. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hada M and Georgakilas AG: Formation of
clustered DNA damage after high-LET irradiation: a review. J Radiat
Res. 49:203–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pinto M, Prise KM and Michael BD: Evidence
for complexity at the nanometer scale of radiation-induced DNA DSBs
as a determinant of rejoining kinetics. Radiat Res. 164:73–85.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Linstadt D, Blakely E, Phillips TL and
Castro JR: Radiosensitization produced by iododeoxyuridine with
high linear energy transfer heavy ion beams. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 15:703–710. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Oliveira NG, Castro M, Rodrigues AS, et
al: Wortmannin enhances the induction of micronuclei by low and
high LET radiation. Mutagenesis. 18:37–44. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Skarsgard LD: Radiobiology with heavy
charged particles: a historical review. Phys Med. 14(Suppl 1):
1–19. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hamada N, Imaoka T, Masunaga S, et al:
Recent advances in the biology of heavy-ion cancer therapy. J
Radiat Res. 51:365–383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nagasawa H and Little JB: Effect of tumor
promoters, protease inhibitors, and repair processes on
X-ray-induced sister chromatid exchanges in mouse cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 76:1943–1947. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Terasima T and Tolmach LJ: Changes in
X-ray sensitivity of HeLa cells during the division cycle. Nature.
190:1210–1211. 1961. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kanai T, Endo M, Minohara S, et al:
Biophysical characteristics of HIMAC clinical irradiation system
for heavy-ion radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
44:201–210. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kanai T, Matsufuji N, Miyamoto T, et al:
Examination of GyE system for HIMAC carbon therapy. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 64:650–656. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Matsufuji N, Fukumura A, Komori M, Kanai T
and Kohno T: Influence of fragment reaction of relativistic heavy
charged particles on heavy-ion radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol.
48:1605–1623. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Matsufuji N, Kanai T, Kanematsu N, et al:
Specification of carbon ion dose at the National Institute of
Radiological Sciences (NIRS). J Radiat Res. 48(Suppl A): A81–A86.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rogakou EP, Boon C, Redon C and Bonner WM:
Megabase chromatin domains involved in DNA double-strand breaks in
vivo. J Cell Biol. 146:905–915. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rogakou EP, Boon C and Bonner WM:
Formation of a novel histone derivative, H2AX phosphorylated on
serine-139, is an immediate cellular response to non-lethal and
lethal amounts of ionizing radiation, and is also found during
apoptosis and in germ cells. Mol Biol Cell. 8:1858. 1997.
|
|
37
|
Banath JP, MacPhail SH and Olive PL:
Radiation sensitivity, H2AX phosphorylation, and kinetics of repair
of DNA strand breaks in irradiated cervical cancer cell lines.
Cancer Res. 64:7144–7149. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kuhne M, Riballo E, Rief N, Rothkamm K,
Jeggo PA and Lobrich M: A double-strand break repair defect in
ATM-deficient cells contributes to radiosensitivity. Cancer Res.
64:500–508. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kato TA, Nagasawa H, Weil MM, Little JB
and Bedford JS: Levels of gamma-H2AX foci after low-dose-rate
irradiation reveal a DNA DSB rejoining defect in cells from human
ATM heterozygotes in two at families and in another apparently
normal individual. Radiat Res. 166:443–453. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang Y, Pantelias GE and Iliakis G:
Mechanism of radiosensitization by halogenated pyrimidines: the
contribution of excess DNA and chromosome damage in BrdU
radiosensitization may be minimal in plateau-phase cells. Int J
Radiat Biol. 66:133–142. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Prise KM, Folkard M, Newman HC and Michael
BD: Effect of radiation quality on lesion complexity in cellular
DNA. Int J Radiat Biol. 66:537–542. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chapman JD, Doern SD, Reuvers AP, et al:
Radioprotection by DMSO of mammalian cells exposed to X-rays and to
heavy charged-particle beams. Radiat Environ Biophys. 16:29–41.
1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang TC, Craise LM, Mei MT and Tobias CA:
Neoplastic cell transformation by heavy charged particles. Radiat
Res Suppl. 8:S177–S187. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fukumura A, Tsujii H, Kamada T, et al:
Carbon-ion radiotherapy: clinical aspects and related dosimetry.
Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 137:149–155. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|