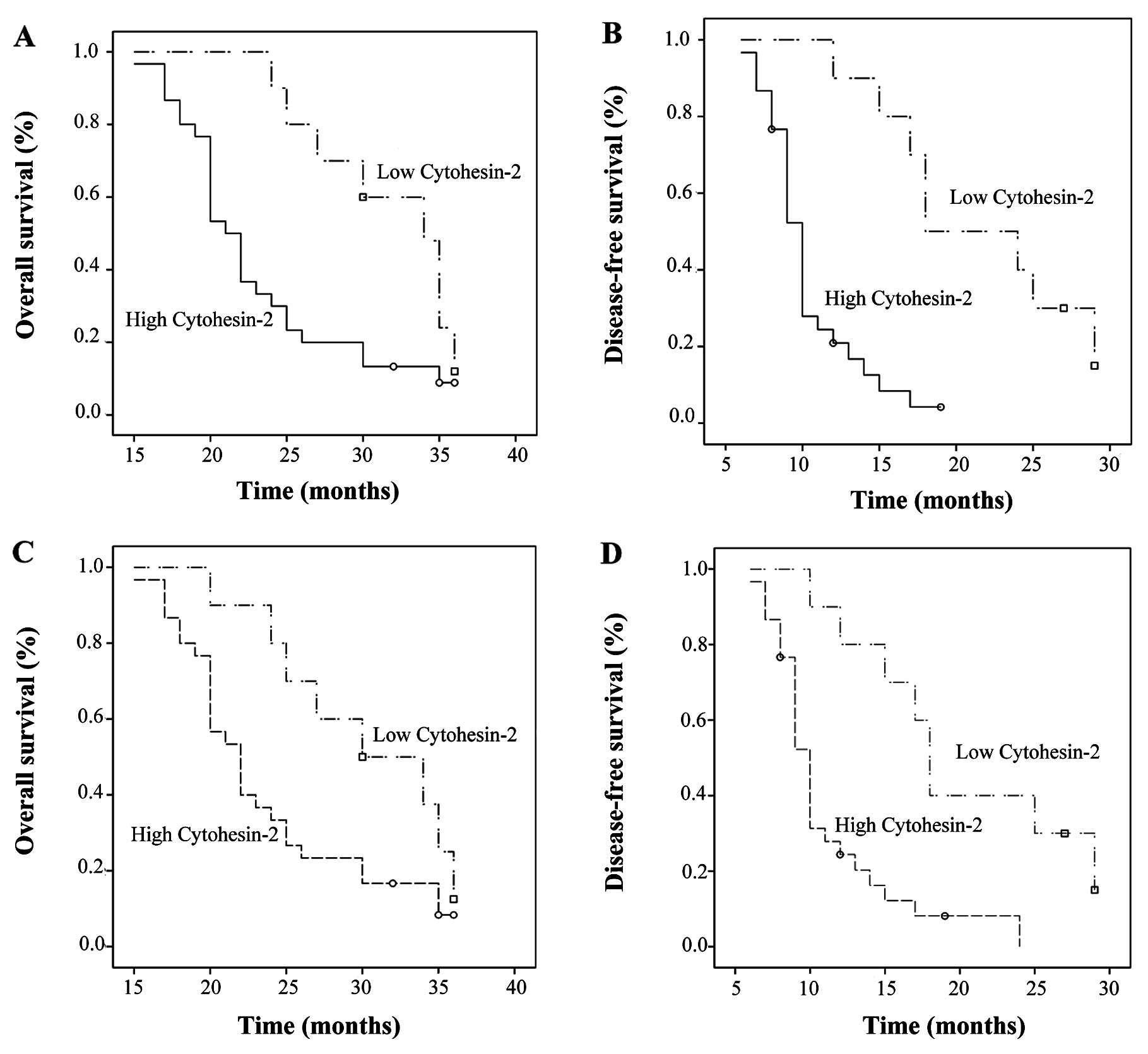
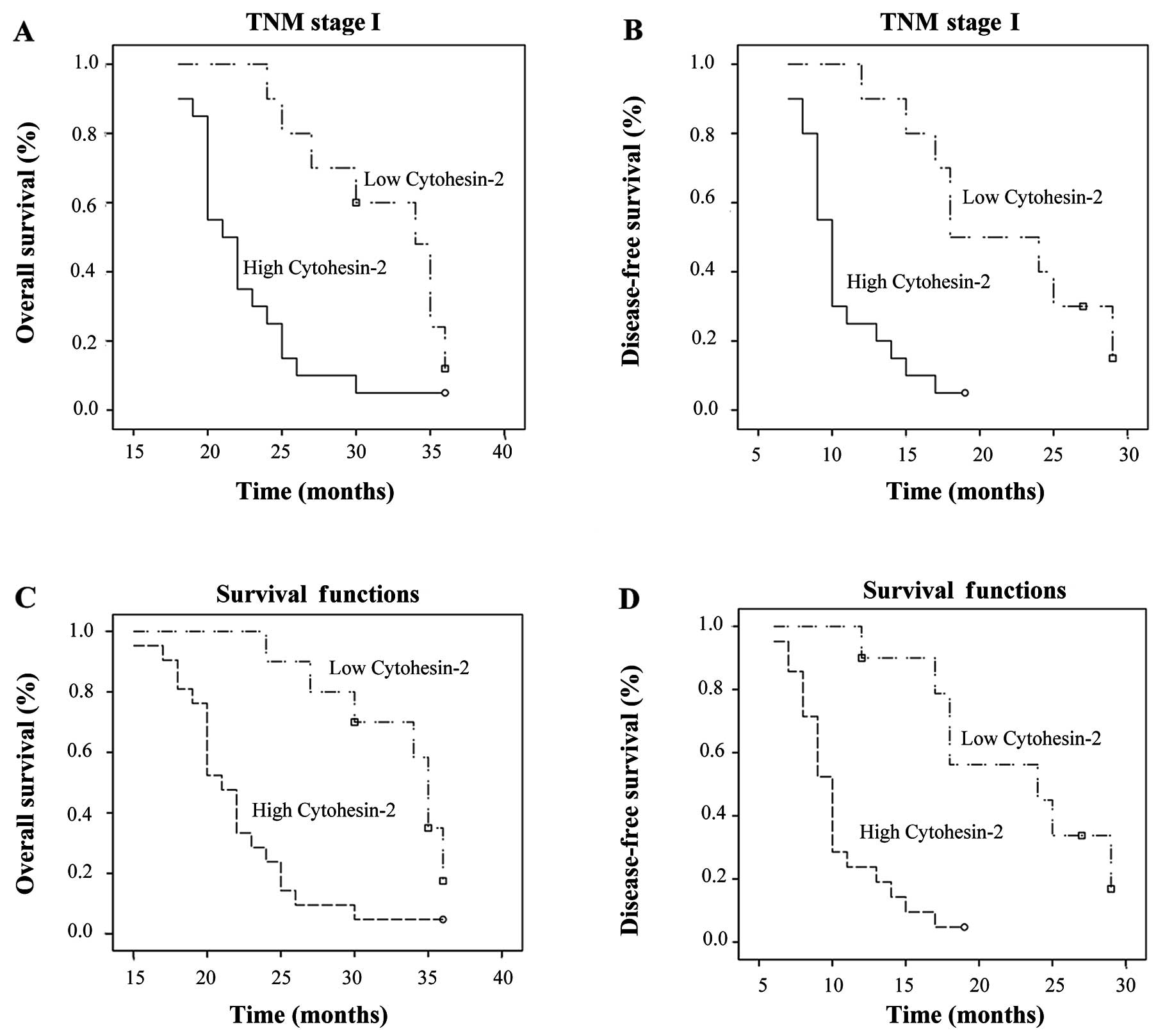
|
1
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph L: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. Ca Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. Ca Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kitisin K, Pishvaian MJ, Johnson LB and
Mishra L: Liver stem cells and molecular signaling pathways in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 1(Suppl 2):
S13–S21. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dragani TA: Risk of HCC: Genetic
heterogeneity and complex genetics. J Hepatol. 52:252–257. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bill A, Schmitz A, Albertoni B, et al:
Cytohesins are cytoplasmic ErbB receptor activators. Cell.
143:201–211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bos JL, Rehmann H and Wittinghofer A: GEFs
and GAPs: Critical elements in the control of small G proteins.
Cell. 129:865–877. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Casanova JE: Regulation of arf activation:
the sec7 family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Traffic.
8:1476–1485. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kolanus W: Guanine nucleotide exchange
factors of the cytohesin family and their roles in signal
transduction. Immunol Rev. 218:102–113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kolanus W, Nagel W, Schiller B, et al:
Alpha L beta 2 integrin/LFA-1 binding to ICAM-1 induced by
cytohesin-1, a cytoplasmic regulatory molecule. Cell. 86:233–242.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lim J, Zhou M, Veenstra TD and Morrison
DK: The CNK1 scaffold binds cytohesins and promotes insulin pathway
signaling. Genes Dev. 24:1496–1506. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thomas M: Molecular targeted therapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 44:136–141. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kannangai R, Sahin F and Torbenson MS:
EGFR is phosphorylated at Ty845 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mod
Pathol. 19:1456–1461. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mannell HK, Pircher J, Chaudhry DI, et al:
ARNO regulates VEGF-dependent tissue responses by stabilizing
endothelial VEGFR-2 surface expression. Cardiovasc Res. 93:111–119.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shirahata A, Fan W, Sakuraba K, et al:
MACC 1 as a marker for vascular invasive hepatocellular carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 31:777–780. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang L, Chen S, Zhang M, et al: Legumain:
A biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of human ovarian cancer. J
Cell Biochem. 113:2679–2686. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tu K, Zheng X, Zan X, Han S, Yao Y and Liu
Q: Evaluation of Fbxw7 expression and its correlation with the
expression of c-Myc, cyclin E and p53 in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 42:904–910. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tan NS, Michalik L, Di-Poi N, et al:
Essential role of Smad3 in the inhibition of inflammation-induced
PPAR beta/delta expression. EMBO J. 23:4211–4221. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen XP, Qiu FZ, Wu ZD, et al: Effects of
location and extension of portal vein tumor thrombus on long-term
outcomes of surgical treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann
Surg Oncol. 13:940–946. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cherqui D, Laurent A, Mocellin N, et al:
Liver resection for transplantable hepatocellular carcinoma:
long-term survival and role of secondary liver transplantation. Ann
Surg. 250:738–746. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cammà C, Schepis F, Orlando A, et al:
Transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Radiology. 224:47–54. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fujioka M, Nakashima Y, Nakashima O and
Kojiro M: Immunohistologic study on the expressions of
α-fetoprotein and protein induced by vitamin K absence or
antagonist II in surgically resected small hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 34:1128–1134. 2001.
|
|
23
|
Hafner M, Schmitz A, Grüne I, et al:
Inhibition of cytohesins by SecinH3 leads to hepatic insulin
resistance. Nature. 444:941–944. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|