|
1
|
Zhou XD: Recurrence and metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma: progress and prospects. Hepatobiliary
Pancreat Dis Int. 1:35–41. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tang Z, Zhou X, Lin Z, et al: Surgical
treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma and related basic research
with special reference to recurrence and metastasis. Chin Med J.
112:887–891. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Balabanian K, Lagane B, Infantino S, et
al: The chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12 binds to and signals through the
orphan receptor RDC1 in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem.
280:35760–35766. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burns JM, Summers BC, Wang Y, et al: A
novel chemokine receptor for SDF-1 and I-TAC involved in cell
survival, cell adhesion, and tumor development. J Exp Med.
203:2201–2213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ben-Baruch A: Organ selectivity in
metastasis: regulation by chemokines and their receptors. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 25:345–356. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang J, Shiozawa Y, Wang Y, et al: The
role of CXCR7/RDC1 as a chemokine receptor for CXCL12/SDF-1 in
prostate cancer. J Biol Chem. 283:4283–4294. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Iwakiri S, Mino N, Takahashi T, et al:
Higher expression of chemokine receptor CXCR7 is linked to early
and metastatic recurrence in pathological stage I non small cell
lung cancer. Cancer. 115:2580–2593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zheng K, Li HY, Su XL, et al: Chemokine
receptor CXCR7 regulates the invasion, angiogenesis and tumor
growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 29:312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Monnier J, Boissan M, L’Helgoualc’h A, et
al: CXCR7 is up-regulated in human and murine hepatocellular
carcinoma and is specifically expressed by endothelial cells. Eur J
Cancer. 48:138–148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xue TC, Chen RX, Han D, et al:
Down-regulation of CXCR7 inhibits the growth and lung metastasis of
human hepatocellular carcinoma cells with highly metastatic
potential. Exp Ther Med. 3:117–123. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun HC, Zhuang PY, Qin LX, et al:
Incidence and prognostic values of lymph node metastasis in
operable hepatocellular carcinoma and evaluation of routine
complete lymphadenectomy. J Surg Oncol. 96:37–45. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
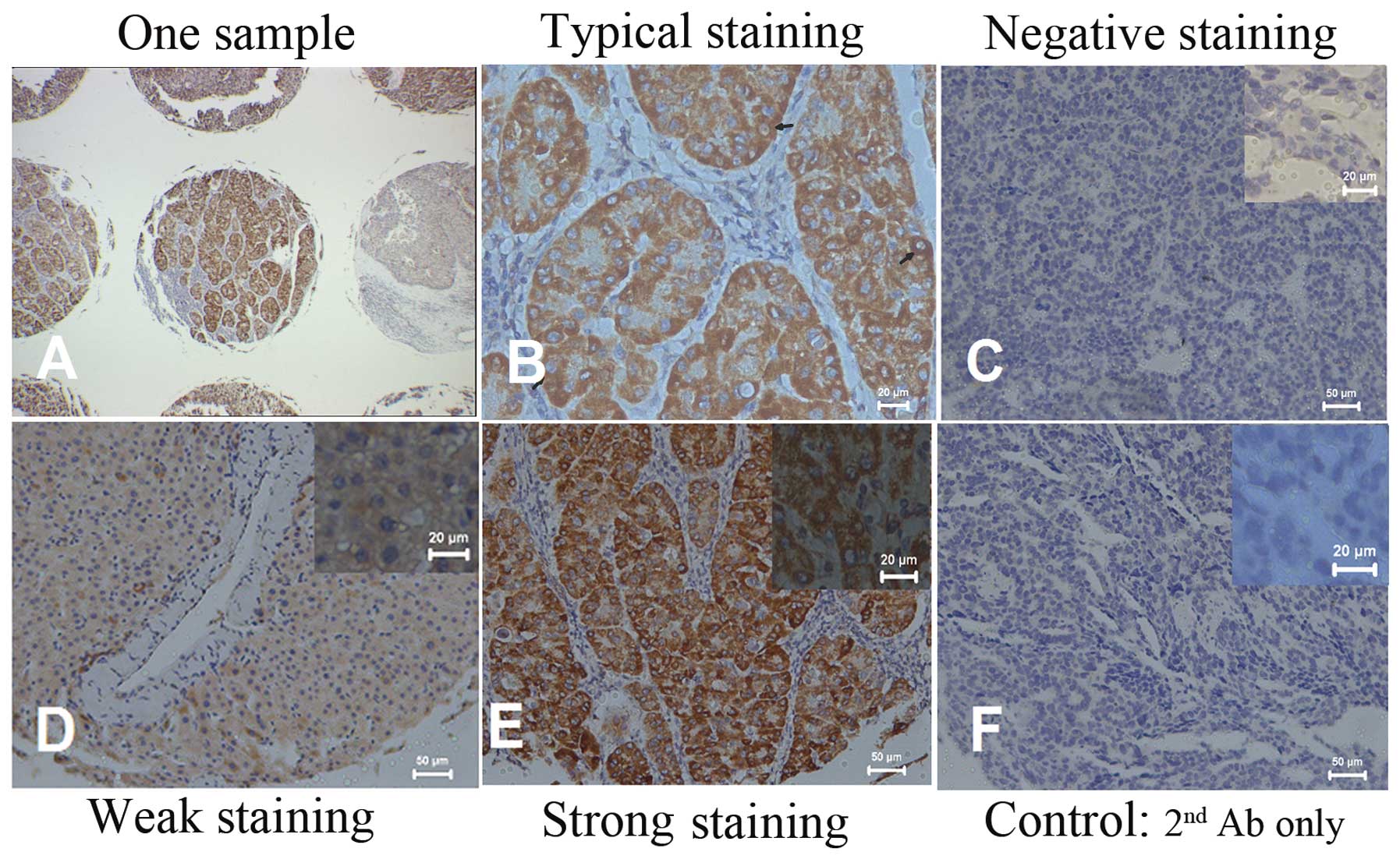
Simon R, Mirlacher M and Sauter G: Tissue
microarrays. Methods Mol Med. 97:377–389. 2004.
|
|
13
|
Lugli A, Spichtin H, Maurer R, et al:
EphB2 expression across 138 human tumor types in a tissue
microarray: high levels of expression in gastrointestinal cancers.
Clin Cancer Res. 11:6450–6458. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
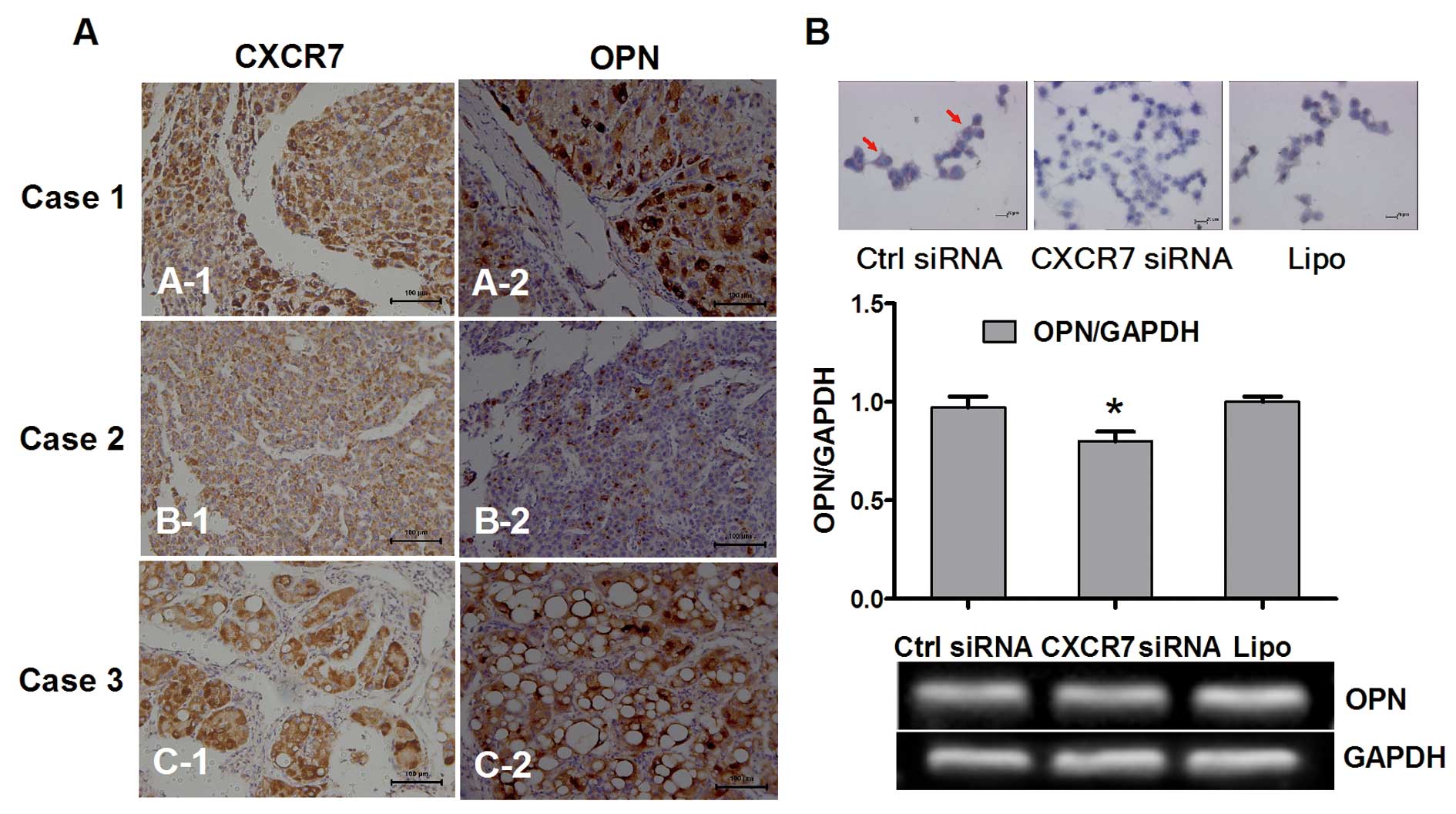
Dalby B, Cates S, Harris A, et al:
Advanced transfection with Lipofectamine 2000 reagent: primary
neurons, siRNA, and high-throughput applications. Methods.
33:95–103. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brooks SA: Basic immunocytochemistry for
light microscopy. Methods Mol Biol. 878:1–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
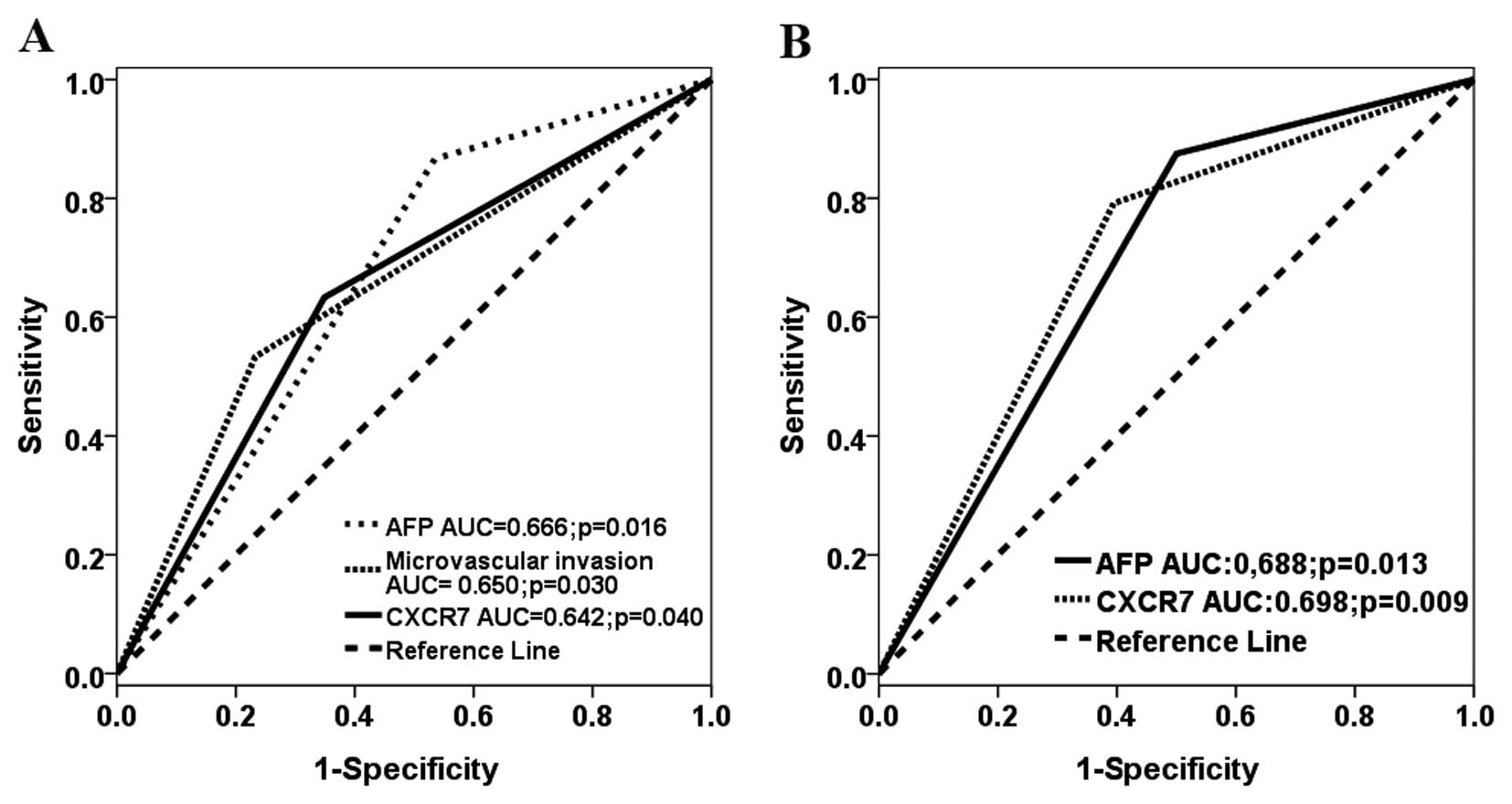
Trevisani F, D’Intino PE, Morselli-Labate
AM, et al: Serum alpha-fetoprotein for diagnosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease: influence of
HBsAg and anti-HCV status. J Hepatol. 34:570–575. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen RX, Xia YH, Cui JF, Xue TC and Ye SL:
Osteopontin, a single marker for predicting the prognosis of
patients with tumor-node-metastasis stage I hepatocellular
carcinoma after surgical resection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
25:1435–1442. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Pan HW, Ou YH, Peng SY, et al:
Overexpression of osteopontin is associated with intrahepatic
metastasis, early recurrence, and poorer prognosis of surgically
resected hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 98:119–127. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nishida N, Fukuda Y, Komeda T, et al:
Prognostic impact of multiple allelic losses on metastatic
recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection.
Oncology. 62:141–148. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sasaki A, Kai S, Endo Y, et al: Hepatitis
B virus infection predicts extrahepatic metastasis after hepatic
resection in patients with large hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg
Oncol. 14:3181–3187. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Emile JF, Lemoine A, Azoulay D, Debuire B,
Bismuth H and Reynes M: Histological, genomic and clinical
heterogeneity of clear cell hepatocellular carcinoma.
Histopathology. 38:225–231. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Unsal H, Yakicier C, Marcais C, et al:
Genetic heterogeneity of hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 91:822–826. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nathan H, Schulick RD, Choti MA and Pawlik
TM: Predictors of survival after resection of early hepatocellular
carcinoma. Ann Surg. 249:799–805. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
An FQ, Matsuda M, Fujii H, et al: Tumor
heterogeneity in small hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of tumor
cell proliferation, expression and mutation of p53 and β-catenin.
Int J Cancer. 93:468–474. 2001.
|
|
25
|
Ben-Porath I, Thomson MW, Carey VJ, et al:
An embryonic stem cell-like gene expression signature in poorly
differentiated aggressive human tumors. Nat Genet. 40:499–507.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee TI, Jenner RG, Boyer LA, et al:
Control of developmental regulators by Polycomb in human embryonic
stem cells. Cell. 125:301–313. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jones SW, Brockbank SM, Mobbs ML, et al:
The orphan G-protein coupled receptor RDC1: evidence for a role in
chondrocyte hypertrophy and articular cartilage matrix turnover.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 14:597–608. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rajagopal S, Kim J, Ahn S, et al:
Beta-arrestin- but not G protein-mediated signaling by the’decoy’
receptor CXCR7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:628–632. 2010.
|
|
29
|
Ravindranath A, Yuen HF, Chan KK, et al:
Wnt-β-catenin-Tcf-4 signalling-modulated invasiveness is dependent
on osteopontin expression in breast cancer. Br J Cancer.
105:542–551. 2011.
|
|
30
|
Rohde F, Rimkus C, Friederichs J, et al:
Expression of osteopontin, a target gene of de-regulated Wnt
signaling, predicts survival in colon cancer. Int J Cancer.
121:1717–1723. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|