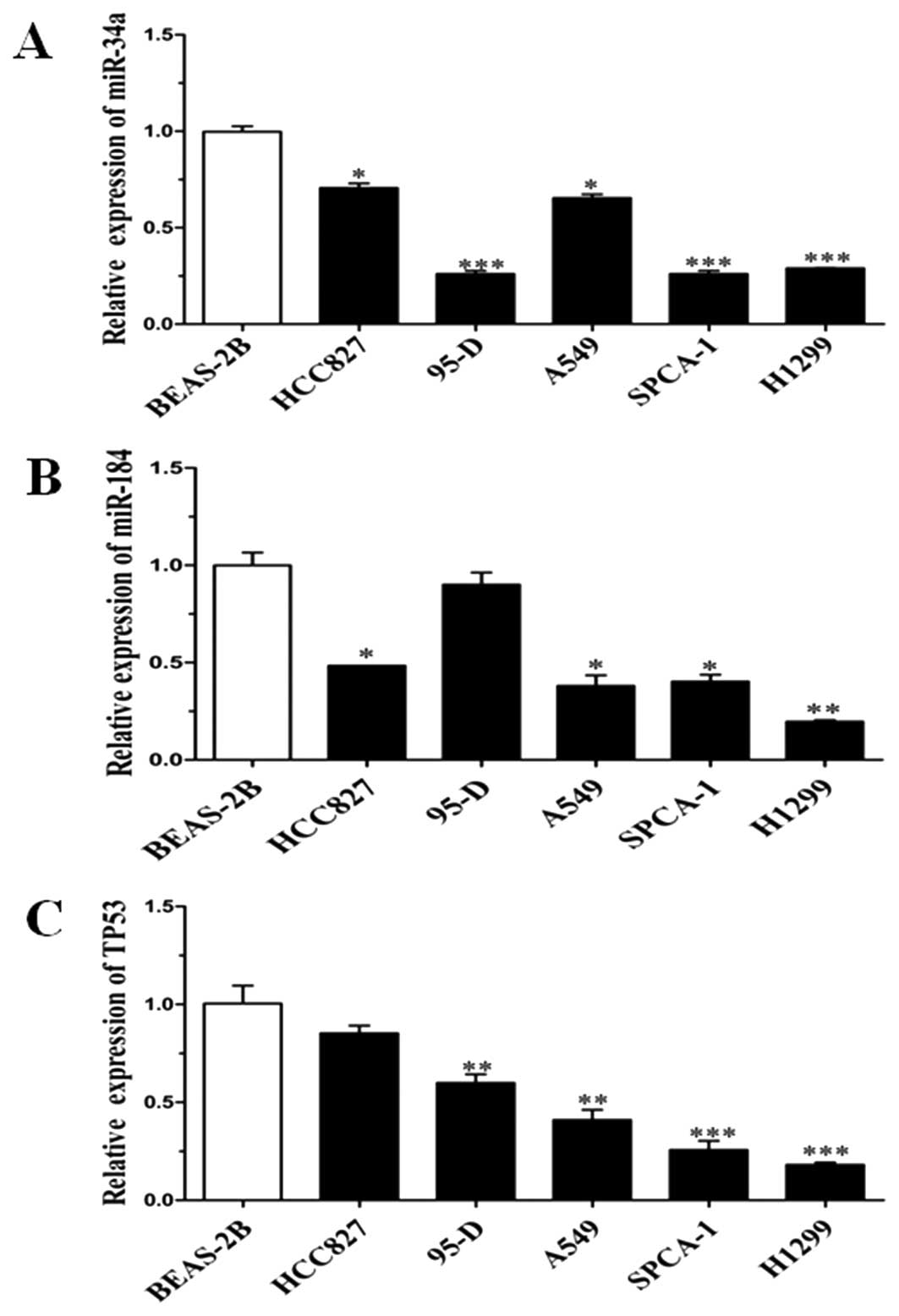
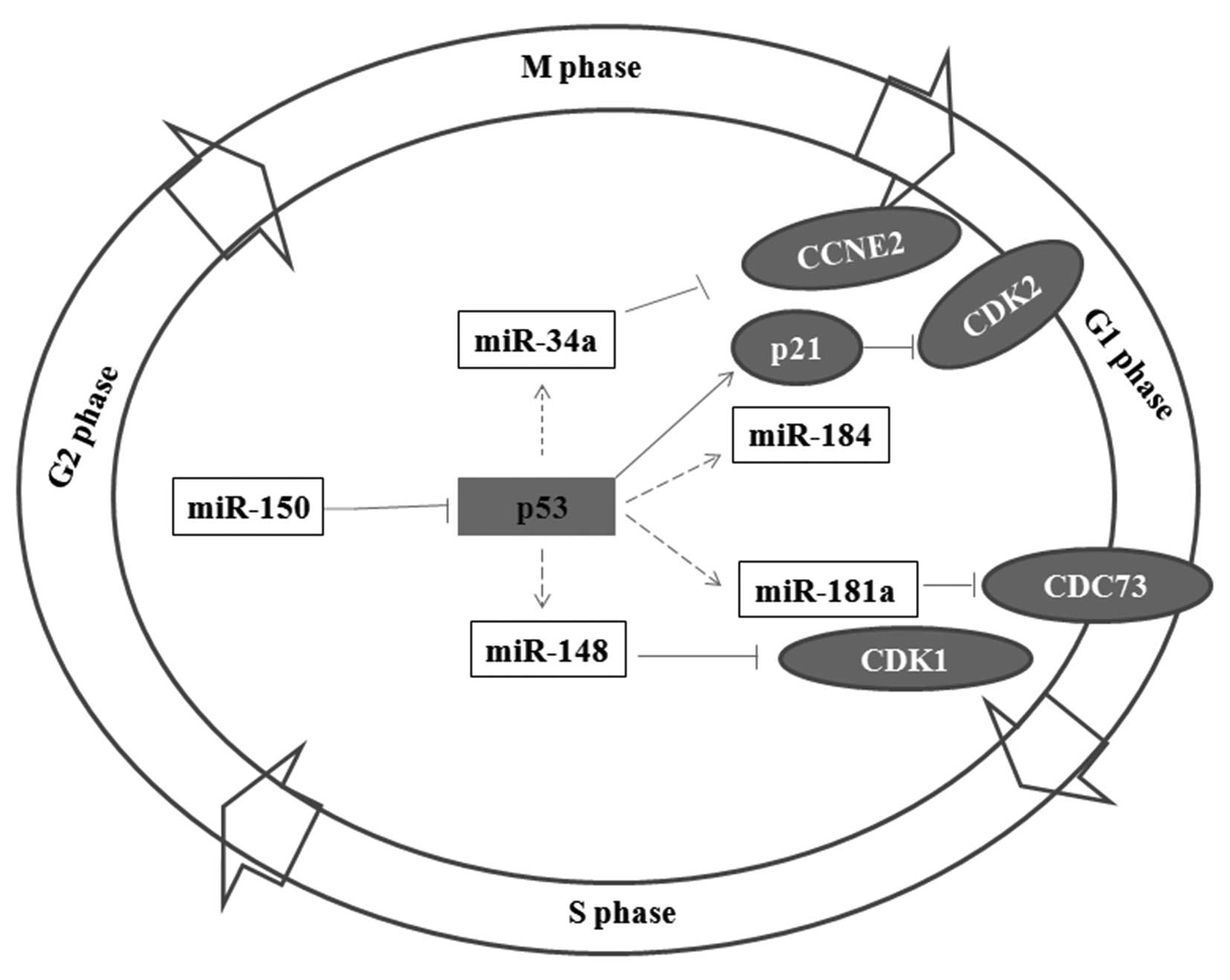
|
1
|
Zabaleta J: MicroRNA: a bridge from H.
pylori infection to gastritis and gastric cancer development.
Front Genet. 3:2942012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Harquail J, Benzina S and Robichaud GA:
MicroRNAs and breast cancer malignancy: an overview of
miRNA-regulated cancer processes leading to metastasis. Cancer
Biomark. 11:269–280. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang F, Sun GP, Zou YF, Hao JQ, Zhong F
and Ren WJ: MicroRNAs as promising biomarkers for gastric cancer.
Cancer Biomark. 11:259–267. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Odjele A, Charest D and Morin PJ: miRNAs
as important drivers of glioblastomas: a no-brainer? Cancer
Biomark. 11:245–252. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eldem V, Celikkol Akcay U, Ozhuner E,
Bakir Y, Uranbey S and Unver T: Genome-wide identification of
miRNAs responsive to drought in peach (Prunus persica) by
high-throughput deep sequencing. PloS One. 7:e502982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Endo H, Muramatsu T, Furuta M, et al:
Potential of tumor-suppressive miR-596 targeting LGALS3BP as a
therapeutic agent in oral cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:560–569. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li KK, Pang JC, Lau KM, et al: miR-383 is
downregulated in medulloblastoma and targets peroxiredoxin 3
(PRDX3). Brain Pathol. Dec 11–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Masuda M, Miki Y, Hata S, et al: An
induction of microRNA, miR-7 through estrogen treatment in breast
carcinoma. J Transl Med. 10(Suppl 1): S22012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Novello C, Pazzaglia L, Cingolani C, et
al: miRNA expression profile in human osteosarcoma: role of miR-1
and miR-133b in proliferation and cell cycle control. Int J Oncol.
42:667–675. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ando H, Okamoto A, Yokota M, et al:
Development of miR-92a delivery system for antiangiogenesis-based
cancer therapy. J Gene Med. 15:20–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Teixeira AL, Gomes M and Medeiros R: EGFR
signaling pathway and related-miRNAs in age-related diseases: the
example of miR-221 and miR-222. Front Genet. 3:2862012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Boldrup L, Coates PJ, Wahlgren M, Laurell
G and Nylander K: Subsite-based alterations in miR-21, miR-125b,
and miR-203 in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and
correlation to important target proteins. J Carcinog. 11:182012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hirata H, Ueno K, Shahryari V, et al:
Oncogenic miRNA-182–5p targets Smad4 and RECK in human bladder
cancer. PloS One. 7:e510562012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hassan F, Nuovo GJ, Crawford M, et al:
MiR-101 and miR-144 regulate the expression of the CFTR chloride
channel in the lung. PloS One. 7:e508372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sasaki A, Udaka Y, Tsunoda Y, et al:
Analysis of p53 and miRNA expression after irradiation of
glioblastoma cell lines. Anticancer Res. 32:4709–4713.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suzuki HI and Miyazono K: p53 actions on
microRNA expression and maturation pathway. Methods Mol Biol.
962:165–181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gurtler A, Kunz N, Gomolka M, et al:
Stain-Free technology as a normalization tool in Western blot
analysis. Anal Biochem. 433:105–111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hirano S: Western blot analysis. Methods
Mol Biol. 926:87–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kao CH, Cheng CM, Chuang KH, et al: A
regularly spaced and self-revealing protein ladder for anti-tag
Western blot analysis. Anal Biochem. 431:1–3. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nybo K: Molecular biology techniques
Q&A. Western blot: protein migration. Biotechniques. 53:23–24.
2012.
|
|
21
|
Li XJ, Ji MH, Zhong SL, et al:
MicroRNA-34a modulates chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells to
adriamycin by targeting Notch1. Arch Med Res. 43:514–521. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Siemens H, Neumann J, Jackstadt R, et al:
Detection of miR-34a promoter methylation in combination with
elevated expression of c-Met and β-catenin predicts distant
metastasis of colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:710–720.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang HS, Chen XY, Wu TC, Sang WW and Ruan
Z: MiR-34a is involved in Tat-induced HIV-1 long terminal repeat
(LTR) transactivation through the SIRT1/NFkappaB pathway. FEBS
Lett. 586:4203–4207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Candas D, Fan M, Nantajit D, et al:
CyclinB1/Cdk1 phosphorylates mitochondrial antioxidant MnSOD in
cell adaptive response to radiation stress. J Mol Cell Biol. Jan
31–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
25
|
Haflidadottir BS, Bergsteinsdottir K,
Praetorius C and Steingrimsson E: miR-148 regulates Mitf in
melanoma cells. PloS One. 5:e115742010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Iovino N, Pane A and Gaul U: miR-184 has
multiple roles in Drosophila female germline development.
Dev Cell. 17:123–133. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu C, Teng ZQ, Santistevan NJ, et al:
Epigenetic regulation of miR-184 by MBD1 governs neural stem cell
proliferation and differentiation. Cell Stem Cell. 6:433–444. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen Y, Tsai YH and Tseng SH: Inhibition
of cyclin-dependent kinase 1-induced cell death in neuroblastoma
cells through the microRNA-34a-MYCN-survivin pathway. Surgery.
153:4–16. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang C, Yao Z, Zhu M, et al: Inhibitory
effects of microRNA-34a on cell migration and invasion of invasive
urothelial bladder carcinoma by targeting Notch1. J Huazhong Univ
Sci Technolog Med Sci. 32:375–382. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Venta R, Valk E, Koivomagi M and Loog M:
Double-negative feedback between S-phase cyclin-CDK and CKI
generates abruptness in the G1/S switch. Front Physiol. 3:4592012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nagle AA, Gan FF, Jones G, So CL, Wells G
and Chew EH: Induction of tumor cell death through targeting
tubulin and evoking dysregulation of cell cycle regulatory proteins
by multifunctional cinnamaldehydes. PloS One. 7:e501252012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chow JP and Poon RY: The CDK1 inhibitory
kinase MYT1 in DNA damage checkpoint recovery. Oncogene. Nov
12–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
33
|
Guarnieri V, Battista C, Muscarella LA, et
al: CDC73 mutations and parafibromin immunohistochemistry in
parathyroid tumors: clinical correlations in a single-centre
patient cohort. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 35:411–422. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Amrich CG, Davis CP, Rogal WP, et al:
Cdc73 subunit of Paf1 complex contains C-terminal Ras-like domain
that promotes association of Paf1 complex with chromatin. J Biol
Chem. 287:10863–10875. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang JH, Seigneur EM, Pandey M, et al:
The EIF4EBP3 translational repressor is a marker of CDC73 tumor
suppressor haploinsufficiency in a parathyroid cancer syndrome.
Cell Death Dis. 3:2662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Masi G, Barzon L, Iacobone M, et al:
Clinical, genetic, and histopathologic investigation of
CDC73-related familial hyperparathyroidism. Endocr Relat Cancer.
15:1115–1126. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang Y, Zhang XY, Sun L, et al: Methyl
methanesulfonate induces apoptosis in p53-deficient H1299 and Hep3B
cells through a caspase 2- and mitochondria-associated pathway.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 34:694–704. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Debernardi S, Skoulakis S, Molloy G,
Chaplin T, Dixon-McIver A and Young BD: MicroRNA miR-181a
correlates with morphological sub-class of acute myeloid leukaemia
and the expression of its target genes in global genome-wide
analysis. Leukemia. 21:912–916. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shin KH, Bae SD, Hong HS, Kim RH, Kang MK
and Park NH: miR-181a shows tumor suppressive effect against oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells by downregulating K-ras. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 404:896–902. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xie W, Li Z, Li M, Xu N and Zhang Y:
miR-181a and inflammation: miRNA homeostasis response to
inflammatory stimuli in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
430:647–652. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kashat M, Azzouz L, Sarkar SH, Kong D, Li
Y and Sarkar FH: Inactivation of AR and Notch-1 signaling by
miR-34a attenuates prostate cancer aggressiveness. Am J Transl Res.
4:432–442. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xia J, Duan Q, Ahmad A, et al: Genistein
inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis through up-regulation of
miR-34a in pancreatic cancer cells. Curr Drug Targets.
13:1750–1756. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|