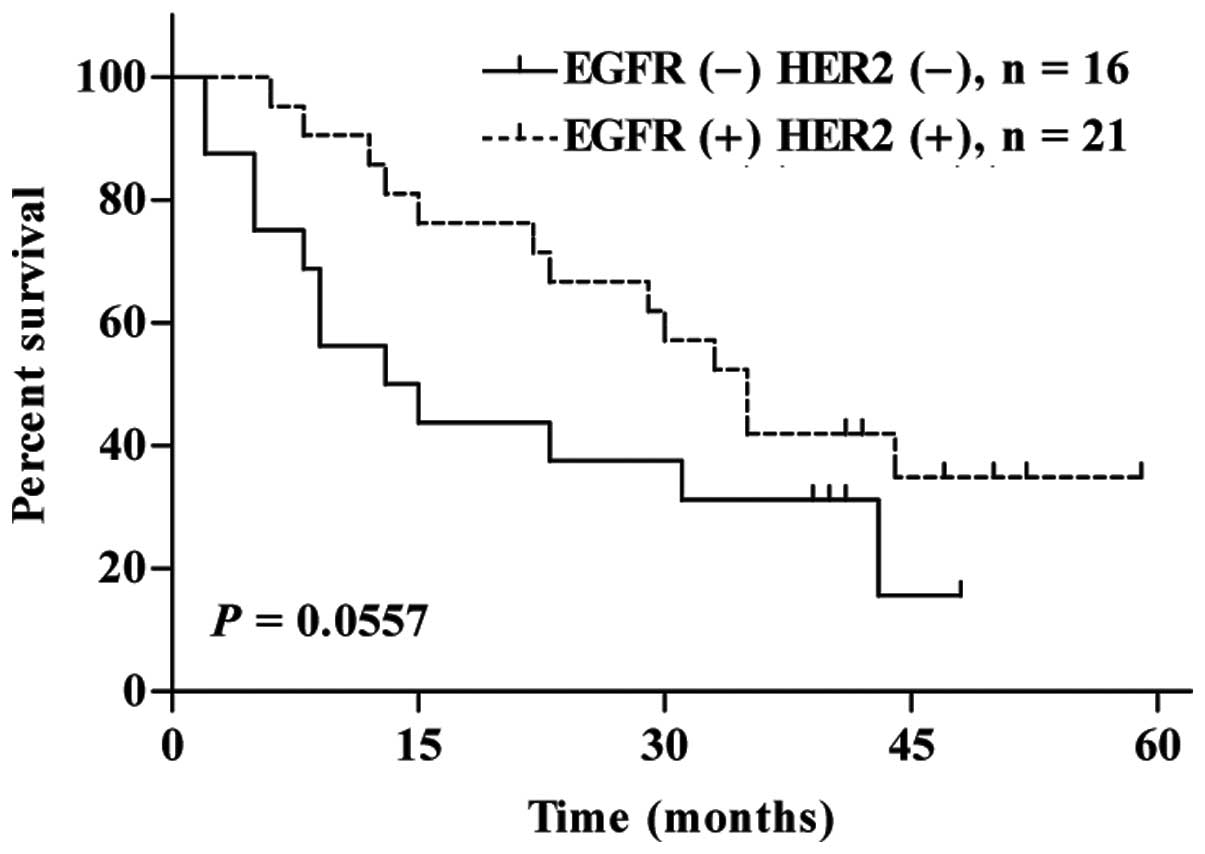
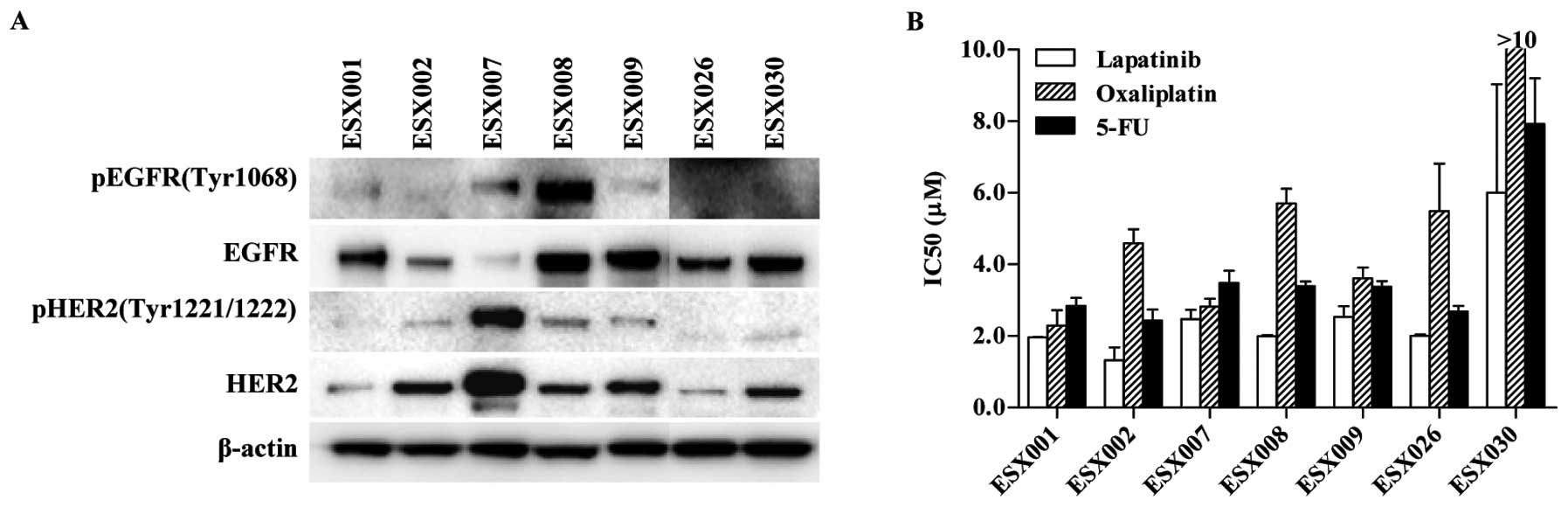
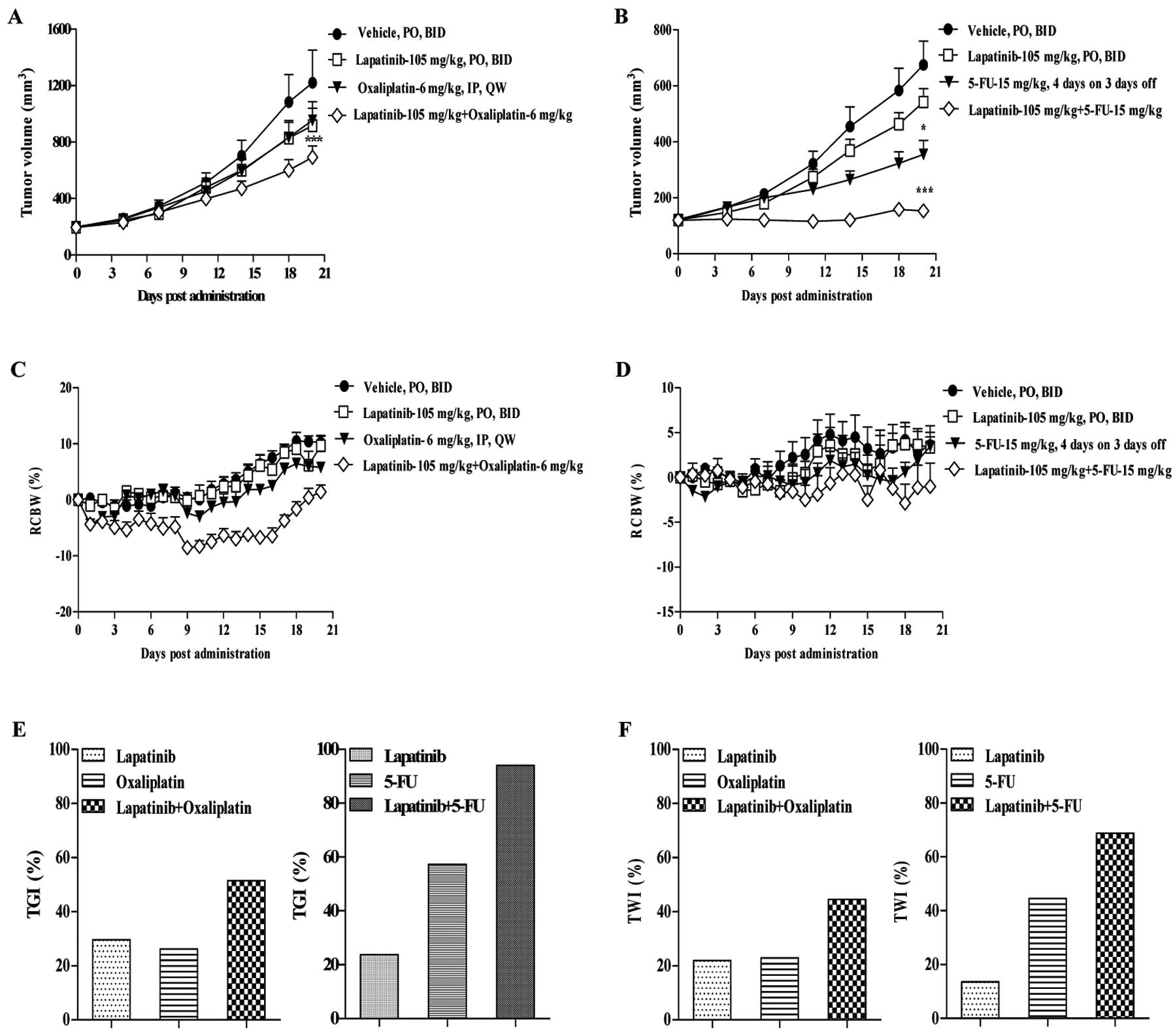
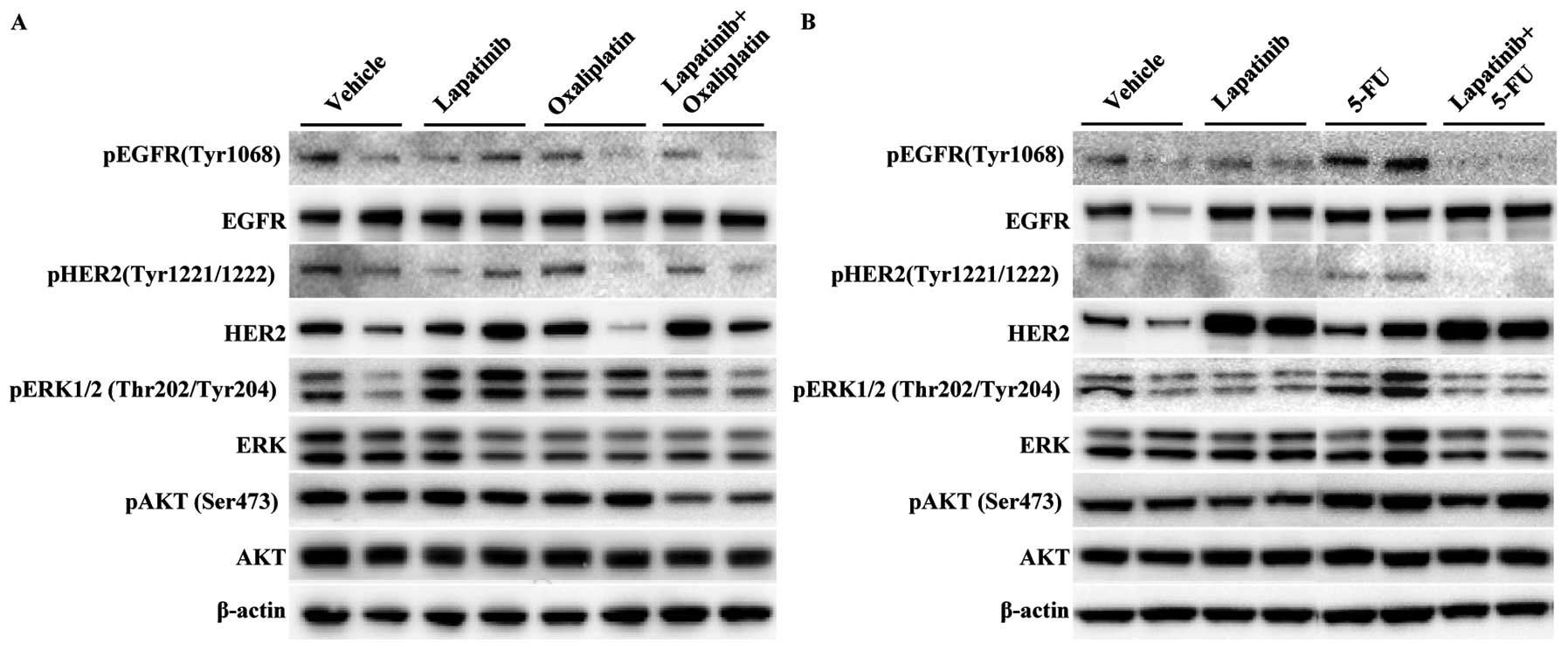
|
1
|
Demeester SR: Epidemiology and biology of
esophageal cancer. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 3:S2–S5.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Blot W, McLaughlin J and Fraumeni J:
Esophageal cancer. New Jersey Comprehensive Cancer Control Plan,
2008–2012. Schottenfeld D and Fraumeni J: Oxford University Press;
New York: pp. 697–706. 2006
|
|
4
|
Ishikura S, Nihei K, Ohtsu A, et al:
Long-term toxicity after definitive chemoradiotherapy for squamous
cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. J Clin Oncol.
21:2697–2702. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tepper J, Krasna MJ, Niedzwiecki D, et al:
Phase III trial of trimodality therapy with cisplatin,
fluorouracil, radiotherapy, and surgery compared with surgery alone
for esophageal cancer: CALGB 9781. J Clin Oncol. 26:1086–1092.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Del Campo JM, Hitt R, Sebastian P, et al:
Effects of lapatinib monotherapy: results of a randomised phase II
study in therapy-naive patients with locally advanced squamous cell
carcinoma of the head and neck. Br J Cancer. 105:618–627.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scaltriti M and Baselga J: The epidermal
growth factor receptor pathway: a model for targeted therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:5268–5272. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Klapper LN, Kirschbaum MH, Sela M and
Yarden Y: Biochemical and clinical implications of the ErbB/HER
signaling network of growth factor receptors. Adv Cancer Res.
77:25–79. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Baselga J and Arteaga CL: Critical update
and emerging trends in epidermal growth factor receptor targeting
in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:2445–2459. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Roskoski R Jr: The ErbB/HER receptor
protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
319:1–11. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Witton CJ, Reeves JR, Going JJ, Cooke TG
and Bartlett JM: Expression of the HER1–4 family of receptor
tyrosine kinases in breast cancer. J Pathol. 200:290–297. 2003.
|
|
12
|
Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, et al:
Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian
cancer. Science. 244:707–712. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moasser MM: The oncogene HER2: its
signaling and transforming functions and its role in human cancer
pathogenesis. Oncogene. 26:6469–6487. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hanawa M, Suzuki S, Dobashi Y, et al: EGFR
protein overexpression and gene amplification in squamous cell
carcinomas of the esophagus. Int J Cancer. 118:1173–1180. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mimura K, Kono K, Hanawa M, et al:
Frequencies of HER-2/neu expression and gene amplification in
patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
92:1253–1260. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kawaguchi Y, Kono K, Mimura K, et al:
Targeting EGFR and HER-2 with cetuximab- and trastuzumab-mediated
immunotherapy in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
97:494–501. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Higuchi K, Koizumi W, Tanabe S, et al:
Current management of esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma in Japan
and other countries. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 3:153–161.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ilson DH: Esophageal cancer chemotherapy:
recent advances. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2:85–92. 2008.
|
|
19
|
Rusnak DW, Alligood KJ, Mullin RJ, et al:
Assessment of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR, ErbB1) and
HER2 (ErbB2) protein expression levels and response to lapatinib
(Tykerb, GW572016) in an expanded panel of human normal and tumour
cell lines. Cell Prolif. 40:580–594. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Xia W, Mullin RJ, Keith BR, et al:
Anti-tumor activity of GW572016: a dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor
blocks EGF activation of EGFR/erbB2 and downstream Erk1/2 and AKT
pathways. Oncogene. 21:6255–6263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mimura K, Kono K, Maruyama T, et al:
Lapatinib inhibits receptor phosphorylation and cell growth and
enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of EGFR- and
HER2-overexpressing esophageal cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer.
129:2408–2416. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kim HP, Yoon YK, Kim JW, et al: Lapatinib,
a dual EGFR and HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, downregulates
thymidylate synthase by inhibiting the nuclear translocation of
EGFR and HER2. PLoS One. 4:e59332009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Blackwell KL, Burstein HJ, Storniolo AM,
et al: Randomized study of Lapatinib alone or in combination with
trastuzumab in women with ErbB2-positive, trastuzumab-refractory
metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28:1124–1130. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cameron D, Casey M, Press M, et al: A
phase III randomized comparison of lapatinib plus capecitabine
versus capecitabine alone in women with advanced breast cancer that
has progressed on trastuzumab: updated efficacy and biomarker
analyses. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 112:533–543. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chung KY, Shia J, Kemeny NE, et al:
Cetuximab shows activity in colorectal cancer patients with tumors
that do not express the epidermal growth factor receptor by
immunohistochemistry. J Clin Oncol. 23:1803–1810. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Geyer CE, Forster J, Lindquist D, et al:
Lapatinib plus capecitabine for HER2-positive advanced breast
cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2733–2743. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wainberg ZA, Anghel A, Desai AJ, et al:
Lapatinib, a dual EGFR and HER2 kinase inhibitor, selectively
inhibits HER2-amplified human gastric cancer cells and is
synergistic with trastuzumab in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res.
16:1509–1519. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang D, Pal A, Bornmann WG, et al:
Activity of lapatinib is independent of EGFR expression level in
HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:1846–1850. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Konecny GE, Pegram MD, Venkatesan N, et
al: Activity of the dual kinase inhibitor lapatinib (GW572016)
against HER-2-overexpressing and trastuzumab-treated breast cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 66:1630–1639. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo XF, Zhu XF, Zhong GS, Deng BG, Gao ZT
and Wang H: Lapatinib, a dual inhibitor of EGFR and HER2, has
synergistic effects with 5-fluorouracil on esophageal carcinoma.
Oncol Rep. 27:1639–1645. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nolan GP: What’s wrong with drug screening
today. Nat Chem Biol. 3:187–191. 2007.
|
|
32
|
Kamb A: What’s wrong with our cancer
models? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4:161–165. 2005.
|
|
33
|
Masters JR: HeLa cells 50 years on: the
good, the bad and the ugly. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:315–319.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Scaltriti M, Verma C, Guzman M, et al:
Lapatinib, a HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces stabilization
and accumulation of HER2 and potentiates trastuzumab-dependent cell
cytotoxicity. Oncogene. 28:803–814. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dragovich T, McCoy S, Fenoglio-Preiser CM,
et al: Phase II trial of erlotinib in gastroesophageal junction and
gastric adenocarcinomas: SWOG 0127. J Clin Oncol. 24:4922–4927.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ferry DR, Anderson M, Beddard K, et al: A
phase II study of gefitinib monotherapy in advanced esophageal
adenocarcinoma: evidence of gene expression, cellular, and clinical
response. Clin Cancer Res. 13:5869–5875. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Janmaat ML, Gallegos-Ruiz MI, Rodriguez
JA, et al: Predictive factors for outcome in a phase II study of
gefitinib in second-line treatment of advanced esophageal cancer
patients. J Clin Oncol. 24:1612–1619. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hecht J, Urba S, Koehler M, et al:
Lapatinib monotherapy in recurrent upper gastrointestinal
malignancy: phase II efficacy and biomarker analyses. Proc GI
Cancer Symposium. 2008.
|