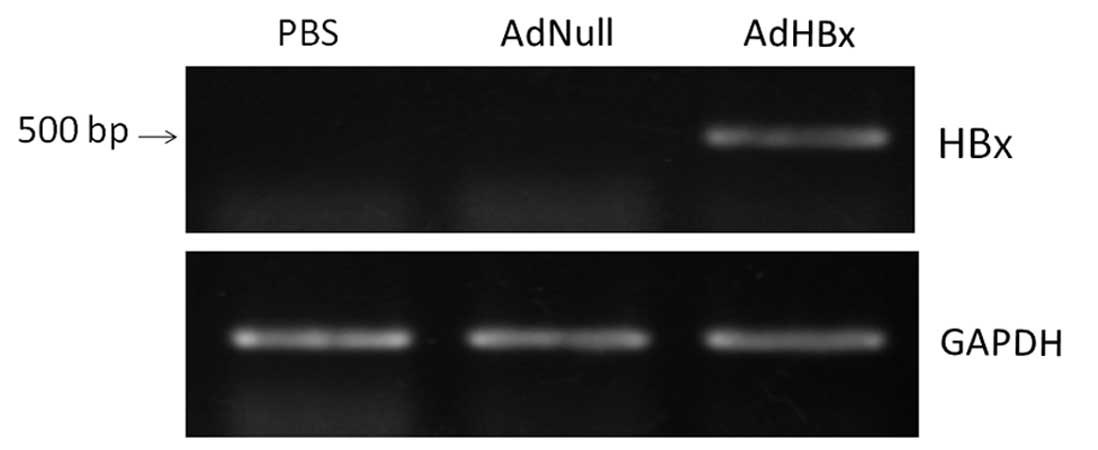
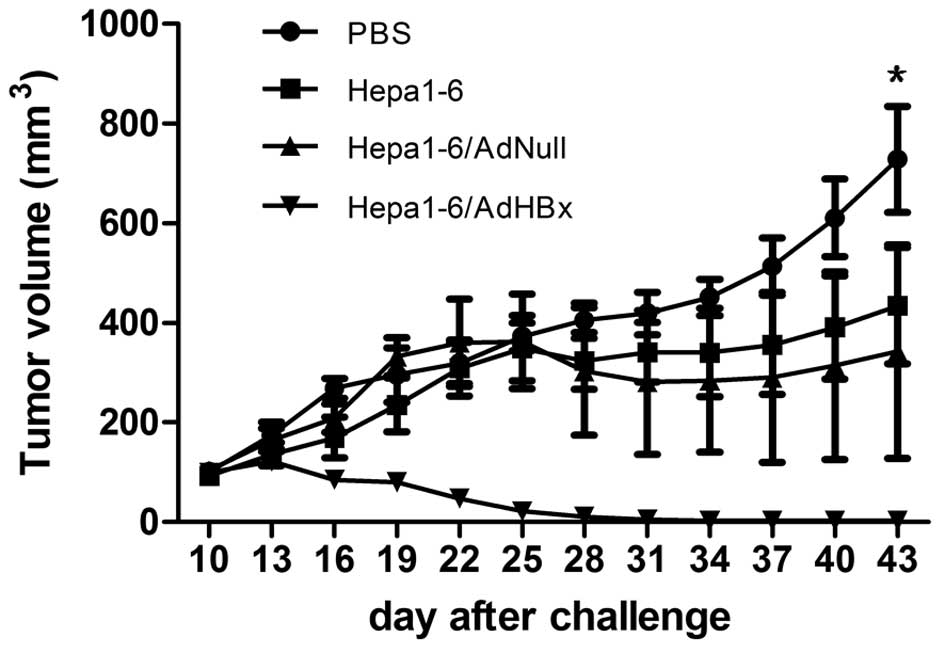
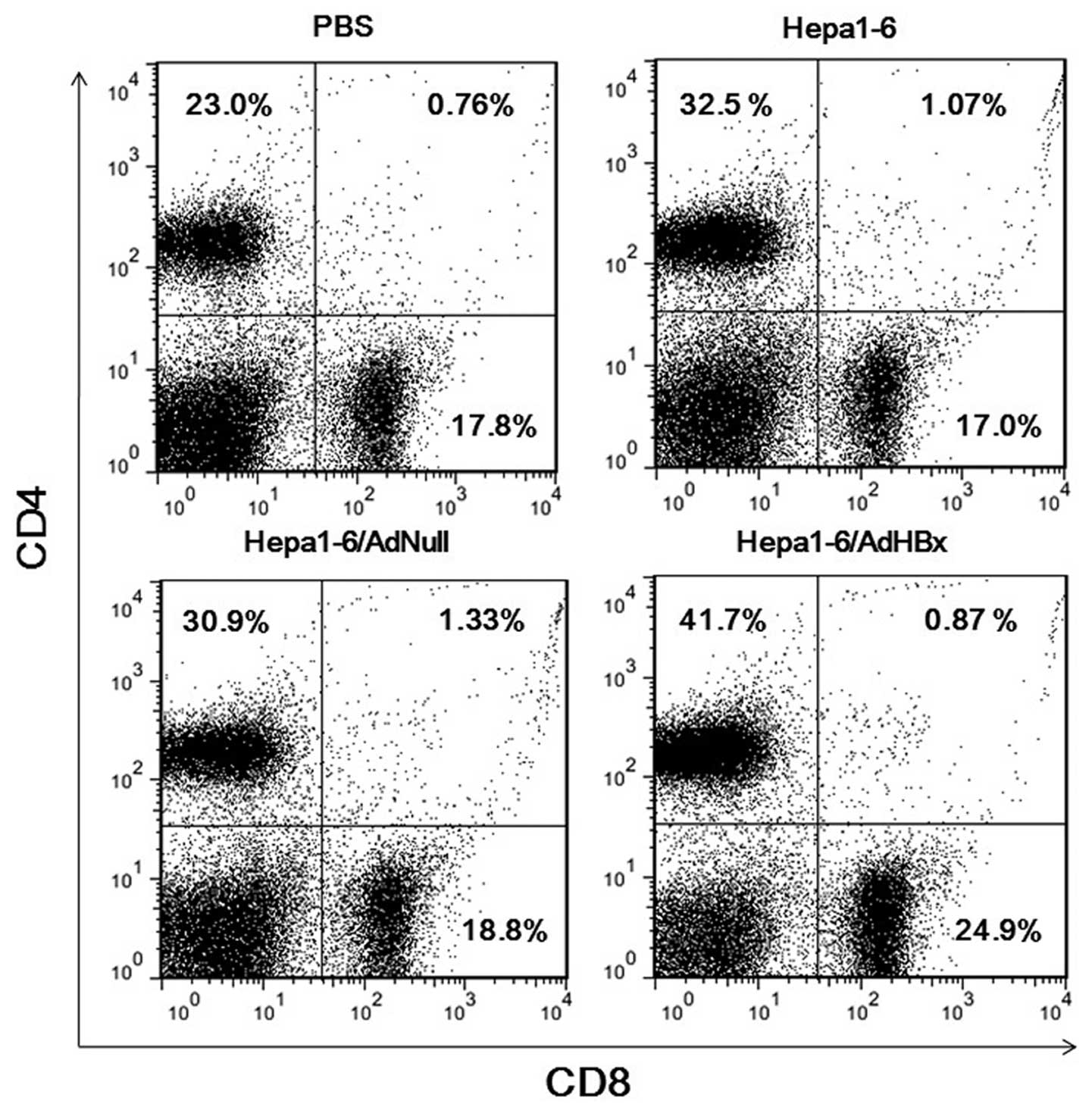
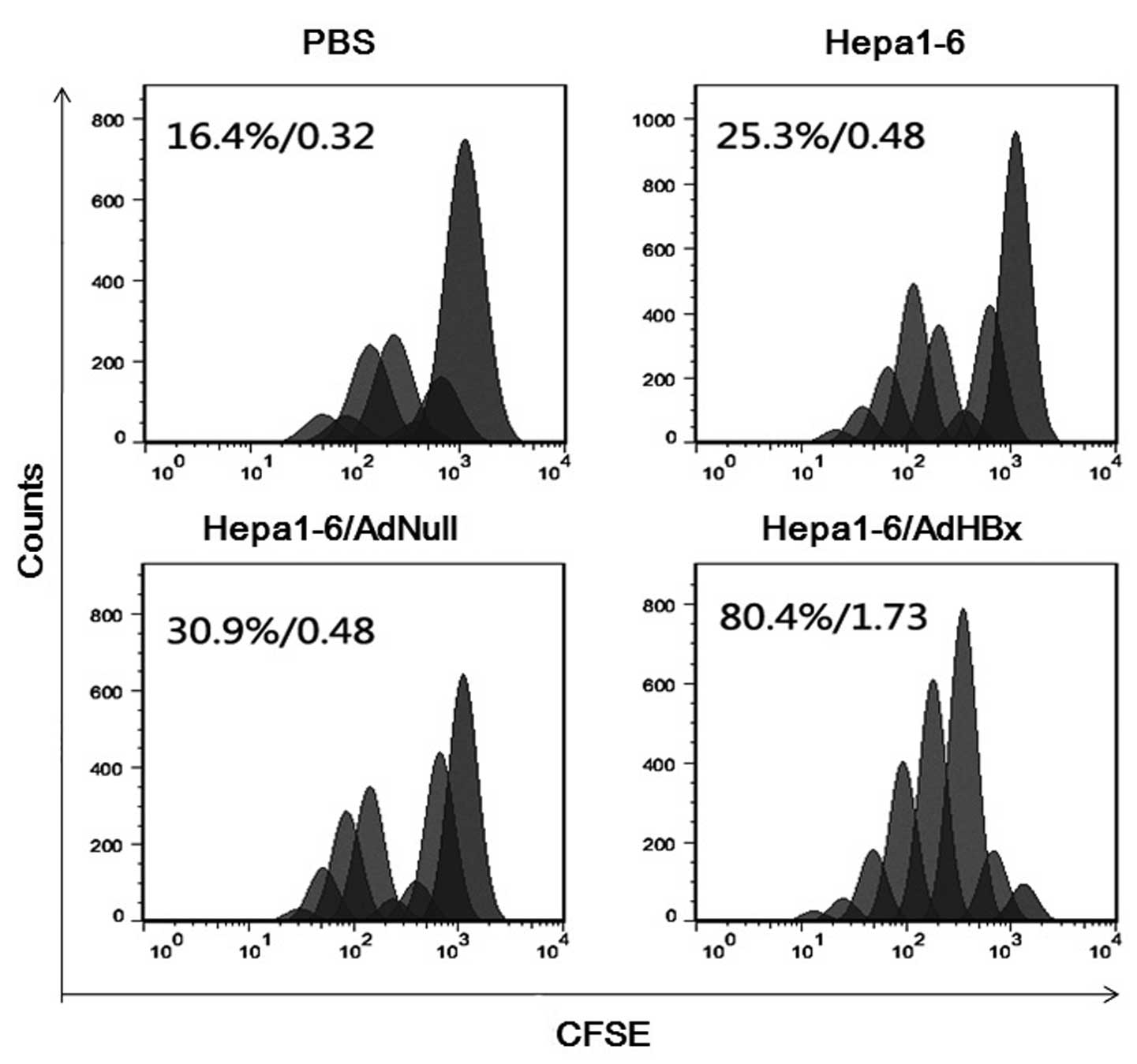
|
1
|
Du Y, Kong G, You X, et al: Elevation of
highly up-regulated in liver cancer (HULC) by hepatitis B virus X
protein promotes hepatoma cell proliferation via down-regulating
p18. J Biol Chem. 287:26302–26311. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li Y, Cheng P, Wen Y, et al: T lymphocyte
responses against hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular
carcinoma induced by adenovirus vaccine encoding HBx. Int J Mol
Med. 26:869–876. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dan Q, Sanchez R, Delgado C, et al:
Non-immunogenic murine hepatocellular carcinoma Hepa1-6 cells
expressing the membrane form of macrophage colony stimulating
factor are rejected in vivo and lead to CD8+ T-cell immunity
against the parental tumor. Mol Ther. 4:427–437. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA and Reichman ME:
Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival trends
in the United States from 1975 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 27:1485–1491.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rehermann B and Nascimbeni M: Immunology
of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Rev
Immunol. 5:215–229. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hsieh JL, Wu CL, Lee CH and Shiau AL:
Hepatitis B virus X protein sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma
cells to cytolysis induced by E1B-deleted adenovirus through the
disruption of p53 function. Clin Cancer Res. 9:338–345. 2003.
|
|
7
|
Malmassari S, Lone YC, Zhang M, Transy C
and Michel ML: In vivo hierarchy of immunodominant and subdominant
HLA-A*0201-restricted T-cell epitopes of HBx antigen of hepatitis B
virus. Microbes Infect. 7:626–634. 2005.
|
|
8
|
Ding FX, Wang F, Lu YM, et al:
Multiepitope peptide-loaded virus-like particles as a vaccine
against hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 49:1492–1502. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rosenthal FM, Zier KS and Gansbacher B:
Human tumor vaccines and genetic engineering of tumors with
cytokine and histocompatibility genes to enhance immunogenicity.
Curr Opin Oncol. 6:611–615. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yannelli JR and Wroblewski JM: On the road
to a tumor cell vaccine: 20 years of cellular immunotherapy.
Vaccine. 23:97–113. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chun E, Lee J, Cheong HS and Lee KY: Tumor
eradication by hepatitis B virus X antigen-specific CD8+
T cells in xenografted nude mice. J Immunol. 170:1183–1190. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang YJ, Hou Y, Huang H, Liu GR, White AP
and Liu SL: Two oral HBx vaccines delivered by live attenuated
Salmonella: both eliciting effective anti-tumor immunity.
Cancer Lett. 263:67–76. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bailly M, Bertrand S and Doré JF:
Increased spontaneous mutation rates and prevalence of karyotype
abnormalities in highly metastatic human melanoma cell lines.
Melanoma Res. 3:51–61. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hicklin DJ, Marincola FM and Ferrone S:
HLA class I antigen downregulation in human cancers: T-cell
immunotherapy revives an old story. Mol Med Today. 5:178–186. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li MO, Wan YY, Sanjabi S, Robertson AK and
Flavell RA: Transforming growth factor-β regulation of immune
responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 24:99–146. 2006.
|
|
16
|
Nelson WG, Simons JW, Mikhak B, et al:
Cancer cells engineered to secrete granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor using ex vivo gene transfer as vaccines
for the treatment of genitourinary malignancies. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 46(Suppl): S67–S72. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Salgia R, Lynch T, Skarin A, et al:
Vaccination with irradiated autologous tumor cells engineered to
secrete granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor augments
antitumor immunity in some patients with metastatic non-small-cell
lung carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 21:624–630. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lutz E, Yeo CJ, Lillemoe KD, et al: A
lethally irradiated allogeneic granulocyte-macrophage colony
stimulating factor-secreting tumor vaccine for pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. A Phase II trial of safety, efficacy, and immune
activation. Ann Surg. 253:328–335. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cheng P, Li Y, Yang L, et al: Hepatitis B
virus X protein (HBx) induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis through
sustained activation of cyclin B1-CDK1 kinase. Oncol Rep.
22:1101–1107. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kong G, Zhang J, Zhang S, Shan C, Ye L and
Zhang X: Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatoma cell
proliferation via upregulation of MEKK2. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
32:1173–1180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Godoy-Ramirez K, Mäkitalo B, Thorstensson
R, Sandström E, Biberfeld G and Gaines H: A novel assay for
assessment of HIV-specific cytotoxicity by multiparameter flow
cytometry. Cytometry A. 68:71–80. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hao S, Li P, Zhao J, Hu Y and Hou Y:
17β-estradiol suppresses cytotoxicity and proliferative capacity of
murine splenic NK1. 1+ cells. Cell Mol Immunol.
5:357–364. 2008.
|
|
23
|
Lee YI, Kang-Park S, Do SI and Lee YI: The
hepatitis B virus-X protein activates a phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase-dependent survival signaling cascade. J Biol Chem.
276:16969–16977. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shan C, Xu F, Zhang S, et al: Hepatitis B
virus X protein promotes liver cell proliferation via a positive
cascade loop involving arachidonic acid metabolism and p-ERK1/2.
Cell Res. 20:563–575. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ou DP, Tao YM, Tang FQ and Yang LY: The
hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatocellular carcinoma
metastasis by upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Int J
Cancer. 120:1208–1214. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gearhart TL and Bouchard MJ: The hepatitis
B virus X protein modulates hepatocyte proliferation pathways to
stimulate viral replication. J Virol. 84:2675–2686. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Neering SJ, Hardy SF, Minamoto D, Spratt
SK and Jordan CT: Transduction of primitive human hematopoietic
cells with recombinant adenovirus vectors. Blood. 88:1147–1155.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nilsson M, Ljungberg J, Richter J, et al:
Development of an adenoviral vector system with adenovirus serotype
35 tropism; efficient transient gene transfer into primary
malignant hematopoietic cells. J Gene Med. 6:631–641. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tatsis N and Ertl HC: Adenoviruses as
vaccine vectors. Mol Ther. 10:616–629. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pichla-Gollon SL, Lin SW, Hensley SE, et
al: Effect of preexisting immunity on an adenovirus vaccine vector:
in vitro neutralization assays fail to predict inhibition by
antiviral antibody in vivo. J Virol. 83:5567–5573. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vatakis DN, Koya RC, Nixon CC, et al:
Antitumor activity from antigen-specific CD8 T cells generated in
vivo from genetically engineered human hematopoietic stem cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:E1408–E1416. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Martorelli D, Muraro E, Merlo A, Turrini
R, Rosato A and Dolcetti R: Role of CD4+ cytotoxic T
lymphocytes in the control of viral diseases and cancer. Int Rev
Immunol. 29:371–402. 2010.
|
|
33
|
Tang H, Da L, Mao Y, et al: Hepatitis B
virus X protein sensitizes cells to starvation-induced autophagy
via up-regulation of beclin 1 expression. Hepatology. 49:60–71.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sir D, Tian Y, Chen WL, Ann DK, Yen TS and
Ou JH: The early autophagic pathway is activated by hepatitis B
virus and required for viral DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 107:4383–4388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Crotzer VL and Blum JS: Autophagy and
adaptive immunity. Immunology. 131:9–17. 2010.
|
|
36
|
Münz C: Antigen processing via autophagy -
not only for MHC class II presentation anymore? Curr Opin Immunol.
22:89–93. 2010.
|