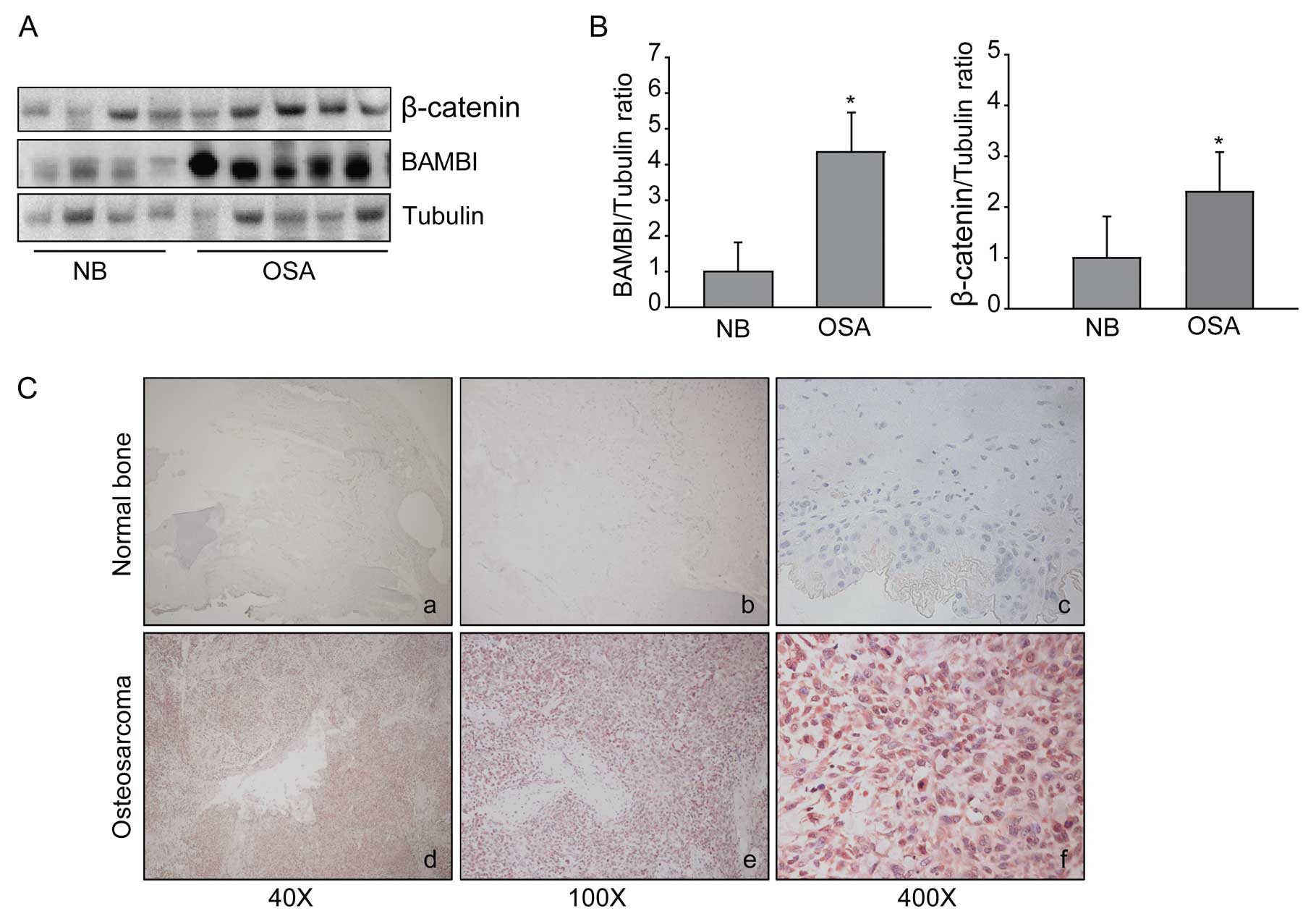
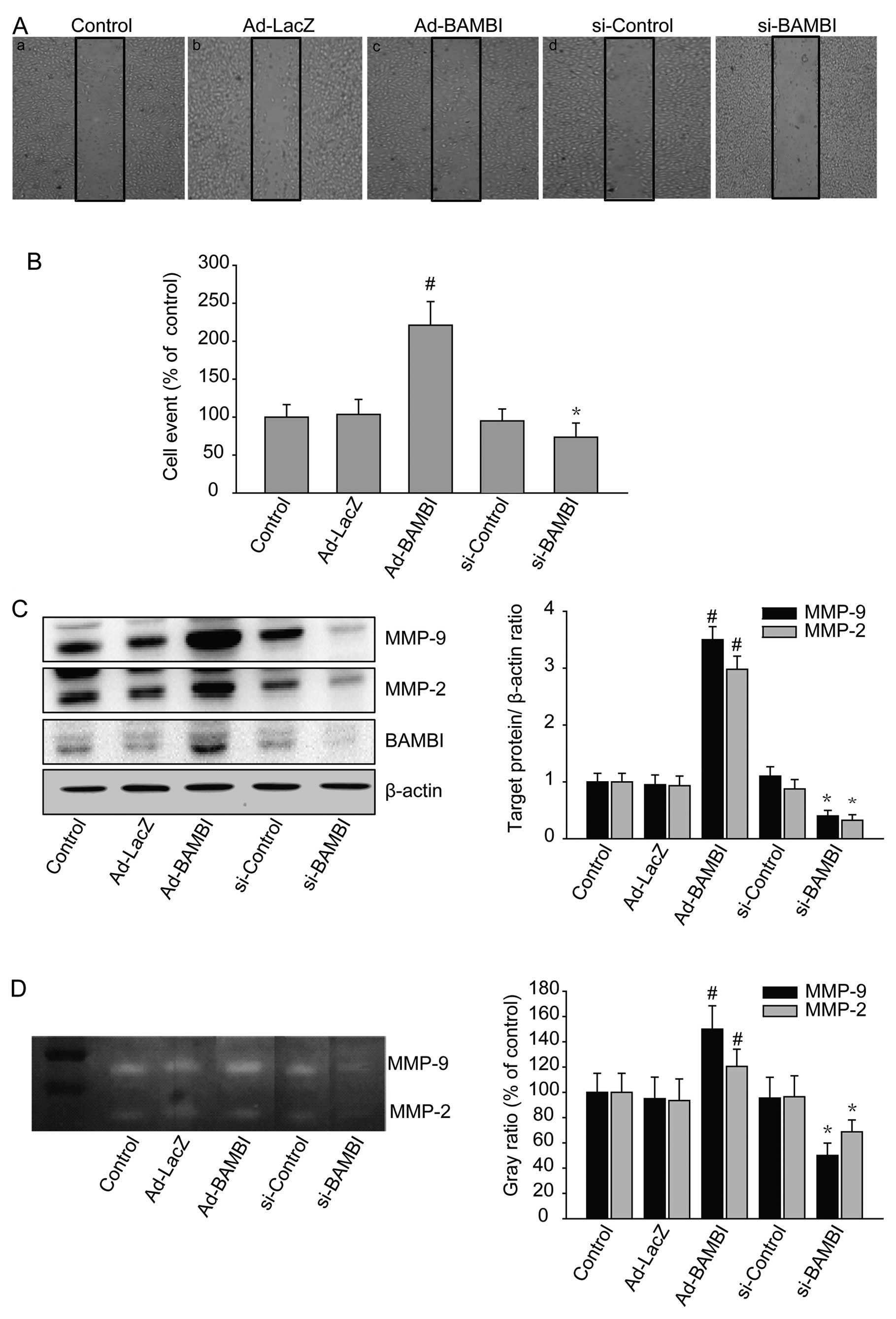
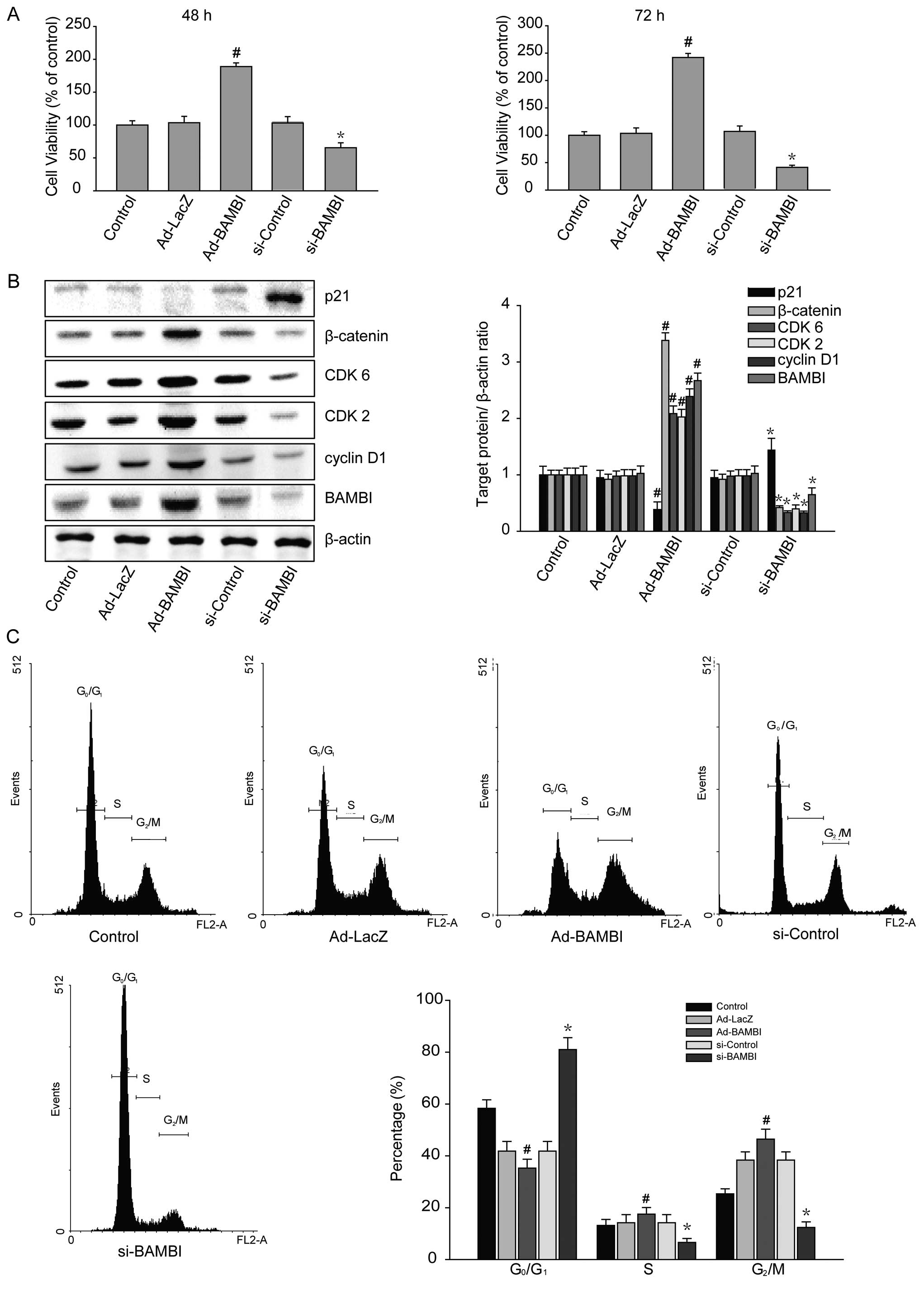
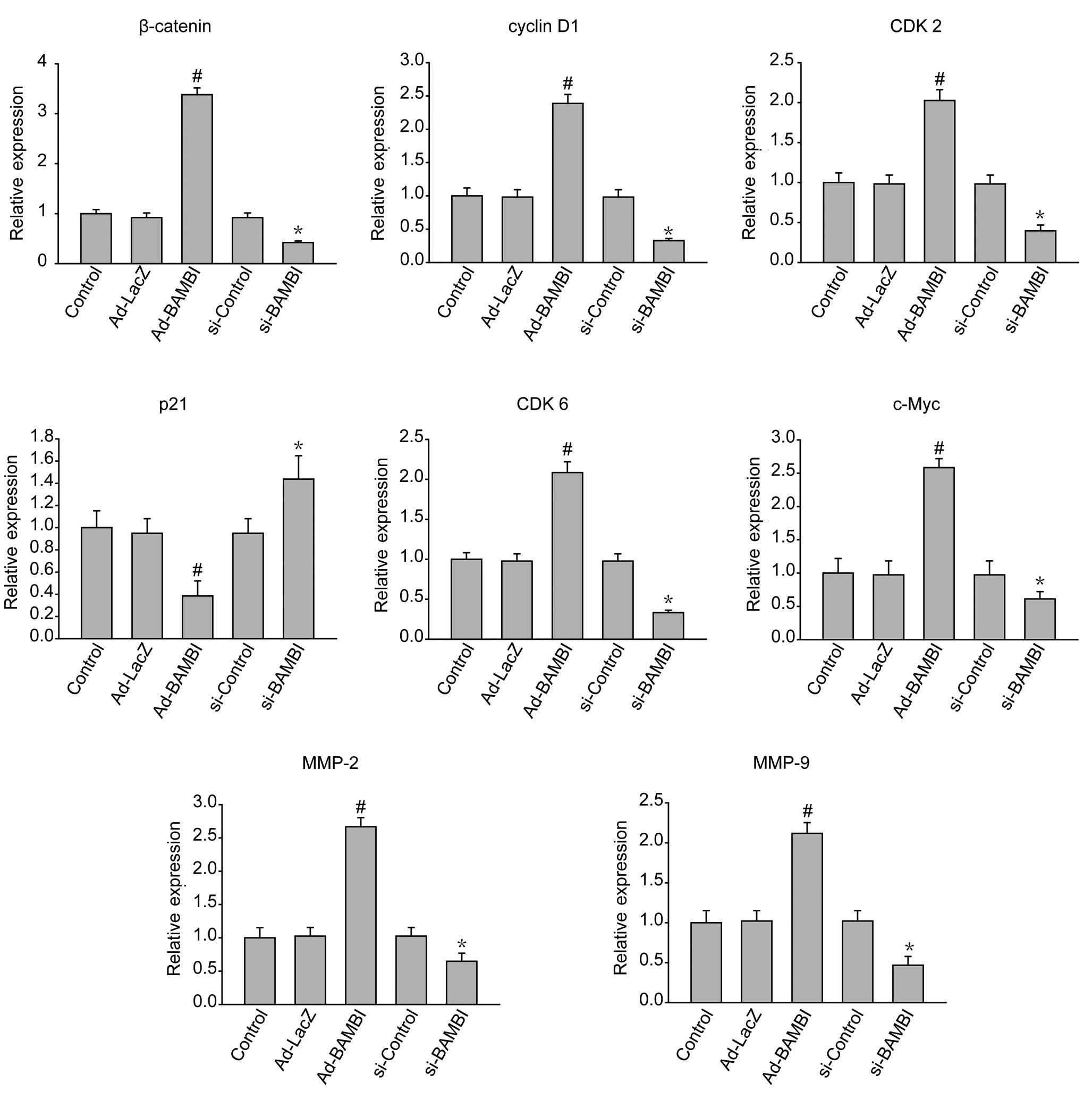
|
1
|
Bacci G, Longhi A, Versari M, Mercuri M,
Briccoli A and Picci P: Prognostic factors for osteosarcoma of the
extremity treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy: 15-year experience
in 789 patients treated at a single institution. Cancer.
106:1154–1161. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferguson WS and Goorin AM: Current
treatment of osteosarcoma. Cancer Invest. 19:292–315. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bacci G, Briccoli A, Ferrari S, et al:
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for osteosarcoma of the extremities with
synchronous lung metastases: treatment with cisplatin, adriamycin
and high dose of methotrexate and ifosfamide. Oncol Rep. 7:339–346.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Saeter G, Hoie J, Stenwig AE, Johansson
AK, Hannisdal E and Solheim OP: Systemic relapse of patients with
osteogenic sarcoma. Prognostic factors for long term survival.
Cancer. 75:1084–1093. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Massague J: TGFbeta in cancer. Cell.
134:215–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Osuna D and de Alava E: Molecular
pathology of sarcomas. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 4:12–26. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Massague J, Blain SW and Lo RS: TGFβ
signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell.
103:295–309. 2000.
|
|
8
|
Onichtchouk D, Chen YG, Dosch R, et al:
Silencing of TGF-β signalling by the pseudoreceptor BAMBI. Nature.
401:480–485. 1999.
|
|
9
|
Fritzmann J, Morkel M, Besser D, et al: A
colorectal cancer expression profile that includes transforming
growth factor β inhibitor BAMBI predicts metastatic potential.
Gastroenterology. 137:165–175. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yan X, Lin Z, Chen F, et al: Human BAMBI
cooperates with Smad7 to inhibit transforming growth factor-β
signaling. J Biol Chem. 284:30097–30104. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Seki E, De Minicis S, Osterreicher CH, et
al: TLR4 enhances TGF-β signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med.
13:1324–1332. 2007.
|
|
12
|
van Amerongen R, Mikels A and Nusse R:
Alternative Wnt signaling is initiated by distinct receptors. Sci
Signal. 1:re92008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nusse R and Varmus HE: Wnt genes. Cell.
69:1073–1087. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Polakis P: Wnt signaling in cancer. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lee JH, Song MY, Song EK, et al:
Overexpression of SIRT1 protects pancreatic β-cells against
cytokine toxicity by suppressing the nuclear factor-κB signaling
pathway. Diabetes. 58:344–351. 2009.
|
|
16
|
Aizawa J, Sakayama K, Kamei S, et al:
Effect of troglitazone on tumor growth and pulmonary metastasis
development of the mouse osteosarcoma cell line LM8. BMC Cancer.
10:512010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: β-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999.
|
|
18
|
Khin SS, Kitazawa R, Win N, et al: BAMBI
gene is epigenetically silenced in subset of high-grade bladder
cancer. Int J Cancer. 125:328–338. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Subramaniam N, Sherman MH, Rao R, et al:
Metformin-mediated Bambi expression in hepatic stellate cells
induces prosurvival Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cancer Prev Res.
5:553–561. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin Z, Gao C, Ning Y, He X, Wu W and Chen
YG: The pseudoreceptor BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor
positively modulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Biol Chem.
283:33053–33058. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu C, Li Y, Semenov M, et al: Control of
β-catenin phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism.
Cell. 108:837–847. 2002.
|
|
22
|
Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V, et al:
Activation of beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by
mutations in β-catenin or APC. Science. 275:1787–1790. 1997.
|
|
23
|
Willert K and Jones KA: Wnt signaling: is
the party in the nucleus? Genes Dev. 20:1394–1404. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stetler-Stevenson WG, Aznavoorian S and
Liotta LA: Tumor cell interactions with the extracellular matrix
during invasion and metastasis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 9:541–573.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shapiro GI: Cyclin-dependent kinase
pathways as targets for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol.
24:1770–1783. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xiong Y, Hannon GJ, Zhang H, Casso D,
Kobayashi R and Beach D: p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin
kinases. Nature. 366:701–704. 1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou L, Park BH, Park JH, et al:
Overexpression of the prolyl isomerase PIN1 promotes cell growth in
osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep. 29:193–198. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|