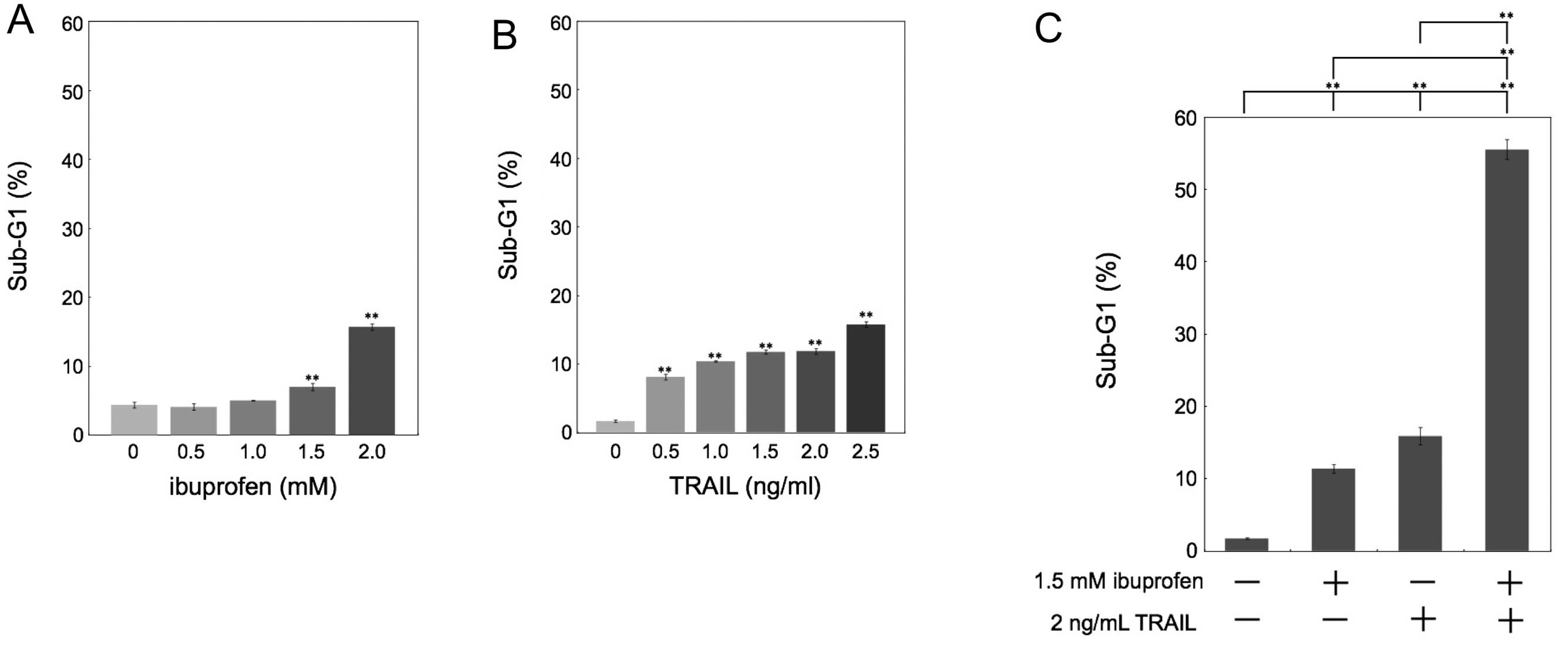
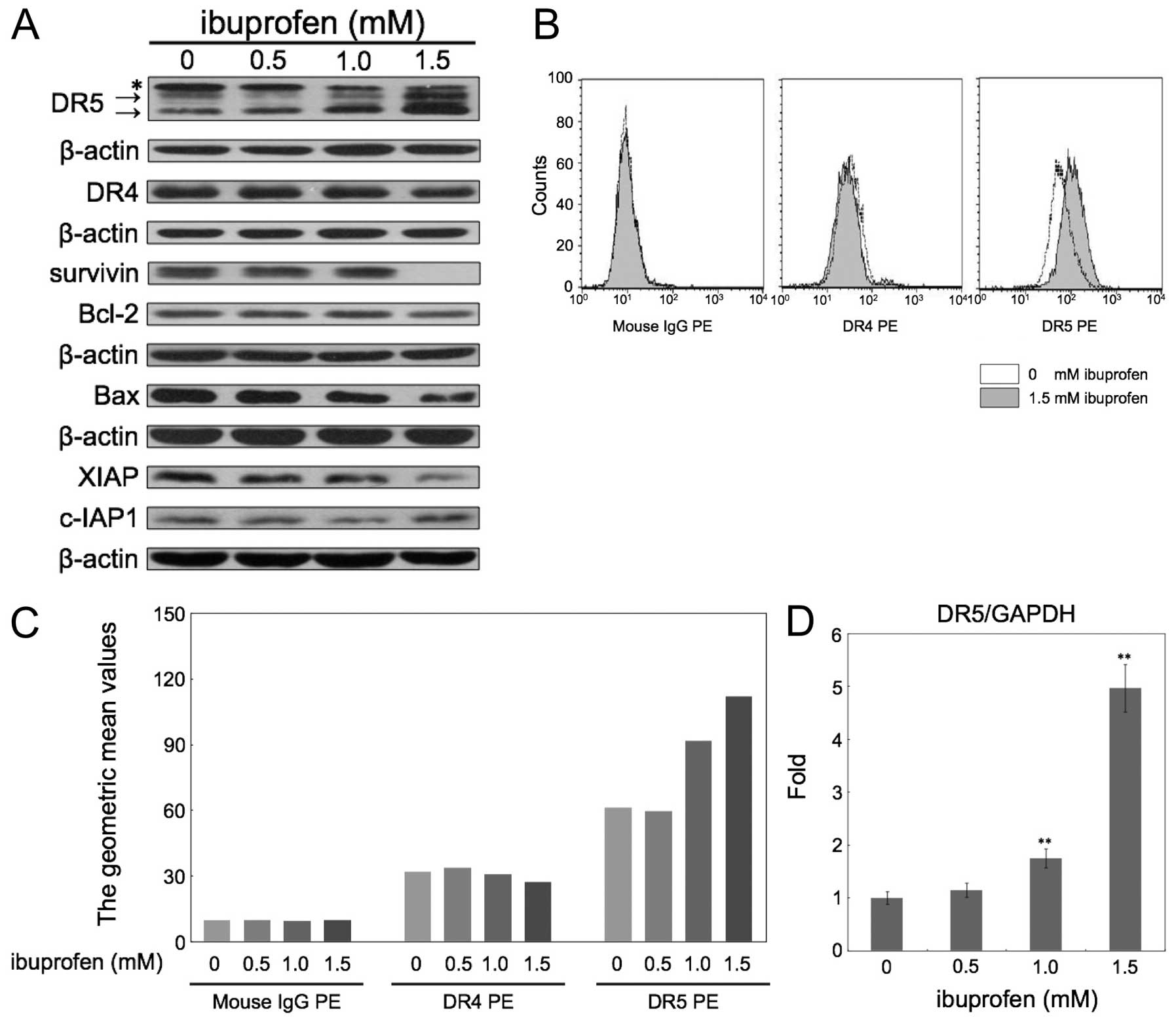
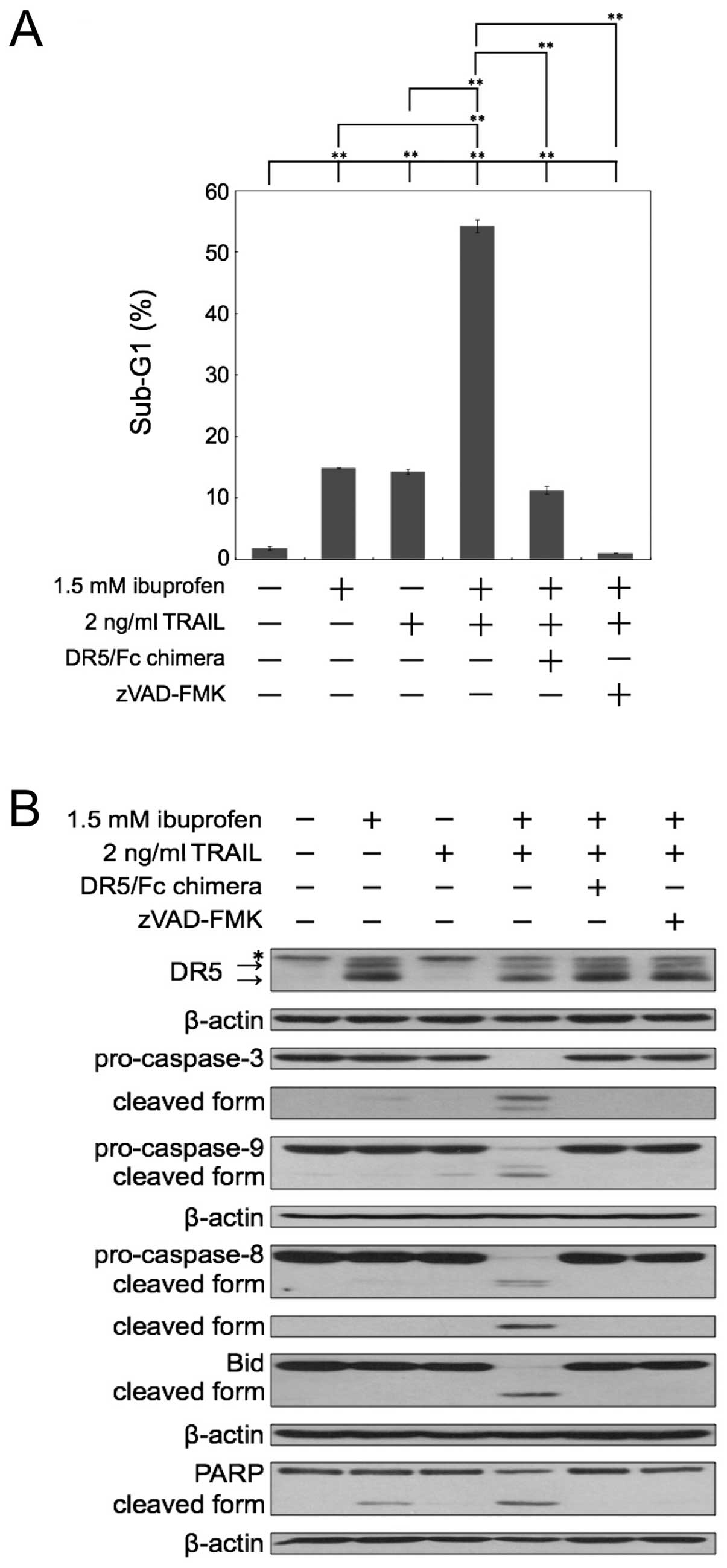
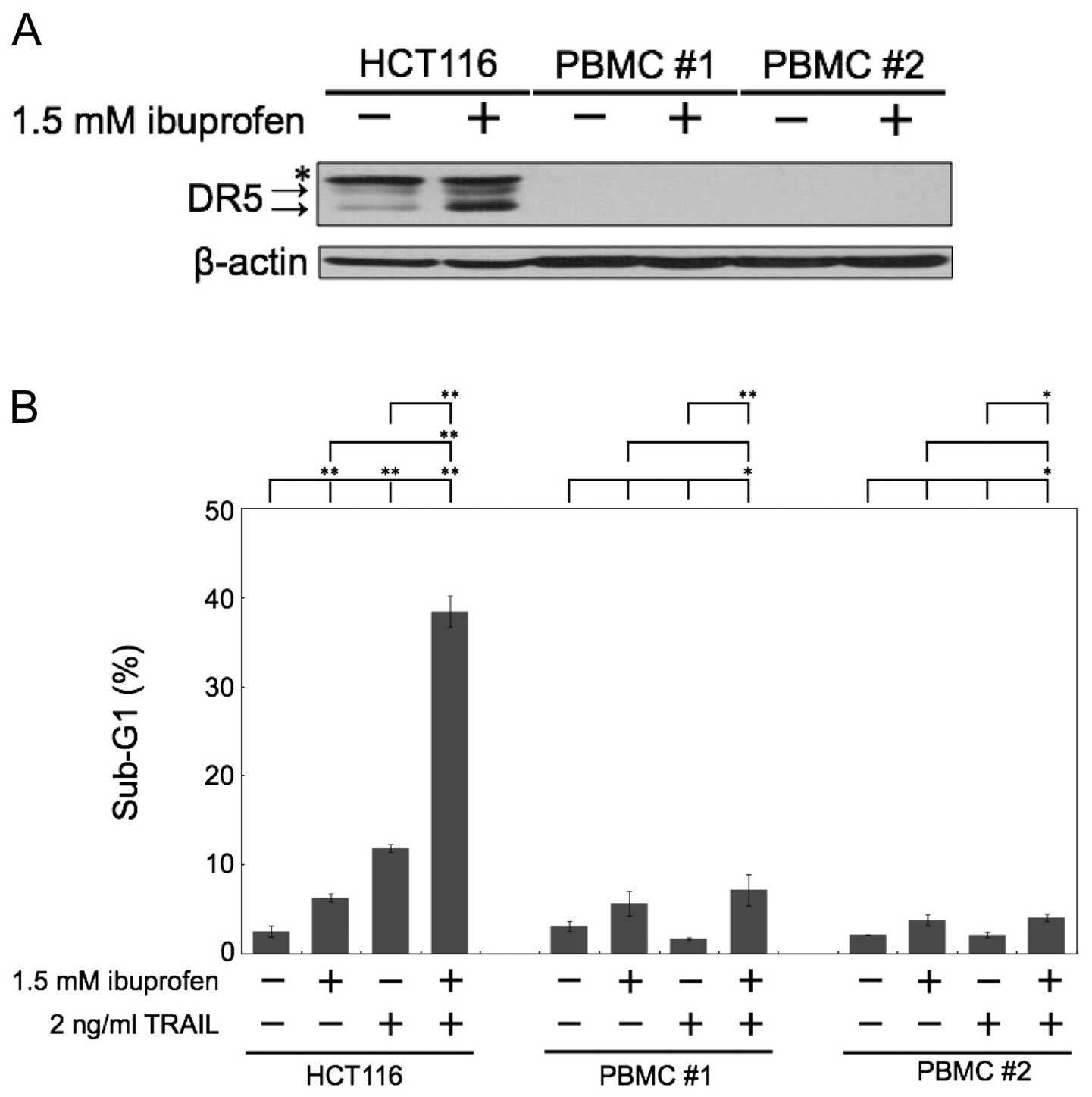
|
1
|
Weitz J, Koch M, Debus J, Höhler T, Galle
PR and Büchler MW: Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 365:153–165. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Brasky TM, Bonner MR, Moysich KB, et al:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and breast cancer
risk: differences by molecular subtype. Cancer Causes Control.
22:965–975. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Walter RB, Milano F, Brasky TM and White
E: Long-term use of acetaminophen, aspirin, and other nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of hematologic malignancies:
results from the prospective Vitamins and Lifestyle (VITAL) study.
J Clin Oncol. 29:2424–2431. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Thun MJ, Namboodiri MM and Heath CW Jr:
Aspirin use and reduced risk of fatal colon cancer. N Engl J Med.
325:1593–1596. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baron JA, Cole BF, Sandler RS, et al: A
randomized trial of aspirin to prevent colorectal adenomas. N Engl
J Med. 348:891–899. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rothwell PM, Wilson M, Elwin CE, et al:
Long-term effect of aspirin on colorectal cancer incidence and
mortality: 20-year follow-up of five randomised trials. Lancet.
376:1741–1750. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rothwell PM, Wilson M, Price JF, et al:
Effect of daily aspirin on risk of cancer metastasis: a study of
incident cancers during randomised controlled trials. Lancet.
379:1591–1601. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ishikawa H, Nakamura T, Kawano A, Gondo N
and Sakai T: Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer in Japan: a brief
introduction to current clinical trials. J Gastroenterol. 44:77–81.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ishikawa H, Wakabayashi K, Suzuki S, et
al: Preventive effects of low-dose aspirin on colorectal adenoma
growth in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis:
double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Cancer Med. 2:50–56. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Antithrombotic Trialists’ Collaboration.
Collaborative meta-analysis of randomised trials of antiplatelet
therapy for prevention of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke
in high risk patients. BMJ. 324:71–86. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Adams SS, McCullough KF and Nicholson JS:
The pharmacological properties of ibuprofen, an anti-inflammatory,
analgesic and antipyretic agent. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther.
178:115–129. 1969.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chan AT, Ogino S and Fuchs CS: Aspirin and
the risk of colorectal cancer in relation to the expression of
COX-2. N Engl J Med. 356:2131–2142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ogino S, Kirkner GJ, Nosho K, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is an independent predictor of poor
prognosis in colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:8221–8227. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kawamori T, Rao CV, Seibert K and Reddy
BS: Chemopreventive activity of celecoxib, a specific
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, against colon carcinogenesis. Cancer
Res. 58:409–412. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Solomon SD, McMurray JJ, Pfeffer MA, et
al: Cardiovascular risk associated with celecoxib in a clinical
trial for colorectal adenoma prevention. N Engl J Med.
352:1071–1080. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baron JA, Sandler RS, Bresalier RS, et al:
A randomized trial of rofecoxib for the chemoprevention of
colorectal adenomas. Gastroenterology. 131:1674–1682. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Harris RE, Beebe-Donk J and Alshafie GA:
Similar reductions in the risk of human colon cancer by selective
and nonselective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors. BMC Cancer.
14:2372008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schönthal AH, Chen TC, Hofman FM, et al:
Celecoxib analogs that lack COX-2 inhibitory function: preclinical
development of novel anticancer drugs. Expert Opin Investig Drugs.
17:197–208. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bonelli P, Tuccillo FM, Calemma R, et al:
Changes in the gene expression profile of gastric cancer cells in
response to ibuprofen: a gene pathway analysis. Pharmacogenomics J.
11:412–428. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Greenspan EJ, Madigan JP, Boardman LA and
Rosenberg DW: Ibuprofen inhibits activation of nuclear β-catenin in
human colon adenomas and induces the phosphorylation of GSK-3β.
Cancer Prev Res. 4:161–171. 2011.
|
|
21
|
Harris RE, Beebe-Donk J, Doss H and Burr
Doss D: Aspirin, ibuprofen, and other non-steroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs in cancer prevention: A critical review of
non-selective COX-2 blockade (Review). Oncol Rep. 13:559–583.
2005.
|
|
22
|
Taniguchi H, Horinaka M, Yoshida T, et al:
Targeting the glyoxalase pathway enhances TRAIL efficacy in cancer
cells by downregulating the expression of antiapoptotic molecules.
Mol Cancer Ther. 11:2294–2300. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Taniguchi H, Yoshida T, Horinaka M, et al:
Baicalein overcomes tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance via two different
cell-specific pathways in cancer cells but not in normal cells.
Cancer Res. 68:8918–8927. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yoshida T, Maoka T, Das SK, et al:
Halocynthiaxanthin and peridinin sensitize colon cancer cell lines
to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Mol
Cancer Res. 5:615–625. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Horinaka M, Yoshida T, Shiraishi T, et al:
The dietary flavonoid apigenin sensitizes malignant tumor cells to
tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Mol Cancer
Ther. 5:945–951. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, et al:
Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 5:157–163.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, et al: Safety
and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin
Invest. 104:155–162. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fesik SW: Promoting apoptosis as a
strategy for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:876–885.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Soria JC, Smit E, Khayat D, et al: Phase
1b study of dulanermin (recombinant human Apo2L/TRAIL) in
combination with paclitaxel, carboplatin, and bevacizumab in
patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J
Clin Oncol. 28:1527–1533. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Leong S, Cohen RB, Gustafson DL, et al:
Mapatumumab, an antibody targeting TRAIL-R1, in combination with
paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced solid
malignancies: results of a phase I and pharmacokinetic study. J
Clin Oncol. 27:4413–4421. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zerafa N, Westwood JA, Cretney E, et al:
Cutting edge: TRAIL deficiency accelerates hematological
malignancies. J Immunol. 175:5586–5590. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nakata S, Yoshida T, Horinaka M, Shiraishi
T, Wakada M and Sakai T: Histone deacetylase inhibitors upregulate
death receptor 5/TRAIL-R2 and sensitize apoptosis induced by
TRAIL/APO2-L in human malignant tumor cells. Oncogene.
23:6261–6271. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kim KM, Song JJ, An JY, Kwon YT and Lee
YJ: Pretreatment of acetylsalicylic acid promotes tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by
down-regulating BCL-2 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 49:41047–41056.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Braun FK, Al-Yacoub N, Plötz M, Möbs M,
Sterry W and Eberle J: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs induce
apoptosis in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cells and enhance their
sensitivity for TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. J Invest
Dermatol. 132:429–439. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang Y, He Q, Hillman MJ, Rong R and
Sheikh MS: Sulindac sulfide-induced apoptosis involves death
receptor 5 and the caspase 8-dependent pathway in human colon and
prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 61:6918–6924. 2001.
|
|
36
|
Sinicrope FA and Penington RC: Sulindac
sulfide-induced apoptosis is enhanced by a small-molecule Bcl-2
inhibitor and by TRAIL in human colon cancer cells overexpressing
Bcl-2. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:1475–1483. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Heijink DM, Jalving M, Oosterhuis D, et
al: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand cooperates with NSAIDs
via activated Wnt signalling in (pre)malignant colon cells. J
Pathol. 223:378–389. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ricchi P, Zarrilli R, Di Palma A and
Acquaviva AM: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in colorectal
cancer: from prevention to therapy. Br J Cancer. 88:803–807. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sheng H, Shao J, Kirkland SC, et al:
Inhibition of human colon cancer cell growth by selective
inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2. J Clin Invest. 99:2254–2259. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bjarnason I: Gastrointestinal safety of
NSAIDs and over-the-counter analgesics. Int J Clin Pract (Suppl).
178:37–42. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schnitzer TJ, Burmester GR, Mysler E, et
al: Comparison of lumiracoxib with naproxen and ibuprofen in the
Therapeutic Arthritis Research and Gastrointestinal Event Trial
(TARGET), reduction in ulcer complications: randomised controlled
trial. Lancet. 364:665–674. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lugardon S, Lapeyre-Mestre M and
Montastruc JL: Upper gastrointestinal adverse drug reactions and
cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors (celecoxib and rofecoxib): a
case/non-case study from the French Pharmacovigilance Database. Eur
J Clin Pharmacol. 60:673–677. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Van GE, Jones JK, Moore N, Parc JM, Wall R
and Schneid H: A large simple clinical trial prototype for
assessment of OTC drug effects using patient-reported data.
Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 14:249–255. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Horinaka M, Yoshida T, Kishi A, et al:
Lactobacillus strains induce TRAIL production and facilitate
natural killer activity against cancer cells. FEBS Lett.
584:577–582. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|