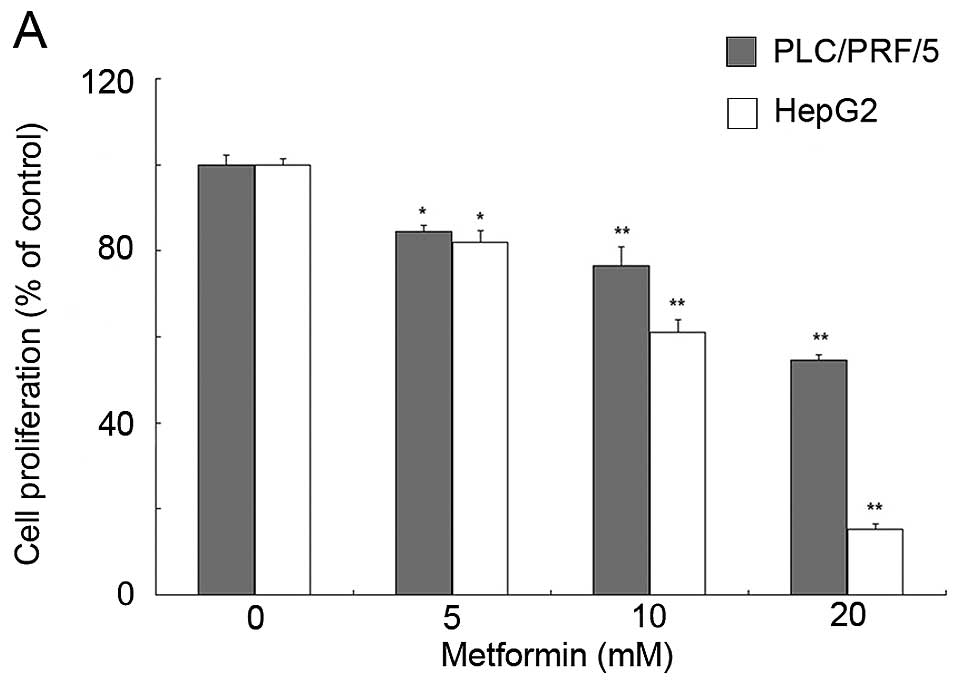
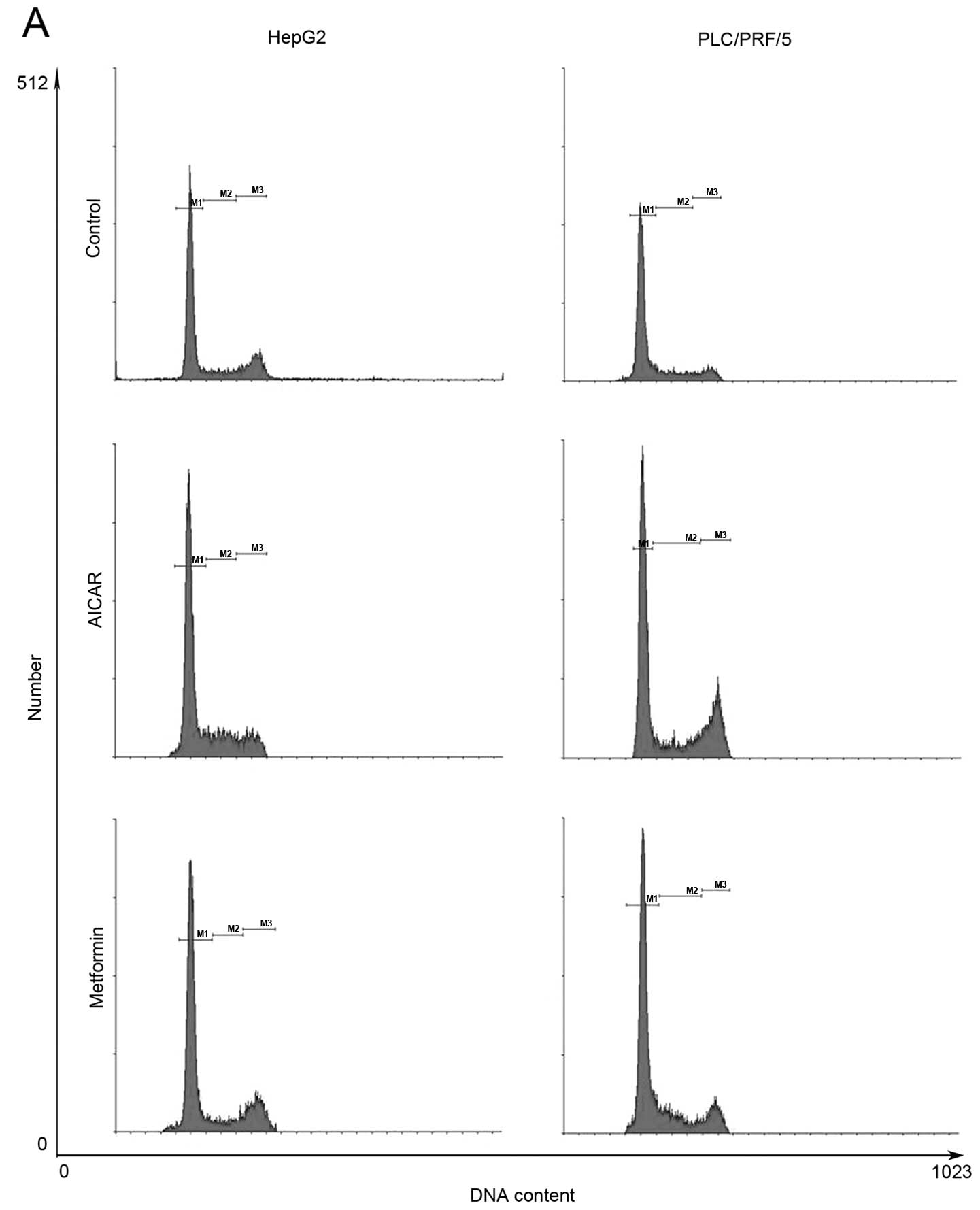
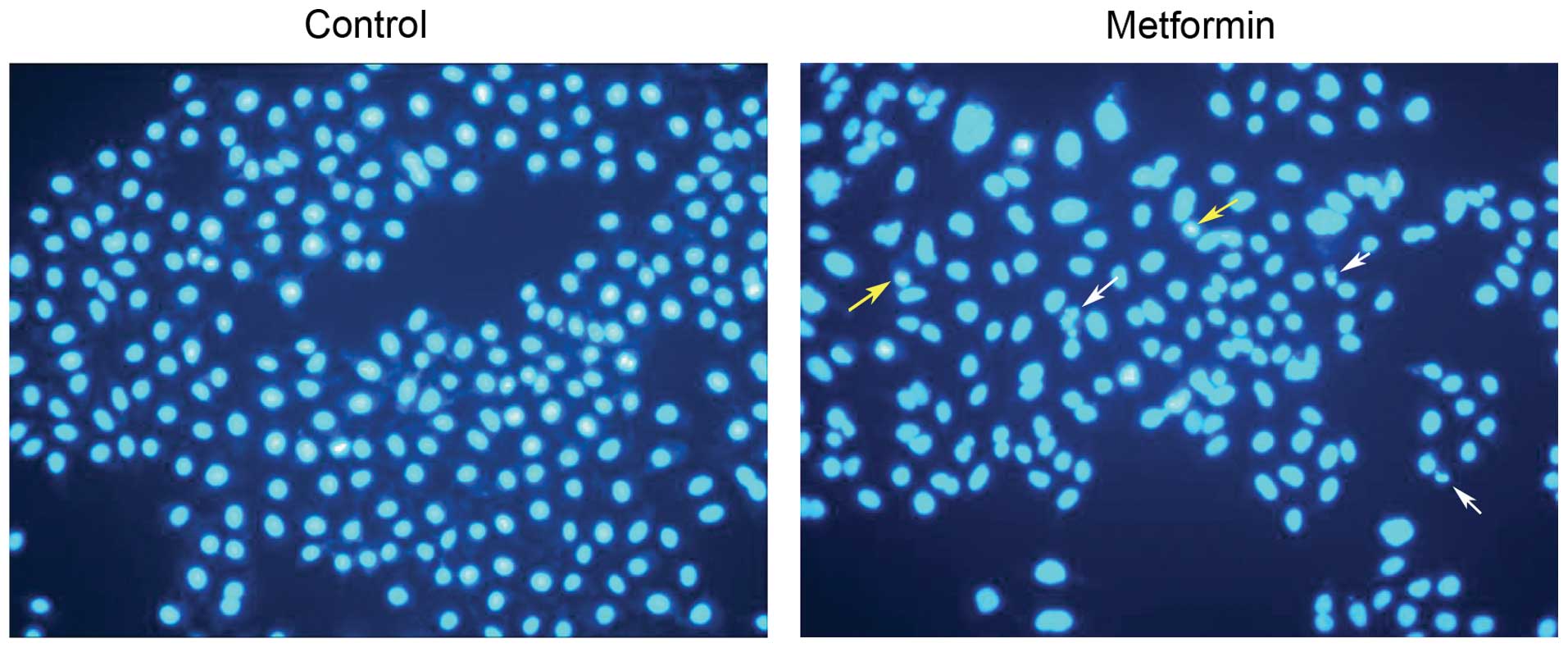
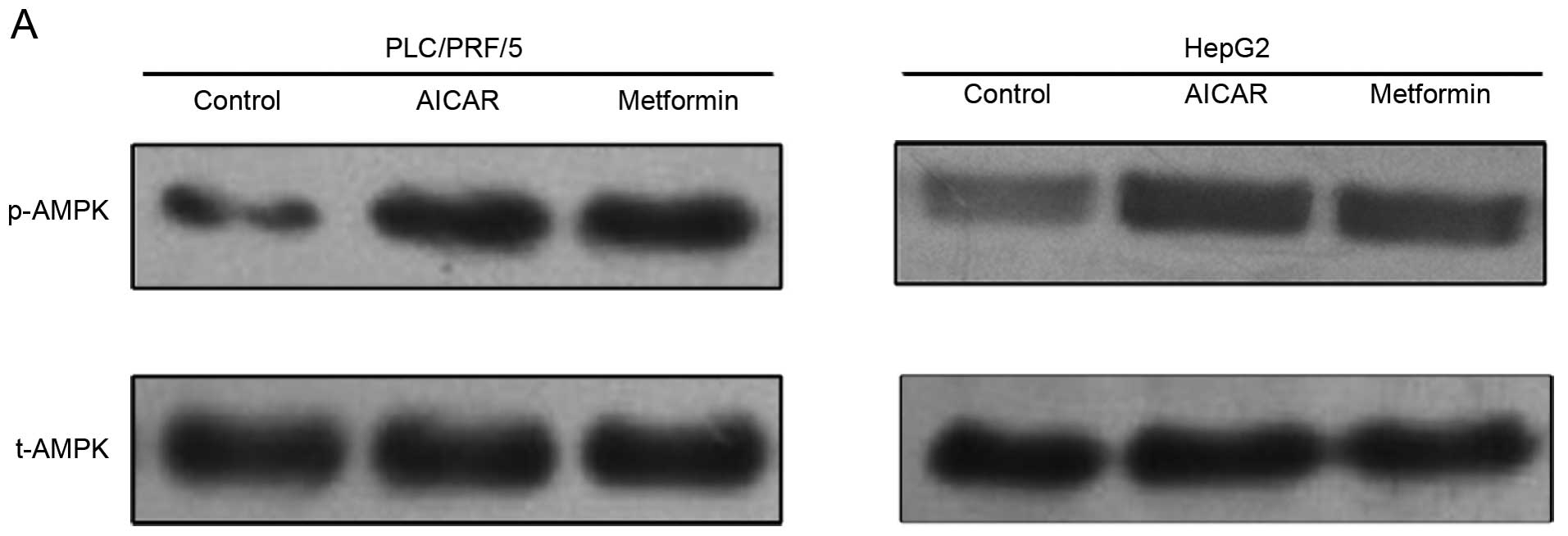
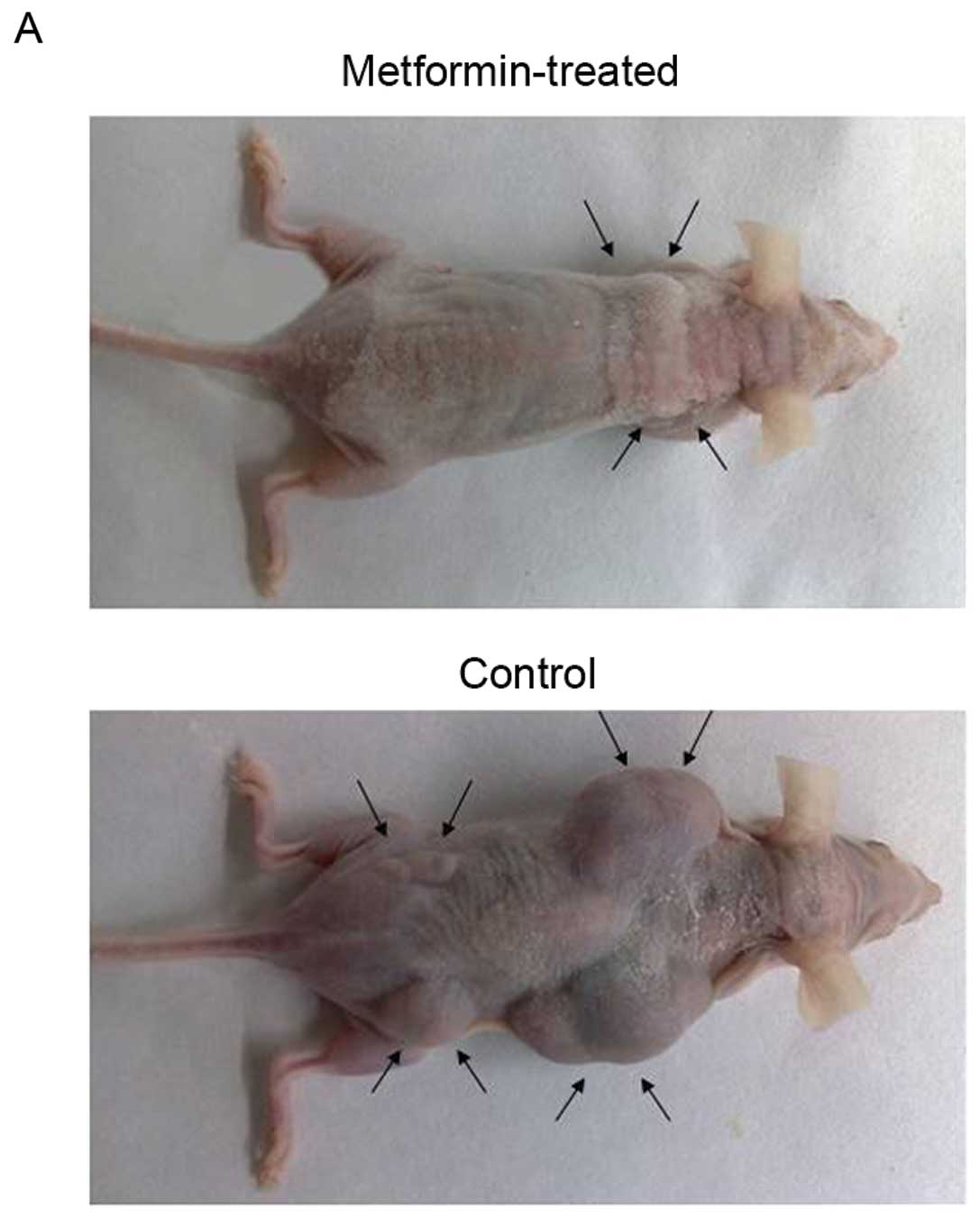
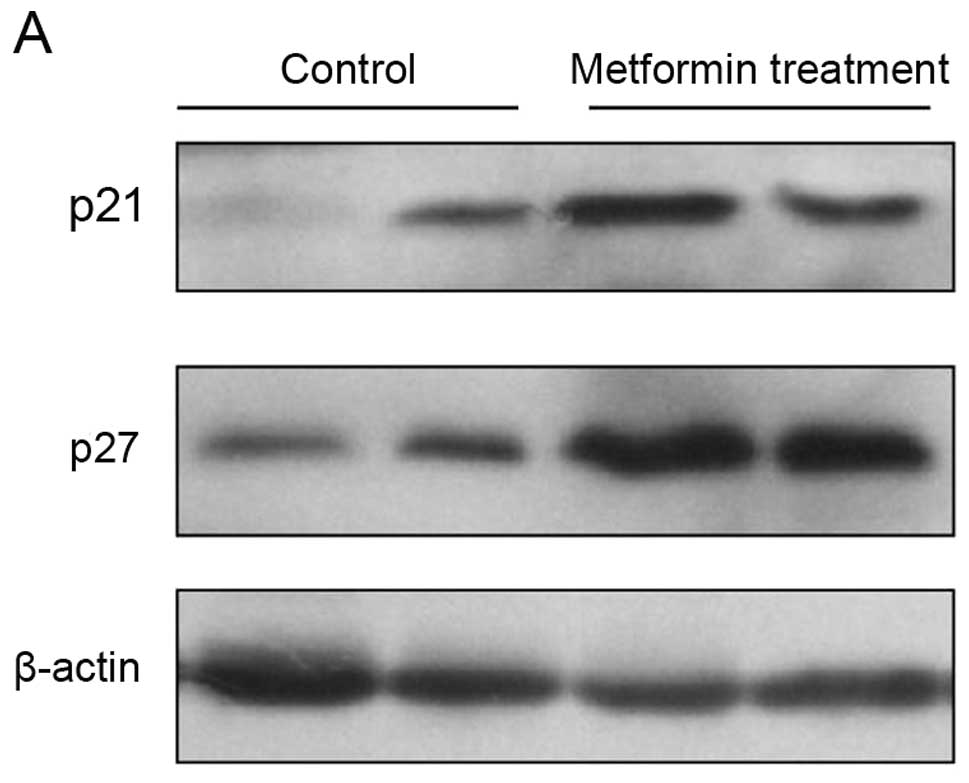
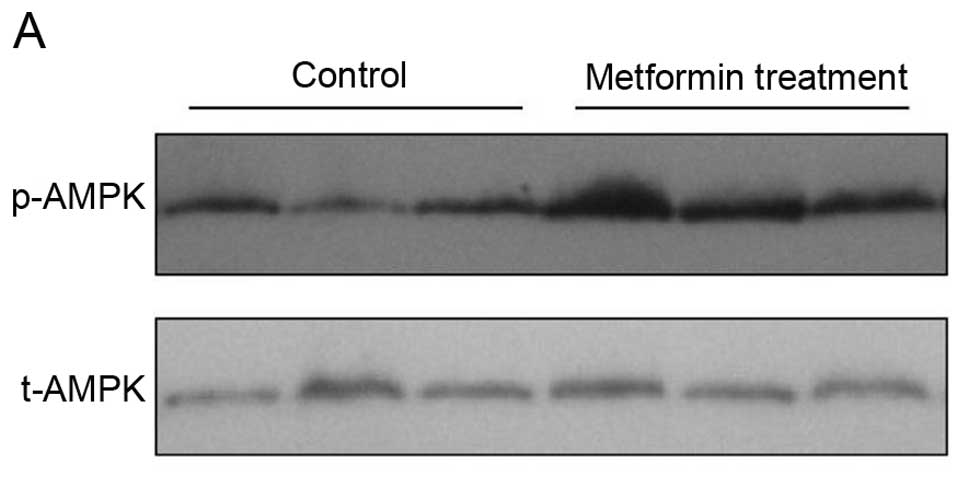
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M and Cléries R:
Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends.
Gastroenterology. 127(Suppl 1): S5–S16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA and Reichman ME:
Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival trends
in the United States from 1975 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 27:1485–1491.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen DS: Hepatocellular carcinoma in
Taiwan. Hepatol Res. 37(Suppl 2): S101–S105. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hundal RS, Krssak M, Dufour S, et al:
Mechanism by which metformin reduces glucose production in type 2
diabetes. Diabetes. 49:2063–2069. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Libby G, Donnelly LA, Donnan PT, Alessi
DR, Morris AD and Evans JM: New users of metformin are at low risk
of incident cancer: a cohort study among people with type 2
diabetes. Diabetes Care. 32:1620–1625. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bowker SL, Majumdar SR, Veugelers P and
Johnson JA: Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with
type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin. Diabetes Care.
29:254–258. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gotlieb WH, Saumet J, Beauchamp MC, et al:
In vitro metformin anti-neoplastic activity in epithelial ovarian
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 110:246–250. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang ZJ, Zheng ZJ, Shi R, Su Q, Jiang Q
and Kip KE: Metformin for liver cancer prevention in patients with
type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 97:2347–2353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vernon G, Baranova A and Younossi ZM:
Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 34:274–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Starley BQ, Calcagno CJ and Harrison SA:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: a
weighty connection. Hepatology. 51:1820–1832. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baig NA, Herrine SK and Rubin R: Liver
disease and diabetes mellitus. Clin Lab Med. 21:193–207.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, et
al: Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. CA Cancer J Clin.
60:207–221. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Stickel F and Hellerbrand C: Non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease as a risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma:
mechanisms and implications. Gut. 59:1303–1307. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hardie DG: Minireview: the AMP-activated
protein kinase cascade: the key sensor of cellular energy status.
Endocrinology. 144:5179–5183. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kyriakis J: At the crossroads:
AMP-activated kinase and the LKB1 tumor suppressor link cell
proliferation to metabolic regulation. J Biol. 2:262003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Baas AF, Kuipers J, van der Wel NN, et al:
Complete polarization of single intestinal epithelial cells upon
activation of LKB1 by STRAD. Cell. 116:457–466. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Corradetti MN, Inoki K, Bardeesy N,
DePinho RA and Guan KL: Regulation of the TSC pathway by LKB1:
evidence of a molecular link between tuberous sclerosis complex and
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Genes Dev. 18:1533–1538. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Slattery ML and Fitzpatrick FA:
Convergence of hormones, inflammation, and energy-related factors:
a novel pathway of cancer etiology. Cancer Prev Res. 2:922–930.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu J, Li M, Song B, et al: Metformin
inhibits renal cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo xenograft. Urol
Oncol. 31:264–270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schneider MB, Matsuzaki H, Haorah J, et
al: Prevention of pancreatic cancer induction in hamsters by
metformin. Gastroenterology. 120:1263–1270. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhuang Y and Miskimins WK: Cell cycle
arrest in Metformin treated breast cancer cells involves activation
of AMPK, downregulation of cyclin D1, and requires
p27Kip1 or p21Cip1. J Mol Signal. 3:182008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rattan R, Graham RP, Maguire JL, Giri S
and Shridhar V: Metformin suppresses ovarian cancer growth and
metastasis with enhancement of cisplatin cytotoxicity in vivo.
Neoplasia. 13:483–491. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Algire C, Amrein L, Zakikhani M, Panasci L
and Pollak M: Metformin blocks the stimulative effect of a
high-energy diet on colon carcinoma growth in vivo and is
associated with reduced expression of fatty acid synthase. Endocr
Relat Cancer. 17:351–360. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zakikhani M, Dowling RJO, Sonenberg N and
Pollak MN: The effects of adiponectin and metformin on prostate and
colon neoplasia involve activation of AMP-activated protein kinase.
Cancer Prev Res. 1:369–375. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yasmeen A, Beauchamp MC, Piura E, Segal E,
Pollak M and Gotlieb WH: Induction of apoptosis by metformin in
epithelial ovarian cancer: involvement of the Bcl-2 family
proteins. Gynecol Oncol. 121:492–498. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hassan MM, Curley SA, Li D, et al:
Association of diabetes duration and diabetes treatment with the
risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 116:1938–1946. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen HP, Shieh JJ, Chang CC, et al:
Metformin decreases hepatocellular carcinoma risk in a
dose-dependent manner: population-based and in vitro studies. Gut.
62:606–615. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ouyang J, Parakhia RA and Ochs RS:
Metformin activates AMP kinase through inhibition of AMP deaminase.
J Biol Chem. 286:1–11. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bhalla K, Hwang BJ, Dewi RE, et al:
Metformin prevents liver tumorigenesis by inhibiting pathways
driving hepatic lipogenesis. Cancer Prev Res. 5:544–552. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xiong Y, Lu QJ, Zhao J and Wu GY:
Metformin inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
inducing apoptosis via mitochondrion-mediated pathway. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 13:3275–3279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qu Z, Zhang Y, Liao M, Chen Y, Zhao J and
Pan Y: In vitro and in vivo antitumoral action of metformin on
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 42:922–933. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nielsen NH, Arnerlöv C, Emdin SO and
Landberg G: Cyclin E overexpression, a negative prognostic factor
in breast cancer with strong correlation to oestrogen receptor
status. Br J Cancer. 74:874–880. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Biliran HJ, Wang Y, Banerjee S, et al:
Overexpression of cyclin D1 promotes tumor cell growth and confers
resistance to cisplatin-mediated apoptosis in an elastase-myc
transgene-expressing pancreatic tumor cell line. Clin Cancer Res.
11:6075–6086. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Polyak K, Kato JY, Solomon MJ, et al:
p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth
factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev.
8:9–22. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cheng F, McLaughlin P, Verderame M and
Zagon I: The OGF-OGFr axis utilizes the p21 pathway to restrict
progression of human pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 7:52008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cayrol C, Knibiehler M and Ducommun B: p21
binding to PCNA causes G1 and G2 cell cycle arrest in p53-deficient
cells. Oncogene. 16:311–320. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gardner LB, Li Q, Park MS, Flanagan WM,
Semenza GL and Dang CV: Hypoxia inhibits G1/S transition through
regulation of p27 expression. J Biol Chem. 276:7919–7926. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Toyoshima H and Hunter T: p27, a novel
inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to
p21. Cell. 78:67–74. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Weinberg RA: The retinoblastoma protein
and cell cycle control. Cell. 81:323–330. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|