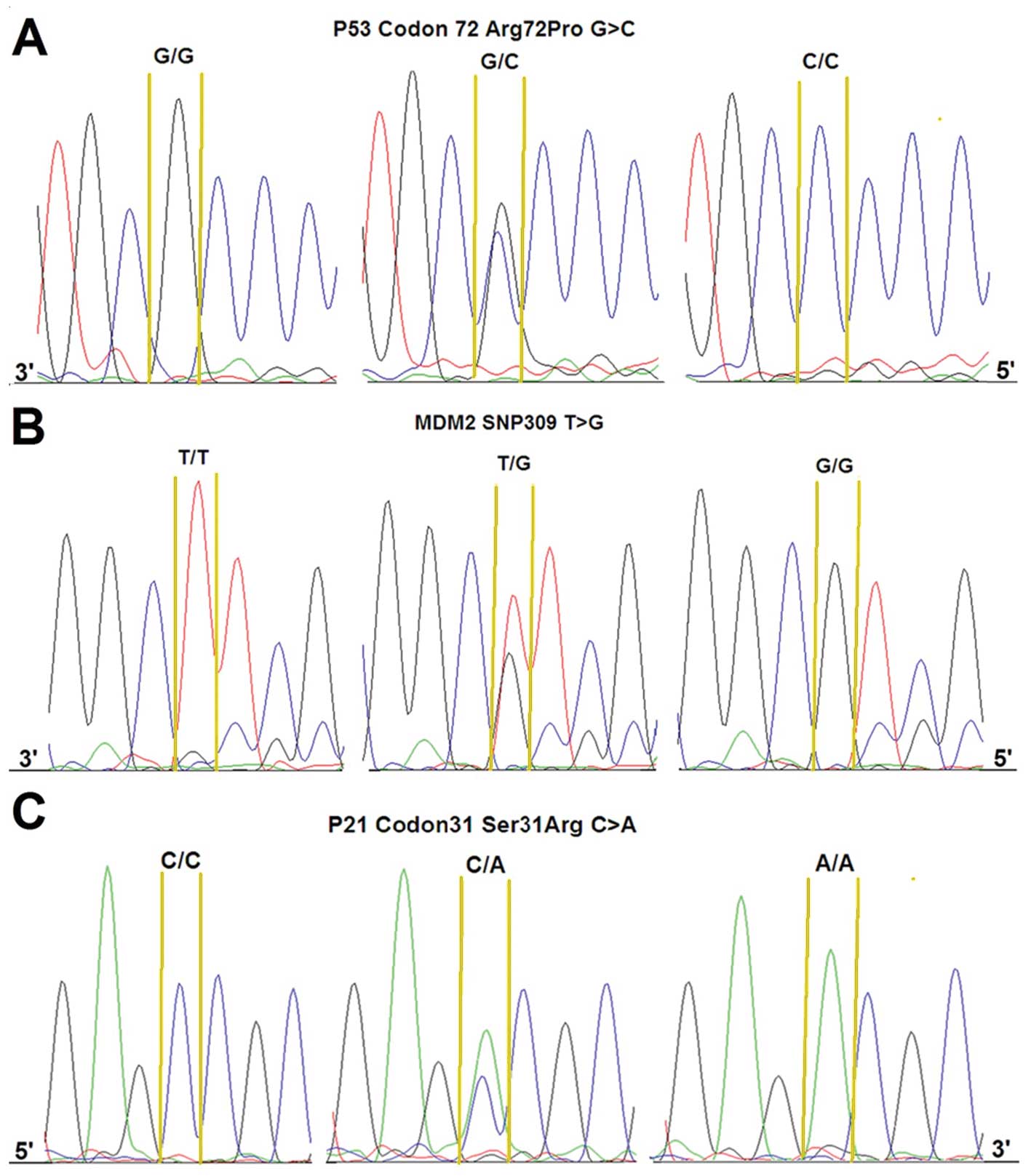
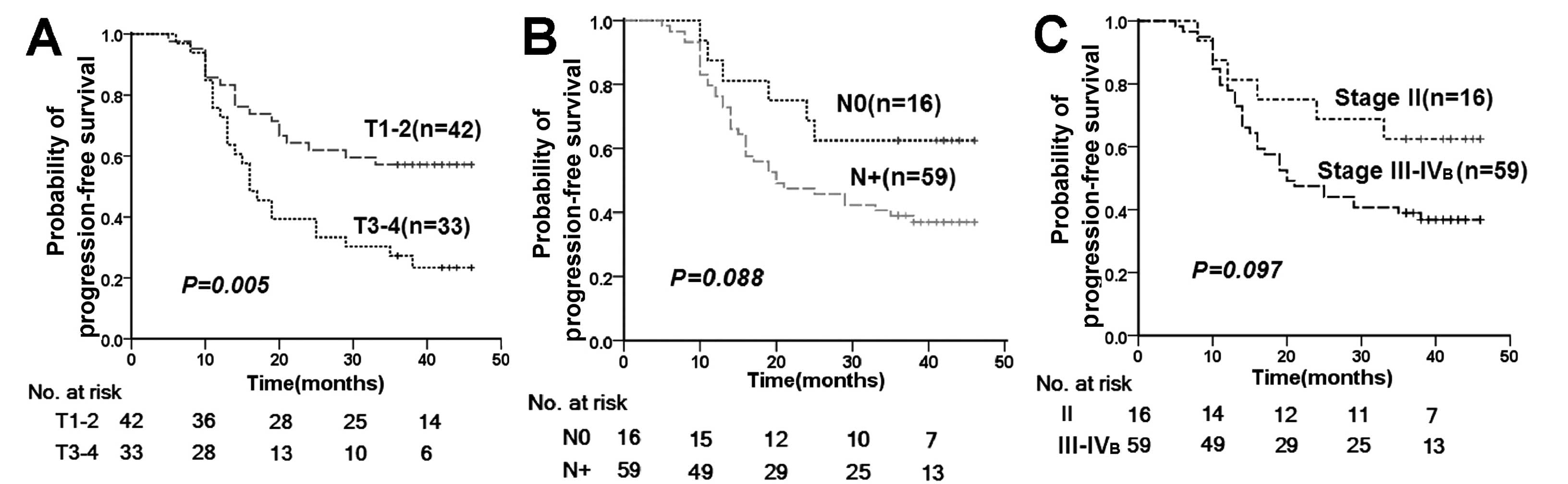
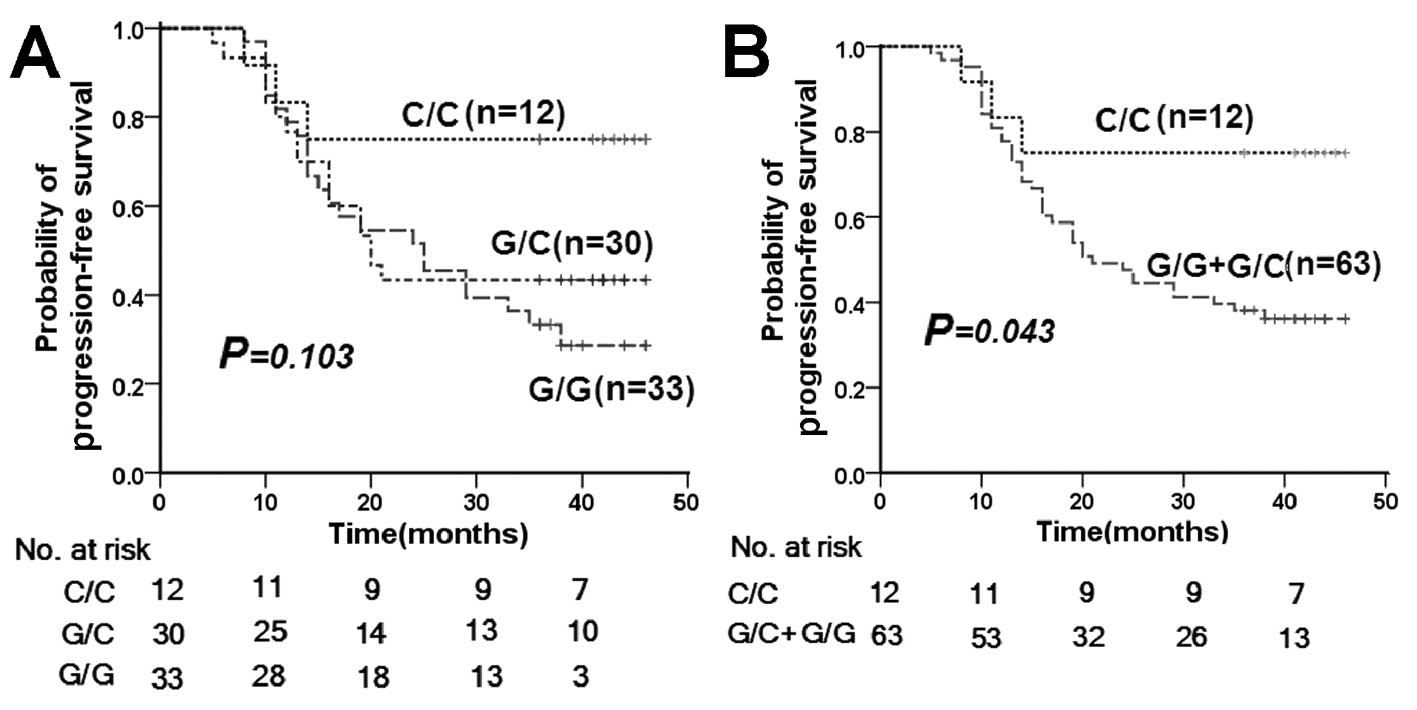
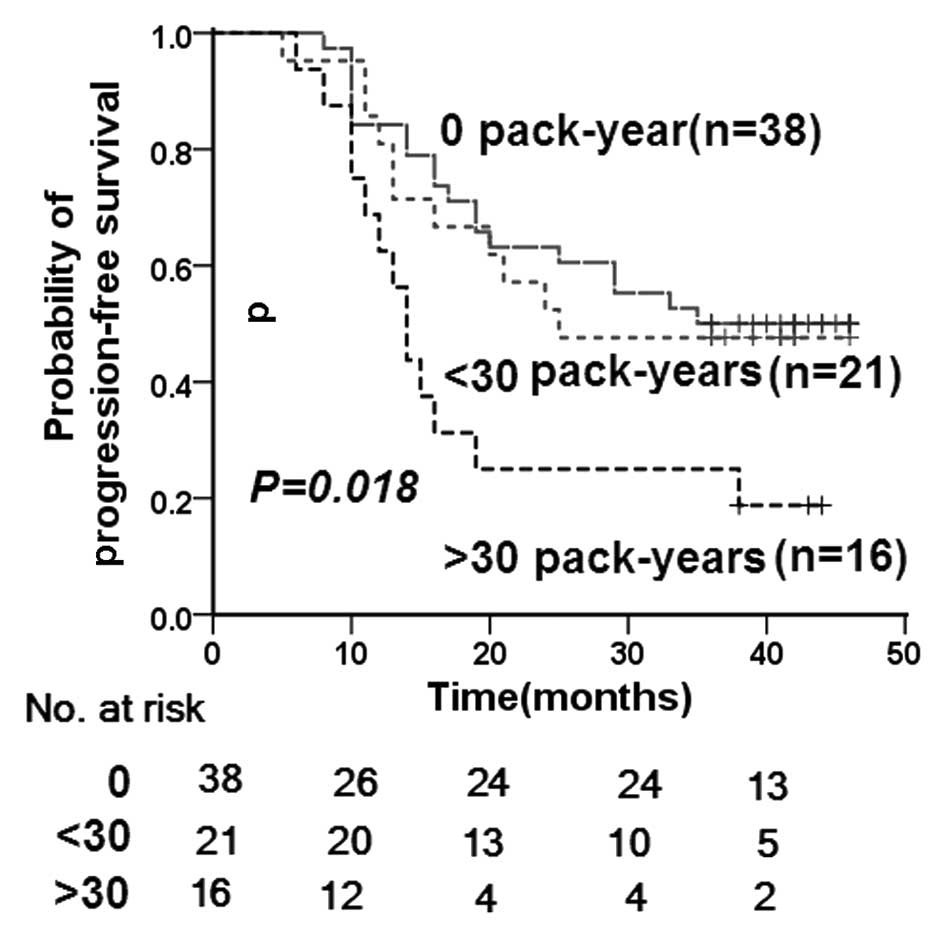
|
1
|
Buchman VL, Chumakov PM, Ninkina NN,
Samarina OP and Georgiev GP: A variation in the structure of the
protein-coding region of the human p53 gene. Gene. 70:245–252.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thomas M, Kalita A, Labrecque S, Pim D,
Banks L and Matlashewski G: Two polymorphic variants of wild-type
p53 differ biochemically and biologically. Mol Cell Biol.
19:1092–1100. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dumont P, Leu JI, Della Pietra AC III,
George DL and Murphy M: The codon 72 polymorphic variants of p53
have markedly different apoptotic potential. Nat Genet. 33:357–365.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sullivan A, Syed N, Gasco M, Bergamaschi
D, Trigiante G, Attard M, et al: Polymorphism in wild-type p53
modulates response to chemotherapy in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene.
23:3328–3337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pim D and Banks L: p53 polymorphic
variants at codon 72 exert different effects on cell cycle
progression. Int J Cancer. 108:196–199. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, Sullivan A,
Zvelebil M, Breyssens H, Bisso A, et al: iASPP preferentially binds
p53 proline-rich region and modulates apoptotic function of codon
72-polymorphic p53. Nat Genet. 38:1133–1141. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vannini I, Zoli W, Tesei A, Rosetti M,
Sansone P, Storci G, et al: Role of p53 codon 72 arginine allele in
cell survival in vitro and in the clinical outcome of patients with
advanced breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 29:145–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim JG, Sohn SK, Chae YS, Song HS, Kwon
KY, Do YR, et al: TP53 codon 72 polymorphism associated with
prognosis in patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with
paclitaxel and cisplatin. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 64:355–360.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bergamaschi D, Gasco M, Hiller L, Sullivan
A, Syed N, Trigiante G, et al: p53 polymorphism influences response
in cancer chemotherapy via modulation of p73-dependent apoptosis.
Cancer Cell. 3:387–402. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lo KW and Huang DP: Genetic and epigenetic
changes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 12:451–462.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhuo XL, Cai L, Xiang ZL, Zhuo WL, Wang Y
and Zhang XY: TP53 codon 72 polymorphism contributes to
nasopharyngeal cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Arch Med
Res. 40:299–305. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bond GL, Hu W, Bond EE, Robins H, Lutzker
SG, Arva NC, et al: A single nucleotide polymorphism in the MDM2
promoter attenuates the p53 tumor suppressor pathway and
accelerates tumor formation in humans. Cell. 119:591–602. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bond GL and Levine AJ: A single nucleotide
polymorphism in the p53 pathway interacts with gender,
environmental stresses and tumor genetics to influence cancer in
humans. Oncogene. 26:1317–1323. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hu Z, Jin G, Wang L, Chen F, Wang X and
Shen H: MDM2 promoter polymorphism SNP309 contributes to tumor
susceptibility: evidence from 21 case-control studies. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:2717–2723. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tu HF, Chen HW, Kao SY, Lin SC, Liu CJ and
Chang KW: MDM2 SNP 309 and p53 codon 72 polymorphisms are
associated with the outcome of oral carcinoma patients receiving
postoperative irradiation. Radiother Oncol. 87:243–252. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chaar I, Arfaoui TA, El Amine el HO,
Mahmoud LB, Khiari M, Sammoud S, et al: Impact of MDM2
polymorphism: increased risk of developing colorectal cancer and a
poor prognosis in the Tunisian population. Eur J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 24:320–327. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zawlik I, Kita D, Vaccarella S,
Mittelbronn M, Franceschi S and Ohgaki H: Common polymorphisms in
the MDM2 and TP53 genes and the relationship between TP53 mutations
and patient outcomes in glioblastomas. Brain Pathol. 19:188–194.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou G, Zhai Y, Cui Y, Zhang X, Dong X,
Yang H, et al: MDM2 promoter SNP309 is associated with risk of
occurrence and advanced lymph node metastasis of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma in Chinese population. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2627–2633.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sousa H, Pando M, Breda E, Catarino R and
Medeiros R: Role of the MDM2 SNP309 polymorphism in the initiation
and early age of onset of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Carcinog.
50:73–79. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brugarolas J, Chandrasekaran C, Gordon JI,
Beach D, Jacks T and Hannon GJ: Radiation-induced cell cycle arrest
compromised by p21 deficiency. Nature. 377:552–557. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Deng C, Zhang P, Harper JW, Elledge SJ and
Leder P: Mice lacking p21CIP1/WAF1 undergo normal
development, but are defective in G1 checkpoint control. Cell.
82:675–684. 1995.
|
|
22
|
Macleod KF, Sherry N, Hannon G, Beach D,
Tokino T, Kinzler K, et al: p53-dependent and independent
expression of p21 during cell growth, differentiation, and DNA
damage. Genes Dev. 9:935–944. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Abbas T and Dutta A: p21 in cancer:
intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:400–414. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Birgander R, Själander A, Saha N, Spitsyn
V, Beckman L and Beckman G: The codon 31 polymorphism of the
p53-inducible gene p21 shows distinct differences between major
ethnic groups. Hum Hered. 46:148–154. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Su L, Sai Y, Fan R, Thurston SW, Miller
DP, Zhou W, et al: P53 (codon 72) and P21 (codon 31) polymorphisms
alter in vivo mRNA expression of p21. Lung Cancer. 40:259–266.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Johnson GG, Sherrington PD, Carter A, Lin
K, Liloglou T, Field JK and Pettitt AR: A novel type of p53 pathway
dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia resulting from two
interacting single nucleotide polymorphisms within the p21 gene.
Cancer Res. 69:5210–5217. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tan XL, Popanda O, Ambrosone CB, Kropp S,
Helmbold I, von Fournier D, et al: Association between TP53 and p21
genetic polymorphisms and acute side effects of radiotherapy in
breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 97:255–262. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsai MH, Chen WC and Tsai FJ: Correlation
of p21 gene codon 31 polymorphism and TNF-alpha gene polymorphism
with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Clin Lab Anal. 16:146–150. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Marin MC, Jost CA, Brooks LA, Irwin MS,
O’Nions J, Tidy JA, et al: A common polymorphism acts as an
intragenic modifier of mutant p53 behaviour. Nat Genet. 25:47–54.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alhopuro P, Ylisaukko-Oja SK, Koskinen WJ,
Bono P, Arola J, Järvinen HJ, et al: The MDM2 promoter polymorphism
SNP309T→G and the risk of uterine leiomyosarcoma, colorectal
cancer, and squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Med
Genet. 42:694–698. 2005.
|
|
31
|
Giordana MT, Duo D, Gasverde S, Trevisan
E, Boghi A, Morra I, et al: MDM2 overexpression is associated with
short survival in adults with medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol.
4:115–122. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Haitel A, Wiener HG, Baethge U, Marberger
M and Susani M: Mdm2 expression as a prognostic indicator in clear
cell renal cell carcinoma: comparison with p53 overexpression and
clinic pathological parameters. Clin Cancer Res. 6:1840–1844.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Polsky D, Melzer K, Hazan C, Panageas KS,
Busam K, Drobnjak M, et al: HDM2 protein overexpression and
prognosis in primary malignant melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst.
94:1803–1806. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ranuncolo SM, Varela M, Morandi A, Lastiri
J, Christiansen S, Bal de Kier Joffé E, et al: Prognostic value of
Mdm2, p53 and p16 in patients with astrocytomas. J Neurooncol.
68:113–121. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hoff CM, Grau C and Overgaard J: Effect of
smoking on oxygen delivery and outcome in patients treated with
radiotherapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma - a
prospective study. Radiother Oncol. 103:38–44. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|