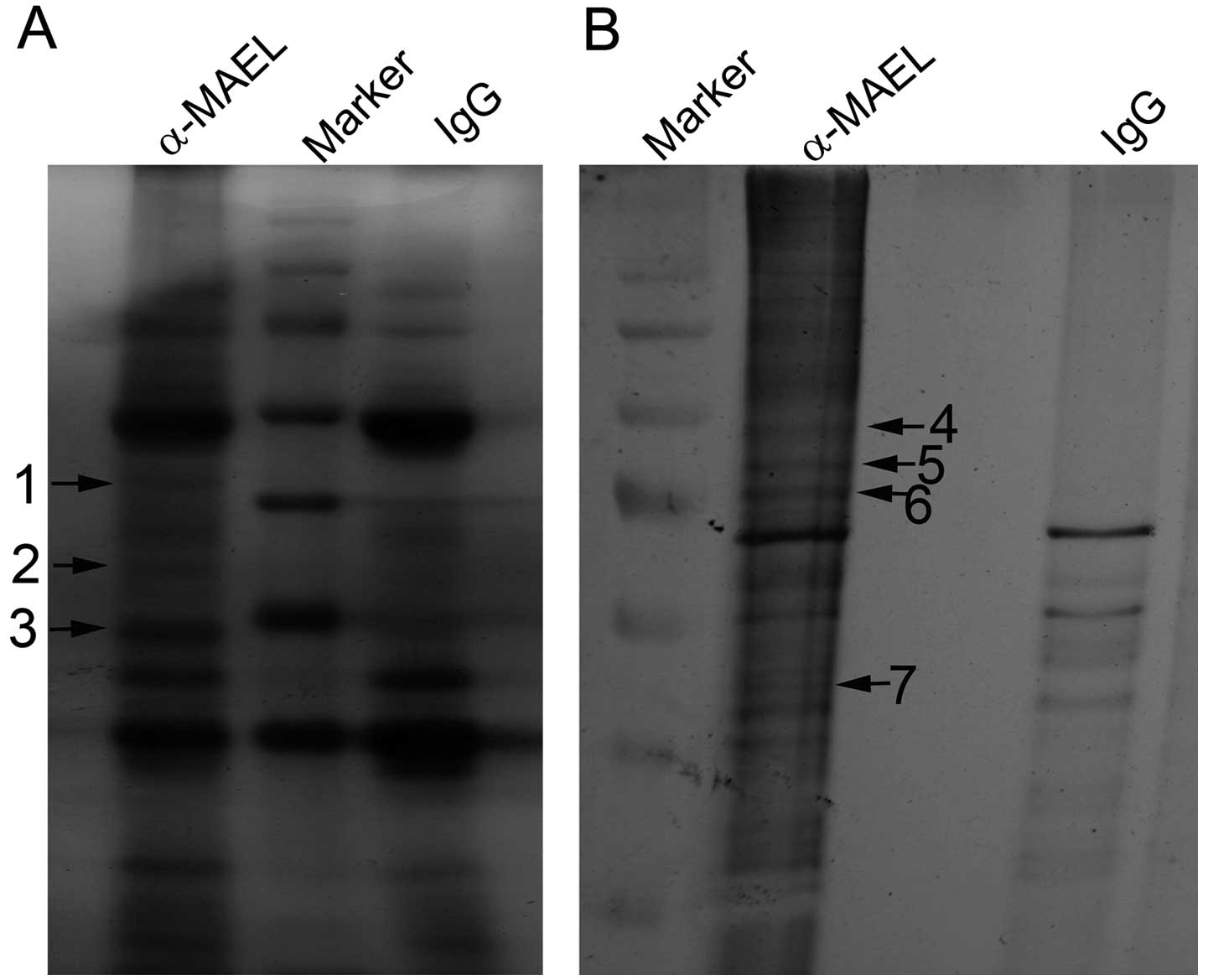
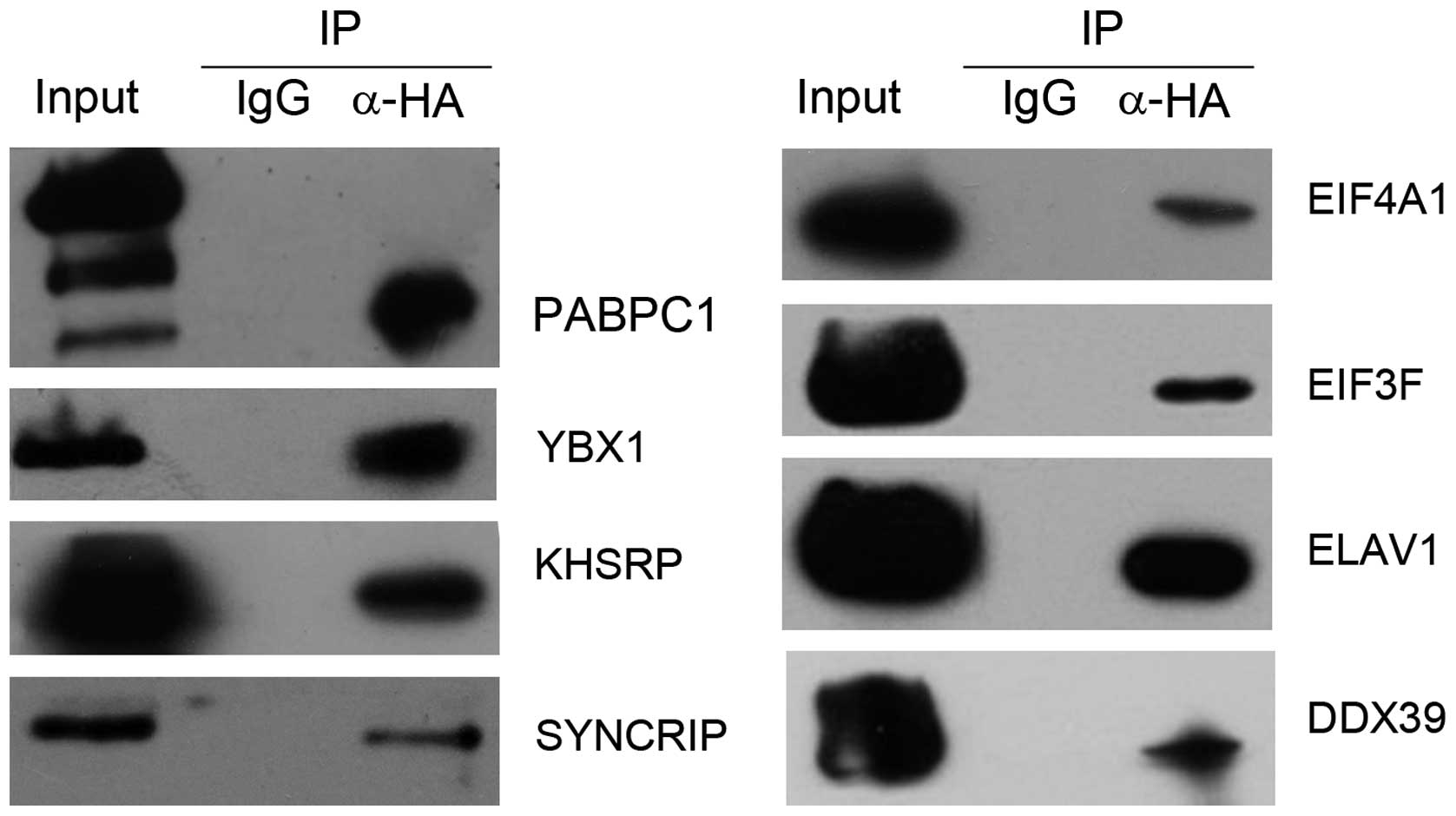
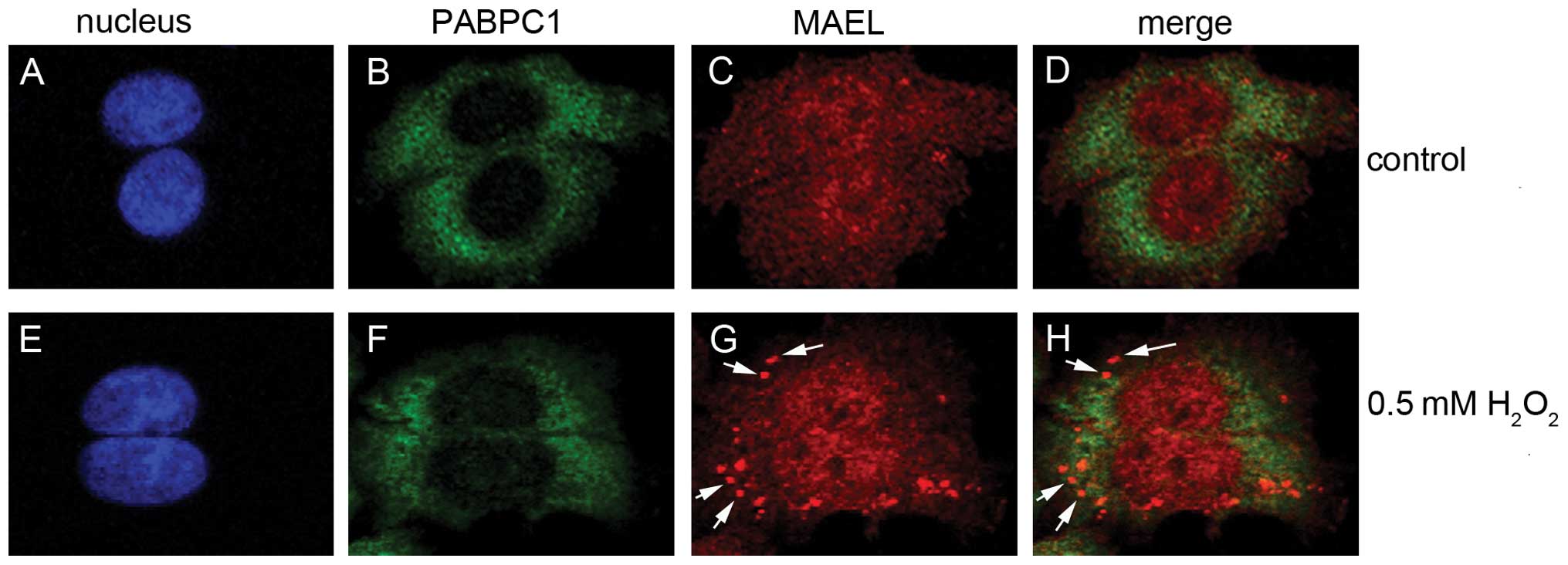
|
1
|
Clegg NJ, Frost DM, Larkin MK,
Subrahmanyan L, Bryant Z and Ruohola-Baker H: maelstrom is
required for an early step in the establishment of
Drosophila oocyte polarity: posterior localization of
grk mRNA. Development. 124:4661–4671. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Clegg NJ, Findley SD, Mahowald AP and
Ruohola-Baker H: Maelstrom is required to position the MTOC in
stage 2–6 Drosophila oocytes. Dev Genes Evol. 211:44–48.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Findley SD, Tamanaha M, Clegg NJ and
Ruohola-Baker H: Maelstrom, a Drosophila
spindle-class gene, encodes a protein that colocalizes with
Vasa and RDE1/AGO1 homolog, Aubergine, in nuage. Development.
130:859–871. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Pek JW, Patil VS and Kai T: piRNA pathway
and the potential processing site, the nuage, in the
Drosophila germline. Dev Growth Differ. 54:66–77. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lim AK and Kai T: Unique germ-line
organelle, nuage, functions to repress selfish genetic elements in
Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:6714–6719. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Costa Y, Speed RM, Gautier P, et al: Mouse
MAELSTROM: the link between meiotic silencing of unsynapsed
chromatin and microRNA pathway? Hum Mol Genet. 15:2324–2334. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Soper SF, van der Heijden GW, Hardiman TC,
et al: Mouse maelstrom, a component of nuage, is essential for
spermatogenesis and transposon repression in meiosis. Dev Cell.
15:285–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aravin AA, van der Heijden GW, Castaneda
J, Vagin VV, Hannon GJ and Bortvin A: Cytoplasmic
compartmentalization of the fetal piRNA pathway in mice. PLoS
Genet. 5:e10007642009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yokota S: Nuage proteins: their
localization in subcellular structures of spermatogenic cells as
revealed by immunoelectron microscopy. Histochem Cell Biol.
138:1–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Takebe M, Onohara Y and Yokota S:
Expression of MAEL in nuage and non-nuage compartments of rat
spermatogenic cells and colocalization with DDX4, DDX25 and MIWI.
Histochem Cell Biol. 140:169–181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pek JW, Lim AK and Kai T:
Drosophila maelstrom ensures proper germline stem cell
lineage differentiation by repressing microRNA-7. Dev Cell.
17:417–424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xiao L, Wang Y, Zhou Y, et al:
Identification of a novel human cancer/testis gene MAEL that is
regulated by DNA methylation. Mol Biol Rep. 37:2355–2360. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Janic A, Mendizabal L, Llamazares S,
Rossell D and Gonzalez C: Ectopic expression of germline genes
drives malignant brain tumor growth in Drosophila. Science.
330:1824–1827. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hofmann O, Caballero OL, Stevenson BJ, et
al: Genome-wide analysis of cancer/testis gene expression. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:20422–20427. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De Smet C and Loriot A: DNA
hypomethylation and activation of germline-specific genes in
cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 754:149–166. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim R, Kulkarni P and Hannenhalli S:
Derepression of cancer/testis antigens in cancer is associated with
distinct patterns of DNA hypomethylation. BMC Cancer. 13:1442013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim YH, Lee HC, Kim SY, et al: Epigenomic
analysis of aberrantly methylated genes in colorectal cancer
identifies genes commonly affected by epigenetic alterations. Ann
Surg Oncol. 18:2338–2347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Landthaler M, Gaidatzis D, Rothballer A,
et al: Molecular characterization of human Argonaute-containing
ribonucleoprotein complexes and their bound target mRNAs. RNA.
14:2580–2596. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lin Z, Crockett DK, Lim MS and
Elenitoba-Johnson KS: High-throughput analysis of protein/peptide
complexes by immunoprecipitation and automated LC-MS/MS. J Biomol
Tech. 14:149–155. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Keller A, Eng J, Zhang N, Li XJ and
Aebersold R: A uniform proteomics MS/MS analysis platform utilizing
open XML file formats. Mol Syst Biol. 1:2005.0017. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Keller A, Nesvizhskii AI, Kolker E and
Aebersold R: Empirical statistical model to estimate the accuracy
of peptide identifications made by MS/MS and database search. Anal
Chem. 74:5383–5392. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nesvizhskii AI, Keller A, Kolker E and
Aebersold R: A statistical model for identifying proteins by tandem
mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 75:4646–4658. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou J, Qiao X, Xiao L, et al:
Identification and characterization of the novel protein CCDC106
that interacts with p53 and promotes its degradation. FEBS Lett.
584:1085–1090. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kedersha N, Stoecklin G, Ayodele M, et al:
Stress granules and processing bodies are dynamically linked sites
of mRNP remodeling. J Cell Biol. 169:871–884. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rothe F, Gueydan C, Bellefroid E, Huez G
and Kruys V: Identification of FUSE-binding proteins as interacting
partners of TIA proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 343:57–68.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Onishi H, Kino Y, Morita T, Futai E,
Sasagawa N and Ishiura S: MBNL1 associates with YB-1 in cytoplasmic
stress granules. J Neurosci Res. 86:1994–2002. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Quaresma AJ, Bressan GC, Gava LM, Lanza
DC, Ramos CH and Kobarg J: Human hnRNP Q re-localizes to
cytoplasmic granules upon PMA, thapsigargin, arsenite and
heat-shock treatments. Exp Cell Res. 315:968–980. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wen F, Zhou R, Shen A, Choi A, Uribe D and
Shi J: The tumor suppressive role of eIF3f and its function in
translation inhibition and rRNA degradation. PLoS One.
7:e341942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wolf A, Krause-Gruszczynska M, Birkenmeier
O, Ostareck-Lederer A, Huttelmaier S and Hatzfeld M: Plakophilin 1
stimulates translation by promoting eIF4A1 activity. J Cell Biol.
188:463–471. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Buchan JR, Yoon JH and Parker R:
Stress-specific composition, assembly and kinetics of stress
granules in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci.
124:228–239. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gallouzi IE, Brennan CM, Stenberg MG, et
al: HuR binding to cytoplasmic mRNA is perturbed by heat shock.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:3073–3078. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guil S, Long JC and Caceres JF: hnRNP A1
relocalization to the stress granules reflects a role in the stress
response. Mol Cell Biol. 26:5744–5758. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim HJ, Kim NC, Wang YD, et al: Mutations
in prion-like domains in hnRNPA2B1 and hnRNPA1 cause multisystem
proteinopathy and ALS. Nature. 495:467–473. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shih JW, Wang WT, Tsai TY, Kuo CY, Li HK
and Wu Lee YH: Critical roles of RNA helicase DDX3 and its
interactions with eIF4E/PABP1 in stress granule assembly and stress
response. Biochem J. 441:119–129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Goodier JL, Zhang L, Vetter MR and
Kazazian HH Jr: LINE-1 ORF1 protein localizes in stress granules
with other RNA-binding proteins, including components of RNA
interference RNA-induced silencing complex. Mol Cell Biol.
27:6469–6483. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wippich F, Bodenmiller B, Trajkovska MG,
Wanka S, Aebersold R and Pelkmans L: Dual specificity kinase DYRK3
couples stress granule condensation/dissolution to mTORC1
signaling. Cell. 152:791–805. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Anderson P and Kedersha N: Stress
granules: the Tao of RNA triage. Trends Biochem Sci. 33:141–150.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Decker CJ and Parker R: P-bodies and
stress granules: possible roles in the control of translation and
mRNA degradation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:a0122862012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Anderson P and Kedersha N: RNA granules:
post-transcriptional and epigenetic modulators of gene expression.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:430–436. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gjerstorff MF, Rosner HI, Pedersen CB, et
al: GAGE cancer-germline antigens are recruited to the nuclear
envelope by germ cell-less (GCL). PLoS One. 7:e458192012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Simpson AJ, Caballero OL, Jungbluth A,
Chen YT and Old LJ: Cancer/testis antigens, gametogenesis and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:615–625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Costa FF, Le Blanc K and Brodin B: Concise
review: cancer/testis antigens, stem cells, and cancer. Stem Cells.
25:707–711. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yamada R, Takahashi A, Torigoe T, et al:
Preferential expression of cancer/testis genes in cancer stem-like
cells: proposal of a novel sub-category, cancer/testis/stem gene.
Tissue Antigens. 81:428–434. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bahena I, Xu E, Betancourt M, et al: Role
of Mael in early oogenesis and during germ-cell
differentiation from embryonic stem cells in mice in vitro.
Zygote. 1–8. 2013.[Epub ahead of print].
|