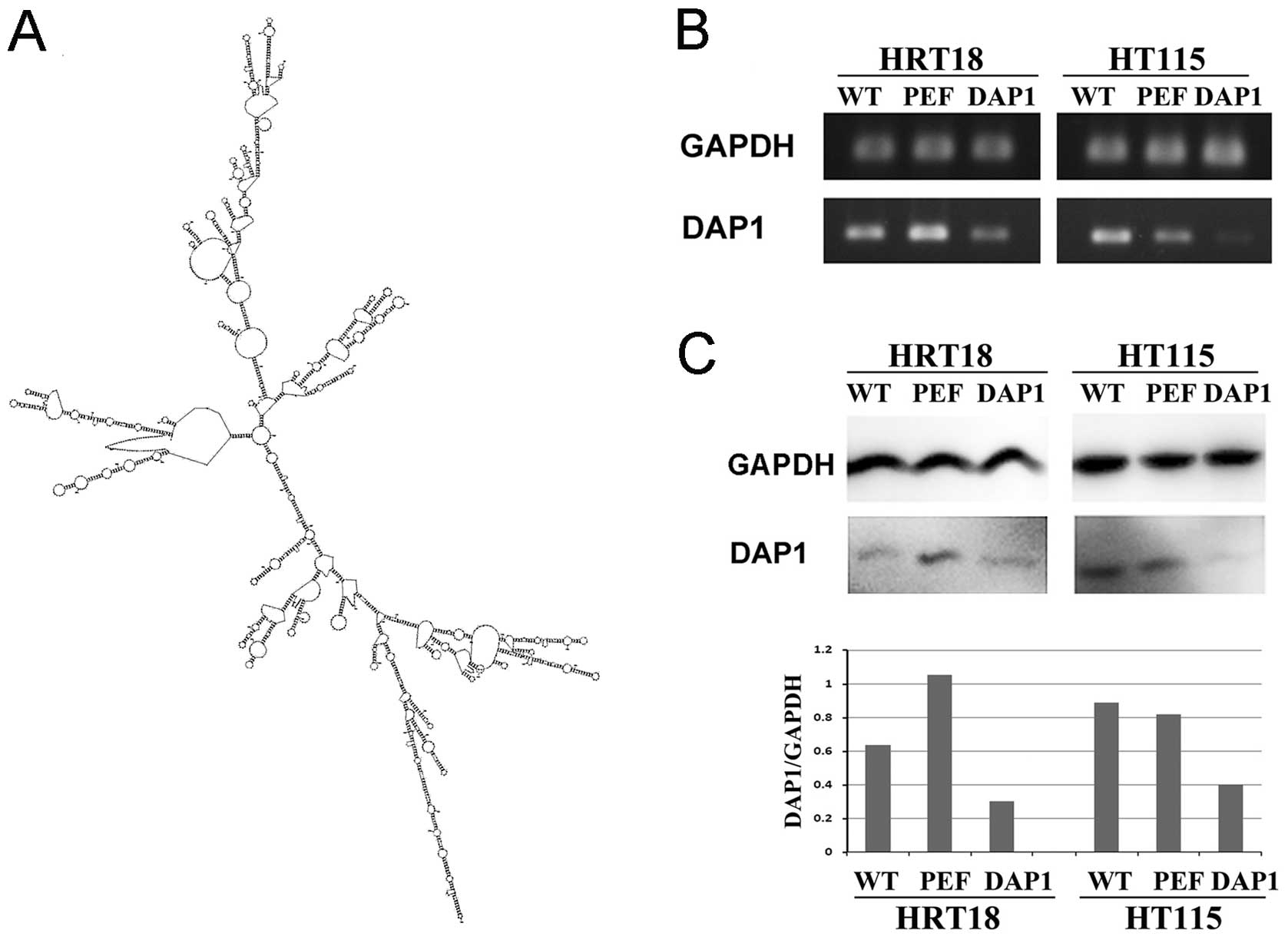
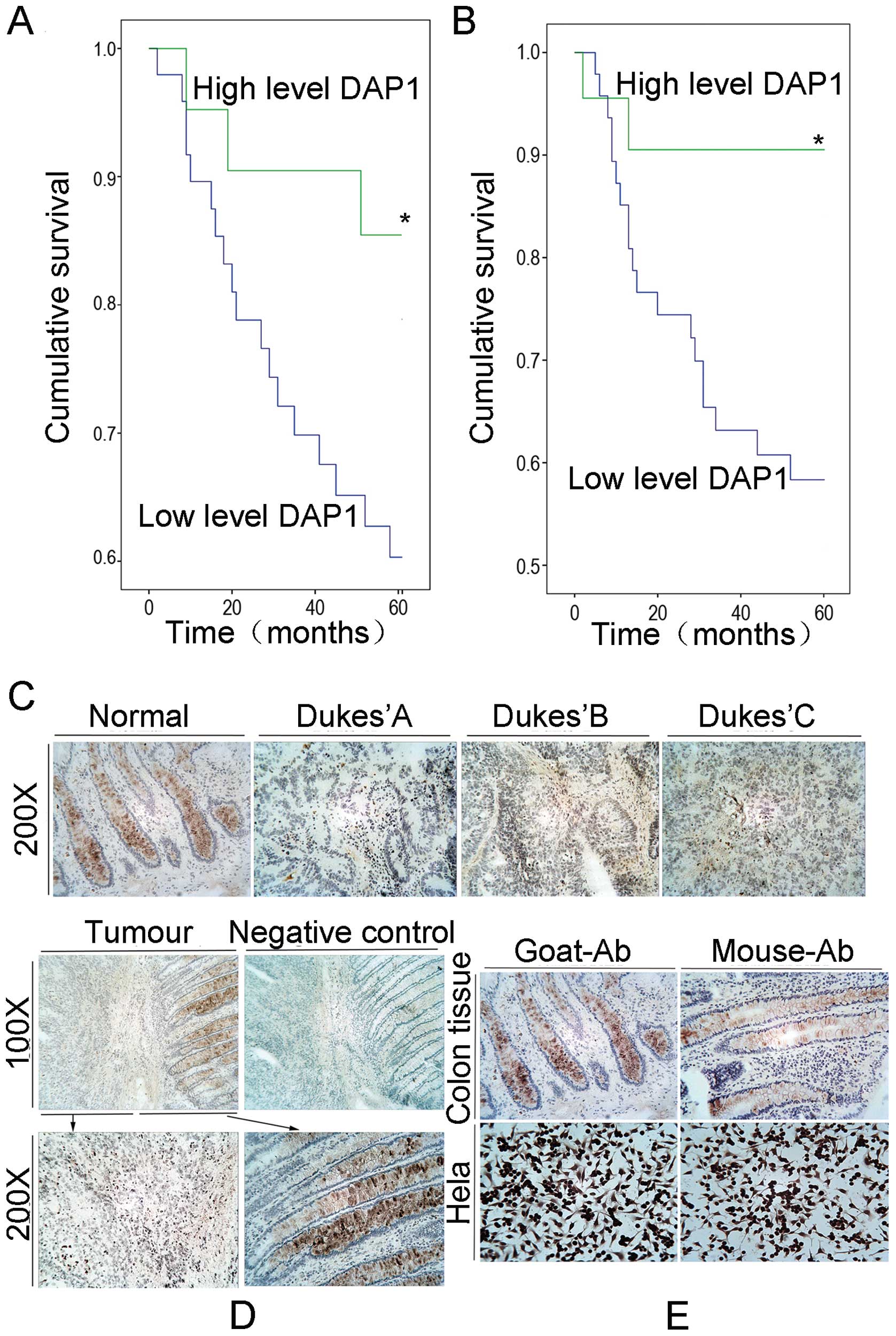
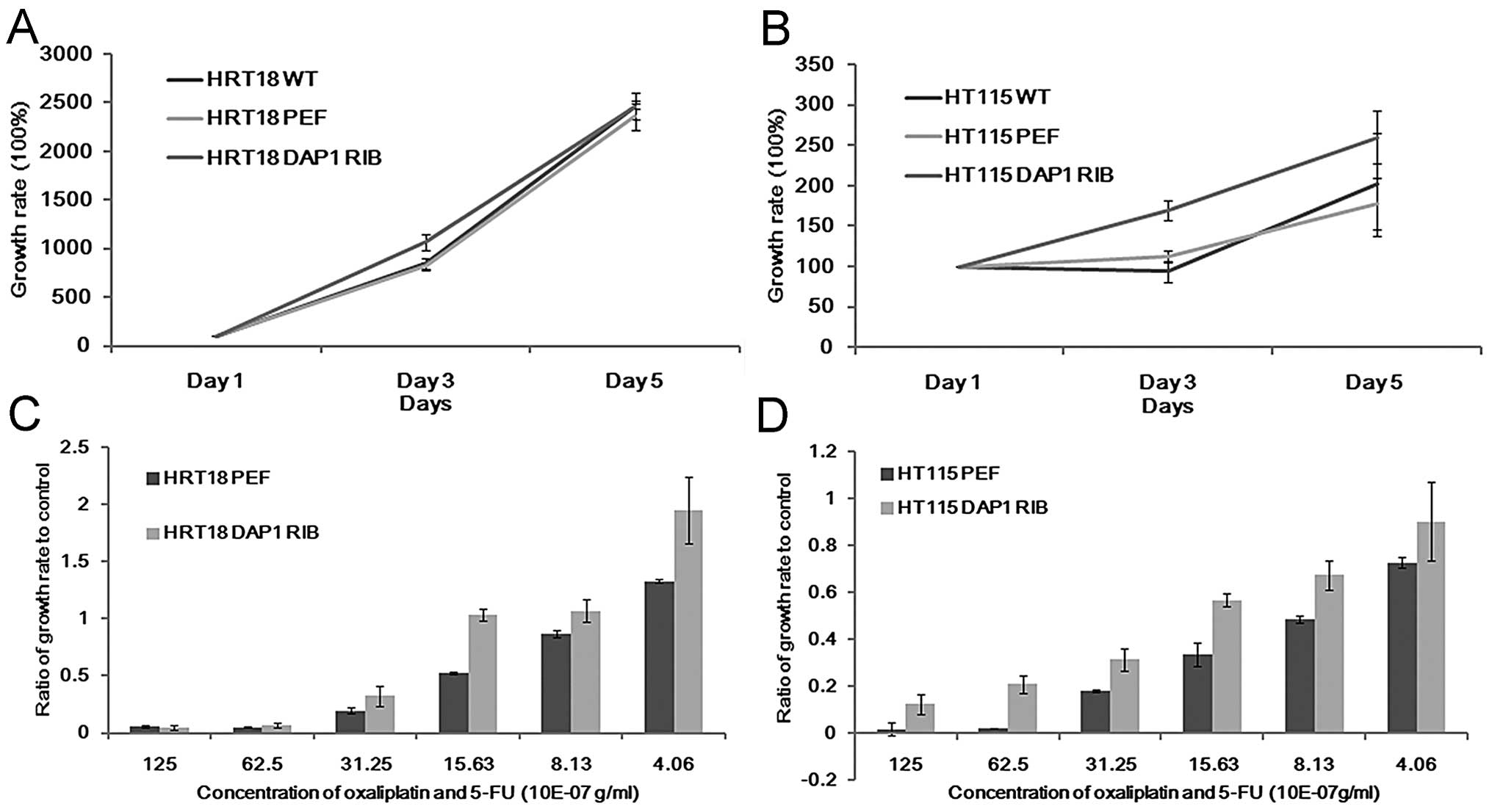
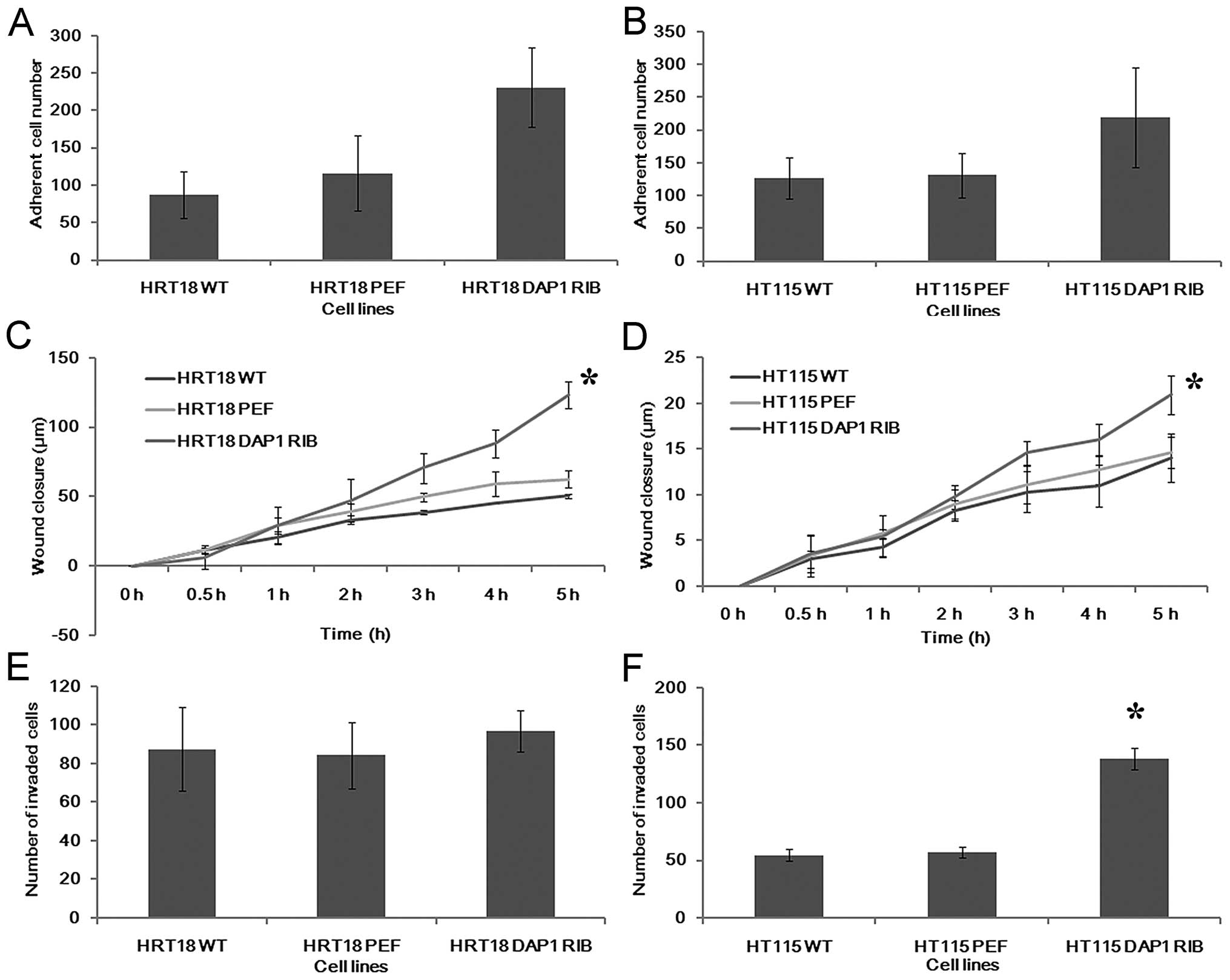
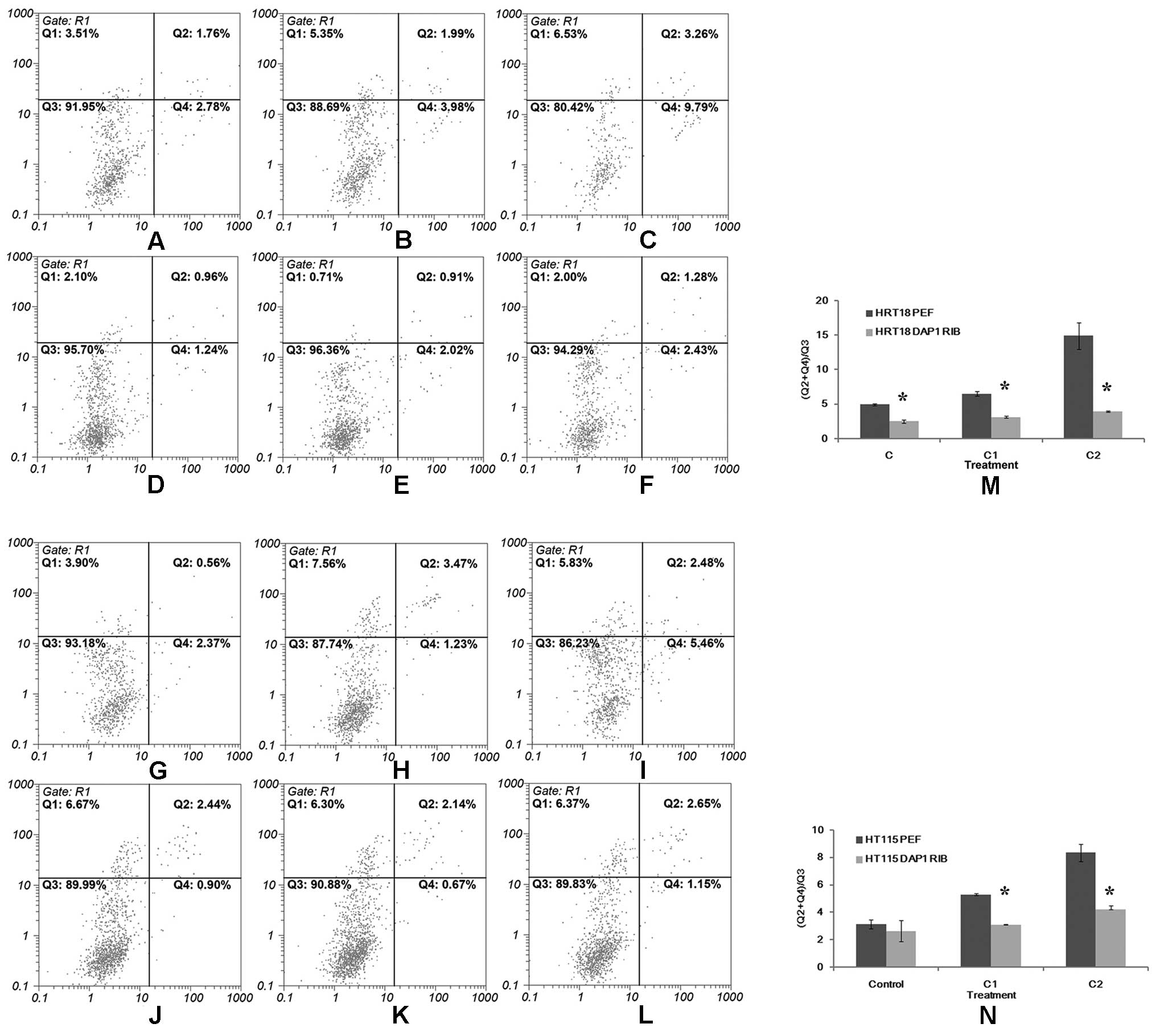
|
1
|
Inbal B, Shani G, Cohen O, Kissil JL and
Kimchi A: Death-associated protein kinase-related protein 1, a
novel serine/threonine kinase involved in apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol.
20:1044–1054. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cohen O, Inbal B, Kissil JL, et al:
DAP-kinase participates in TNF-α- and Fas-induced apoptosis and its
function requires the death domain. J Cell Biol. 146:141–148.
1999.
|
|
3
|
Inbal B, Cohen O, Polak-Charcon S, et al:
DAP kinase links the control of apoptosis to metastasis. Nature.
390:180–184. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lehmann U, Celikkaya G, Hasemeier B,
Länger F and Kreipe H: Promoter hypermethylation of the
death-associated protein kinase gene in breast cancer is
associated with the invasive lobular subtype. Cancer Res.
62:6634–6638. 2002.
|
|
5
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Korsmeyer SJ, Wei MC, Saito M, Weiler S,
Oh KJ and Schlesinger PH: Pro-apoptotic cascade activates BID,
which oligomerizes BAK or BAX into pores that result in the release
of cytochrome c. Cell Death Differ. 7:1166–1173. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kroemer G and Reed JC: Mitochondrial
control of cell death. Nat Med. 6:513–519. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Martinou JC and Green DR: Breaking the
mitochondrial barrier. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:63–67. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sugita H, Iida S, Inokuchi M, et al:
Methylation of BNIP3 and DAPK indicates lower
response to chemotherapy and poor prognosis in gastric cancer.
Oncol Rep. 25:513–518. 2011.
|
|
10
|
Jiang WG, Watkins G, Lane J, et al:
Prognostic value of rho GTPases and rho guanine nucleotide
dissociation inhibitors in human breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res.
9:6432–6440. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nazarenko IA, Bhatnagar SK and Hohman RJ:
A closed tube format for amplification and detection of DNA based
on energy transfer. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:2516–2521. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zuker M: Mfold web server for nucleic acid
folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res.
31:3406–3415. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang WG, Hiscox S, Hallett MB, Scott C,
Horrobin DF and Puntis MC: Inhibition of hepatocyte growth
factor-induced motility and in vitro invasion of human colon cancer
cells by gamma-linolenic acid. Br J Cancer. 71:744–752. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang WG, Hiscox SE, Parr C, et al:
Antagonistic effect of NK4, a novel hepatocyte growth factor
variant, on in vitro angiogenesis of human vascular endothelial
cells. Clin Cancer Res. 5:3695–3703. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ye L, Kynaston H and Jiang WG: Bone
morphogenetic protein-9 induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells,
the role of prostate apoptosis response-4. Mol Cancer Res.
6:1594–1606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kissil JL, Feinstein E, Cohen O, et al:
DAP-kinase loss of expression in various carcinoma and B-cell
lymphoma cell lines: possible implications for role as tumor
suppressor gene. Oncogene. 15:403–407. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Esteller M, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Rosell R,
Sidransky D, Baylin SB and Herman JG: Detection of aberrant
promoter hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes in serum DNA
from non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Res. 59:67–70.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sanchez-Cespedes M, Esteller M, Wu L, et
al: Gene promoter hypermethylation in tumors and serum of head and
neck cancer patients. Cancer Res. 60:892–895. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sasaki H, Ide N, Yukiue H, et al: Arg and
DAP3 expression was correlated with human thymoma stage. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 21:507–513. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jacques C, Fontaine JF, Franc B, et al:
Death-associated protein 3 is overexpressed in human thyroid
oncocytic tumours. Br J Cancer. 101:132–138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Suzuki T, Terasaki M, Takemoto-Hori C, et
al: Proteomic analysis of the mammalian mitochondrial ribosome.
Identification of protein components in the 28 S small subunit. J
Biol Chem. 276:33181–33195. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cavdar Koc E, Burkhart W, Blackburn K,
Moseley A and Spremulli LL: The small subunit of the mammalian
mitochondrial ribosome. Identification of the full complement of
ribosomal proteins present. J Biol Chem. 276:19363–19374.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z and Gerstein M: Identification and
characterization of over 100 mitochondrial ribosomal protein
pseudogenes in the human genome. Genomics. 81:468–480. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mukamel Z and Kimchi A: Death-associated
protein 3 localizes to the mitochondria and is involved in the
process of mitochondrial fragmentation during cell death. J Biol
Chem. 279:36732–36738. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cavdar Koc E, Ranasinghe A, Burkhart W, et
al: A new face on apoptosis: death-associated protein 3 and PDCD9
are mitochondrial ribosomal proteins. FEBS Lett. 492:166–170.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|