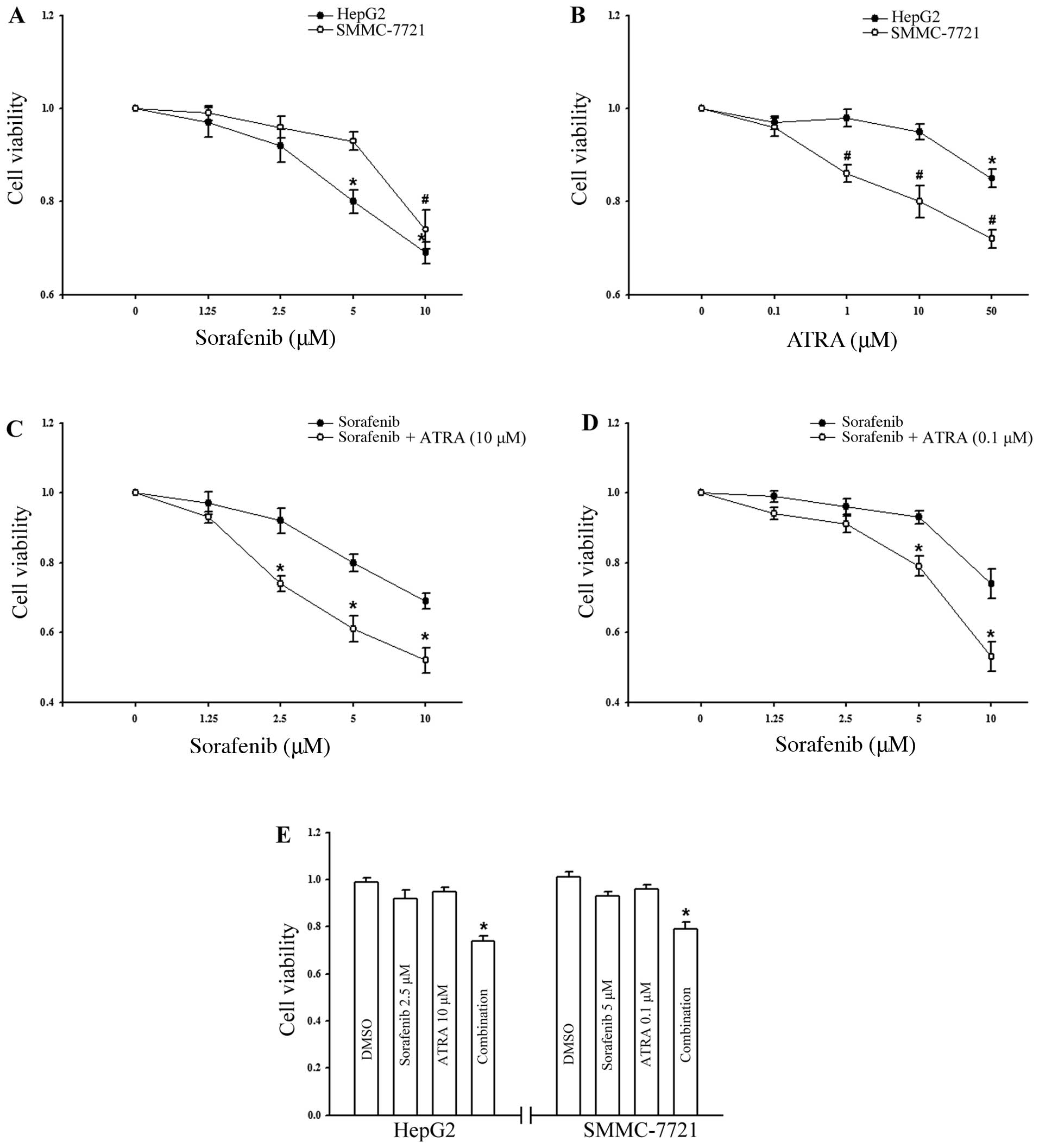
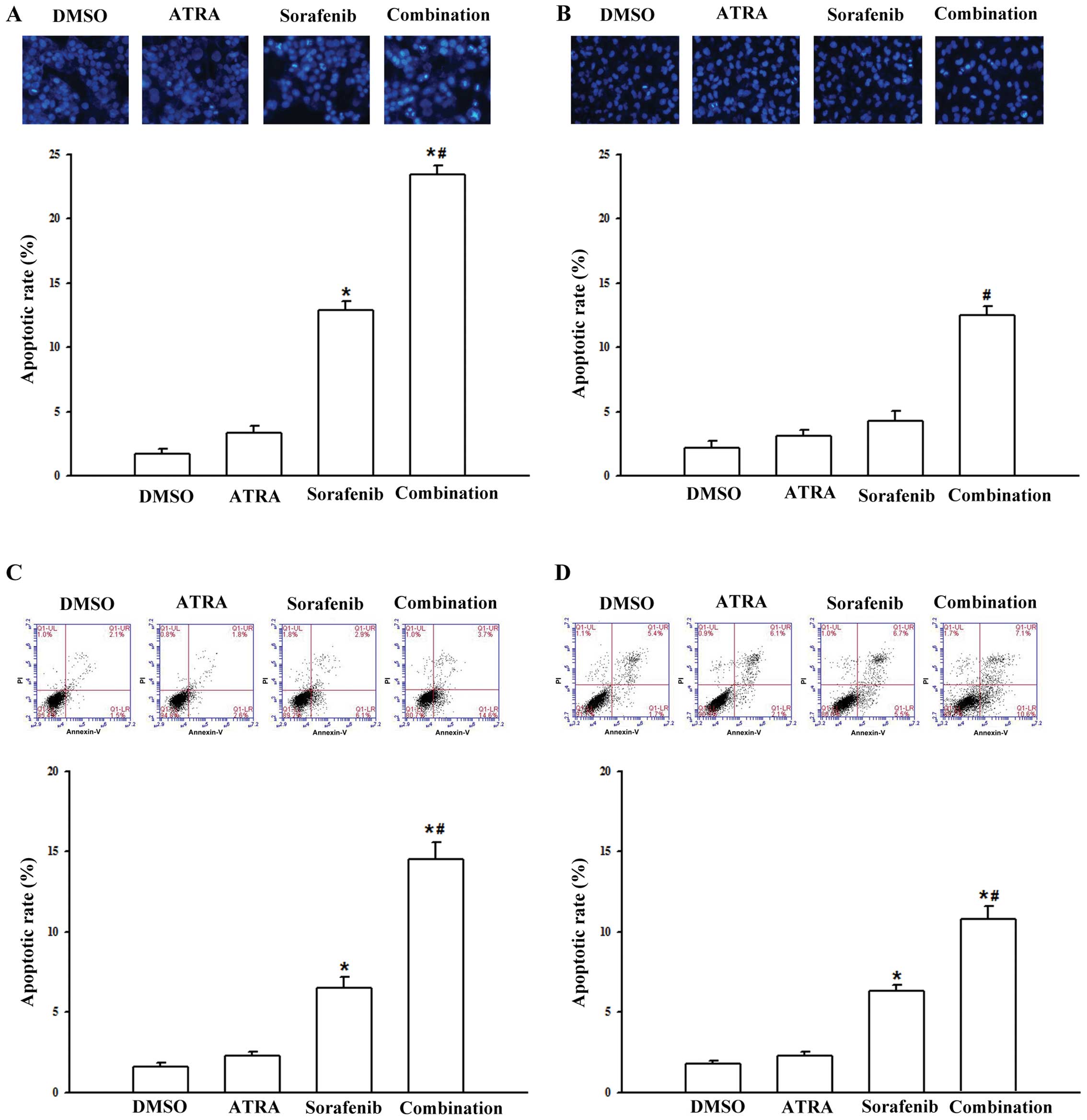
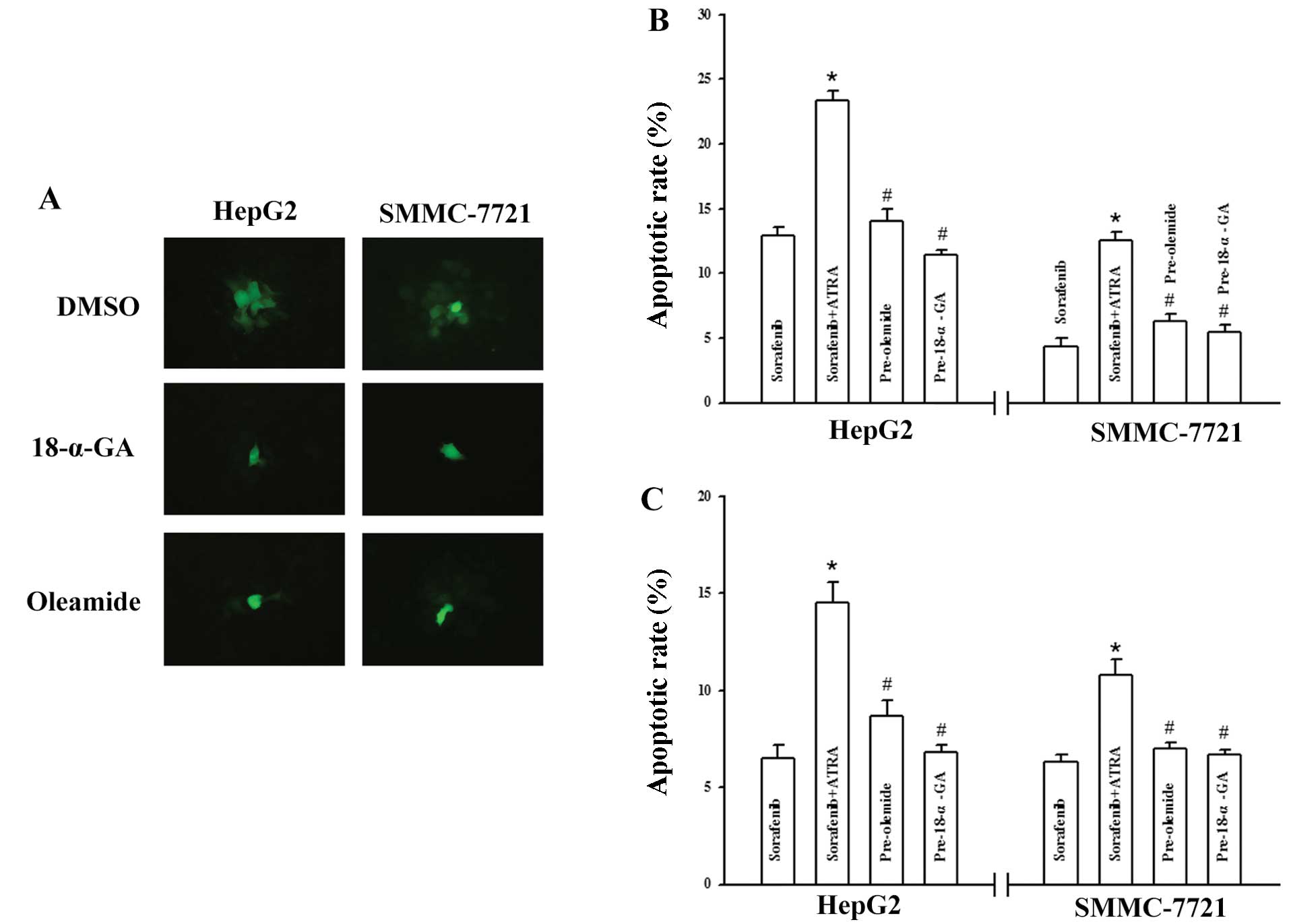
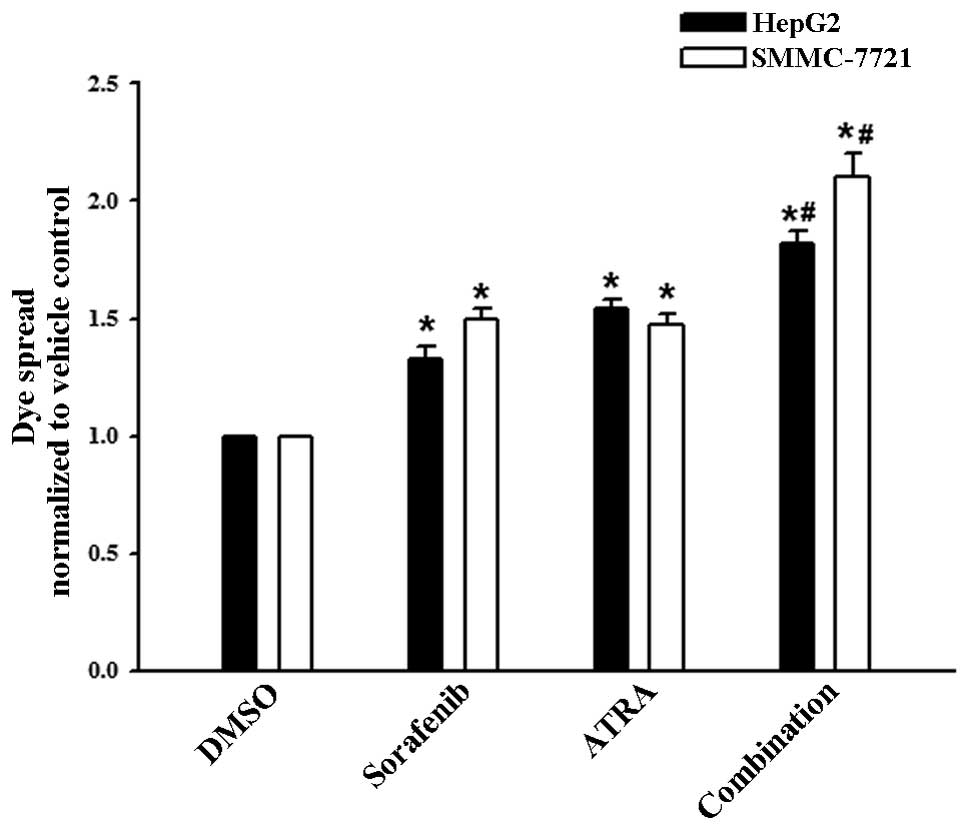
|
1
|
Verslype C, Rosmorduc O and Rougier P:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO-ESDO Clinical Practice Guidelines
for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 23(Suppl 7):
vii41–vii48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, et al: BAY
43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets
the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in
tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 64:7099–7109. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, et al: Sorafenib
blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and
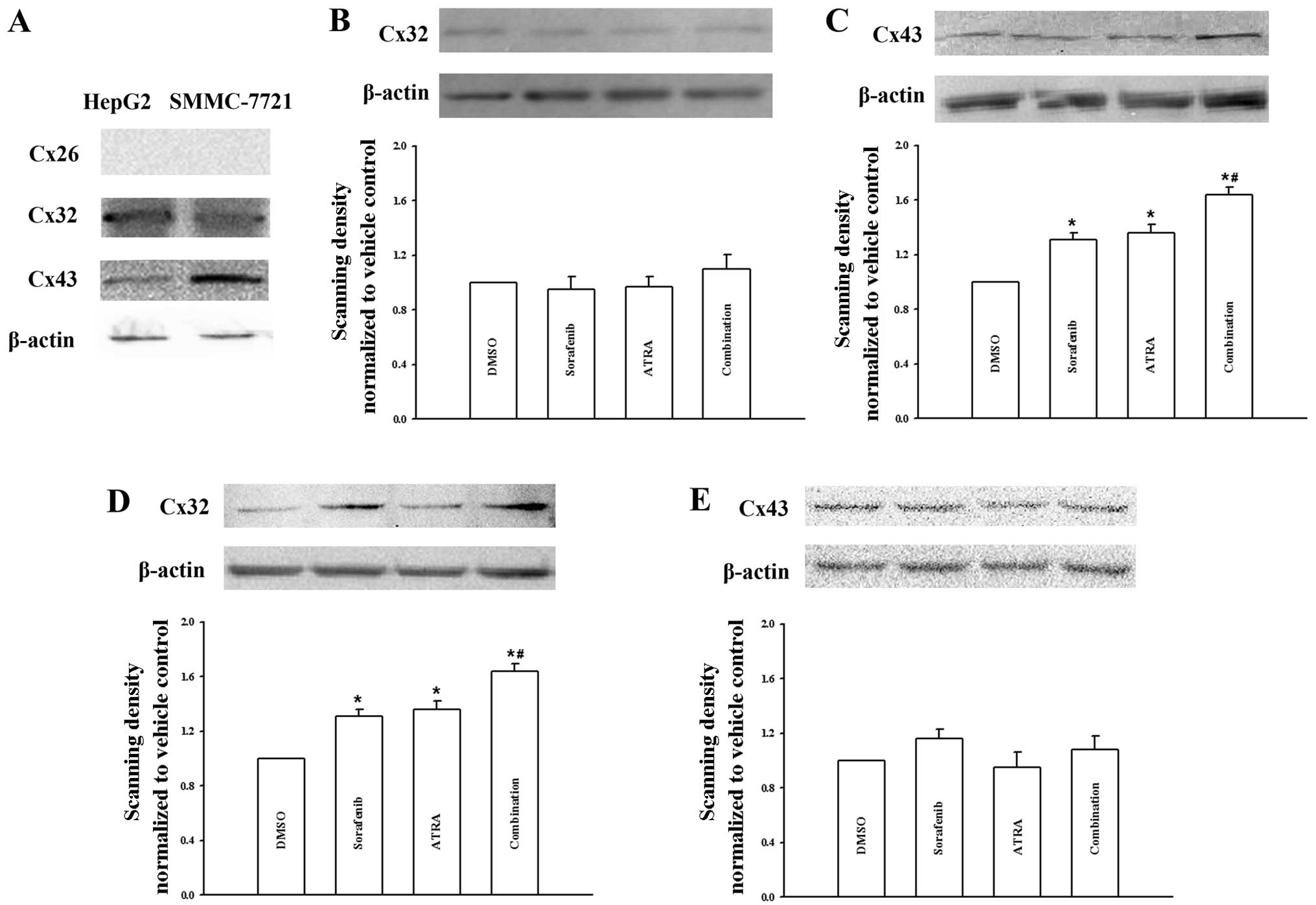
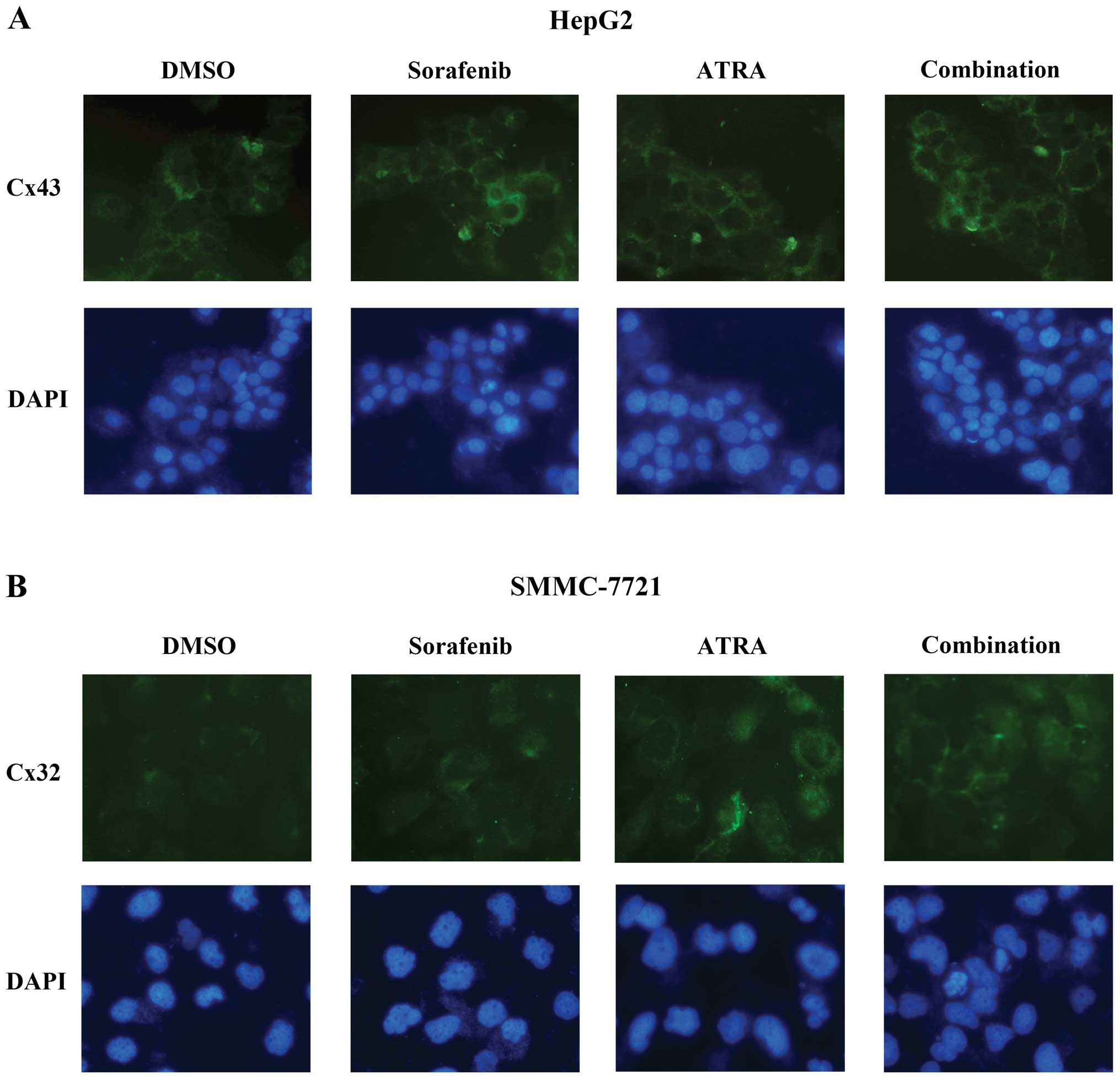
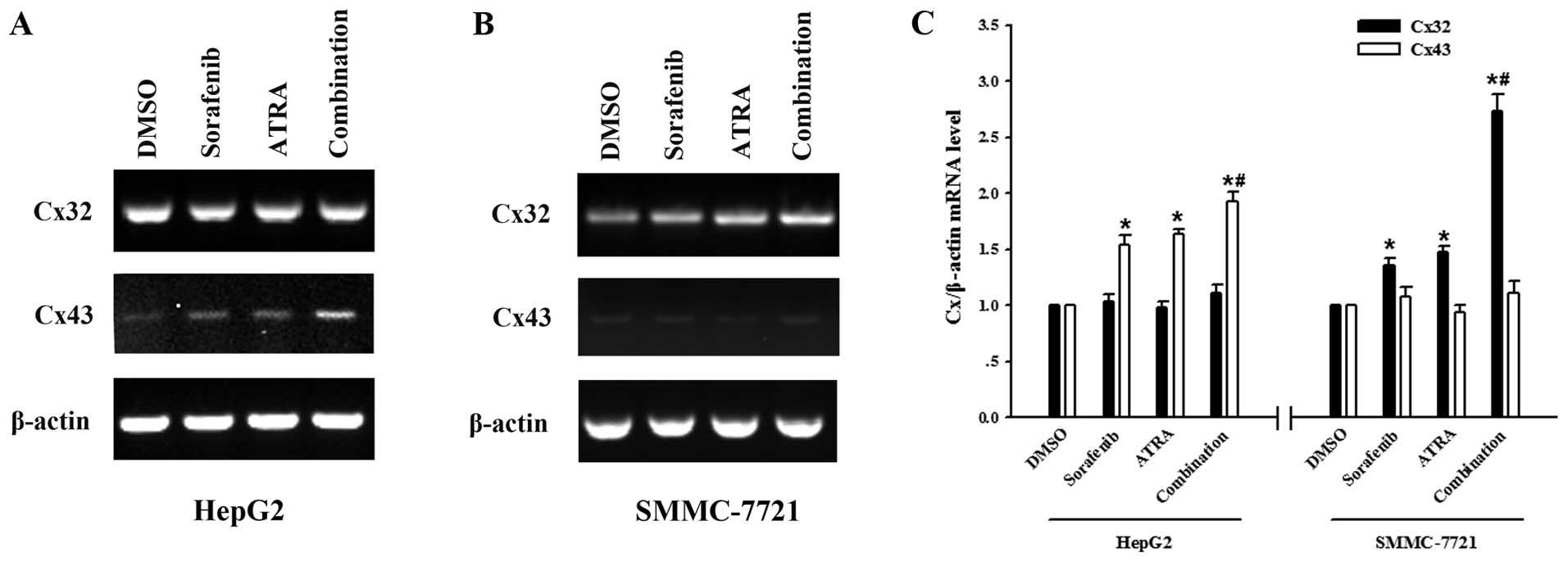
induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model
PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res. 66:11851–11858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao X, Tian C, Puszyk WM, et al: OPA1
downregulation is involved in sorafenib-induced apoptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Lab Invest. 93:8–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al:
Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med.
359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, et al: Efficacy
and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:25–34.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wilhelm SM, Adnane L, Newell P, Villanueva
A, Llovet JM and Lynch M: Preclinical overview of sorafenib, a
multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF and PDGF
receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3129–3140.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Abou-Alfa GK, Schwartz L, Ricci S, et al:
Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 24:4293–4300. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nojiri K, Sugimoto K, Shiraki K, et al:
Sorafenib and TRAIL have synergistic effect on hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 42:101–108. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shen ZX, Shi ZZ, Fang J, et al:
All-trans retinoic
acid/As2O3combination yields a high quality
remission and survival in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic
leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:5328–5335. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ferrara FF, Fazi F, Bianchini A, et al:
Histone deacetylase-targeted treatment restores retinoic acid
signaling and differentiation in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer
Res. 61:2–7. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maeda Y, Yamaguchi T, Hijikata Y, et al:
Clinical efficacy of all-trans retinoic acid for treating
adult T cell leukemia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 134:673–677.
2008.
|
|
13
|
Sun SY, Wan H, Yue P, Hong WK and Lotan R:
Evidence that retinoic acid receptor beta induction by retinoids is
important for tumor cell growth inhibition. J Biol Chem.
275:17149–17153. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Newsome PN, Beldon I, Moussa Y, et al: Low
serum retinol levels are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma
in patients with chronic liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
14:1295–1301. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yuan JM, Gao YT, Ong CN, Ross RK and Yu
MC: Prediagnostic level of serum retinol in relation to reduced
risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 98:482–490.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim DG, Jo BH, You KR and Ahn DS:
Apoptosis induced by retinoic acid in Hep 3B cells in vitro. Cancer
Lett. 107:149–159. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hsu SL, Lin HM and Chou CK: Suppression of
the tumorigenicity of human hepatoma hep3B cells by long-term
retinoic acid treatment. Cancer Lett. 99:79–85. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Falasca L, Favale A, Gualandi G, Maietta G
and Conti Devirgiliis L: Retinoic acid treatment induces apoptosis
or expression of a more differentiated phenotype on different
fractions of cultured fetal rat hepatocytes. Hepatology.
28:727–737. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Falasca L, Marcellini P, Ara C, Rufo A and
Devirgiliis LC: Growth inhibition and induction of specific hepatic
phenotype expression by retinoic acid in HEPG2 cells. Anticancer
Res. 19:3283–3292. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Arce F, Gatjens-Boniche O, Vargas E,
Valverde B and Diaz C: Apoptotic events induced by naturally
occurring retinoids ATRA and 13-cis retinoic acid on human
hepatoma cell lines Hep3B and HepG2. Cancer Lett. 229:271–281.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Watanabe J, Nomata K, Noguchi M, et al:
All-trans retinoic acid enhances gap junctional
intercellular communication among renal epithelial cells in vitro
treated with renal carcinogens. Eur J Cancer. 35:1003–1008.
1999.
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Dai Y, Huang Y, et al:
All-trans retinoic acid restores gap junctional
intercellular communication between oral cancer cells with
upregulation of Cx32 and Cx43 expressions in vitro. Med Oral Patol
Oral Cir Bucal. 18:e569–e577. 2013.
|
|
23
|
Harris AL: Connexin channel permeability
to cytoplasmic molecules. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 94:120–143. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Herve JC and Derangeon M:
Gap-junction-mediated cell-to-cell communication. Cell Tissue Res.
352:21–31. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Krutovskikh VA, Piccoli C and Yamasaki H:
Gap junction intercellular communication propagates cell death in
cancerous cells. Oncogene. 21:1989–1999. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jensen R and Glazer PM:
Cell-interdependent cisplatin killing by Ku/DNA-dependent protein
kinase signaling transduced through gap junctions. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 101:6134–6139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hong X, Wang Q, Yang Y, et al: Gap
junctions propagate opposite effects in normal and tumor testicular
cells in response to cisplatin. Cancer Lett. 317:165–171. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mesnil M: Connexins and cancer. Biol Cell.
94:493–500. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Leithe E, Sirnes S, Omori Y and Rivedal E:
Downregulation of gap junctions in cancer cells. Crit Rev Oncog.
12:225–256. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang Y, Cao MH, Wang Q, Yuan DD, Li L and
Tao L: The effects of 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate and
diphenylboronic anhydride on gap junctions composed of Connexin43
in TM(4) sertoli cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1390–1397. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ara C, Massimi M and Devirgiliis Conti L:
Retinoic acid modulates gap junctional intercellular communication
in hepatocytes and hepatoma cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 59:1758–1765.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bai D, del Corsso C, Srinivas M and Spray
DC: Block of specific gap junction channel subtypes by
2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB). J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
319:1452–1458. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guo Y, Martinez-Williams C, Gilbert KA and
Rannels DE: Inhibition of gap junction communication in alveolar
epithelial cells by 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid. Am J Physiol.
276:L1018–L1026. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bolognesi M, Zampieri F, Di Pascoli M, et
al: Increased myoendothelial gap junctions mediate the enhanced
response to epoxyeicosatrienoic acid and acetylcholine in
mesenteric arterial vessels of cirrhotic rats. Liver Int.
31:881–890. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guan X, Cravatt BF, Ehring GR, et al: The
sleep-inducing lipid oleamide deconvolutes gap junction
communication and calcium wave transmission in glial cells. J Cell
Biol. 139:1785–1792. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Boger DL, Patterson JE, Guan X, Cravatt
BF, Lerner RA and Gilula NB: Chemical requirements for inhibition
of gap junction communication by the biologically active lipid
oleamide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:4810–4815. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu CL, Huang YS, Hosokawa M, Miyashita K
and Hu ML: Inhibition of proliferation of a hepatoma cell line by
fucoxanthin in relation to cell cycle arrest and enha-nced gap
junctional intercellular communication. Chem Biol Interact.
182:165–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kalemkerian GP, Jiroutek M, Ettinger DS,
Dorighi JA, Johnson DH and Mabry M: A phase II study of
all-trans-retinoic acid plus cisplatin and etoposide in
patients with extensive stage small cell lung carcinoma: an Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group Study. Cancer. 83:1102–1108.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee JS, Newman RA, Lippman SM, et al:
Phase I evaluation of all-trans-retinoic acid in adults with solid
tumors. J Clin Oncol. 11:959–966. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dasmahapatra G, Yerram N, Dai Y, Dent P
and Grant S: Synergistic interactions between vorinostat and
sorafenib in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells involve Mcl-1 and
p21CIP1down-regulation. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4280–4290.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Eicher C, Dewerth A, Kirchner B, Warmann
SW, Fuchs J and Armeanu-Ebinger S: Treatment effects of the
multikinase inhibitor sorafenib on hepatoblastoma cell lines and
xenografts in NMRI-Foxn1 nu mice. Liver Int. 32:574–581. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Strumberg D, Richly H, Hilger RA, et al:
Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of the Novel Raf kinase
and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor BAY
43-9006 in patients with advanced refractory solid tumors. J Clin
Oncol. 23:965–972. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Umhauer S, Ruch RJ and Fanning J: Gap
junctional intercellular communication and connexin 43 expression
in ovarian carcinoma. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 182:999–1000. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gershon E, Plaks V and Dekel N: Gap
junctions in the ovary: expression, localization and function. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 282:18–25. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang JT and Nicholson BJ: The topological
structure of connexin 26 and its distribution compared to connexin
32 in hepatic gap junctions. J Membr Biol. 139:15–29. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kawasaki Y, Omori Y, Li Q, et al:
Cytoplasmic accumulation of connexin32 expands cancer stem cell
population in human HuH7 hepatoma cells by enhancing its
self-renewal. Int J Cancer. 128:51–62. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Carystinos GD, Alaoui-Jamali MA, Phipps J,
Yen L and Batist G: Upregulation of gap junctional intercellular
communication and connexin 43 expression by cyclic-AMP and
all-trans-retinoic acid is associated with glutathione
depletion and chemosensitivity in neuroblastoma cells. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 47:126–132. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Matono S, Tanaka T, Sueyoshi S, Yamana H,
Fujita H and Shirouzu K: Bystander effect in suicide gene therapy
is directly proportional to the degree of gap junctional
intercellular communication in esophageal cancer. Int J Oncol.
23:1309–1315. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lawrence TS, Rehemtulla A, Ng EY, Wilson
M, Trosko JE and Stetson PL: Preferential cytotoxicity of cells
transduced with cytosine deaminase compared to bystander cells
after treatment with 5-flucytosine. Cancer Res. 58:2588–2593.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Edwards GO, Jondhale S, Chen T and Chipman
JK: A quantitative inverse relationship between connexin32
expression and cell proliferation in a rat hepatoma cell line.
Toxicology. 253:46–52. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang ZJ, Song L, Guo LC, Yin M and Sun YN:
Induction of differentiation by panaxydol in human hepatocarcinoma
SMMC-7721 cells via cAMP and MAP kinase dependent mechanism.
Yakugaku Zasshi. 131:993–1000. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|