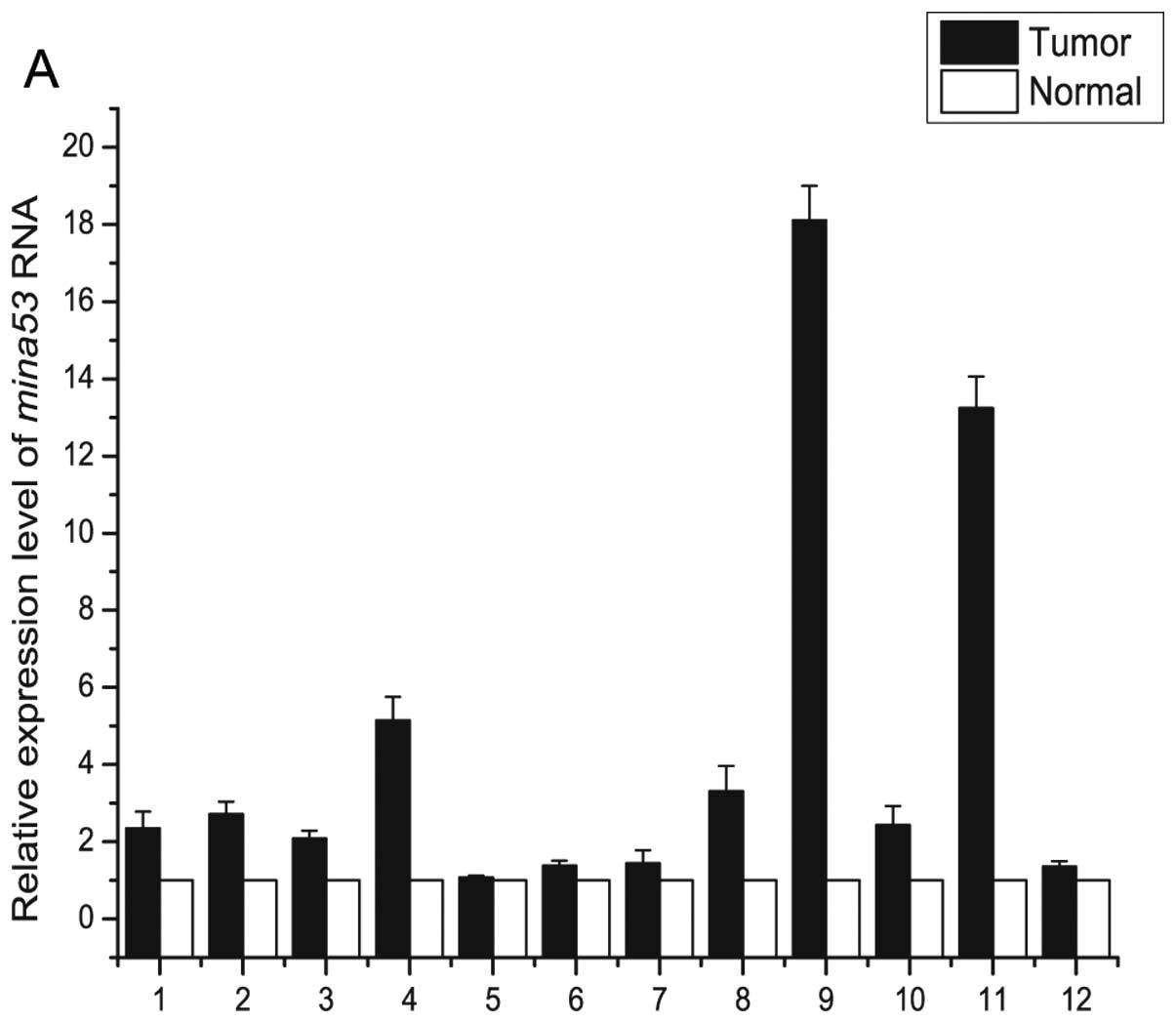
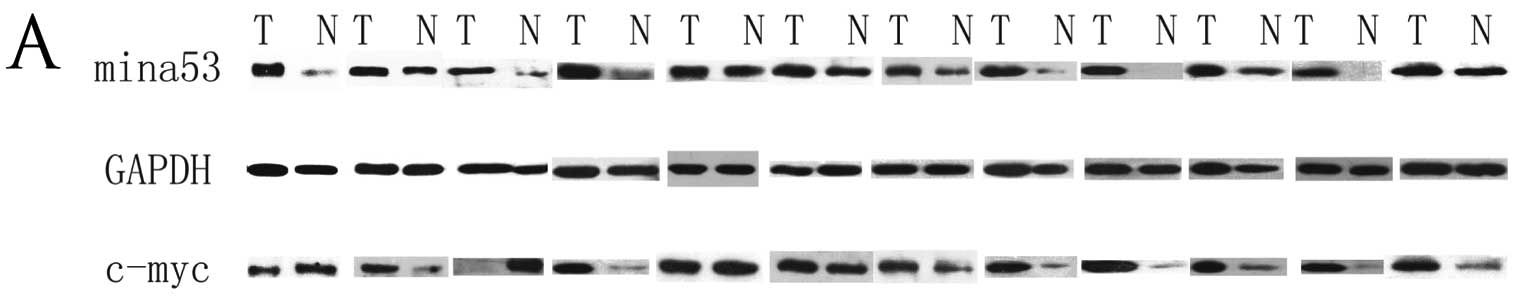
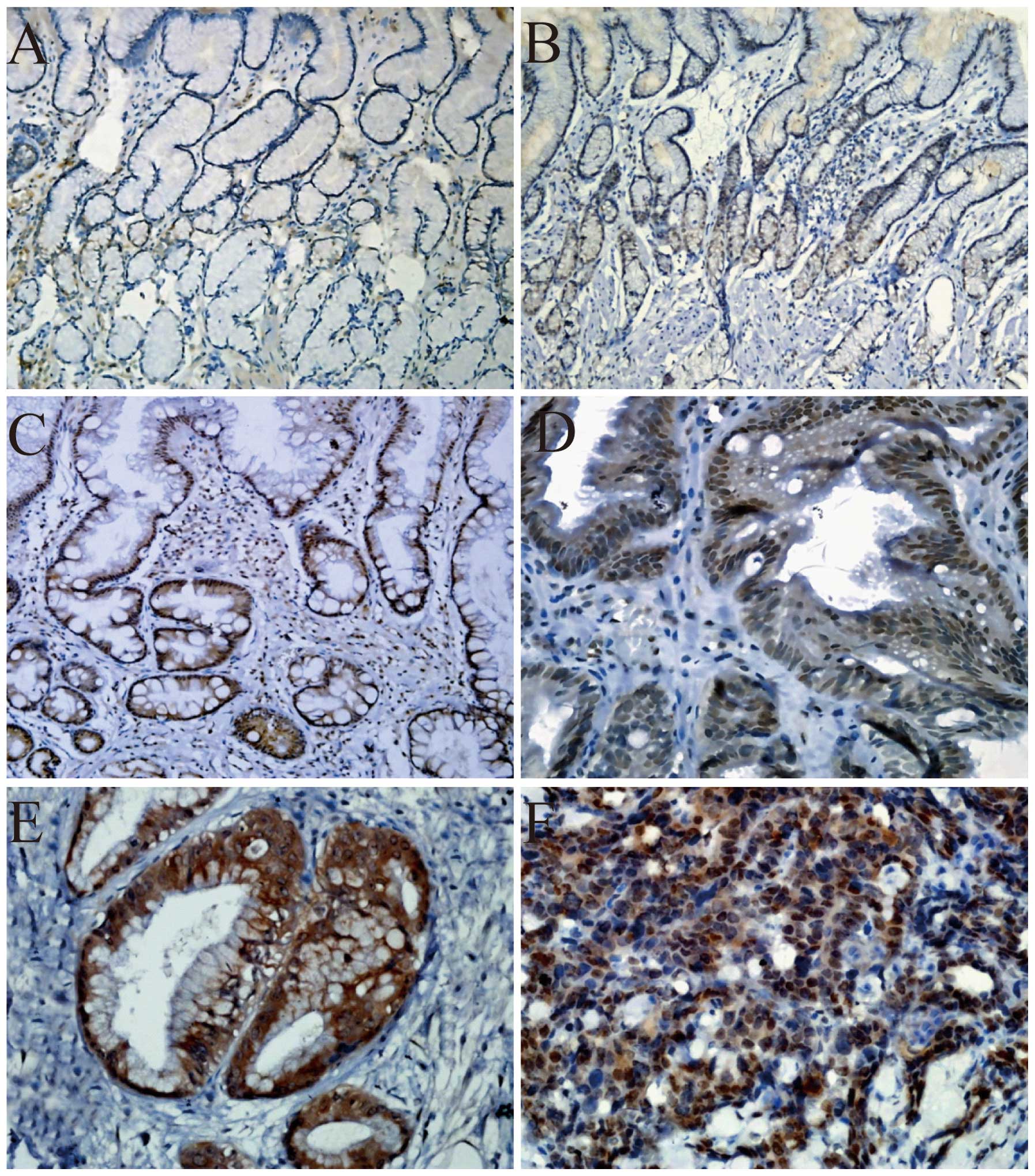
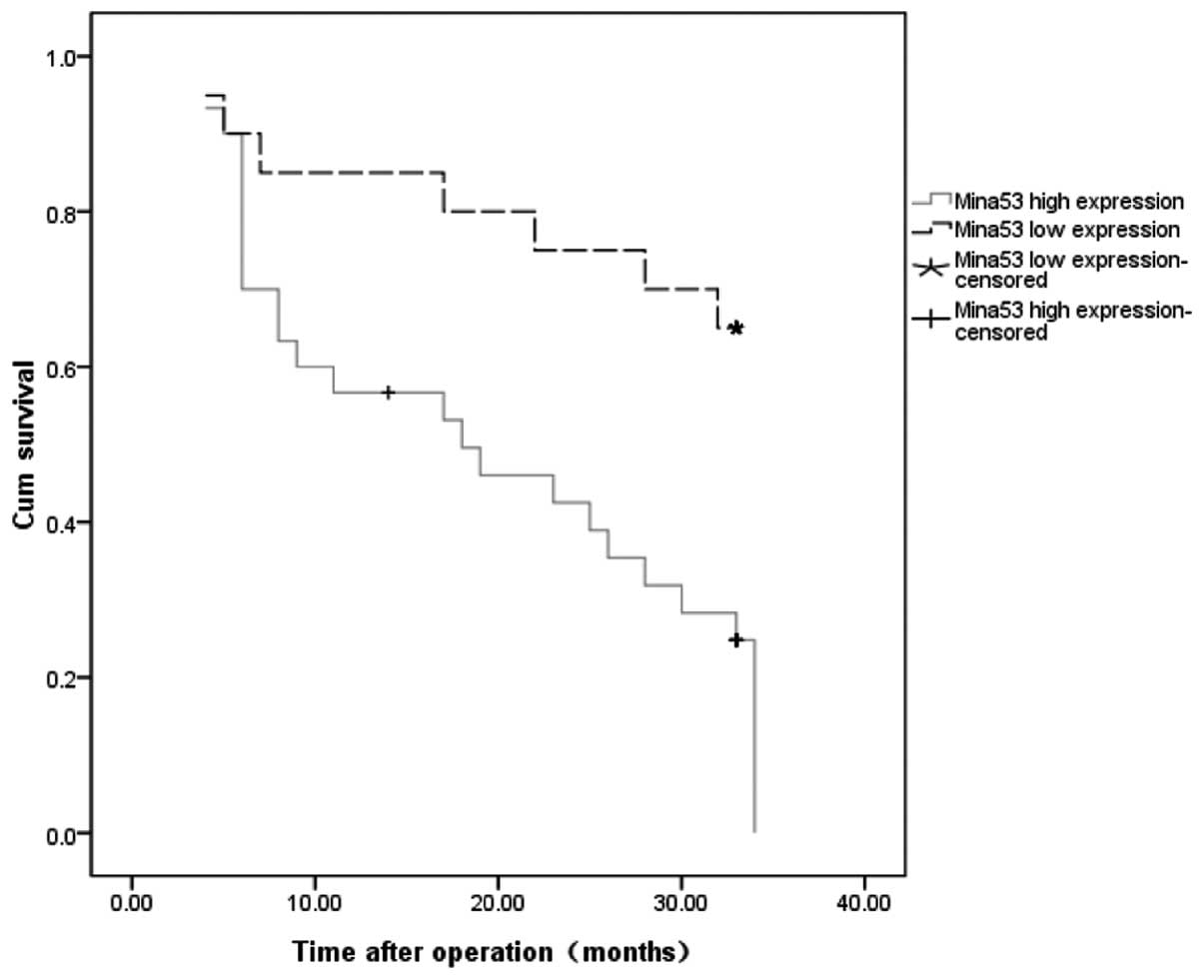
|
1
|
Huang CY, Chen YM, Zhao JJ, et al:
Decreased expression of transcription elongation factor A-like 7 is
associated with gastric adenocarcinoma prognosis. PLoS One.
8:e546712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang L, Huang X, Chen Y, Jin X, Li Q and
Yi TN: Prognostic value of TP/PD-ECGF and thrombocytosis in gastric
carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 38:568–573. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pourhoseingholi MA, Moghimi-Dehkordi B,
Safaee A, Hajizadeh E, Solhpour A and Zali MR: Prognostic factors
in gastric cancer using log-normal censored regression model.
Indian J Med Res. 129:262–267. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Henning GT, Schild SE, Stafford SL, et al:
Results of irradiation or chemo irradiation following resection of
gastric adenocarcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 46:589–598.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gostissa M, Ranganath S, Bianco JM and Alt
FW: Chromosomal location targets different MYC family gene members
for oncogenic translocations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:2265–2270. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ruggero D: The role of Myc-induced protein
synthesis in cancer. Cancer Res. 69:8839–8843. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tsuneoka M, Koda Y, Soejima M, Teye K and
Kimura H: A novel myc target gene, mina53, that is involved
in cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 277:35450–35459. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Teye K, Tsuneoka M, Arima N, et al:
Increased expression of a Myc target gene Mina53 in human
colon cancer. Am J Pathol. 164:205–216. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tsuneoka M, Fujita H, Arima N, et al:
Mina53 as a potential prognostic factor for esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 10:7347–7356. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ogasawara S, Komuta M, Nakashima O, Akiba
J, Tsuneoka M and Yano H: Accelerated expression of a Myc target
gene Mina53 in aggressive hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol
Res. 40:330–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tan XP, Zhang Q, Dong WG, Lei XW and Yang
ZR: Upregulated expression of Mina53 in cholangiocarcinoma and its
clinical significance. Oncol Lett. 3:1037–1041. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Y, Antonopoulos DA, Zhu X, et al:
Laser captured microdissection and metagenomic analysis of intact
mucosa-associated microbial communities of human colon. Appl
Microbiol Biotechnol. 88:1333–1342. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang L, Zheng L, Wang SY, Zhu TF and Zhu
HG: Clonal analysis of gastric carcinoma and precancerous lesions
and its relation to Ki-67 protein expression. Neoplasma. 56:48–55.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee HJ, Nam KT, Park HS, et al: Gene
expression profiling of metaplastic lineages identifies CDH17 as a
prognostic marker in early stage gastric cancer. Gastroenterology.
139:213–225. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Z, Li M, Zhang G, Fang P, Yao H,
Xiao Z and Chen Z: Identification of human gastric carcinoma
biomarkers by differential protein expression analysis using
18O labeling and nanoLC-MS/MS coupled with laser capture
microdissection. Med Oncol. 27:296–303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gutierrez-Gonzalez L, Graham TA,
Rodriguez-Justo M, et al: The clonal origins of dysplasia from
intestinal metaplasia in the human stomach. Gastroenterology.
140:1251–1260. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gürbüz Y, Kahlke V and Klöppel G: How do
gastric carcinoma classification systems relate to mucin expression
patterns? An immunohistochemical analysis in a series of advanced
gastric carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 440:505–511. 2002.
|
|
18
|
Ishizaki H, Yano H, Tsuneoka M, et al:
Overexpression of the myc target gene Mina53 in advanced renal cell
carcinoma. Pathol Int. 57:672–680. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Komiya K, Sueoka-Aragane N, Sato A, et al:
Expression of Mina53, a novel c-Myc target gene, is a favorable
prognostic marker in early stage lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
69:232–238. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|