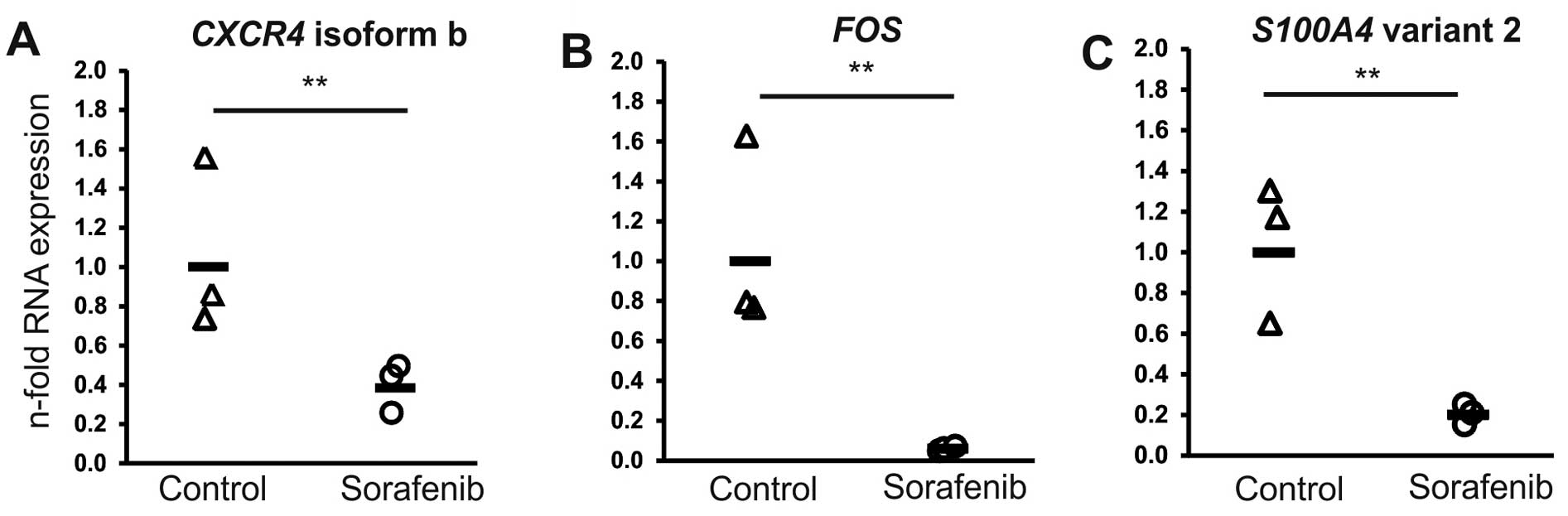
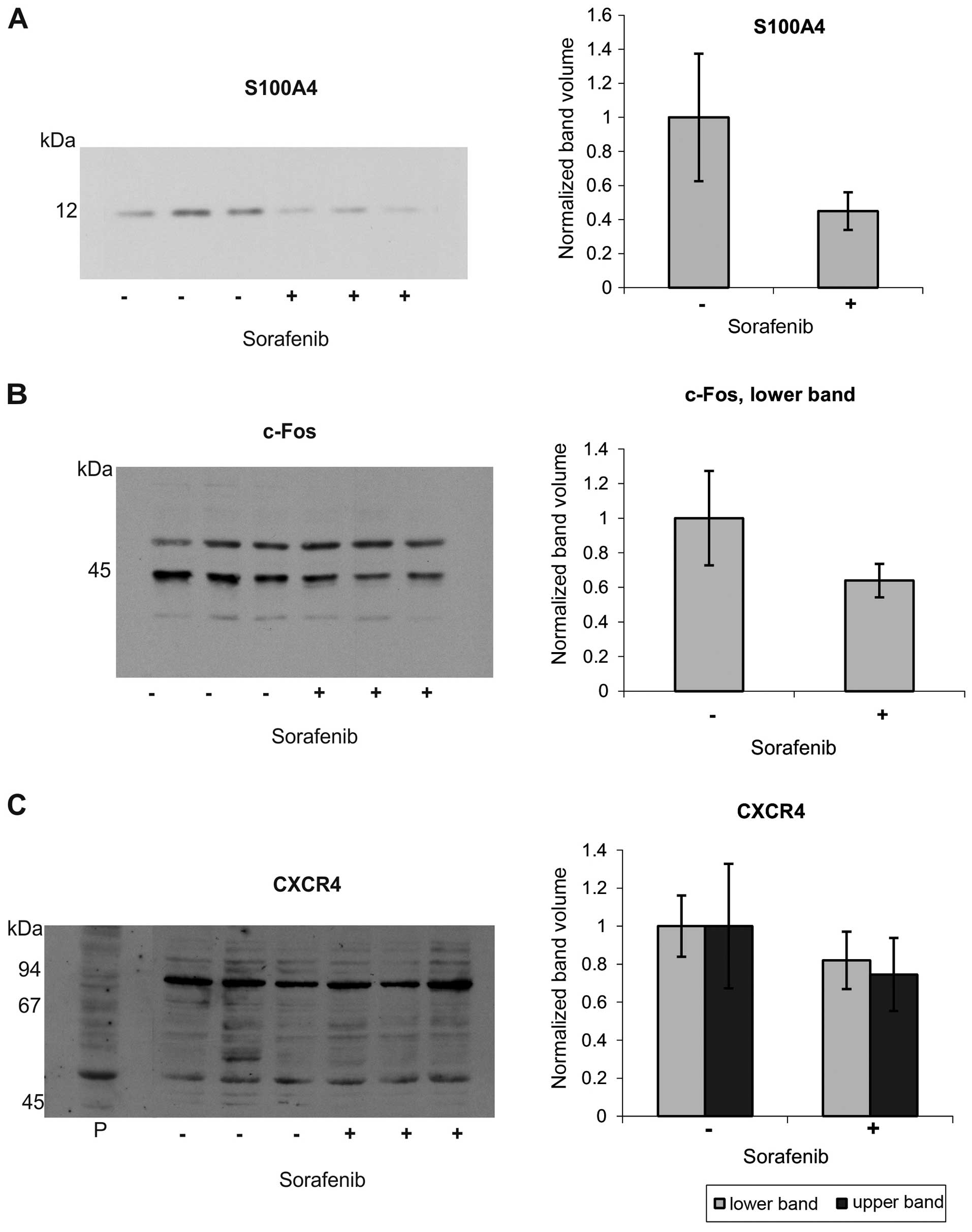
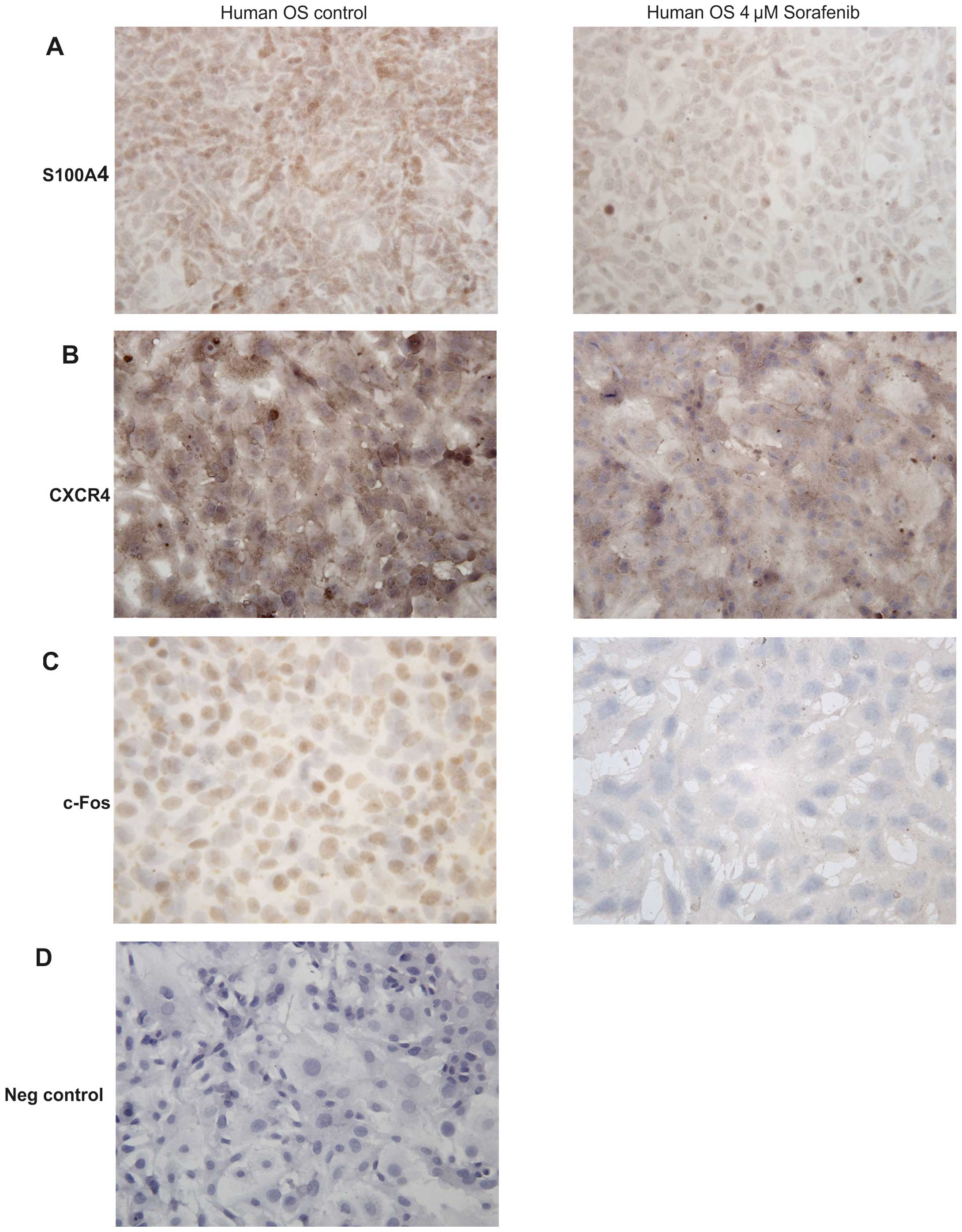
|
1
|
Kansara M and Thomas DM: Molecular
pathogenesis of osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 26:1–18. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ta HT, Dass CR, Choong PF and Dunstan DE:
Osteosarcoma treatment: state of the art. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:247–263. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Withrow SJ, Powers BE, Straw RC and
Wilkins RM: Comparative aspects of osteosarcoma. Dog versus man.
Clin Orthop Relat Res. 270:159–168. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kaya M, Wada T, Akatsuka T, Kawaguchi S,
Nagoya S, Shindoh M, Higashino F, Mezawa F, Okada F and Ishii S:
Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in untreated
osteosarcoma is predictive of pulmonary metastasis and poor
prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 6:572–577. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Smithey BE, Pappo AS and Hill DA: C-kit
expression in pediatric solid tumours: a comparative
immunohistochemical study. Am J Surg Pathol. 26:486–492. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McGary EC, Weber K, Mills L, Doucet M,
Lewis V, Lev DC, Fidler IJ and Bar-Eli M: Inhibition of
platelet-derived growth factor-mediated proliferation of
osteosarcoma cells by the novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI571.
Clin Cancer Res. 8:3584–3591. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kaya M, Wada T, Nagoya S, Sasaki M,
Matsumura T and Yamashita T: The level of vascular endothelial
growth factor as a predictor of a poor prognosis in osteosarcoma. J
Bone Joint Surg Br. 91:784–788. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Steeghs N, Nortier JW and Gelderblom H:
Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of solid
tumours: an update of recent developments. Ann Surg Oncol.
14:942–953. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, et al: BAY
43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumour activity and
targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases
involved in tumour progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res.
64:7099–7109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mulder SF, Jacobs JF, Olde Nordkamp MA, et
al: Cancer patients treated with sunitinib or sorafenib have
sufficient antibody and cellular immune responses to warrant
influenza vaccination. Clin Cancer Res. 17:4541–4549. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Blechacz BR, Smoot RL, Bronk SF, Werneburg
NW, Sirica AE and Gores GJ: Sorafenib inhibits signal transducer
and activator of transcription-3 signaling in cholangiocarcinoma
cells by activating the phosphatase shatterproof 2. Hepatology.
50:1861–1870. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou C, Liu J, Li Y, Liu L, Zhang X, Ma
CY, Hua SC, Yang M and Yuan Q: microRNA-1274a, a modulator of
sorafenib induced a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 9 (ADAM9)
down-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett.
585:1828–1834. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ramakrishnan V, Timm M, Haug JL, Kimlinger
TK, Wellik LE, Witzig TE, Rajkumar SV, Adjei AA and Kumar S:
Sorafenib, a dual Raf kinase/vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor inhibitor has significant anti-myeloma activity and
synergizes with common anti-myeloma drugs. Oncogene. 29:1190–1202.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zeng Z, Shi YX, Samudio IJ, et al:
Targeting the leukemia microenvironment by CXCR4 inhibition
overcomes resistance to kinase inhibitors and chemotherapy in AML.
Blood. 113:6215–6224. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pignochino Y, Grignani G, Cavalloni G, et
al: Sorafenib blocks tumour growth, angiogenesis and metastatic
potential in preclinical models of osteosarcoma through a mechanism
potentially involving the inhibition of ERK1/2, MCL-1 and ezrin
pathways. Mol Cancer. 8:1182009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wolfesberger B, Tonar Z, Gerner W,
Skalicky M, Heiduschka G, Egerbacher M, Thalhammer JG and Walter I:
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor sorafenib decreases cell number and
induces apoptosis in a canine osteosarcoma cell line. Res Vet Sci.
88:94–100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Warde-Farley D, Donaldson SL, Comes O, et
al: The GeneMANIA prediction server: biological network integration
for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids
Res. 38:W214–W220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Alibes A, Yankilevich P, Canada A and
Diaz-Uriarte R: IDconverter and IDClight: conversion and annotation
of gene and protein IDs. BMC Bioinformatics. 8:92007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Duncan D, Prodduturi N and Zhang B:
WebGestalt2: an updated and expanded version of the Web-based Gene
Set Analysis Toolkit. BMC Bioinformatics. 11:P102010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zuker M: Mfold web server for nucleic acid
folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res.
31:3406–3415. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW and Dempfle L:
Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison
and statistical analysis of relative expression results in
real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:e362002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
de Jonge HJ, Fehrmann RS, de Bont ES,
Hofstra RM, Gerbens F, Kamps WA, de Vries EG, van der Zee AG, te
Meerman GJ and ter Elst A: Evidence based selection of housekeeping
genes. PLoS One. 2:e8982007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kwon MJ, Oh E, Lee S, et al:
Identification of novel reference genes using multiplatform
expression data and their validation for quantitative gene
expression analysis. PLoS One. 4:e61622009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, et al: The
MIQE guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of
Quantitative Real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem. 55:611–622.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boye K and Maelandsmo GM: S100A4 and
metastasis: a small actor playing many roles. Am J Pathol.
176:528–535. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jenkinson SR, Barraclough R, West CR and
Rudland PS: S100A4 regulates cell motility and invasion in an in
vitro model for breast cancer metastasis. Br J Cancer.
90:253–262. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sherbet GV: Metastasis promoter S100A4 is
a potentially valuable molecular target for cancer therapy. Cancer
Lett. 280:15–30. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shi Y, Zou M, Collison K, Baitei EY,
Al-Makhalafi Z, Farid NR and Al-Mohanna FA: Ribonucleic acid
interference targeting S100A4 (Mts1) suppresses tumour growth and
metastasis of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma in a mouse model. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 91:2373–2379. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ambartsumian N, Klingelhofer J, Grigorian
M, et al: The metastasis-associated Mts1(S100A4) protein could act
as an angiogenic factor. Oncogene. 20:4685–4695. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schmidt-Hansen B, Klingelhofer J,
Grum-Schwensen B, Christensen A, Andresen S, Kruse C, Hansen T,
Ambartsumian N, Lukanidin E and Grigorian M: Functional
significance of metastasis-inducing S100A4(Mts1) in tumour-stroma
interplay. J Biol Chem. 279:24498–24504. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rudland PS, Platt-Higgins A, Renshaw C,
West CR, Winstanley JH, Robertson L and Barraclough R: Prognostic
significance of the metastasis-inducing protein S100A4 (p9Ka) in
human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 60:1595–1603. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee WY, Su WC, Lin PW, Guo HR, Chang TW
and Chen HH: Expression of S100A4 and Met: potential predictors for
metastasis and survival in early-stage breast cancer. Oncology.
66:429–438. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang YY, Ye ZY, Zhao ZS, Tao HQ and Chu
YQ: High-level expression of S100A4 correlates with lymph node
metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Ann
Surg Oncol. 17:89–97. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Grum-Schwensen B, Klingelhofer J, Berg CH,
El-Naaman C, Grigorian M, Lukanidin E and Ambartsumian N:
Suppression of tumour development and metastasis formation in mice
lacking the S100A4 (mts1) gene. Cancer Res. 65:3772–3780.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mathisen B, Lindstad RI, Hansen J,
El-Gewely SA, Maelandsmo GM, Hovig E, Fodstad O, Loennechen T and
Winberg JO: S100A4 regulates membrane induced activation of matrix
metalloproteinase-2 in osteosarcoma cells. Clin Exp Metastasis.
20:701–711. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ma X, Yang Y, Wang Y, An G and Lv G: Small
interfering RNA-directed knockdown of S100A4 decreases
proliferation and invasiveness of osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Lett.
299:171–181. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ambartsumian N, Tarabykina S, Grigorian M,
Tulchinsky E, Hulgaard E, Georgiev G and Lukanidin E:
Characterization of two splice variants of metastasis-associated
human mts1 gene. Gene. 159:125–130. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mazzucchelli L: Protein S100A4: too long
overlooked by pathologists? Am J Pathol. 160:7–13. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Durchdewald M, Angel P and Hess J: The
transcription factor Fos: a Janus-type regulator in health and
disease. Histol Histopathol. 24:1451–1461. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Eferl R and Wagner EF: AP-1: a
double-edged sword in tumourigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:859–868.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang ZQ, Liang J, Schellander K, Wagner EF
and Grigoriadis AE: c-fos-induced osteosarcoma formation in
transgenic mice: cooperativity with c-jun and the role of
endogenous c-fos. Cancer Res. 55:6244–6251. 1995.
|
|
45
|
Dobrazanski P, Noguchi T, Kovary K, Rizzo
CA, Lazo PS and Bravo R: Both products of the fosB gene, FosB and
its short form, FosB/SF, are transcriptional activators in
fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 11:5470–5478. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wu JX, Carpenter PM, Gresens C, Keh R,
Niman H, Morris JW and Mercola D: The proto oncogene c-fos is
over-expressed in the majority of human osteosarcomas. Oncogene.
5:989–1000. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Franchi A, Calzolari A and Zampi G:
Immunohistochemical detection of c-fos and c-jun expression in
osseous and cartilaginous tumours of the skeleton. Virchows Arch.
432:515–519. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ruther U, Komitowski D, Schubert FR and
Wagner EF: c-fos expression induces bone tumours in transgenic
mice. Oncogene. 4:861–865. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hu E, Mueller E, Oliviero S, Papaioannou
VE, Johnson R and Spiegelman BM: Targeted disruption of the c-fos
gene demonstrates c-fos-dependent and -independent pathways for
gene expression stimulated by growth factors or oncogenes. EMBO J.
13:3094–3103. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pandey MK, Liu G, Cooper TK and Mulder KM:
Knockdown of c-Fos suppresses the growth of human colon carcinoma
cells in athymic mice. Int J Cancer. 130:213–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kakar S, Mihalov M, Chachlani NA, Ghosh L
and Johnstone H: Correlation of c-fos, p53, and PCNA expression
with treatment outcome in osteosarcoma. J Surg Oncol. 73:125–126.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Clark JC, Dass CR and Choong PF: A review
of clinical and molecular prognostic factors in osteosarcoma. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 134:281–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Laverdiere C, Hoang BH, Yang R, Sowers R,
Qin J, Meyers PA, Huvos AG, Healey JH and Gorlick R: Messenger RNA
expression levels of CXCR4 correlate with metastatic behavior and
outcome in patients with osteosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res.
11:2561–2567. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lin F, Zheng SE, Shen Z, Tang LN, Chen P,
Sun YJ, Zhao H and Yao Y: Relationships between levels of CXCR4 and
VEGF and blood-borne metastasis and survival in patients with
osteosarcoma. Med Oncol. 28:649–653. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Baumhoer D, Smida J, Zillmer S, Rosemann
M, Atkinson MJ, Nelson PJ, Jundt G, Luettichau IV and Nathrath M:
Strong expression of CXCL12 is associated with a favorable outcome
in osteosarcoma. Mod Pathol. 25:522–528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Perissinotto E, Cavalloni G, Leone F, et
al: Involvement of chemokine receptor 4/stromal cell-derived factor
1 system during osteosarcoma tumour progression. Clin Cancer Res.
11:490–497. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liang Z, Wu T, Lou H, Yu X, Taichman RS,
Lau SK, Nie S, Umbreit J and Shim H: Inhibition of breast cancer
metastasis by selective synthetic polypeptide against CXCR4. Cancer
Res. 64:4302–4308. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Mori T, Doi R, Koizumi M, et al: CXCR4
antagonist inhibits stromal cell-derived factor 1-induced migration
and invasion of human pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:29–37.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liang Z, Yoon Y, Votaw J, Goodman MM,
Williams L and Shim H: Silencing of CXCR4 blocks breast cancer
metastasis. Cancer Res. 65:967–971. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Carlisle AJ, Lyttle CA, Carlisle RY and
Maris JM: CXCR4 expression heterogeneity in neuroblastoma cells due
to ligand-independent regulation. Mol Cancer. 8:1262009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lapham CK, Romantseva T, Petricoin E, King
LR, Manischewitz J, Zaitseva MB and Golding H: CXCR4 heterogeneity
in primary cells: possible role of ubiquitination. J Leukoc Biol.
72:1206–1214. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Sloane AJ, Raso V, Dimitrov DS, et al:
Marked structural and functional heterogeneity in CXCR4: separation
of HIV-1 and SDF-1α responses. Immunol Cell Biol. 83:129–143.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Grignani G, Palmerini E, Dileo P, et al: A
phase II trial of sorafenib in relapsed and unresectable high-grade
osteosarcoma after failure of standard multimodal therapy: an
Italian Sarcoma Group study. Ann Oncol. 23:508–516. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ho MC, Shi W, Rinaldo-Matthis A, Tyler PC,
Evans GB, Clinch K, Almo SC and Schramm VL: Four generations of
transition-state analogues for human purine nucleoside
phosphorylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:4805–4812. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lewandowicz A, Tyler PC, Evans GB,
Furneaux RH and Schramm VL: Achieving the ultimate physiological
goal in transition state analogue inhibitors for purine nucleoside
phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 278:31465–31468. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|