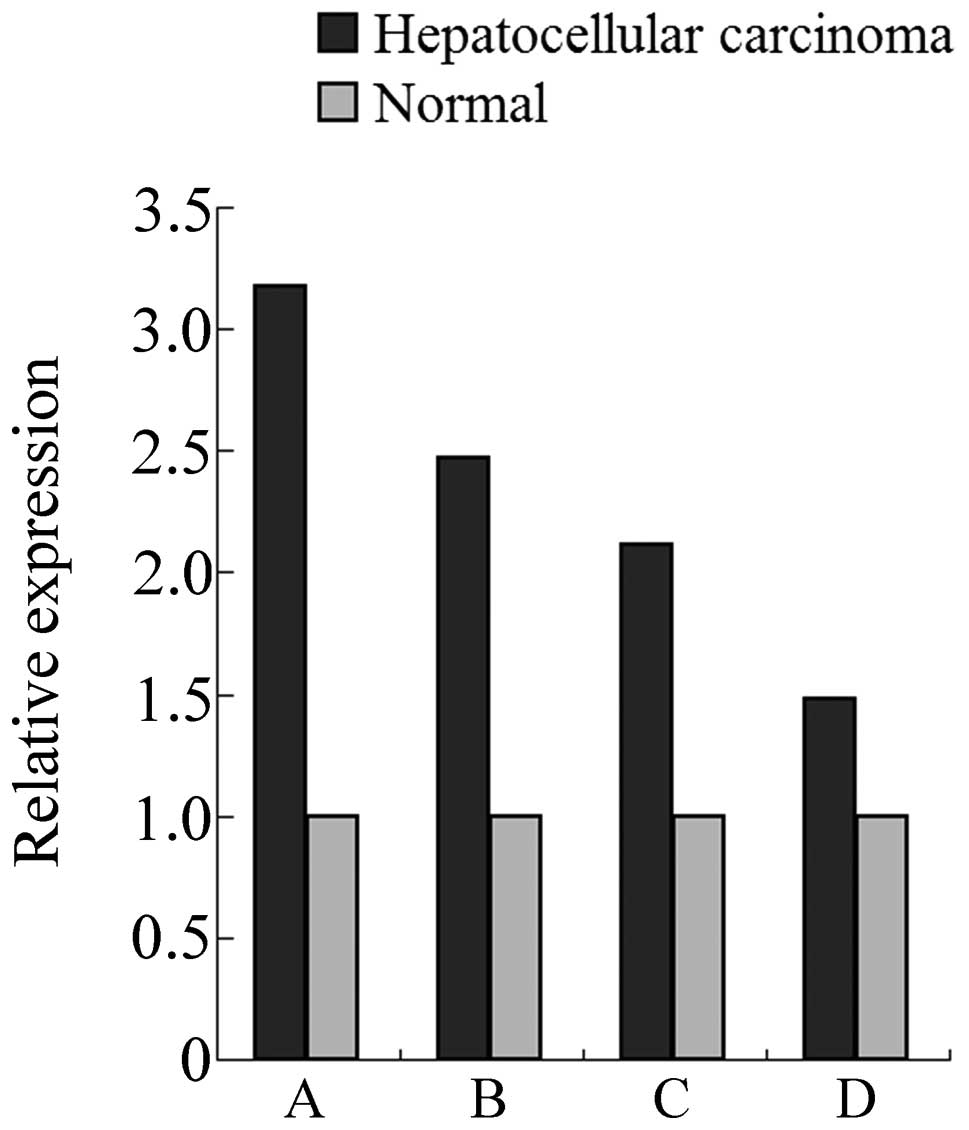
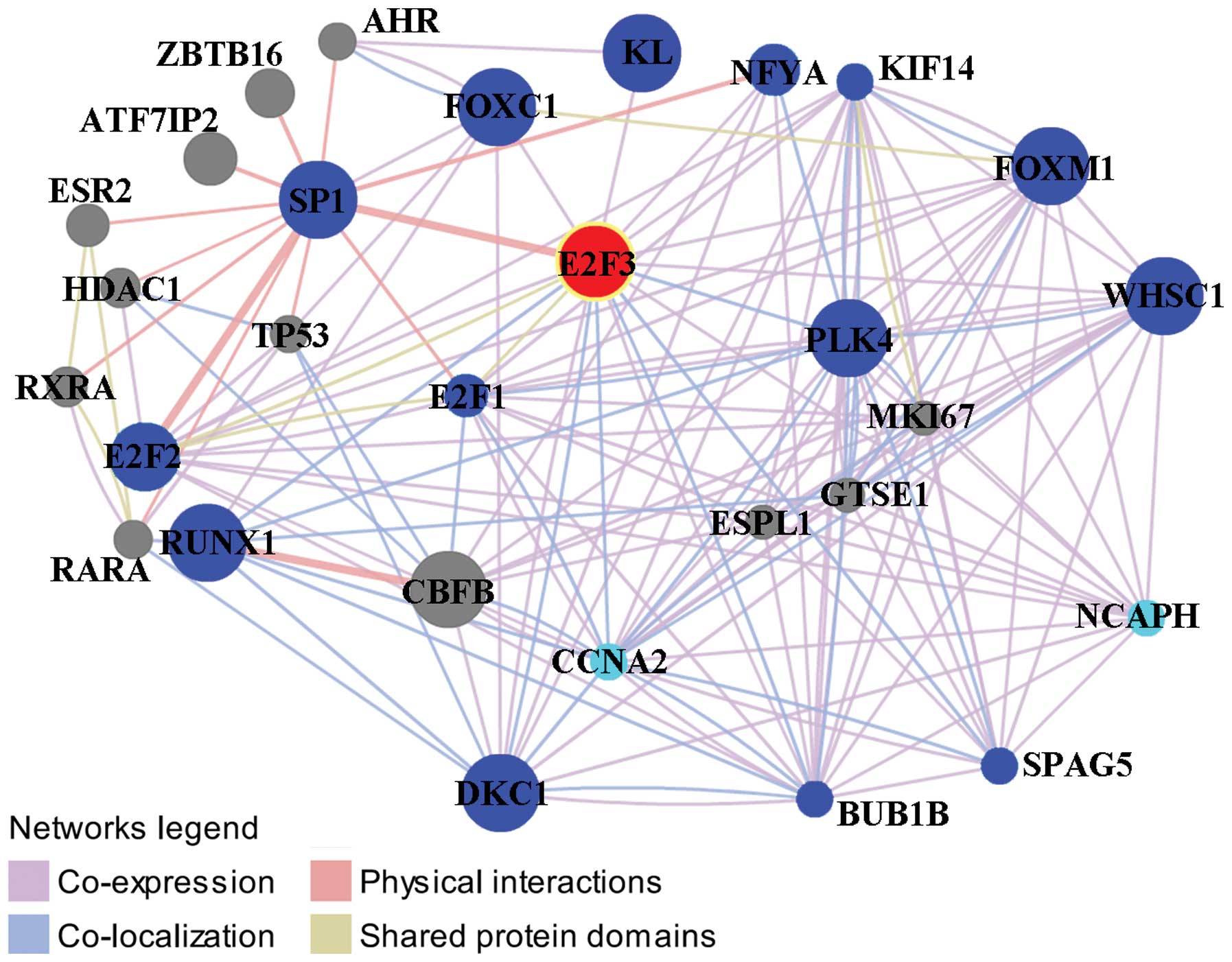
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Singhal A, Jayaraman M, Dhanasekaran DN
and Kohli V: Molecular and serum markers in hepatocellular
carcinoma: predictive tools for prognosis and recurrence. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 82:116–140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Midorikawa Y, Makuuchi M, Tang W and
Aburatani H: Microarray-based analysis for hepatocellular
carcinoma: from gene expression profiling to new challenges. World
J Gastroenterol. 13:1487–1492. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chiriva-Internati M, Grizzi F, Wachtel MS,
Jenkins M, Ferrari R, Cobos E and Frezza EE: Biological treatment
for liver tumor and new potential biomarkers. Dig Dis Sci.
53:836–843. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hao K, Luk JM, Lee NP, Mao M, Zhang C,
Ferguson MD, Lamb J, Dai H, Ng IO, Sham PC and Poon RT: Predicting
prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma after curative surgery with
common clinicopathologic parameters. BMC Cancer. 9:3892009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chao Y, Shih YL, Chiu JH, Chau GY, Lui WY,
Yang WK, Lee SD and Huang TS: Overexpression of cyclin A but not
Skp 2 correlates with the tumor relapse of human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 58:985–990. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ohashi R, Gao C, Miyazaki M, Hamazaki K,
Tsuji T, Inoue Y, Uemura T, Hirai R, Shimizu N and Namba M:
Enhanced expression of cyclin E and cyclin A in human
hepatocellular carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 21:657–662.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Attwooll C, Lazzerini Denchi E and Helin
K: The E2F family: specific functions and overlapping interests.
EMBO J. 23:4709–4716. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leone G, DeGregori J, Yan Z, Jakoi L,
Ishida S, Williams RS and Nevins JR: E2F3 activity is regulated
during the cell cycle and is required for the induction of S phase.
Genes Dev. 12:2120–2130. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lees JA, Saito M, Vidal M, Valentine M,
Look T, Harlow E, Dyson N and Helin K: The retinoblastoma protein
binds to a family of E2F transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol.
13:7813–7825. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Humbert PO, Verona R, Trimarchi JM, Rogers
C, Dandapani S and Lees JA: E2f3 is critical for normal
cellular proliferation. Genes Dev. 14:690–703. 2000.
|
|
12
|
Vuaroqueaux V, Urban P, Labuhn M,
Delorenzi M, Wirapati P, Benz CC, Flury R, Dieterich H, Spyratos F,
Eppenberger U and Eppenberger-Castori S: Low E2F1 transcript levels
are a strong determinant of favorable breast cancer outcome. Breast
Cancer Res. 9:R332007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Justenhoven C, Pierl CB, Haas S, Fischer
HP, Hamann U, Baisch C, Harth V, Spickenheuer A, Rabstein S,
Vollmert C, Illig T, Pesch B, Brüning T, Dippon J, Ko YD and Brauch
H: Polymorphic loci of E2F2, CCND1 and CCND3 are associated with
HER2 status of breast tumors. Int J Cancer. 124:2077–2081. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Feo F, De Miglio MR, Simile MM, Muroni MR,
Calvisi DF, Frau M and Pascale RM: Hepatocellular carcinoma as a
complex polygenic disease. Interpretive analysis of recent
developments on genetic predisposition. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1765:126–147. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono
H and Kanehisa M: KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
Nucleic Acids Res. 27:29–34. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: a cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mostafavi S, Ray D, Warde-Farley D,
Grouios C and Morris Q: GeneMANIA: a real-time multiple association
network integration algorithm for predicting gene function. Genome
Biol. 9(Suppl 1): S42008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk - database: prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011.
|
|
19
|
de Leeuw N, Dijkhuizen T, Hehir-Kwa JY,
Carter NP, Feuk L, Firth HV, Kuhn RM, Ledbetter DH, Martin CL, van
Ravenswaaij-Arts CM, Scherer SW, Shams S, Van Vooren S, Sijmons R,
Swertz M and Hastings R: Diagnostic interpretation of array data
using public databases and internet sources. Hum Mutat. 33:930–940.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miles WO, Tschöp K, Herr A, Ji JY and
Dyson NJ: Pumilio facilitates miRNA regulation of the E2F3
oncogene. Genes Dev. 26:356–368. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Martinez LA, Goluszko E, Chen HZ, Leone G,
Post S, Lozano G, Chen Z and Chauchereau A: E2F3 is a mediator of
DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 30:524–536. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Olsson AY, Feber A, Edwards S, Te Poele R,
Giddings I, Merson S and Cooper CS: Role of E2F3 expression in
modulating cellular proliferation rate in human bladder and
prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 26:1028–1037. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Feng B, Wang R, Song HZ and Chen LB:
MicroRNA-200b reverses chemoresistance of docetaxel-resistant human
lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting E2F3. Cancer. 118:3365–3376.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu T, Zhu Y, Xiong Y, Ge YY, Yun JP and
Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-195 suppresses tumorigenicity and regulates
G1/S transition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Hepatology. 50:113–121. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tryndyak VP, Ross SA, Beland FA and
Pogribny IP: Down-regulation of the microRNAs miR-34a,
miR-127, and miR-200b in rat liver during
hepatocarcinogenesis induced by a methyl-deficient diet. Mol
Carcinog. 48:479–487. 2009.
|
|
26
|
Foster CS, Falconer A, Dodson AR, Norman
AR, Dennis N, Fletcher A, Southgate C, Dowe A, Dearnaley D, Jhavar
S, Eeles R, Feber A and Cooper CS: Transcription factor E2F3
overexpressed in prostate cancer independently predicts clinical
outcome. Oncogene. 23:5871–5879. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wei LX, Zhou RS, Xu HF, Wang JY and Yuan
MH: High expression of FOXC1 is associated with poor clinical
outcome in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Tumour Biol.
34:941–946. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang L, Gu F, Liu CY, Wang RJ, Li J and Xu
JY: High level of FOXC1 expression is associated with poor
prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol.
34:853–858. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ray PS, Bagaria SP, Wang J, Shamonki JM,
Ye X, Sim MS, Steen S, Qu Y, Cui X and Giuliano AE: Basal-like
breast cancer defined by FOXC1 expression offers superior
prognostic value: a retrospective immunohistochemical study. Ann
Surg Oncol. 18:3839–3847. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xia L, Huang W, Tian D, Zhu H, Qi X, Chen
Z, Zhang Y, Hu H, Fan D, Nie Y and Wu K: Overexpression of forkhead
box C1 promotes tumor metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 57:610–624. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang L, Wang X, Jie P, Lu H, Zhang S, Lin
X, Lam EK, Cui Y, Yu J and Jin H: Klotho is silenced through
promoter hypermethylation in gastric cancer. Am J Cancer Res.
1:111–119. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jeschke J, Van Neste L, Glöckner SC, Dhir
M, Calmon MF, Deregowski V, Van Criekinge W, Vlassenbroeck I, Koch
A, Chan TA, Cope L, Hooker CM, Schuebel KE, Gabrielson E,
Winterpacht A, Baylin SB, Herman JG and Ahuja N: Biomarkers for
detection and prognosis of breast cancer identified by a functional
hypermethylome screen. Epigenetics. 7:701–709. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xie B, Zhou J, Yuan L, Ren F, Liu DC, Li Q
and Shu G: Epigenetic silencing of Klotho expression correlates
with poor prognosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol.
44:795–801. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Q, Wang L, Li D, Deng J, Zhao Z, He
S, Zhang Y and Tu Y: Kinesin family member 14 is a candidate
prognostic marker for outcome of glioma patients. Cancer Epidemiol.
37:79–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim TM, Yim SH, Shin SH, Xu HD, Jung YC,
Park CK, Choi JY, Park WS, Kwon MS, Fiegler H, Carter NP, Rhyu MG
and Chung YJ: Clinical implication of recurrent copy number
alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma and putative oncogenes in
recurrent gains on 1q. Int J Cancer. 123:2808–2815. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu N, Jia D, Chen W, Wang H, Liu F, Ge H,
Zhu X, Song Y, Zhang X, Zhang D, Ge D and Bai C: FoxM1 is
associated with poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer
patients through promoting tumor metastasis. PLoS One.
8:e594122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Wen L, Zhao SH, Ai ZH, Guo JZ and
Liu WC: FoxM1 expression is significantly associated with
cisplatin-based chemotherapy resistance and poor prognosis in
advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer.
79:173–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xia L, Mo P, Huang W, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhu
H, Tian D, Liu J, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Hu H, Fan D, Nie Y and Wu K: The
TNF-α/ROS/HIF-1-induced upregulation of FoxMI expression promotes
HCC proliferation and resistance to apoptosis. Carcinogenesis.
33:2250–2259. 2012.
|
|
39
|
Sun HC, Li M, Lu JL, Yan DW, Zhou CZ, Fan
JW, Qin XB, Tang HM and Peng ZH: Overexpression of Forkhead box M1
protein associates with aggressive tumor features and poor
prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 25:1533–1539.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Agnelli L, Forcato M, Ferrari F, Tuana G,
Todoerti K, Walker BA, Morgan GJ, Lombardi L, Bicciato S and Neri
A: The reconstruction of transcriptional networks reveals critical
genes with implications for clinical outcome of multiple myeloma.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:7402–7412. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
de Reyniès A, Assié G, Rickman DS, Tissier
F, Groussin L, René-Corail F, Dousset B, Bertagna X, Clauser E and
Bertherat J: Gene expression profiling reveals a new classification
of adrenocortical tumors and identifies molecular predictors of
malignancy and survival. J Clin Oncol. 27:1108–1115.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu B, Zhang J, Huang C and Liu H:
Dyskerin overexpression in human hepatocellular carcinoma is
associated with advanced clinical stage and poor patient prognosis.
PLoS One. 7:e431472012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu L, Zhang CZ, Cai M, Fu J, Chen GG and
Yun J: Downregulation of polo-like kinase 4 in hepatocellular
carcinoma associates with poor prognosis. PLoS One. 7:e412932012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mendler JH, Maharry K, Radmacher MD,
Mrózek K, Becker H, Metzeler KH, Schwind S, Whitman SP, Khalife J,
Kohlschmidt J, Nicolet D, Powell BL, Carter TH, Wetzler M, Moore
JO, Kolitz JE, Baer MR, Carroll AJ, Larson RA, Caligiuri MA,
Marcucci G and Bloomfield CD: RUNX1 mutations are associated
with poor outcome in younger and older patients with
cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia and with distinct
gene and microRNA expression signatures. J Clin Oncol.
30:3109–3118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Buechler S: Low expression of a few genes
indicates good prognosis in estrogen receptor positive breast
cancer. BMC Cancer. 9:2432009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mamat S, Ikeda J, Tian T, Wang Y, Luo W,
Aozasa K and Morii E: Transcriptional regulation of aldehyde
dehydrogenase 1A1 gene by alternative spliced forms of nuclear
factor Y in tumorigenic population of endometrial adenocarcinoma.
Genes Cancer. 2:979–984. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kong LM, Liao CG, Chen L, Yang HS, Zhang
SH, Zhang Z, Bian HJ, Xing JL and Chen ZN: Promoter hypomethylation
up-regulates CD147 expression through increasing Sp1 binding and
associates with poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Cell Mol Med. 15:1415–1428. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang W, Zhou L, Ding SM, Xie HY, Xu X, Wu
J, Chen QX, Zhang F, Wei BJ, Eldin AT and Zheng SS: Aberrant
methylation of the CADM1 promoter is associated with poor prognosis
in hepatocellular carcinoma treated with liver transplantation.
Oncol Rep. 25:1053–1062. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Song MA, Tiirikainen M, Kwee S, Okimoto G,
Yu H and Wong LL: Elucidating the landscape of aberrant DNA
methylation in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e557612013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang YJ, Chen SY, Chen CJ and Santella
RM: Polymorphisms in cyclin D1 gene and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Mol Carcinog. 33:125–129. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Villanueva A and Hoshida Y: Depicting the
role of TP53 in hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. J Hepatol. 55:724–725. 2011.
|
|
52
|
Stroescu C, Dragnea A, Ivanov B, Pechianu
C, Herlea V, Sgarbura O, Popescu A and Popescu I: Expression of
p53, Bcl-2, VEGF, Ki67 and PCNA and prognostic significance in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 17:411–417.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Laurent-Puig P and Zucman-Rossi J:
Genetics of hepatocellular tumors. Oncogene. 25:3778–3786. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Frau M, Tomasi ML, Simile MM, Demartis MI,
Salis F, Latte G, Calvisi DF, Seddaiu MA, Daino L, Feo CF,
Brozzetti S, Solinas G, Yamashita S, Ushijima T, Feo F and Pascale
RM: Role of transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of
methionine adenosyltransferases in liver cancer progression.
Hepatology. 56:165–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Huang YH, Lin KH, Chen HC, Chang ML, Hsu
CW, Lai MW, Chen TC, Lee WC, Tseng YH and Yeh CT: Identification of
postoperative prognostic microRNA predictors in hepatocellular
carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e371882012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cheng H, Zhang L, Cogdell DE, Zheng H,
Schetter AJ, Nykter M, Harris CC, Chen K, Hamilton SR and Zhang W:
Circulating plasma MiR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic
colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS One. 6:e177452011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu XG, Zhu WY, Huang YY, Ma LN, Zhou SQ,
Wang YK, Zeng F, Zhou JH and Zhang YK: High expression of serum
miR-21 and tumor miR-200c associated with poor prognosis in
patients with lung cancer. Med Oncol. 29:618–626. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen HY, Lin YM, Chung HC, Lang YD, Lin
CJ, Huang J, Wang WC, Lin FM, Chen Z, Huang HD, Shyy JY, Liang JT
and Chen RH: miR-103/107 promote metastasis of colorectal cancer by
targeting the metastasis suppressors DAPK and KLF4. Cancer Res.
72:3631–3641. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Brenner B, Hoshen MB, Purim O, David MB,
Ashkenazi K, Marshak G, Kundel Y, Brenner R, Morgenstern S, Halpern
M, Rosenfeld N, Chajut A, Niv Y and Kushnir M: MicroRNAs as a
potential prognostic factor in gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:3976–3985. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Jamieson NB, Morran DC, Morton JP, Ali A,
Dickson EJ, Carter CR, Sansom OJ, Evans TR, McKay CJ and Oien KA:
MicroRNA molecular profiles associated with diagnosis,
clinicopathologic criteria, and overall survival in patients with
resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
18:534–545. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Hu X, Macdonald DM, Huettner PC, Feng Z,
El Naqa IM, Schwarz JK, Mutch DG, Grigsby PW, Powell SN and Wang X:
A miR-200 microRNA cluster as prognostic marker in advanced ovarian
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 114:457–464. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hiroki E, Akahira J, Suzuki F, Nagase S,
Ito K, Suzuki T, Sasano H and Yaegashi N: Changes in microRNA
expression levels correlate with clinicopathological features and
prognoses in endometrial serous adenocarcinomas. Cancer Sci.
101:241–249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang X, Wang J, Ma H, Zhang J and Zhou X:
Downregulation of miR-195 correlates with lymph node metastasis and
poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Med Oncol. 29:919–927. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Karakatsanis A, Papaconstantinou I,
Gazouli M, Lyberopoulou A, Polymeneas G and Voros D: Expression of
microRNAs, miR-21, miR-31, miR-122, miR-145, miR-146a, miR-200c,
miR-221, miR-222, and miR-223 in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma or intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its prognostic
significance. Mol Carcinog. 52:297–303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yu J, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Sato N,
Kayashima T, Fujita H, Nakata K and Tanaka M: MicroRNA,
hsa-miR-200c, is an independent prognostic factor in pancreatic
cancer and its upregulation inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion but
increases cell proliferation. Mol Cancer. 9:1692010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wong KF, Xu Z, Chen J, Lee NP and Luk JM:
Circulating markers for prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Expert Opin Med Diagn. 7:319–329. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Anzola M: Hepatocellular carcinoma: role
of hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses proteins in
hepatocarcinogenesis. J Viral Hepat. 11:383–393. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yao DF, Dong ZZ and Yao M: Specific
molecular markers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary
Pancreat Dis Int. 6:241–247. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sharan R, Ulitsky I and Shamir R:
Network-based prediction of protein function. Mol Syst Biol.
3:882007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Jenssen TK, Laegreid A, Komorowski J and
Hovig E: A literature network of human genes for high-throughput
analysis of gene expression. Nat Genet. 28:21–28. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Behm-Ansmant I, Rehwinkel J and Izaurralde
E: MicroRNAs silence gene expression by repressing protein
expression and/or by promoting mRNA decay. Cold Spring Harb Symp
Quant Biol. 71:523–530. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Gandhi V, Plunkett
W, Sampath D and Calin GA: miRNAs and their potential for use
against cancer and other diseases. Future Oncol. 3:521–537. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|