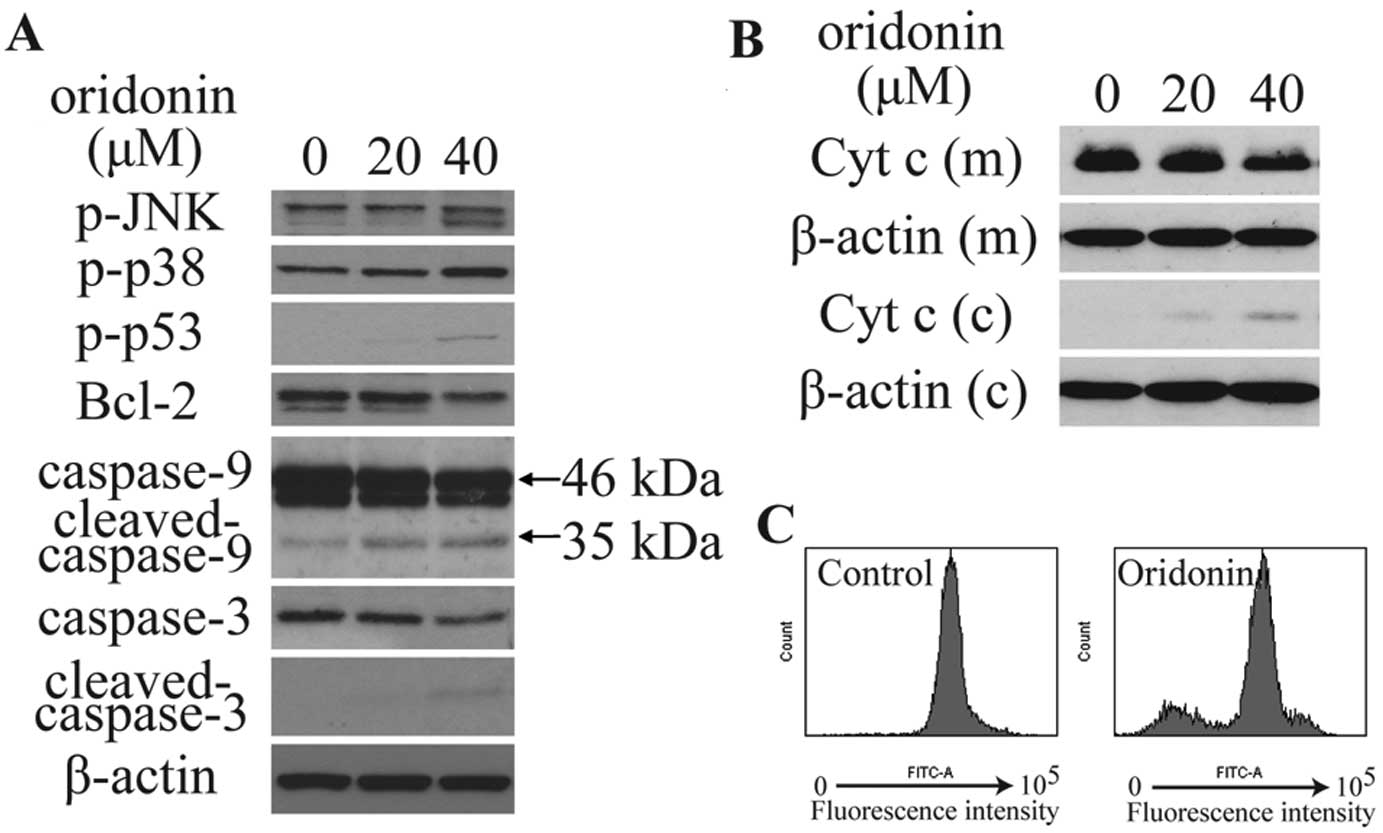
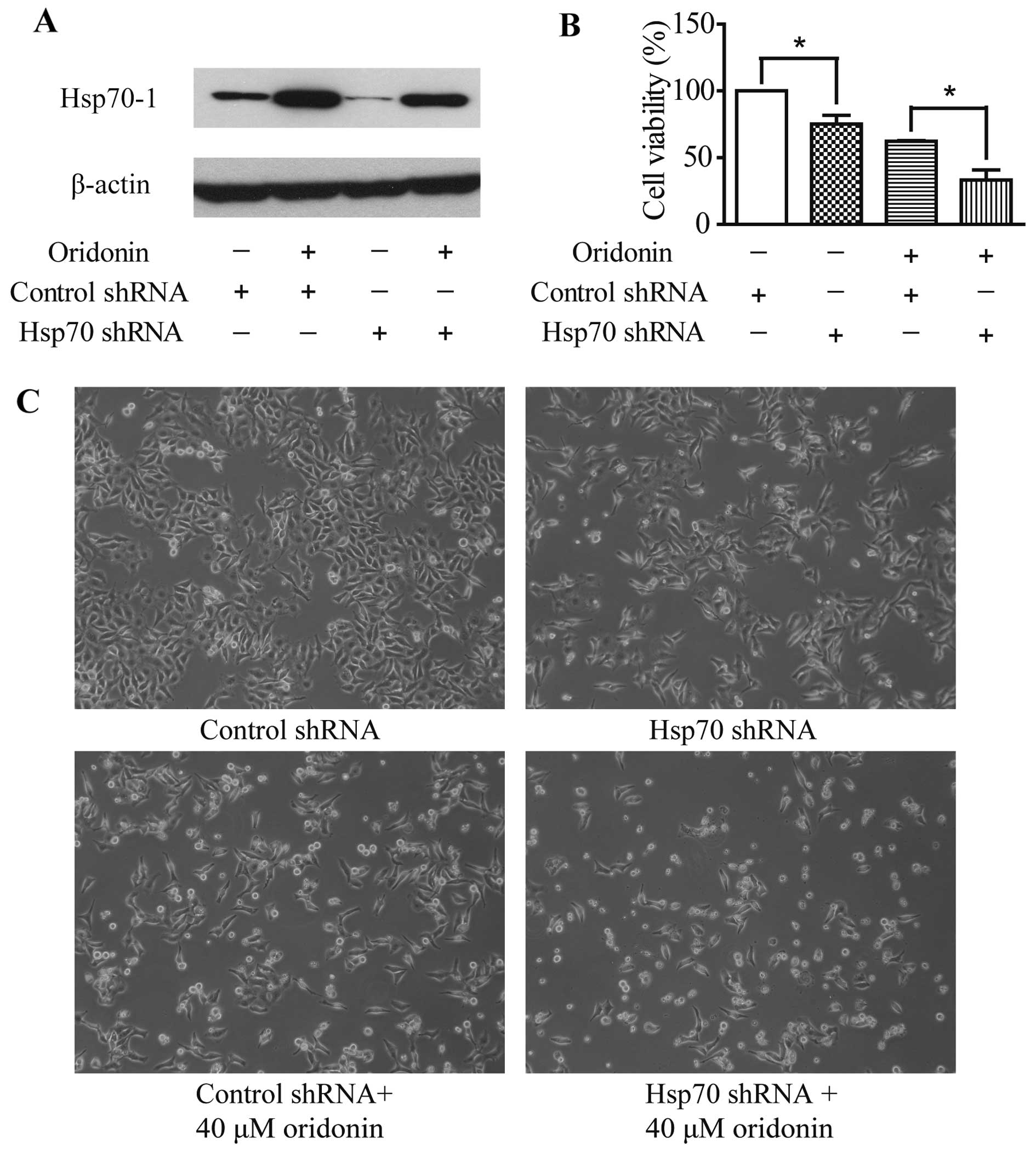
|
1
|
Gao X, Liu SZ, Liu QL, Liu YY, Zeng DL and
Deng MD: Clinical study on anti-cancer effects of Rabdosia
rubescens. Chin J Cancer. 3:201–202. 1984.
|
|
2
|
Zhang JF, Chen GH, Lu MQ and Liu JJ:
Antiproliferation effects of oridonin on hepatocellular carcinoma
BEL-7402 cells and its mechanism. Chin Traditional Patent Med.
28:1325–1329. 2006.
|
|
3
|
Huang J, Wei XY, Sun BH, Wu LJ and Ikejima
T: Oridonin induced HepG2 cell death partially through TNFα signal
pathway. Modern Chin Med. 12:28–32. 2010.
|
|
4
|
Cai DT, Jin H, Xiong QX, et al: ER stress
and ASK1-JNK activation contribute to oridonin-induced apoptosis
and growth inhibition in cultured human hepatoblastoma HuH-6 cells.
Mol Cell Biochem. 379:161–169. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang RL: Therapeutic effects of Isodon
rubescens and oridonin preparations in 31 patients with primary
carcinoma of the liver. Ai Zheng. 3:501984.
|
|
6
|
Ha HL, Shin HJ, Feitelson MA and Yu DY:
Oxidative stress and antioxidants in hepatic pathogenesis. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:6035–6043. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morales-González JA: Oxidative Stress and
Chronic Degenerative Diseases - A Role for Antioxidants. InTech.
http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/45722.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Fang J, Nakamura H and Iyer AK:
Tumor-targeted induction of oxystress for cancer therapy. J Drug
Target. 15:475–486. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Papp E, Nardai G, Soti C and Csermely P:
Molecular chaperones, stress proteins and redox homeostasis.
Biofactors. 17:249–257. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Odunuga OO, Longshaw VM and Blatch GL:
Hop: more than an Hsp70/Hsp90 adaptor protein. Bioessays.
26:1058–1068. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kang SW, Chae HZ, Seo MS, Kim K, Baines IC
and Rhee SG: Mammalian peroxiredoxin isoforms can reduce hydrogen
peroxide generated in response to growth factors and tumor necrosis
factor-α. J Biol Chem. 273:6297–6302. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim H, Lee TH, Park ES, et al: Role of
peroxiredoxins in regulating intracellular hydrogen peroxide and
hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in thyroid cells. J Biol Chem.
275:18266–18270. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fratelli M, Demol H, Puype M, et al:
Identification by redox proteomics of glutathionylated proteins in
oxidatively stressed human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:3505–3510. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Paron I, D’Elia A, D’Ambrosio C, et al: A
proteomic approach to identify early molecular targets of oxidative
stress in human epithelial lens cells. Biochem J. 378:929–937.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cesaratto L, Vascotto C, D’Ambrosio C, et
al: Overoxidation of peroxiredoxins as an immediate and sensitive
marker of oxidative stress in HepG2 cells and its application to
the redox effects induced by ischemia/reperfusion in human liver.
Free Radic Res. 39:255–268. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang T, Tamae D, LeBon T, Shively JE, Yen
Y and Li JJ: The role of peroxiredoxin II in radiation-resistant
MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 65:10338–10346. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pan JS, Hong MZ and Ren JL: Reactive
oxygen species: a double-edged sword in oncogenesis. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:1702–1707. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu GS: The functional interactions between
the p53 and MAPK signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 3:156–161.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shen Y and White E: p53-dependent
apoptosis pathways. Adv Cancer Res. 82:55–84. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang H, Ye Y, Chui JH, et al: Oridonin
induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through MAPK and p53
signaling pathways in HepG2 cells. Oncol Rep. 24:647–651.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang JF, Liu JJ, Liu PQ, Lin DJ, Li XD
and Chen GH: Oridonin inhibits cell growth by induction of
apoptosis on human hepatocelluar carcinoma BEL-7402 cells. Hepatol
Res. 35:104–110. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang H, Ye Y, Chu JH, Zhu GY, Fong WF and
Yu ZL: Proteomic and functional analyses reveal the potential
involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress and α-CP1 in the
anticancer activities of oridonin in HepG2 cells. Integr Cancer
Ther. 10:160–167. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang JF, Chen GH, Lu MQ, Li H, Cai CJ and
Yang Y: Change of Bcl-2 expression and telomerase during apoptosis
induced by oridonin on human hepatocelluar carcinoma cells.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 31:1811–1814. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Yoon SO, Yun CH and Chung AS: Dose effect
of oxidative stress on signal transduction in aging. Mech Ageing
Dev. 123:1597–1604. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu J, Shen HM and Ong CN: Role of
intracellular thiol depletion, mitochondrial dysfunction and
reactive oxygen species in Salvia
miltiorrhiza-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells.
Life Sci. 69:1833–1850. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Datta K, Babbar P, Srivastava T, Sinha S
and Chattopadhyay P: p53 dependent apoptosis in glioma cell lines
in response to hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative stress. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 34:148–157. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Haruna S, Kuroi R, Kajiwara K, et al:
Induction of apoptosis in HL-60 cells by photochemically generated
hydroxyl radicals. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 12:675–676. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Du Y, Villeneuve NF, Wang XJ, et al:
Oridonin confers protection against arsenic-induced toxicity
through activation of the Nrf2-mediated defensive response. Environ
Health Perspect. 116:1154–1161. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zang L, He H, Xu Q, et al: Reactive oxygen
species H2O2 and radical •OH, but not
O2• − promote oridonin-induced phagocytosis of apoptotic
cells by human histocytic lymphoma U937 cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
15:414–423. 2013.
|
|
31
|
Cheng Y, Qiu F, Ye YC, et al: Autophagy
inhibits reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis via activating
p38-nuclear factor-kappa B survival pathways in oridonin-treated
murine fibrosarcoma L929 cells. FEBS J. 276:1291–1306. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Huang J, Wu L, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Reactive oxygen species mediate oridonin-induced HepG2
apoptosis through p53, MAPK, and mitochondrial signaling pathways.
J Pharmacol Sci. 107:370–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu Y, Fan SM, Song JK, Tashiro S, Onodera
S and Ikejima T: Hydroxyl radical (•OH) played a pivotal role in
oridonin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in human epidermoid
carcinoma A431 cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:2148–2159. 2012.
|
|
34
|
McCubrey JA, Lahair MM and Franklin RA:
Reactive oxygen species-induced activation of the MAP kinase
signaling pathways. Antioxid Redox Signal. 8:1775–1789. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schuler M and Green DR: Mechanisms of
p53-dependent apoptosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 29:684–688. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|