|
1
|
Khan S, Chatra L, Prashanth SK, et al:
Pathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis. J Cancer Res Ther.
8:199–203. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Arakeri G and Brennan PA: Oral submucous
fibrosis: an overview of the aetiology, pathogenesis,
classification, and principles of management. Br J Oral
Maxillofacial Surg. 51:587–593. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cox SC and Walker DM: Oral submucous
fibrosis. A review. Aust Dent J. 41:294–299. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mahomed F: Oral submucous fibrosis - a
potentially malignant condition of growing concern. SADJ.
67:562–565. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chole RH, Gondivkar SM, Gadbail AR, et al:
Review of drug treatment of oral submucous fibrosis. Oral Oncol.
48:393–398. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Paissat DK: Oral submucous fibrosis. Int J
Oral Surg. 10:307–312. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aziz SR: Oral submucous fibrosis: an
unusual disease. J N J Dent Assoc. 68:17–19. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
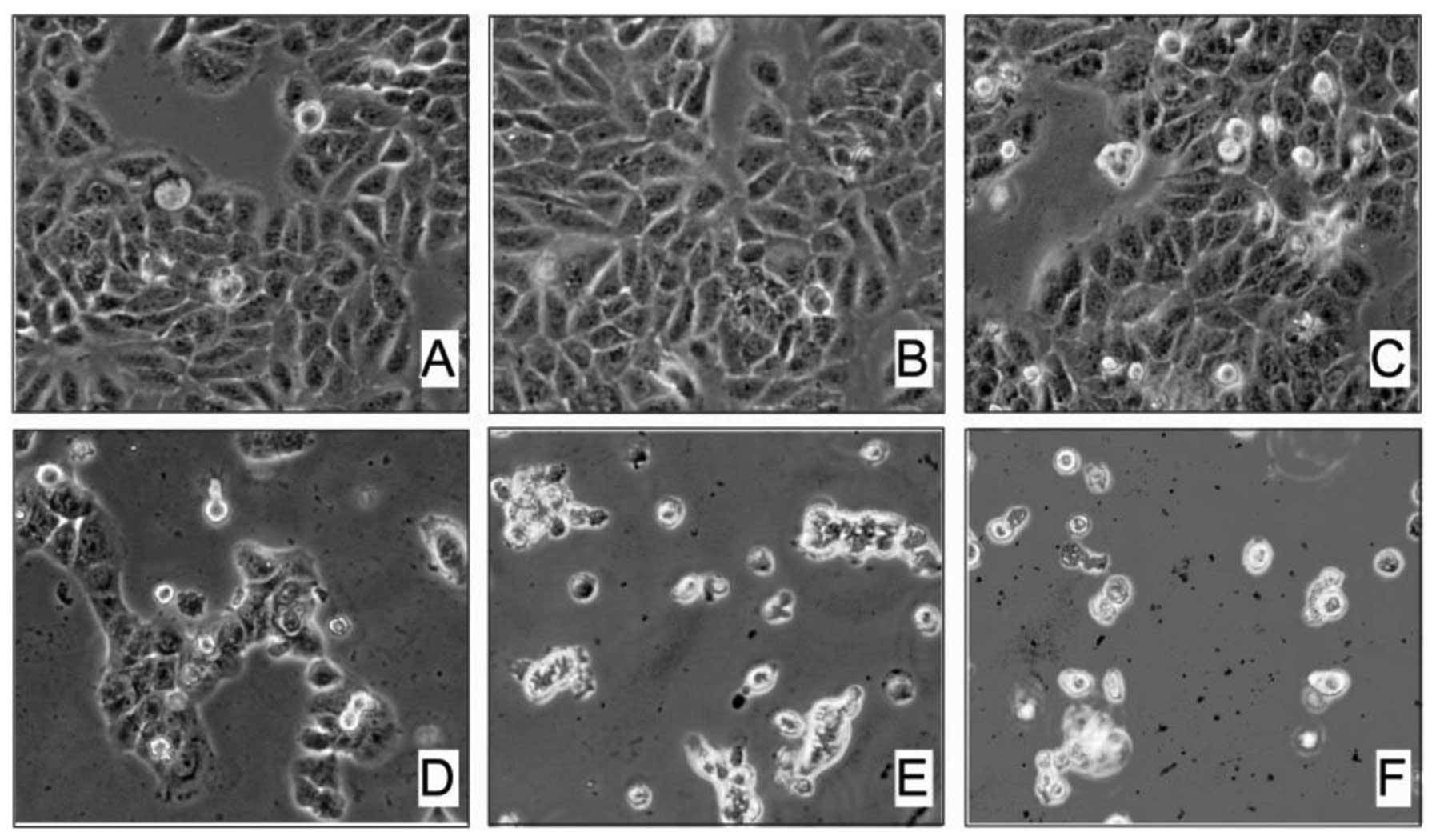
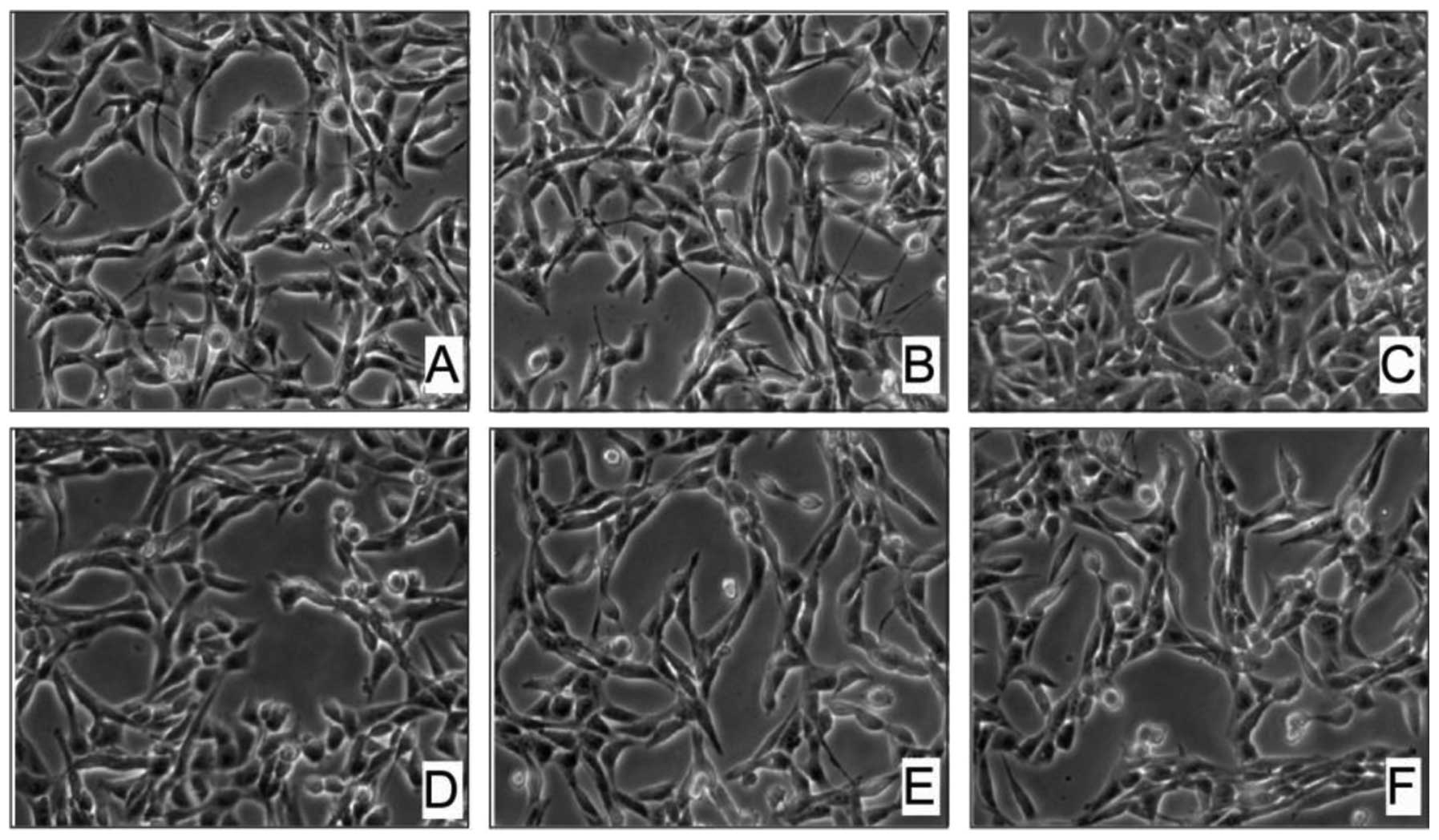
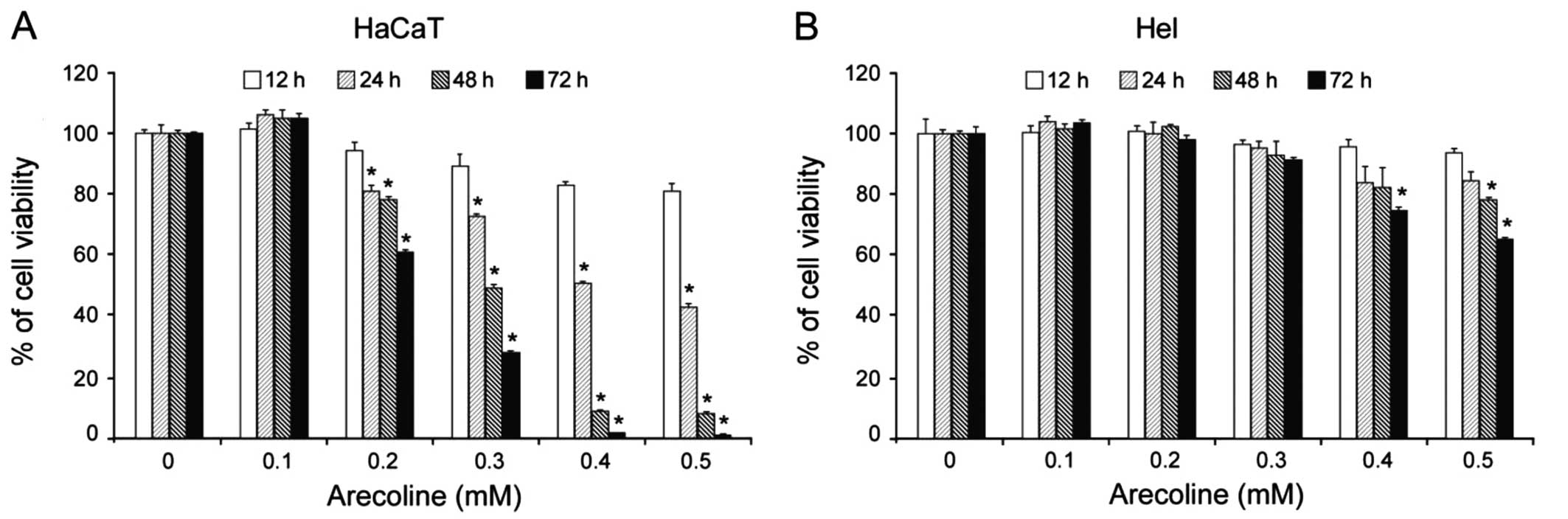
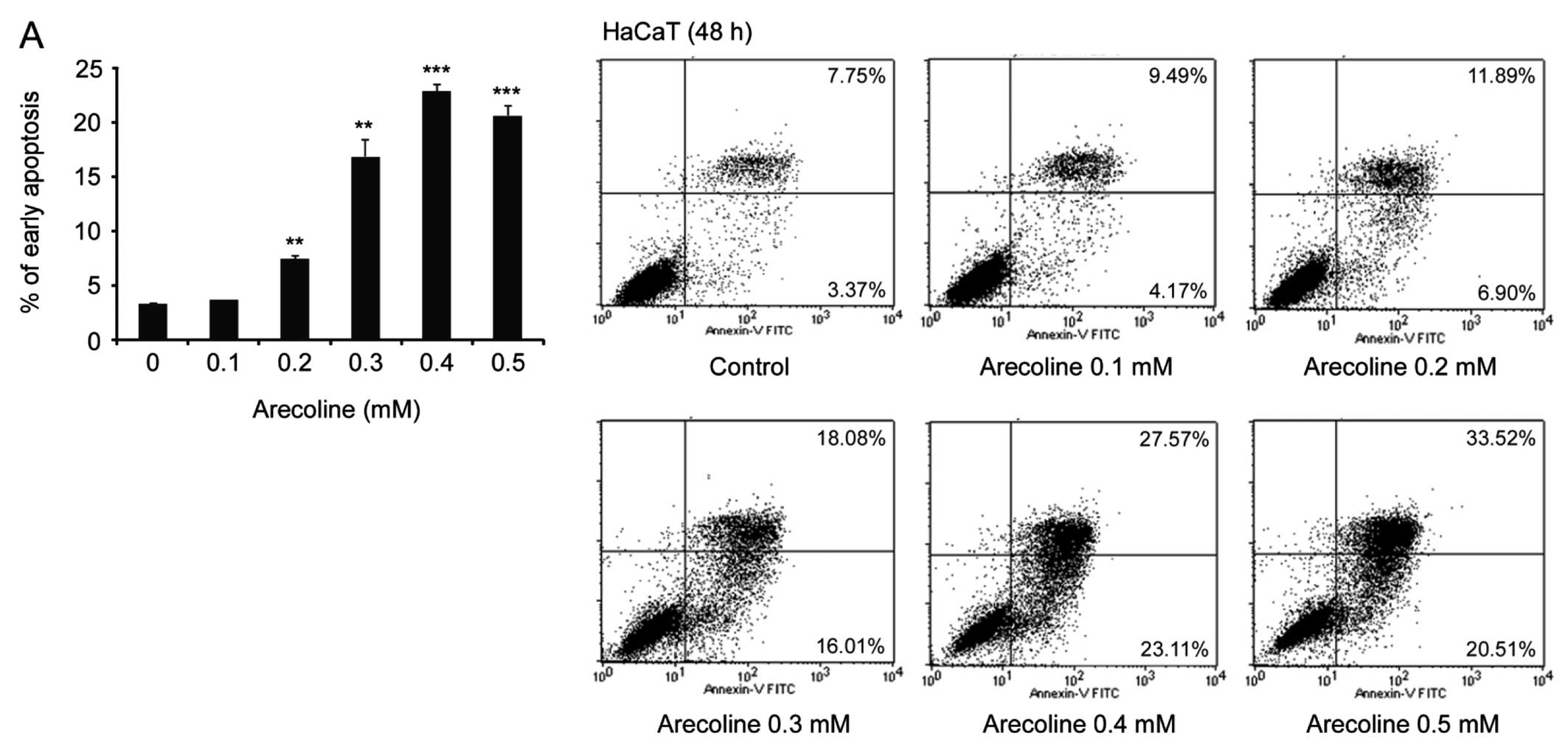
|
8
|
Warnakulasuriya S, Johnson NW and van der
Waal I: Nomenclature and classification of potentially malignant
disorders of the oral mucosa. J Oral Pathol Med. 36:575–580. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tilakaratne WM, Klinikowski MF, Saku T, et
al: Oral submucous fibrosis: review on aetiology and pathogenesis.
Oral Oncol. 42:561–568. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Walvekar RR, Chaukar DA, Deshpande MS, et
al: Verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity: a clinical and
pathological study of 101 cases. Oral Oncol. 45:47–51. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thomas SJ, Bain CJ, Battistutta D, et al:
Betel quid not containing tobacco and oral cancer: a report on a
case-control study in Papua New Guinea and a meta-analysis of
current evidence. Int J Cancer. 120:1318–1323. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ko YC, Huang YL, Lee CH, et al: Betel quid
chewing, cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption related to oral
cancer in Taiwan. J Oral Pathol Med. 24:450–453. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Panigrahi GB and Rao AR:
Chromosome-breaking ability of arecoline, a major betel-nut
alkaloid, in mouse bone-marrow cells in vivo. Mutat Res.
103:197–204. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chou WW, Guh JY, Tsai JF, et al:
Arecoline-induced phosphorylated p53 and p21(WAF1) protein
expression is dependent on ATM/ATR and
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase in clone-9 cells. J Cell Biochem.
107:408–417. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stich HF, Stich W and Lam PP: Potentiation
of genotoxicity by concurrent application of compounds found in
betel quid: arecoline, eugenol, quercetin, chlorogenic acid and
Mn2+. Mutat Res. 90:355–363. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jeng JH, Chang MC and Hahn LJ: Role of
areca nut in betel quid-associated chemical carcinogenesis: current
awareness and future perspectives. Oral Oncol. 37:477–492. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dasgupta R, Saha I, Pal S, et al:
Immunosuppression, hepatotoxicity and depression of antioxidant
status by arecoline in albino mice. Toxicology. 227:94–104. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Grutter MG: Caspases: key players in
programmed cell death. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 10:649–655. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Crowder RN and El-Deiry WS: Caspase-8
regulation of TRAIL-mediated cell death. Exp Oncol. 34:160–164.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cory S and Adams JM: The Bcl2 family:
regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:647–656. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ghiotto F, Fais F and Bruno S: BH3-only
proteins: the death-puppeteer’s wires. Cytometry A. 77:11–21.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tait SW and Green DR: Mitochondria and
cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 11:621–632. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kantari C and Walczak H: Caspase-8 and
bid: caught in the act between death receptors and mitochondria.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:558–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang K, Yin XM, Chao DT, et al: BID: a
novel BH3 domain-only death agonist. Genes Dev. 10:2859–2869. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ, et al: Cleavage of BID
by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway
of apoptosis. Cell. 94:491–501. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, et al: Bid, a
Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release from
mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death
receptors. Cell. 94:481–490. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gross A, Yin XM, Wang K, et al: Caspase
cleaved BID targets mitochondria and is required for cytochrome
c release, while BCL-XL prevents this release but not tumor
necrosis factor-R1/Fas death. J Biol Chem. 274:1156–1163.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reichart PA: Oral cancer and precancer
related to betel and miang chewing in Thailand: a review. J Oral
Pathol Med. 24:241–243. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Trivedy CR, Craig G and Warnakulasuriya S:
The oral health consequences of chewing areca nut. Addict Biol.
7:115–125. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of
Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Betel-quid and areca-nut chewing and
some areca-nut derived nitrosamines. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog
Risks Hum. 85:1–334. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chang MC, Lin LD, Wu HL, et al: Areca
nut-induced buccal mucosa fibroblast contraction and its signaling:
a potential role in oral submucous fibrosis - a precancer
condition. Carcinogenesis. 34:1096–1104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li X, Ling TY, Gao YJ, Tang DS and Li WH:
Arecoline and oral keratinocytes may affect the collagen metabolism
of fibroblasts. J Oral Pathol Med. 38:422–426. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang SF, Hsieh YS, Tsai CH, et al:
Increased plasminogen activator inhibitor-1/tissue type plasminogen
activator ratio in oral submucous fibrosis. Oral Dis. 13:234–238.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chiang SL, Chen PH, Lee CH, et al:
Up-regulation of inflammatory signalings by areca nut extract and
role of cyclooxygenase-2-1195G>a polymorphism reveal risk of
oral cancer. Cancer Res. 68:8489–8498. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shieh DH, Chiang LC and Shieh TY:
Augmented mRNA expression of tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase-1 in buccal mucosal fibroblasts by arecoline and
safrole as a possible pathogenesis for oral submucous fibrosis.
Oral Oncol. 39:728–735. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shieh DH, Chiang LC, Lee CH, et al:
Effects of arecoline, safrole, and nicotine on collagen
phagocytosis by human buccal mucosal fibroblasts as a possible
mechanism for oral submucous fibrosis in Taiwan. J Oral Pathol Med.
33:581–587. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Khan I, Kumar N, Pant I, et al: Activation
of TGF-beta pathway by areca nut constituents: a possible cause of
oral submucous fibrosis. PloS One. 7:e518062012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kale AD, Mane DR and Shukla D: Expression
of transforming growth factor beta and its correlation with
lipodystrophy in oral submucous fibrosis: an immunohistochemical
study. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 18:e12–e18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yu CC, Tsai CH, Hsu HI, et al: Elevation
of S100A4 expression in buccal mucosal fibroblasts by arecoline:
involvement in the pathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis. PloS
One. 8:e551222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Deng YT, Chen HM, Cheng SJ, et al:
Arecoline-stimulated connective tissue growth factor production in
human buccal mucosal fibroblasts: modulation by curcumin. Oral
Oncol. 45:e99–e105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nair J, Ohshima H, Friesen M, et al:
Tobacco-specific and betel nut-specific N-nitroso compounds:
occurrence in saliva and urine of betel quid chewers and formation
in vitro by nitrosation of betel quid. Carcinogenesis. 6:295–303.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shirname LP, Menon MM, Nair J, et al:
Correlation of mutagenicity and tumorigenicity of betel quid and
its ingredients. Nutr Cancer. 5:87–91. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cox S, Vickers ER, Ghu S and Zoellner H:
Salivary arecoline levels during areca nut chewing in human
volunteers. J Oral Pathol Med. 39:465–469. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sundqvist K, Liu Y, Nair J, et al:
Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of areca nut-related compounds in
cultured human buccal epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 49:5294–5298.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee PH, Chang MC, Chang WH, et al:
Prolonged exposure to arecoline arrested human KB epithelial cell
growth: regulatory mechanisms of cell cycle and apoptosis.
Toxicology. 220:81–89. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tseng SK, Chang MC, Su CY, et al:
Arecoline induced cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and cytotoxicity to
human endothelial cells. Clin Oral Investig. 16:1267–1273. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhou ZS, Li M, Gao F, et al: Arecoline
suppresses HaCaT cell proliferation through cell cycle regulatory
molecules. Oncol Rep. 29:2438–2444. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shih YT, Chen PS, Wu CH, et al: Arecoline,
a major alkaloid of the areca nut, causes neurotoxicity through
enhancement of oxidative stress and suppression of the antioxidant
protective system. Free Radic Biol Med. 49:1471–1479. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cheng HL, Su SJ, Huang LW, et al:
Arecoline induces HA22T/VGH hepatoma cells to undergo anoikis -
involvement of STAT3 and RhoA activation. Mol Cancer. 9:1262010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|