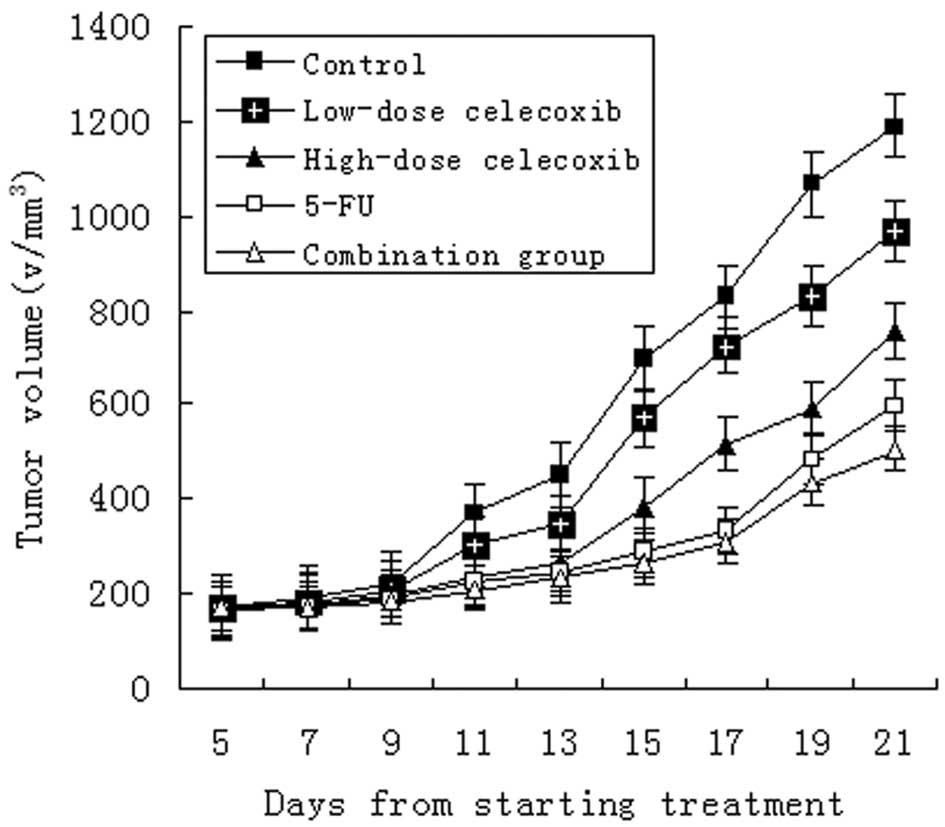
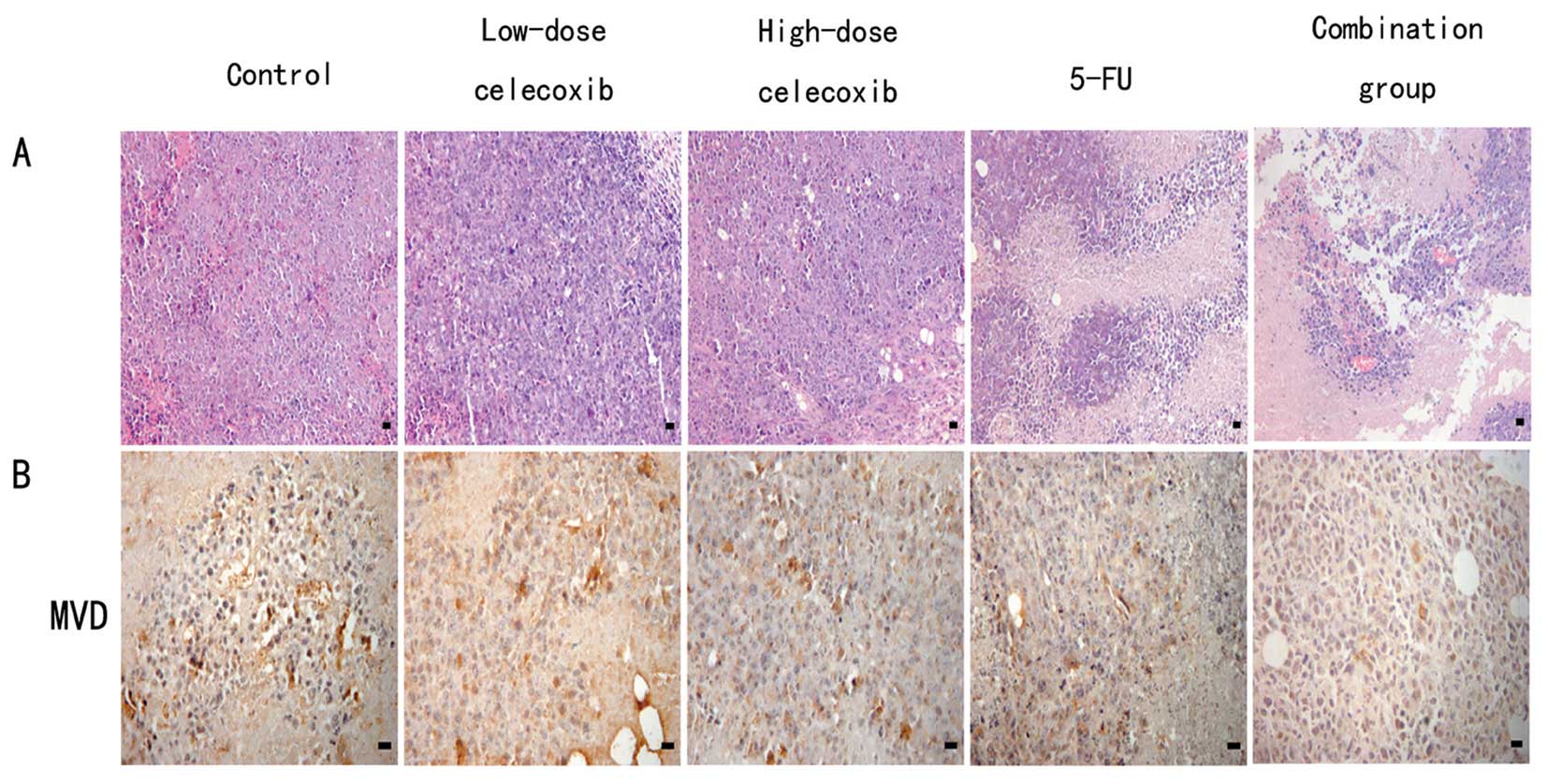
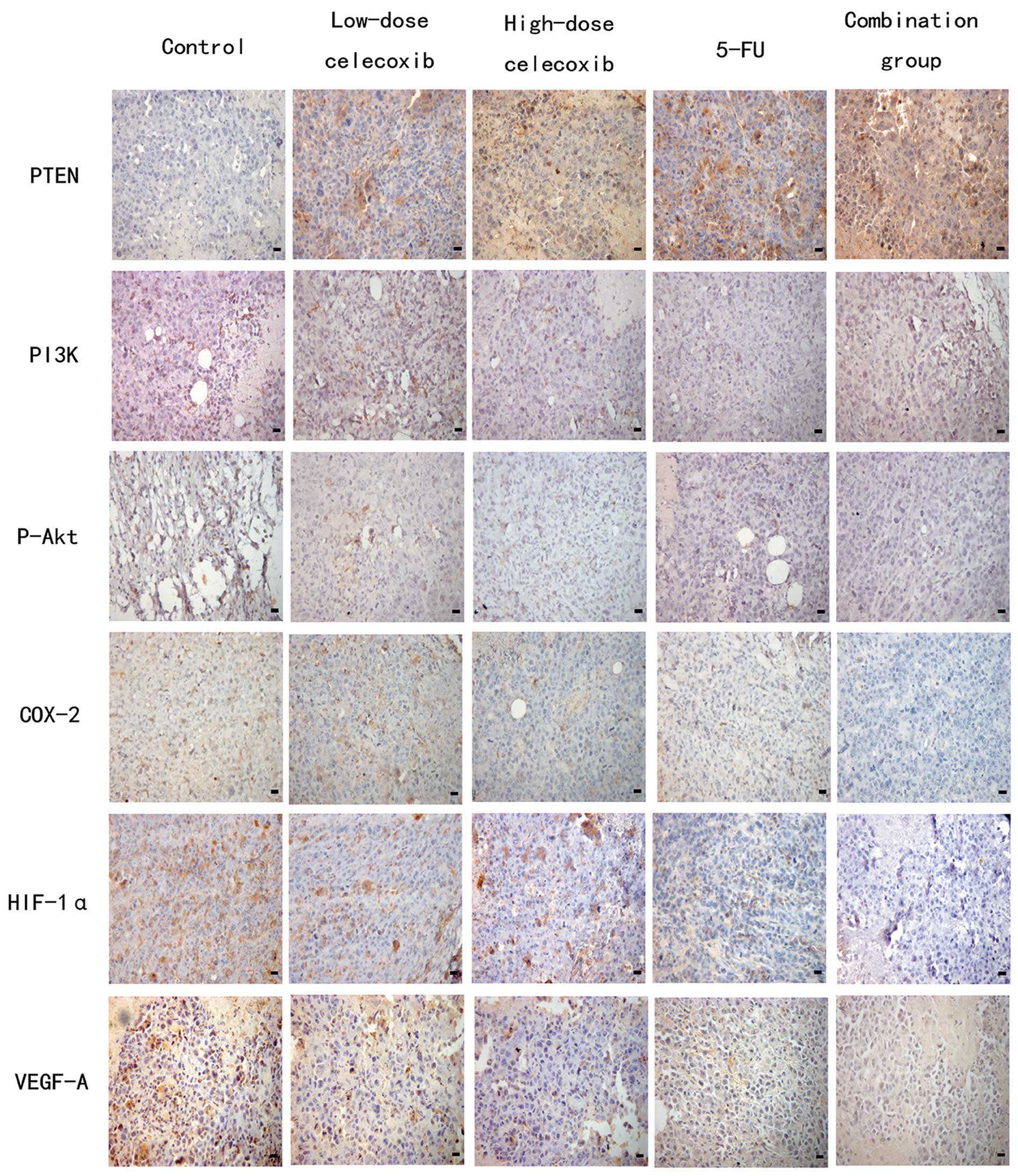
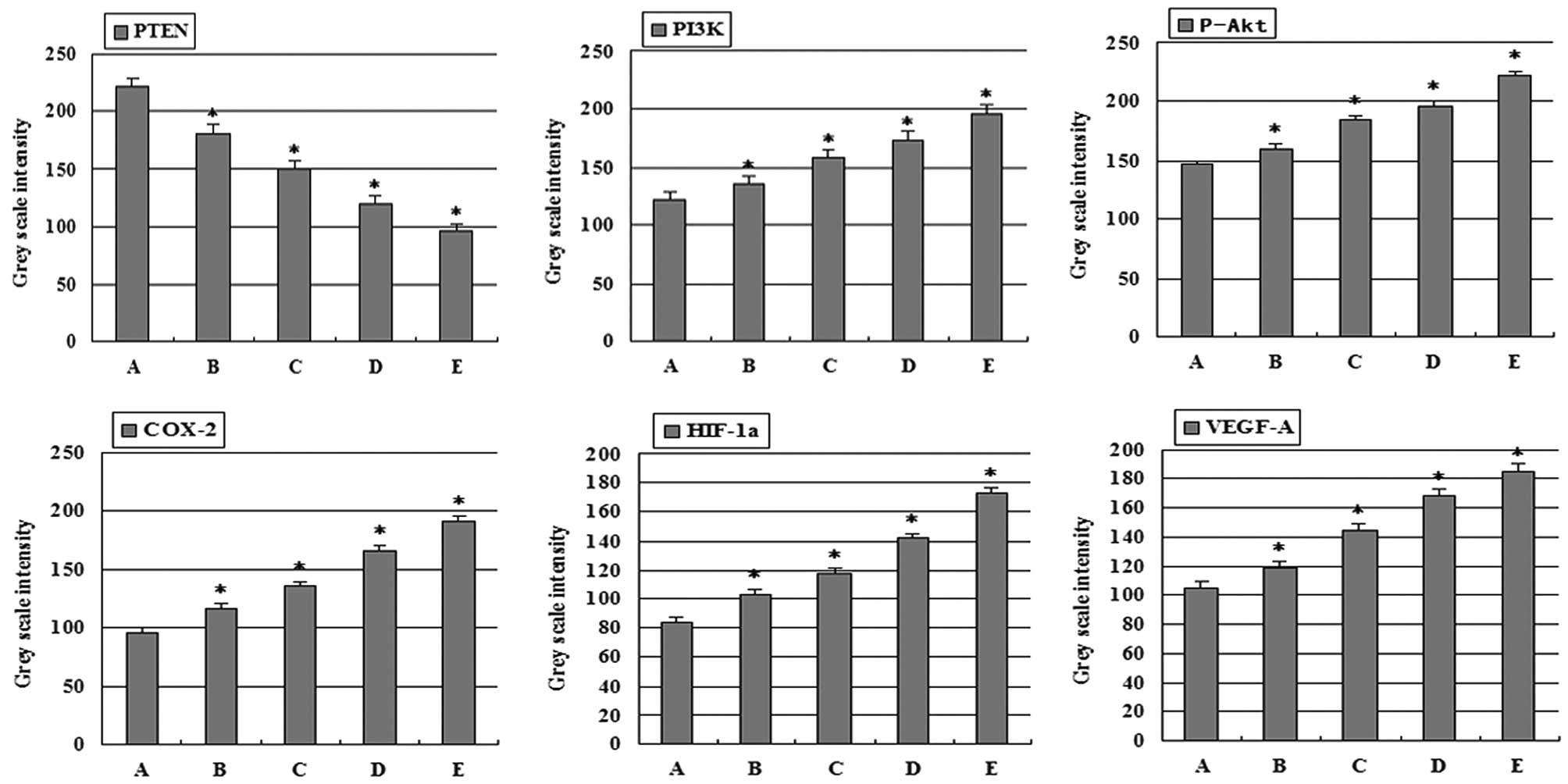
|
1
|
Llovet JM, Burroughs A and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 362:1907–1917. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Nordenstedt H, White DL and El-Serag HB:
The changing pattern of epidemiology in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Dig Liver Dis. 42(Suppl 3): S206–S214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vinogradova Y, Hippisley-Cox J, Coupland C
and Logan RF: Risk of colorectal cancer in patients prescribed
statins, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and cyclooxygenase-2
inhibitors: nested case-control study. Gastroenterology.
133:393–402. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cui W, Yu CH and Hu KQ: In vitro and in
vivo effects and mechanisms of celecoxib-induced growth inhibition
of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res.
11:8213–8221. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim HS, Youm HR, Lee JS, Min KW, Chung JH
and Park CS: Correlation between cyclooxygenase-2 and tumor
angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
42:163–170. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shi H, Xu JM, Hu NZ and Xie HJ: Prognostic
significance of expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and vascular
endothelial growth factor in human gastric carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 9:1421–1426. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yasumaru M, Tsuji S, Tsujii M, et al:
Inhibition of angiotensin II activity enhanced the antitumor effect
of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors via insulin-like growth factor I
receptor pathway. Cancer Res. 63:6726–6734. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Semenza GL: Targeting HIF-1 for cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:721–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zundel W, Schindler C, Haas-Kogan D, et
al: Loss of PTEN facilitates HIF-1-mediated gene expression.
Genes Dev. 14:391–396. 2000.
|
|
10
|
Hudson CC, Liu M, Chiang GG, et al:
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression and function
by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol. 22:7004–7014.
2002.
|
|
11
|
Zhong H, Chiles K, Feldser D, et al:
Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression by the
epidermal growth factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP
pathway in human prostate cancer cells: implications for tumor
angiogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Res. 60:1541–1545. 2000.
|
|
12
|
Carbajo-Pescador S, Ordoñez R, Benet M,
Jover R, García-Palomo A, Mauriz JL and González-Gallego J:
Inhibition of VEGF expression through blockade of Hif1α and STAT3
signalling mediates the anti-angiogenic effect of melatonin in
HepG2 liver cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 109:83–91. 2013.
|
|
13
|
De Francesco EM, Lappano R, Santolla MF,
Marsico S, Caruso A and Maggiolini M: HIF-1α/GPER signaling
mediates the expression of VEGF induced by hypoxia in breast cancer
associated fibroblasts (CAFs). Breast Cancer Res. 15:R642013.
|
|
14
|
Lawlor MA and Alessi DR: PKB/Akt: a key
mediator of cell proliferation, survival and insulin responses? J
Cell Sci. 114:2903–2910. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang BH, Zheng JZ, Aoki M and Vogt PK:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling mediates angiogenesis and
expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in endothelial
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:1749–1753. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Osaki M, Oshimura M and Ito H: PI3K-Akt
pathway: its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis.
9:667–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kulp SK, Yang YT, Hung CC, et al:
3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1/Akt signaling
represents a major cyclooxygenase-2-independent target for
celecoxib in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 64:1444–1451. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Basu GD, Pathangey LB, Tinder TL, Lagioia
M, Gendler SJ and Mukherjee P: Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor induces
apoptosis in breast cancer cells in an in vivo model of spontaneous
metastatic breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2:632–642.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Leahy KM, Ornberg RL, Wang Y, Zweifel BS,
Koki AT and Masferrer JL: Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition by celecoxib
reduces proliferation and induces apoptosis in angiogenic
endothelial cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 62:625–631. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ragel BT, Jensen RL, Gillespie DL,
Prescott SM and Couldwell WT: Celecoxib inhibits meningioma tumor
growth in a mouse xenograft model. Cancer. 109:588–597. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Weidner N, Carroll PR, Flax J, Blumenfeld
W and Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in
invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 143:401–409.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Whittaker S, Marais R and Zhu AX: The role
of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 29:4989–5005. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang FZ, Peng-Jiao, Yang NN, et al:
PF-04691502 triggers cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and inhibits the
angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Toxicol Lett.
220:150–156. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xin X, Majumder M, Girish GV, Mohindra V,
Maruyama T and Lala PK: Targeting COX-2 and EP4 to control tumor
growth, angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and metastasis to the lungs
and lymph nodes in a breast cancer model. Lab Invest. 92:1115–1128.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma JX, Sun YL, Wang YQ, Wu HY, Jin J and
Yu XF: Triptolide induces apoptosis and inhibits the growth and
angiogenesis of human pancreatic cancer cells by downregulating
COX-2 and VEGF. Oncol Res. 20:359–368. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fang J, Zhou Q, Liu LZ, Xia C, Hu X, Shi X
and Jiang BH: Apigenin inhibits tumor angiogenesis through
decreasing HIF-1α and VEGF expression. Carcinogenesis. 28:858–864.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bassiouny AR, Zaky A and Neenaa HM:
Synergistic effect of celecoxib on 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis
in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Ann Hepatol. 9:410–418.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chow LW, Tung SY, Ng TY, et al: Concurrent
celecoxib with 5-fluorouracil/epirubicin/cyclophosphamide followed
by docetaxel for stages II – III invasive breast cancer: the
OOTR-N001 study. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 22:299–307.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Harris AL: Hypoxia - a key regulatory
factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:38–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yuan TL and Cantley LC: PI3K pathway
alterations in cancer: variations on a theme. Oncogene.
27:5497–5510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J and
Claesson-Welsh L: VEGF receptor signalling? in control of vascular
function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:359–371. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Benjamin LE and Keshet E: Conditional
switching of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression
in tumors: induction of endothelial cell shedding and regression of
hemangioblastoma-like vessels by VEGF withdrawal. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 94:8761–8766. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jiang BH, Jiang G, Zheng JZ, Lu Z, Hunter
T and Vogt PK: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling controls
levels of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell Growth Differ.
12:363–369. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yin F, Giuliano AE, Law RE and Van Herle
AJ: Apigenin inhibits growth and induces G2/M arrest by modulating
cyclin-CDK regulators and ERK MAP kinase activation in breast
carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 21:413–420. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Arsham AM, Plas DR, Thompson CB and Simon
MC: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling is neither required
for hypoxic stabilization of HIF-1α nor sufficient for
HIF-1-dependent target gene transcription. J Biol Chem.
277:15162–15170. 2002.
|
|
36
|
Hamada K, Sasaki T, Koni PA, et al: The
PTEN/PI3K pathway governs normal vascular development and tumor
angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 19:2054–2065. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|