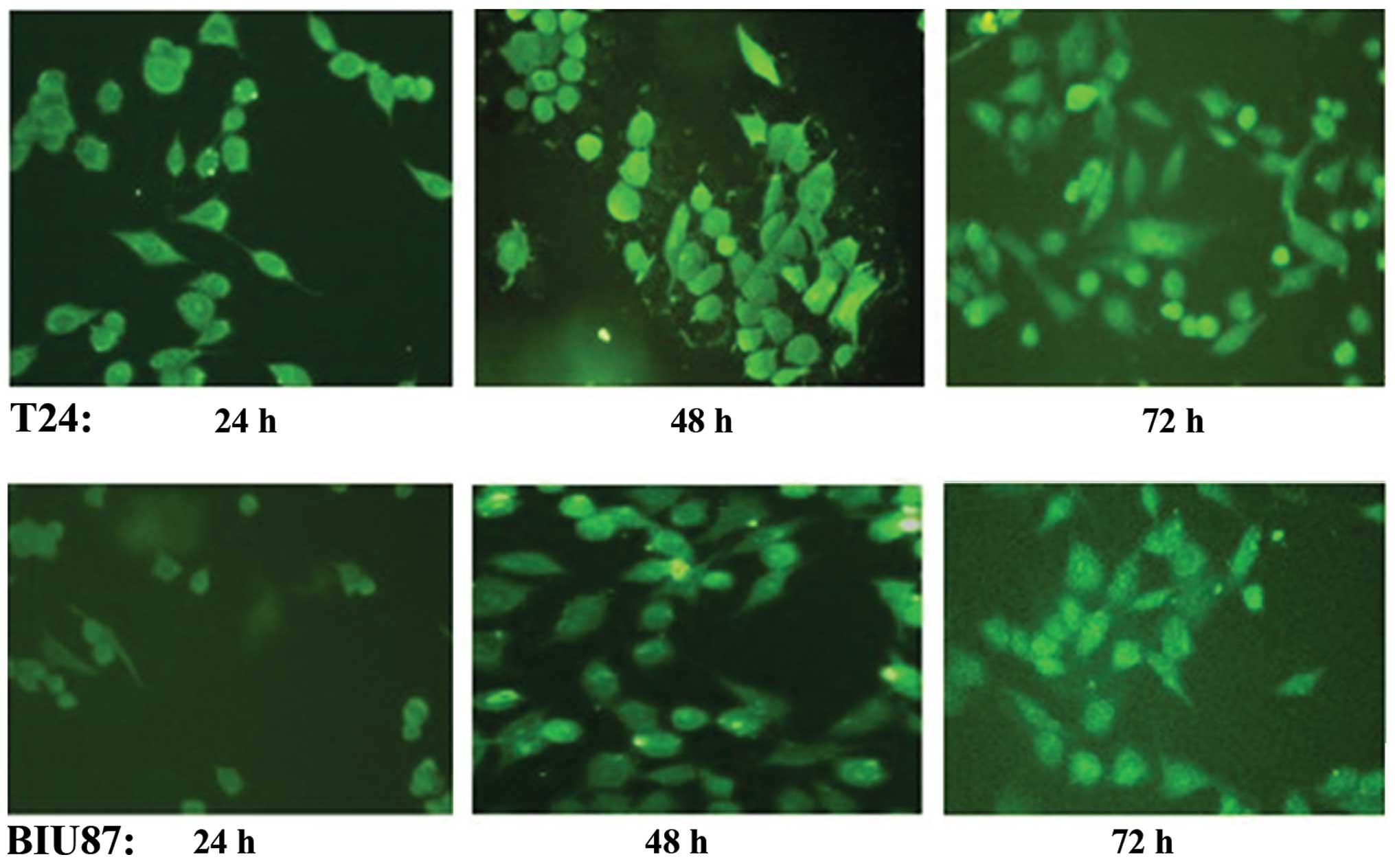
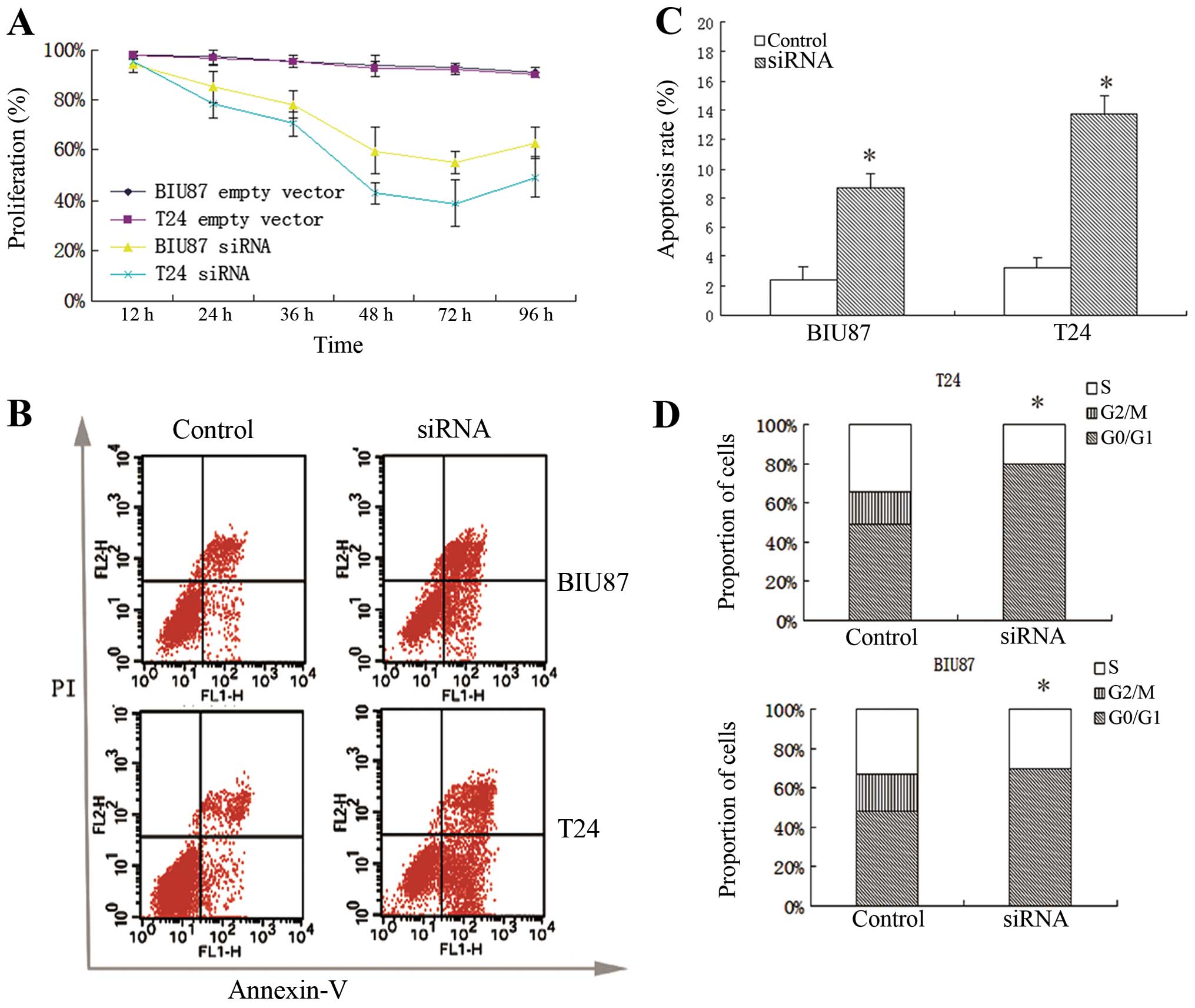
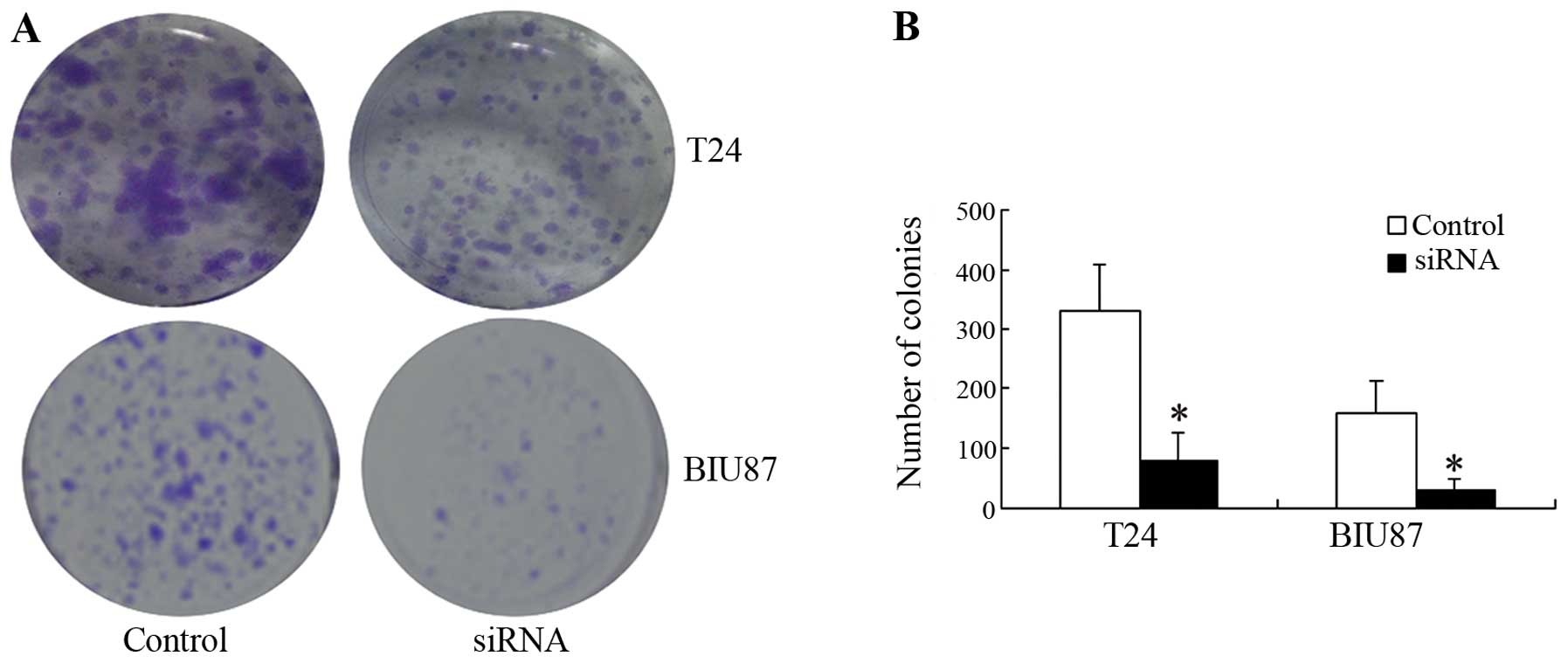
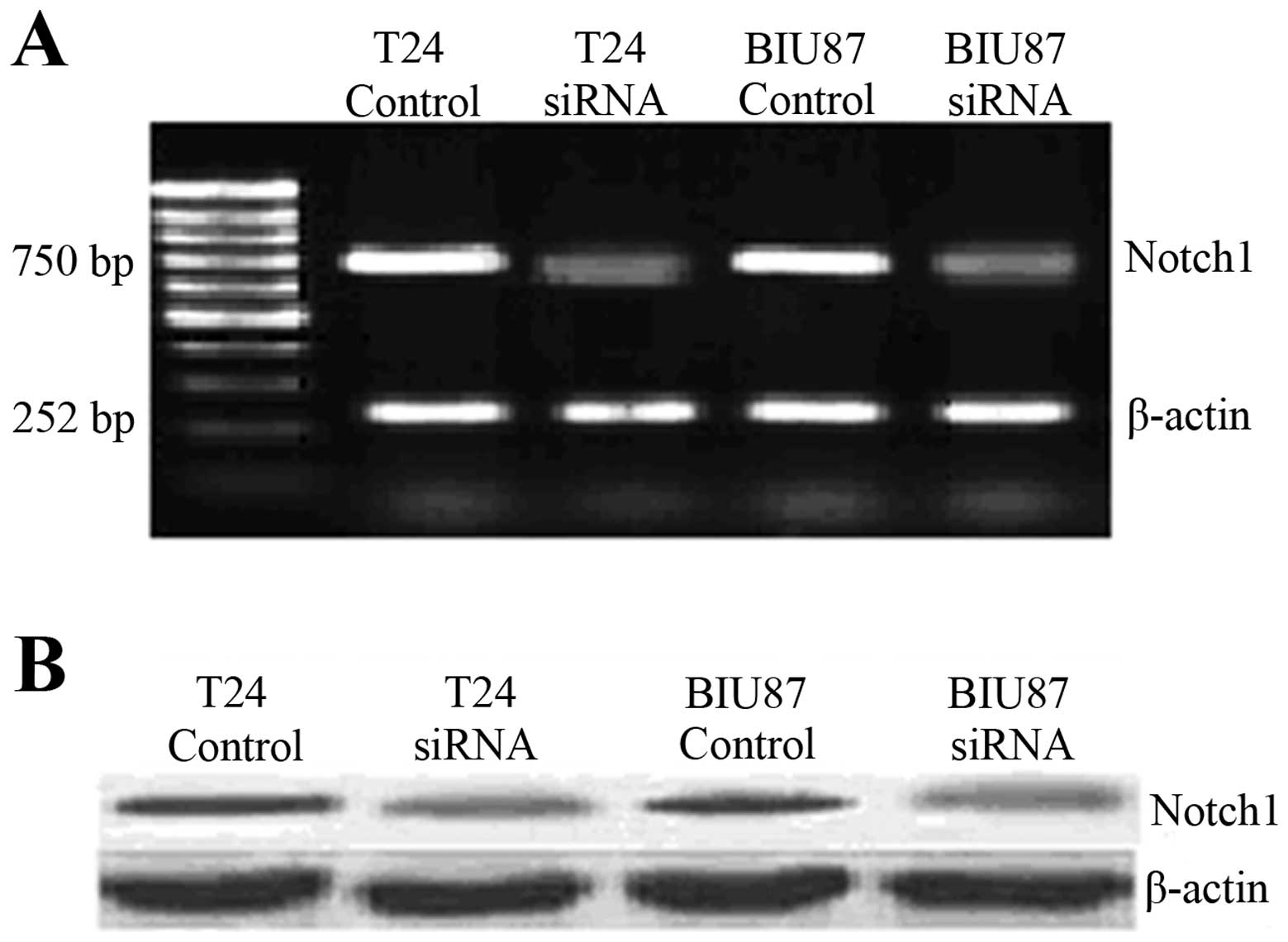
|
1
|
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU and Feldman AS:
Bladder cancer. Lancet. 374:239–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Urist MJ, Di Como CJ, Lu ML, et al: Loss
of p63 expression is associated with tumor progression in bladder
cancer. Am J Pathol. 161:1199–1206. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Junttila TT, Laato M, Vahlberg T, et al:
Identification of patients with transitional cell carcinoma of the
bladder overexpressing ErbB2, ErbB3, or specific ErbB4 isoforms:
real-time reverse transcription-PCR analysis in estimation of ErbB
receptor status from cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 9:5346–5357.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Habuchi T, Marberger M, Droller MJ, et al:
Prognostic markers for bladder cancer: International Consensus
Panel on bladder tumor markers. Urology. 66:64–74. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shinohara N and Koyanagi T: Ras signal
transduction in carcinogenesis and progression of bladder cancer:
molecular target for treatment? Urol Res. 30:273–281. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fletcher A, Choudhury A and Alam N:
Metastatic bladder cancer: a review of current management. ISRN
Urol. 2011:5452412011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hannon GJ: RNA interference. Nature.
418:244–251. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Paddison PJ and Hannon GJ: RNA
interference: the new somatic cell genetics? Cancer Cell. 2:17–23.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mummery-Widmer JL, Yamazaki M, Stoeger T,
et al: Genome-wide analysis of Notch signalling in
Drosophila by transgenic RNAi. Nature. 458:987–992. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Krebs LT, Xue Y, Norton CR, et al: Notch
signaling is essential for vascular morphogenesis in mice. Genes
Dev. 14:1343–1352. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brou C, Logeat F, Gupta N, et al: A novel
proteolytic cleavage involved in Notch signaling: the role of the
disintegrin-metalloprotease TACE. Mol Cell. 5:207–216. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miele L and Osborne B: Arbiter of
differentiation and death: Notch signaling meets apoptosis. J Cell
Physiol. 181:393–409. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu YY, Zheng MH, Zhang R, Liang YM and Han
H: Notch signaling pathway and cancer metastasis. Adv Exp Med Biol.
727:186–198. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Allenspach EJ, Maillard I, Aster JC and
Pear WS: Notch signaling in cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 1:466–476.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ghaleb AM, Aggarwal G, Bialkowska AB,
Nandan MO and Yang VW: Notch inhibits expression of the
Krüppel-like factor 4 tumor suppressor in the intestinal
epithelium. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1920–1927. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bieker JJ: Krüppel-like factors: three
fingers in many pies. J Biol Chem. 276:34355–34358. 2001.
|
|
19
|
Ohnishi S, Ohnami S, Laub F, et al:
Downregulation and growth inhibitory effect of epithelial-type
Krüppel-like transcription factor KLF4, but not KLF5, in bladder
cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 308:251–256. 2003.
|
|
20
|
McConnell BB and Yang VW: Mammalian
Krüppel-like factors in health and diseases. Physiol Rev.
90:1337–1381. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Ai X, Ju HZ and Wu ZH: The construction
and identification of siRNA eukaryotic expression vector targeting
Notch1 gene. J Clin Urol. 5:391–394. 2008.
|
|
22
|
Nicolas M, Wolfer A, Raj K, et al: Notch1
functions as a tumor suppressor in mouse skin. Nat Genet.
33:416–421. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ehebauer M, Hayward P and Arias AM: Notch,
a universal arbiter of cell fate decisions. Science. 314:1414–1415.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Radtke F and Raj K: The role of Notch in
tumorigenesis: oncogene or tumour suppressor? Nat Rev Cancer.
3:756–767. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang L, Qin H, Chen B, Xin X, Li J and Han
H: Overexpressed active Notch1 induces cell growth arrest of HeLa
cervical carcinoma cells. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 17:1283–1292. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Suzuki T, Aoki D, Susumu N, Udagawa Y and
Nozawa S: Imbalanced expression of TAN-1 and human
Notch4 in endometrial cancers. Int J Oncol. 17:1131–1139.
2000.
|
|
27
|
Leethanakul C, Patel V, Gillespie J, et
al: Distinct pattern of expression of differentiation and
growth-related genes in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and
neck revealed by the use of laser capture microdissection and cDNA
arrays. Oncogene. 19:3220–3224. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen Y, De Marco MA, Graziani I, et al:
Oxygen concentration determines the biological effects of Notch-1
signaling in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Cancer Res. 67:7954–7959.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rae FK, Stephenson SA, Nicol DL and
Clements JA: Novel association of a diverse range of genes with
renal cell carcinoma as identified by differential display. Int J
Cancer. 88:726–732. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
van Limpt V, Chan A, Caron H, et al: SAGE
analysis of neuroblastoma reveals a high expression of the human
homologue of the Drosophila Delta gene. Med Pediatr Oncol.
35:554–558. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shi TP, Xu H, Wei JF, et al: Association
of low expression of notch-1 and jagged-1 in human papillary
bladder cancer and shorter survival. J Urol. 180:361–366. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zheng H, Pritchard DM, Yang X, et al: KLF4
gene expression is inhibited by the notch signaling pathway that
controls goblet cell differentiation in mouse gastrointestinal
tract. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 296:G490–G498.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|