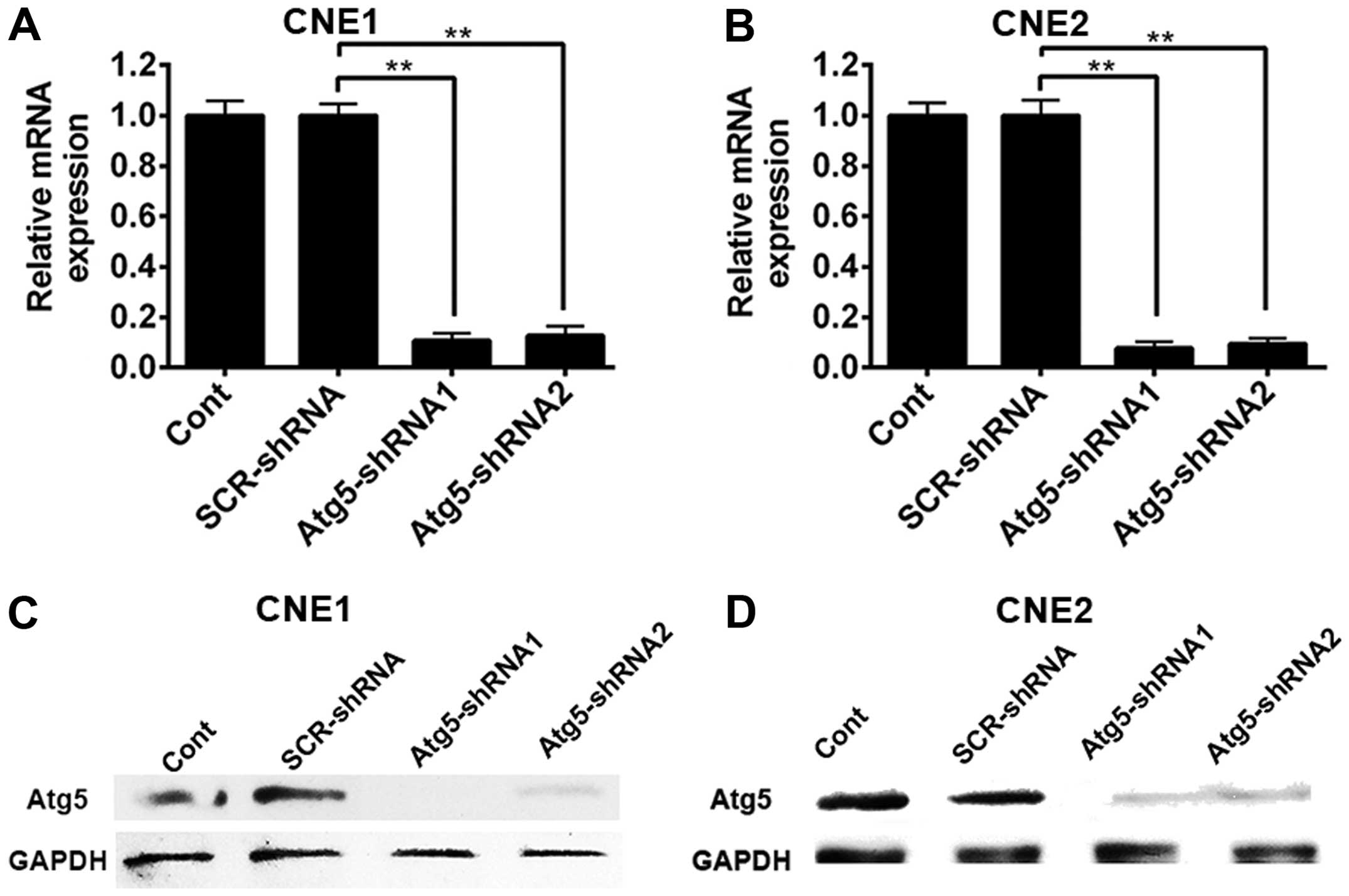
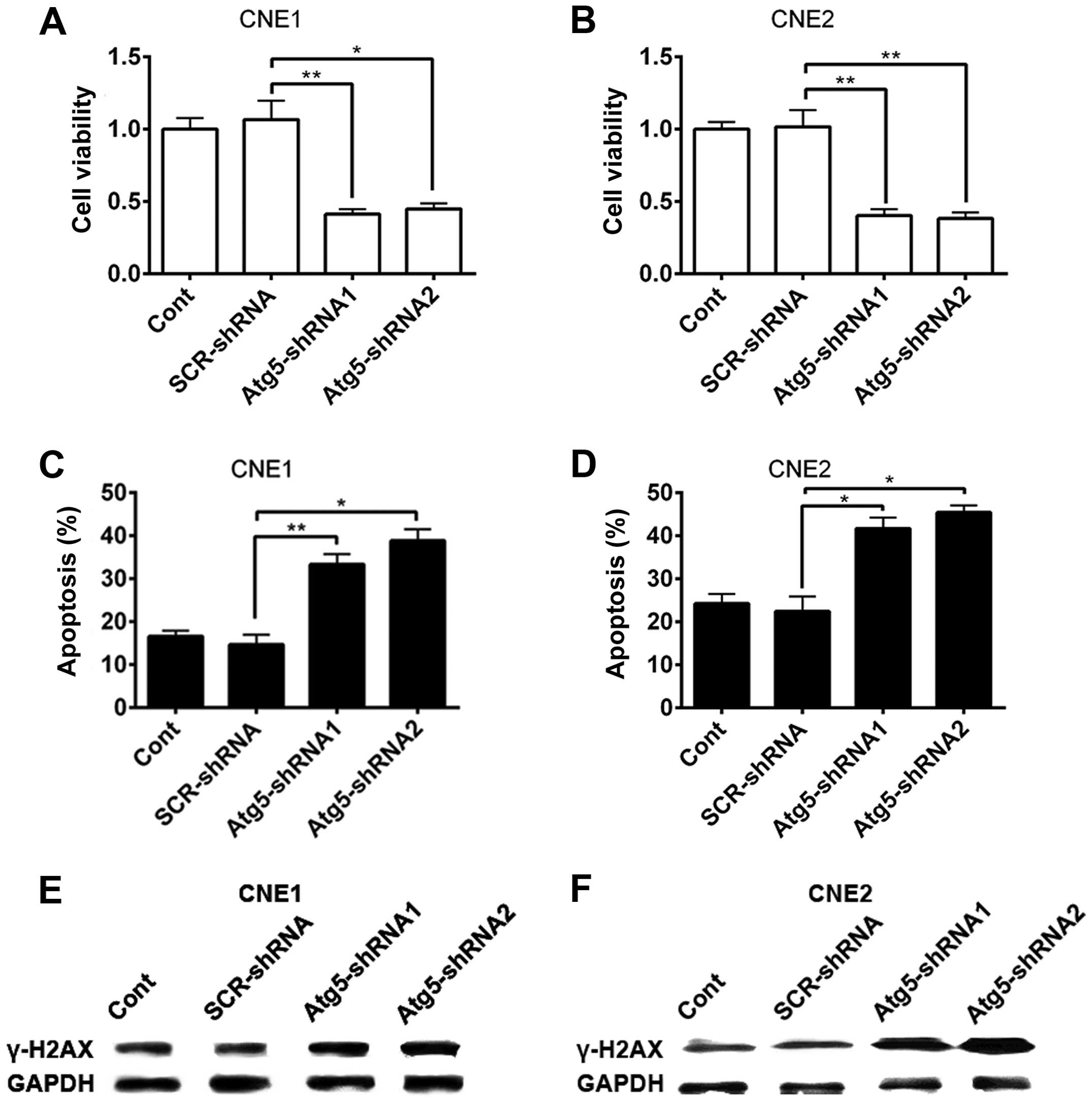
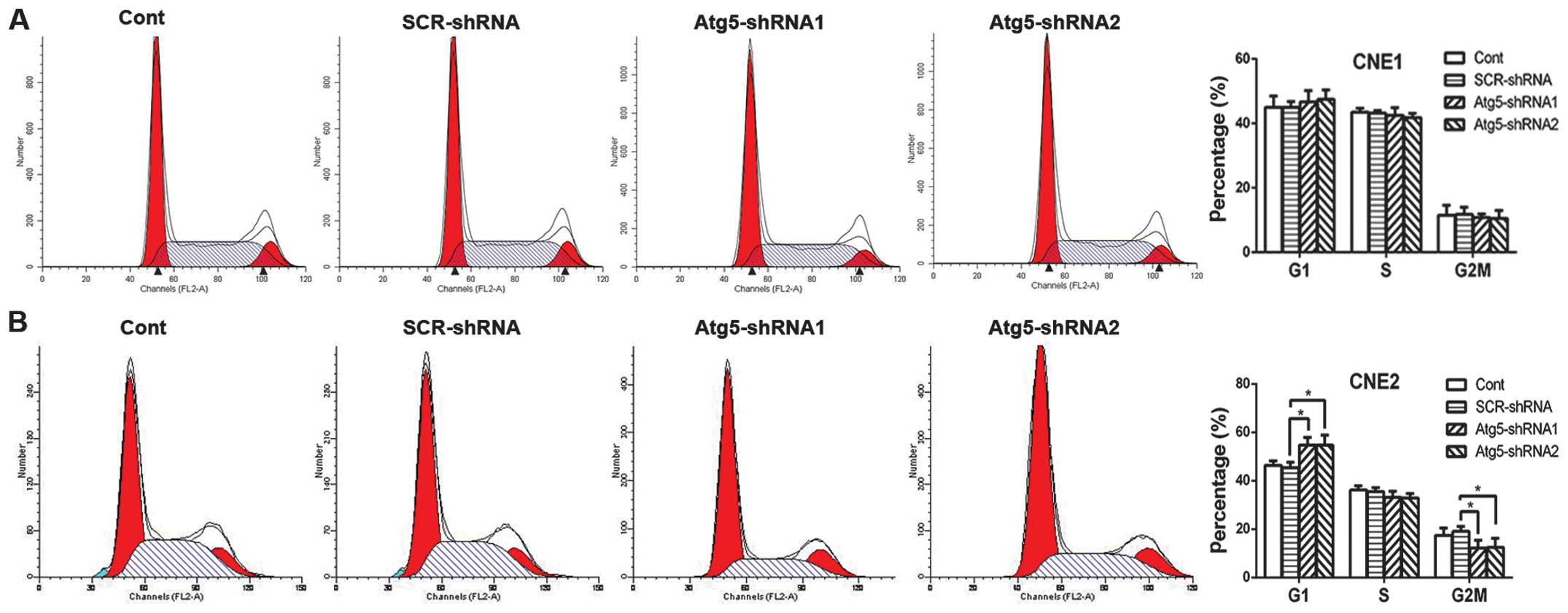
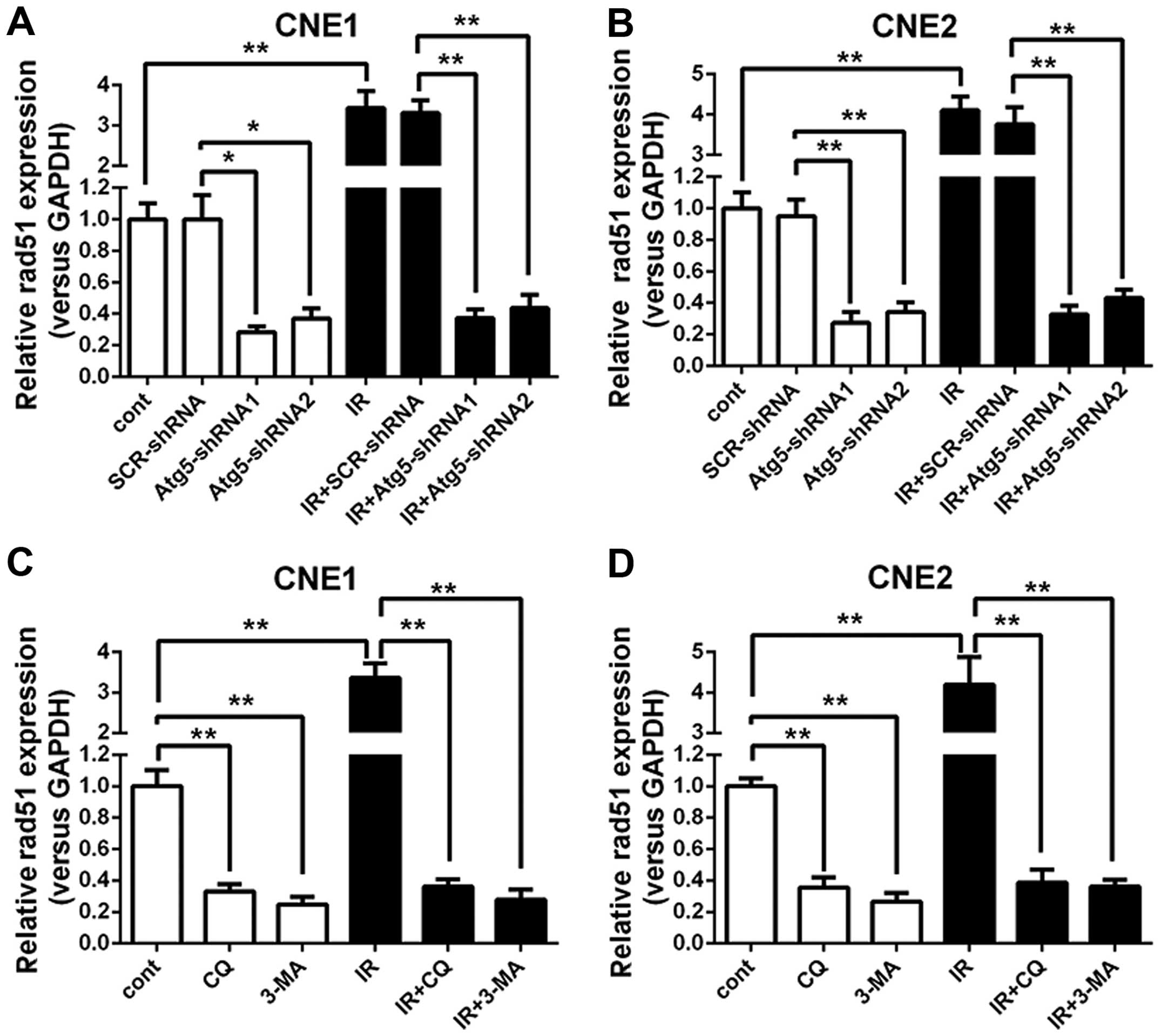
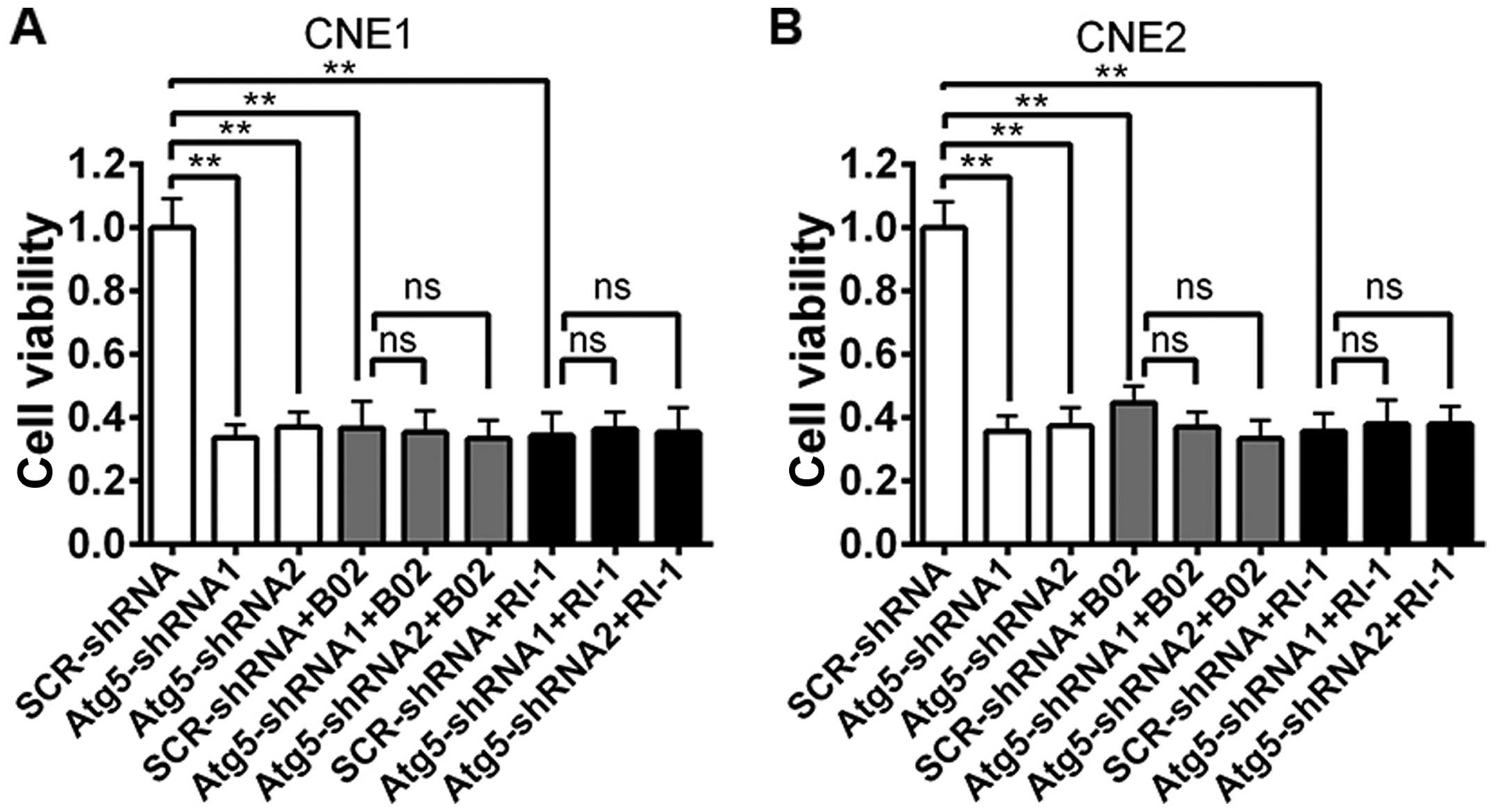
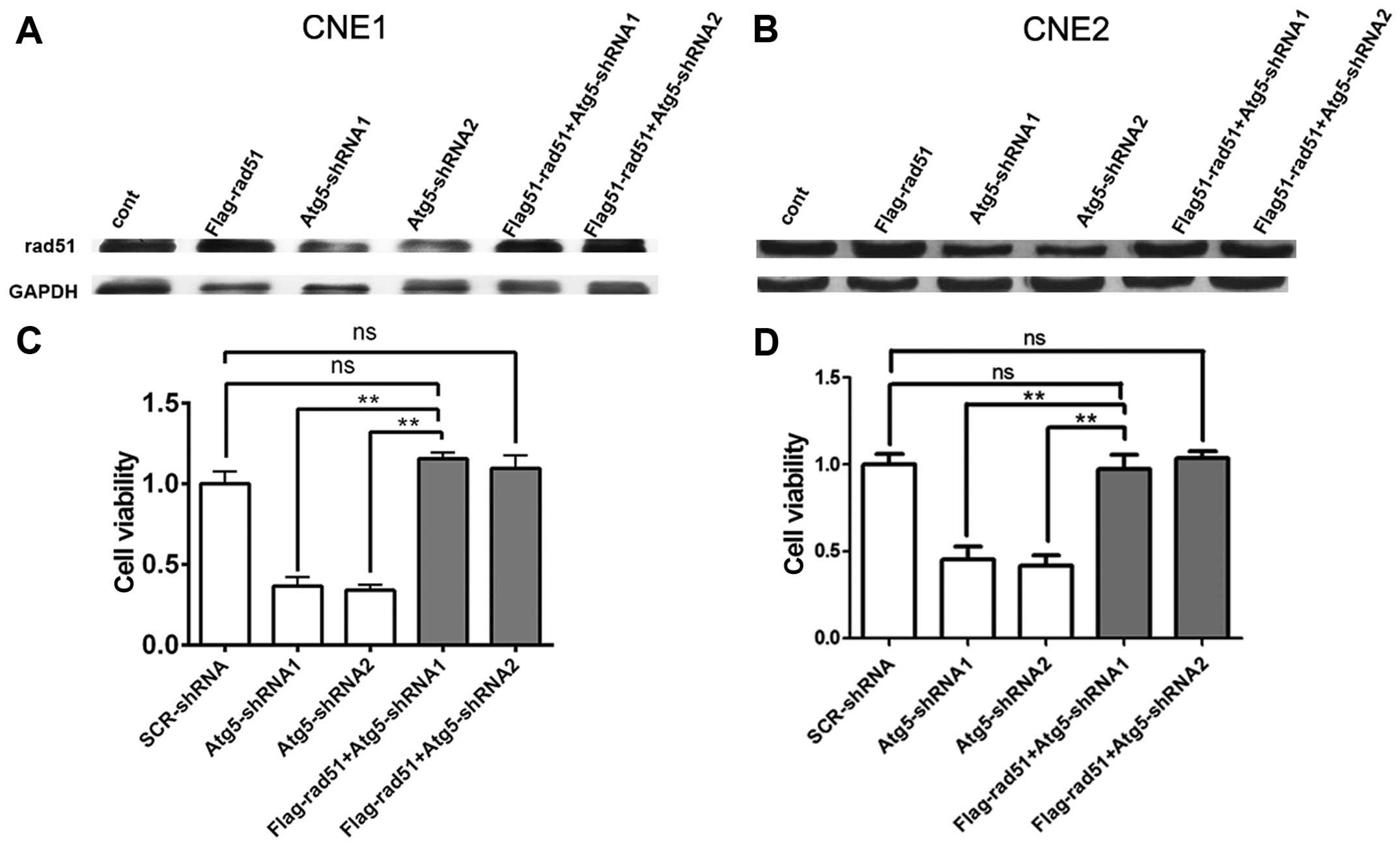
|
1
|
Chang ET and Adami HO: The enigmatic
epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 15:1765–1777. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hou H, Li D, Cheng D, Li L, Liu Y and Zhou
Y: Cellular redox status regulates emodin-induced
radiosensitization of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in vitro and
in vivo. J Pharmaceutics. 2013.2013:
|
|
3
|
Verheij M and Bartelink H:
Radiation-induced apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res. 301:133–142. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zois CE and Koukourakis MI:
Radiation-induced autophagy in normal and cancer cells: towards
novel cytoprotection and radio-sensitization policies? Autophagy.
5:442–450. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu WM, Huang P, Kar N, et al: Lyn
facilitates glioblastoma cell survival under conditions of nutrient
deprivation by promoting autophagy. PloS One. 8:e708042013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oehme I, Linke JP, Böck BC, et al: Histone
deacetylase 10 promotes autophagy-mediated cell survival. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 110:E2592–E2601. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Selvakumaran M, Amaravadi RK, Vasilevskaya
IA and O’Dwyer PJ: Autophagy inhibition sensitizes colon cancer
cells to antiangiogenic and cytotoxic therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
19:2995–3007. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lomonaco SL, Finniss S, Xiang C, et al:
The induction of autophagy by γ-radiation contributes to the
radioresistance of glioma stem cells. Int J Cancer. 125:717–722.
2009.
|
|
9
|
Apel A, Herr I, Schwarz H, Rodemann HP and
Mayer A: Blocked autophagy sensitizes resistant carcinoma cells to
radiation therapy. Cancer Res. 68:1485–1494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Yin W and Zhu X: Blocked autophagy
enhances radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line
CNE-2 in vitro. Acta Otolaryngol. 134:105–110. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mazin AV and Mazina OM: RAD51 is a key
protein of DNA repair and homologous recombination in humans.
281–302. 2013.
|
|
12
|
Vispé S, Cazaux C, Lesca C and Defais M:
Overexpression of Rad51 protein stimulates homologous recombination
and increases resistance of mammalian cells to ionizing radiation.
Nucleic Acids Res. 26:2859–2864. 1998.
|
|
13
|
Somaiah N, Yarnold J, Lagerqvist A,
Rothkamm K and Helleday T: Homologous recombination mediates
cellular resistance and fraction size sensitivity to radiation
therapy. Radiother Oncol. 108:155–161. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou ZR, Zhu XD, Zhao W, et al:
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 regulates the mechanism of
irradiation-induced CNE-2 human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell
autophagy and inhibition of autophagy contributes to the radiation
sensitization of CNE-2 cells. Oncol Rep. 29:2498–2506. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Takasu H, Sugita A, Uchiyama Y, et al:
c-Fos protein as a target of anti-osteoclastogenic action of
vitamin D, and synthesis of new analogs. J Clin Invest.
116:528–535. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Menna-Barreto RF, Salomão K, Dantas AP, et
al: Different cell death pathways induced by drugs in
Trypanosoma cruzi: an ultrastructural study. Micron.
40:157–168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dickey JS, Redon CE, Nakamura AJ, Baird
BJ, Sedelnikova OA and Bonner WM: H2AX: functional roles and
potential applications. Chromosoma. 118:683–692. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bae Y, Jung SH, Kim GY, Rhim H and Kang S:
Hip2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme overcomes radiation-induced G2/M
arrest. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:2911–2921. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Miyata H, Doki Y, Yamamoto H, et al:
Overexpression of CDC25B overrides radiation-induced G2-M arrest
and results in increased apoptosis in esophageal cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 61:3188–3193. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rodemann HP: Molecular radiation biology:
perspectives for radiation oncology. Radiother Oncol. 92:293–298.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang F, Motlekar NA, Burgwin CM, Napper
AD, Diamond SL and Mazin AV: Identification of specific inhibitors
of human RAD51 recombinase using high-throughput screening. ACS
Chem Biol. 6:628–635. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Budke B, Logan HL, Kalin JH, et al: RI-1:
a chemical inhibitor of RAD51 that disrupts homologous
recombination in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:7347–7357.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A and Kimchi A: The
paradox of autophagy and its implication in cancer etiology and
therapy. Apoptosis. 14:376–391. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tsuchihara K, Fujii S and Esumi H:
Autophagy and cancer: dynamism of the metabolism of tumor cells and
tissues. Cancer Lett. 278:130–138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
White E: Deconvoluting the
context-dependent role for autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:401–410. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yenigun VB, Ozpolat B and Kose GT:
Response of CD44+/CD24−/low breast cancer
stem/progenitor cells to tamoxifen- and doxorubicin-induced
autophagy. Int J Mol Med. 31:1477–1483. 2013.
|
|
27
|
Tekirdag KA, Korkmaz G, Ozturk DG, Agami R
and Gozuacik D: MIR181A regulates starvation- and rapamycin-induced
autophagy through targeting of ATG5. Autophagy. 9:374–385. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou Y, Wang HD, Zhu L, et al: Knockdown
of Nrf2 enhances autophagy induced by temozolomide in U251 human
glioma cell line. Oncol Rep. 29:394–400. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liang N, Jia L, Liu Y, et al: ATM pathway
is essential for ionizing radiation-induced autophagy. Cell Signal.
25:2530–2539. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chaachouay H, Ohneseit P, Toulany M,
Kehlbach R, Multhoff G and Rodemann HP: Autophagy contributes to
resistance of tumor cells to ionizing radiation. Radiother Oncol.
99:287–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pawlik TM and Keyomarsi K: Role of cell
cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 59:928–942. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Corcelle E, Nebout M, Bekri S, et al:
Disruption of autophagy at the maturation step by the carcinogen
lindane is associated with the sustained mitogen-activated protein
kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity. Cancer Res.
66:6861–6870. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Takenaka T, Yoshino I, Kouso H, et al:
Combined evaluation of Rad51 and ERCC1 expressions for sensitivity
to platinum agents in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer.
121:895–900. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Du LQ, Wang Y, Wang H, Cao J, Liu Q and
Fan F-Y: Knockdown of Rad51 expression induces radiation- and
chemo-sensitivity in osteosarcoma cells. Med Oncol. 28:1481–1487.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yamamori T, Meike S, Nagane M, Yasui H and
Inanami O: ER stress suppresses DNA double-strand break repair and
sensitizes tumor cells to ionizing radiation by stimulating
proteasomal degradation of Rad51. FEBS Lett. 587:3348–3353. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|