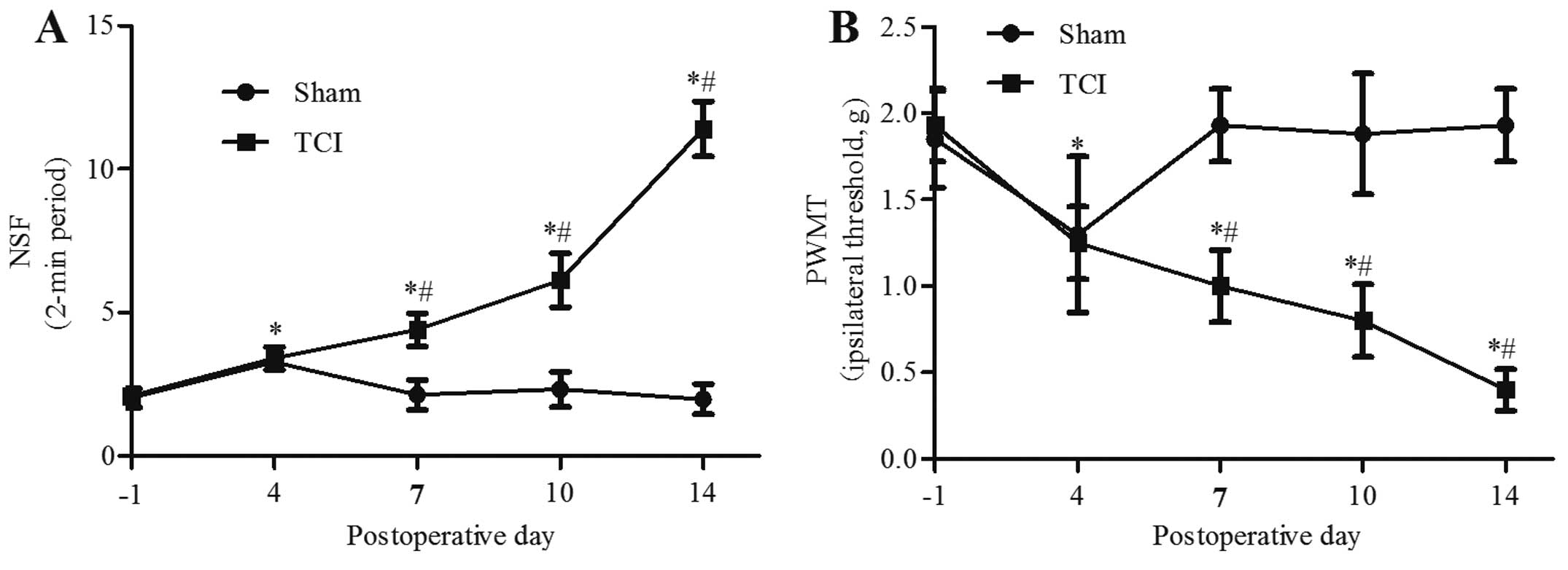
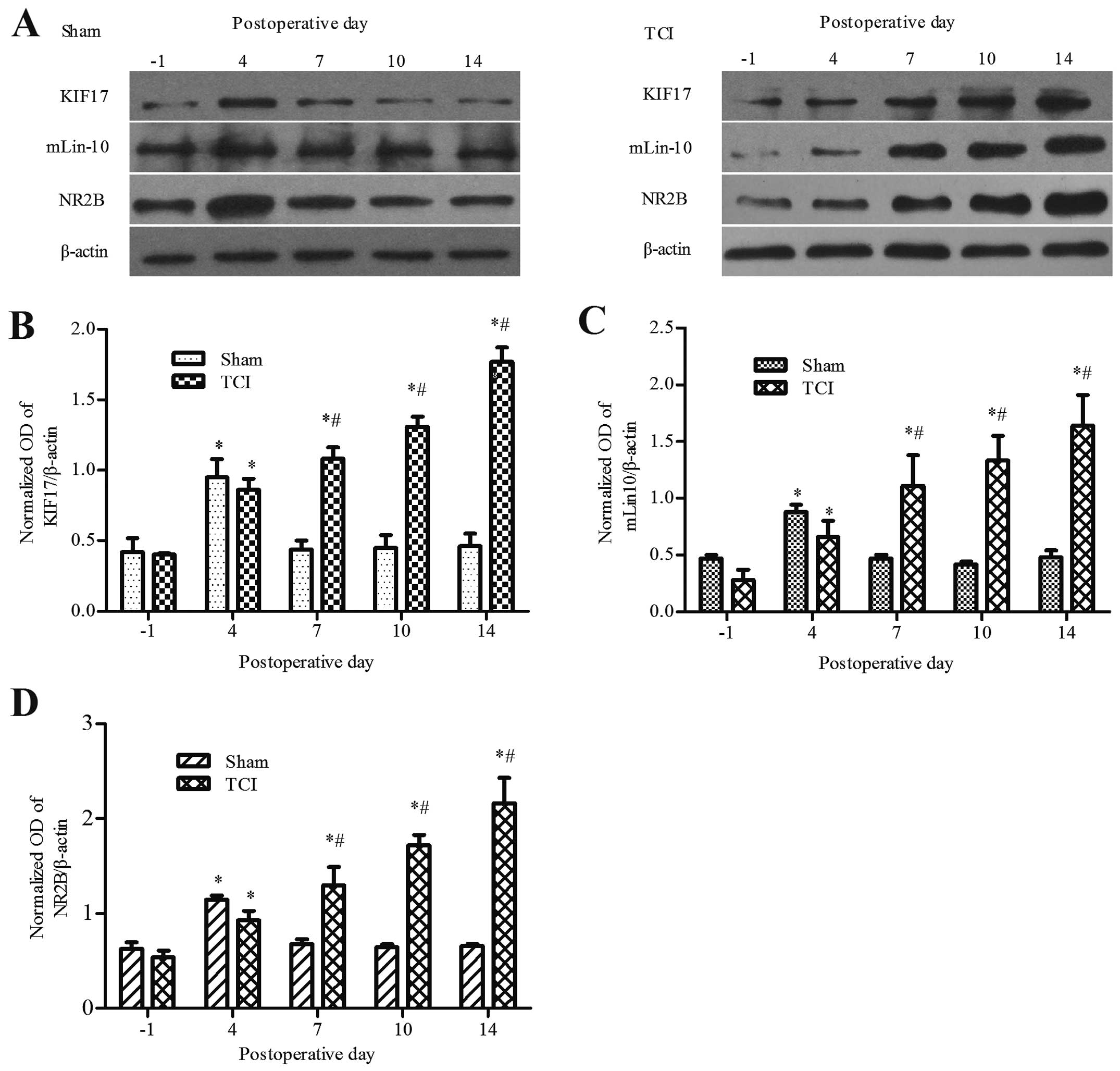
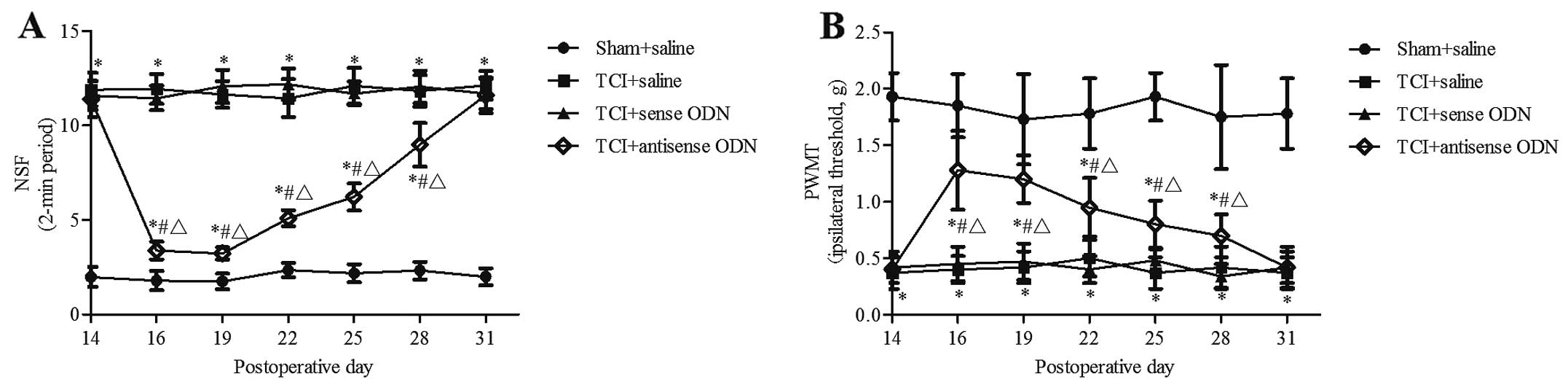
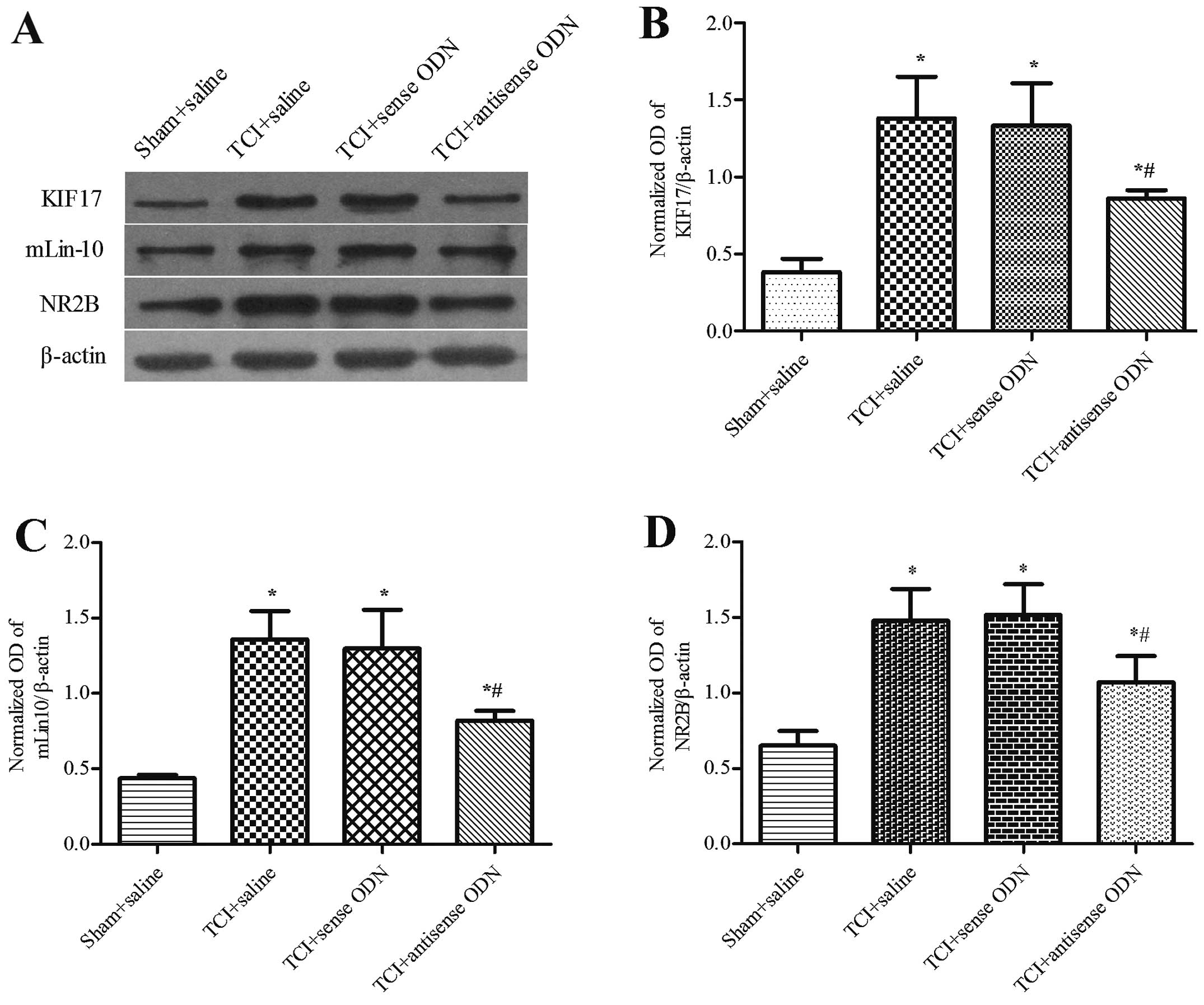
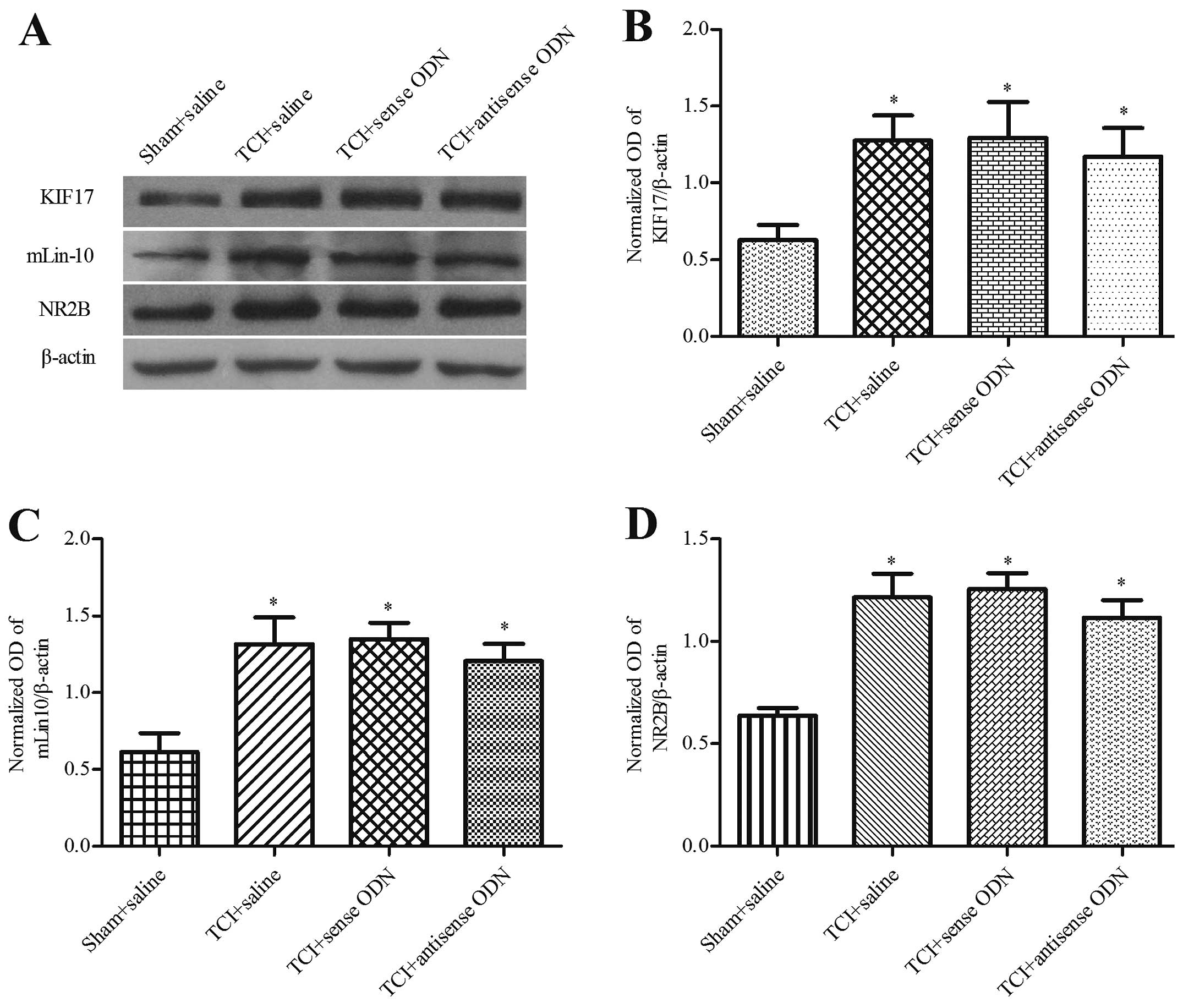
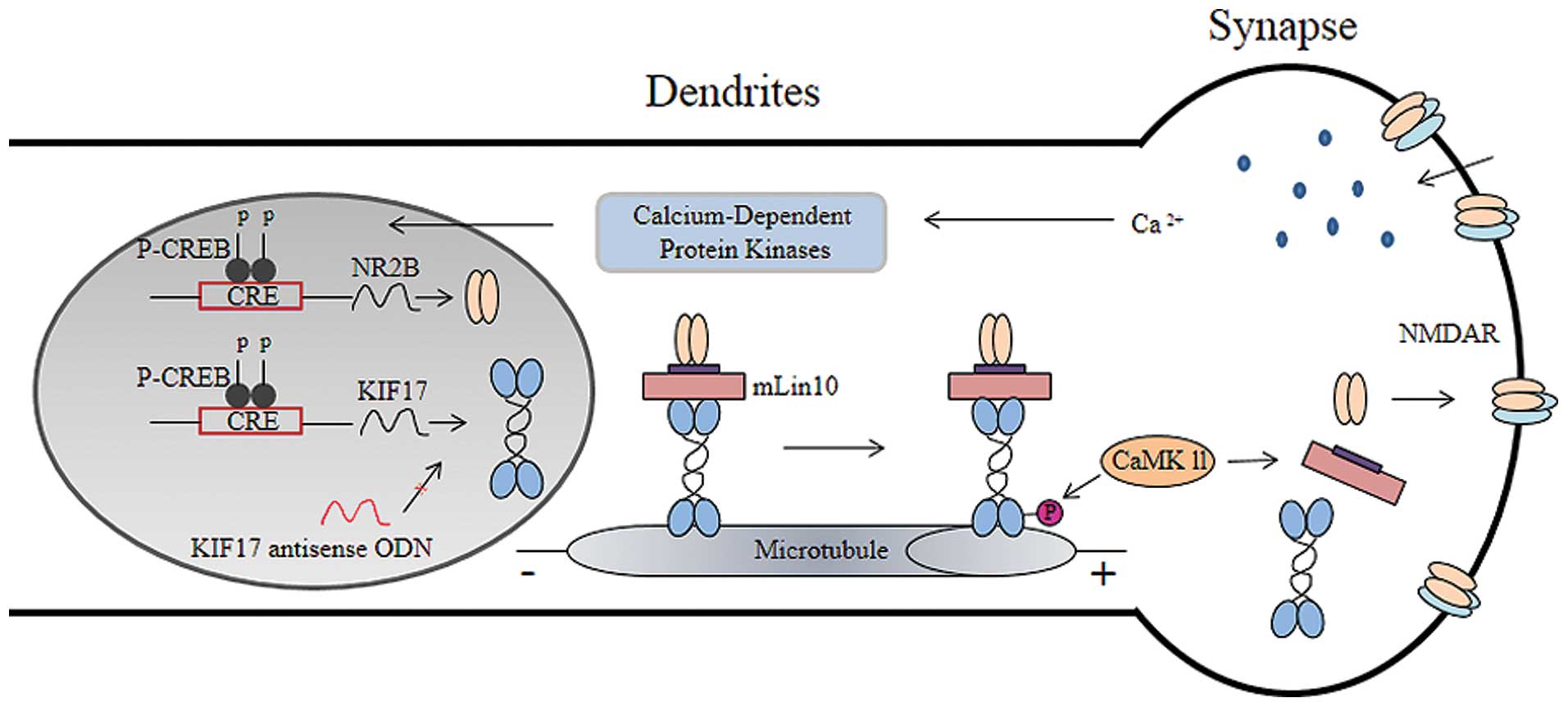
|
1
|
Bray F, Jemal A, Grey N, Ferlay J and
Forman D: Global cancer transitions according to the human
development index (2008–2030): a population-based study. Lancet
Oncol. 13:790–801. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Costantini M, Ripamonti C, Beccaro M, et
al: Prevalence, distress, management, and relief of pain during the
last 3 months of cancer patients’ life. Results of an italian
mortality follow-back survey. Ann Oncol. 20:729–735. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van den Beuken-van Everdingen MH, de Rijke
JM, Kessels AG, Schouten HC, van Kleef M and Patijn J: Prevalence
of pain in patients with cancer: a systematic review of the past 40
years. Ann Oncol. 18:1437–1449. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mantyh P: Bone cancer pain: causes,
consequences, and therapeutic opportunities. Pain. 154:S54–S62.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Goblirsch M, Zwolak P and Clohisy DR:
Advances in understanding bone cancer pain. J Cell Biochem.
96:682–688. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Coleman RE: Clinical features of
metastatic bone disease and risk of skeletal morbidity. Clin Cancer
Res. 12:6243s–6249s. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Laurie DJ, Bartke I, Schoepfer R, Naujoks
K and Seeburg PH: Regional, developmental and interspecies
expression of the four NMDAR2 subunits, examined using monoclonal
antibodies. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 51:23–32. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nagy GG, Watanabe M, Fukaya M and Todd AJ:
Synaptic distribution of the NR1, NR2A and NR2B subunits of the
N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor in the rat lumbar spinal cord
revealed with an antigen-unmasking technique. Eur J Neurosci.
20:3301–3312. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Klein T, Magerl W, Hanschmann A, Althaus M
and Treede RD: Antihyperalgesic and analgesic properties of the
N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist neramexane in a
human surrogate model of neurogenic hyperalgesia. Eur J Pain.
12:17–29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Qu XX, Cai J, Li MJ, et al: Role of the
spinal cord NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the development of
neuropathic pain. Exp Neurol. 215:298–307. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Woolf CJ: Central sensitization:
uncovering the relation between pain and plasticity.
Anesthesiology. 106:864–867. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gu X, Zhang J, Ma Z, et al: The role of
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR2B in spinal cord in cancer
pain. Eur J Pain. 14:496–502. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Paoletti P and Neyton J: NMDA receptor
subunits: function and pharmacology. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 7:39–47.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lau CG and Zukin RS: NMDA receptor
trafficking in synaptic plasticity and neuropsychiatric disorders.
Nat Rev Neurosci. 8:413–426. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guillaud L, Setou M and Hirokawa N: KIF17
dynamics and regulation of NR2B trafficking in hippocampal neurons.
J Neurosci. 23:131–140. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hirokawa N, Niwa S and Tanaka Y: Molecular
motors in neurons: transport mechanisms and roles in brain
function, development, and disease. Neuron. 68:610–638. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yin X, Takei Y, Kido MA and Hirokawa N:
Molecular motor KIF17 is fundamental for memory and learning via
differential support of synaptic NR2A/2B levels. Neuron.
70:310–325. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schwei MJ, Honore P, Rogers SD, et al:
Neurochemical and cellular reorganization of the spinal cord in a
murine model of bone cancer pain. J Neurosci. 19:10886–10897.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luger NM, Sabino MA, Schwei MJ, et al:
Efficacy of systemic morphine suggests a fundamental difference in
the mechanisms that generate bone cancer vs inflammatory pain.
Pain. 99:397–406. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM
and Yaksh TL: Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the
rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 53:55–63. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wong-Riley MT and Besharse JC: The kinesin
superfamily protein KIF17: one protein with many functions. Biomol
Concepts. 3:267–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hirokawa N: Kinesin and dynein superfamily
proteins and the mechanism of organelle transport. Science.
279:519–526. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miki H, Okada Y and Hirokawa N: Analysis
of the kinesin superfamily: insights into structure and function.
Trends Cell Biol. 15:467–476. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wong RW, Setou M, Teng J, Takei Y and
Hirokawa N: Overexpression of motor protein KIF17 enhances spatial
and working memory in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:14500–14505. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guillaud L, Wong R and Hirokawa N:
Disruption of KIF17-Mint1 interaction by CaMKII-dependent
phosphorylation: a molecular model of kinesin-cargo release. Nat
Cell Biol. 10:19–29. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Setou M: Kinesin superfamily motor protein
KIF17 and mLin-10 in NMDA receptor-containing vesicle transport.
Science. 288:1796–1802. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ho A, Morishita W, Hammer RE, Malenka RC
and Sudhof TC: A role for Mints in transmitter release: Mint 1
knockout mice exhibit impaired GABAergic synaptic transmission.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:1409–1414. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ni K, Zhou Y, Sun YE, Liu Y, Gu XP and Ma
ZL: Intrathecal injection of selected peptide Myr-RC-13 attenuates
bone cancer pain by inhibiting KIF17 and NR2B expression. Pharmacol
Biochem Behav. 122:228–233. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|