|
1
|
Marquardt JU and Thorgeirsson SS:
SnapShot: hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 25:5502014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang JD and Roberts LR: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: a global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:448–458.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamanaka Y, Shiraki K, Inoue T, Miyashita
K, Fuke H, Yamaguchi Y, Yamamoto N, Ito K, Sugimoto K and Nakano T:
COX-2 inhibitors sensitize human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to
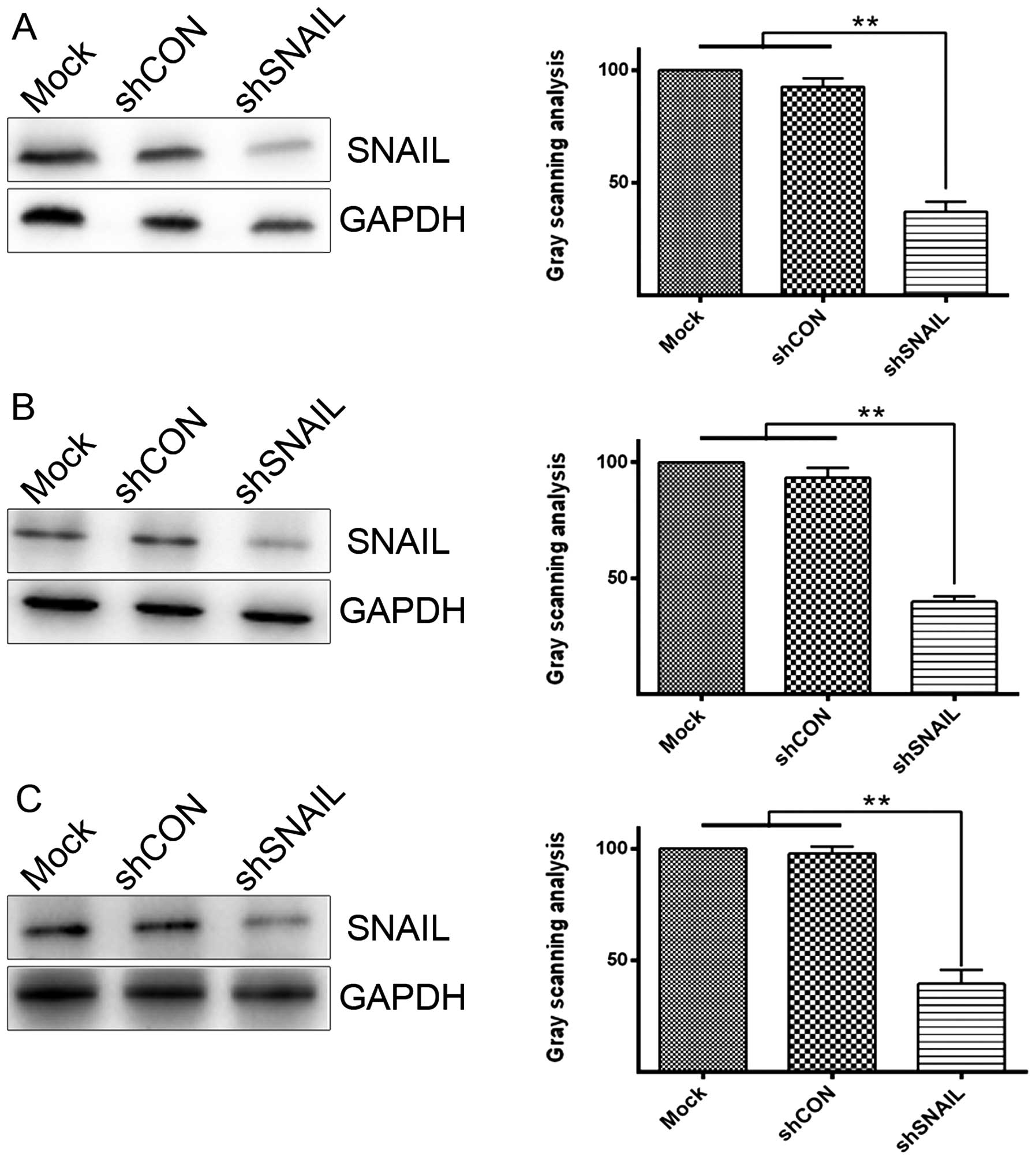
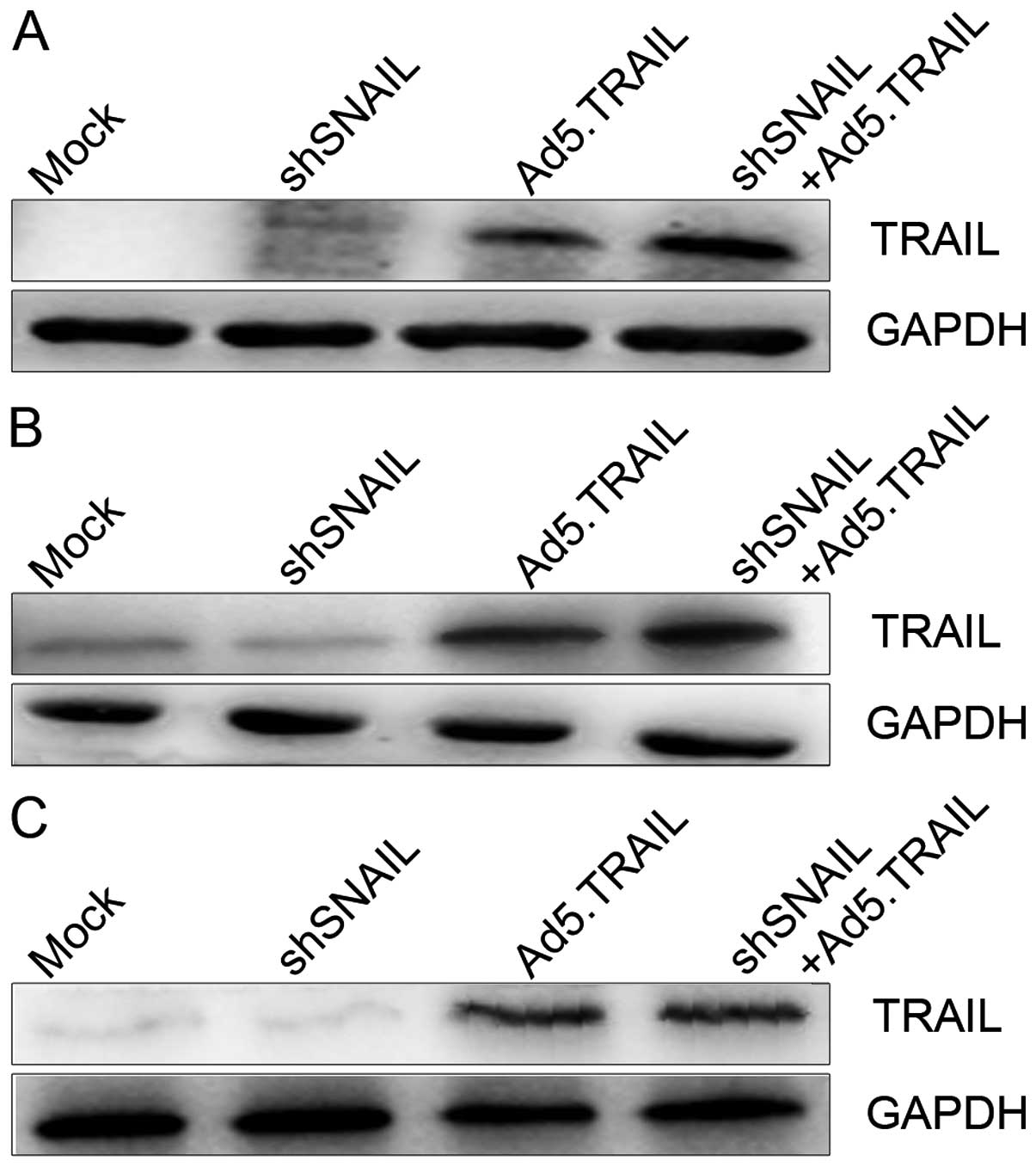
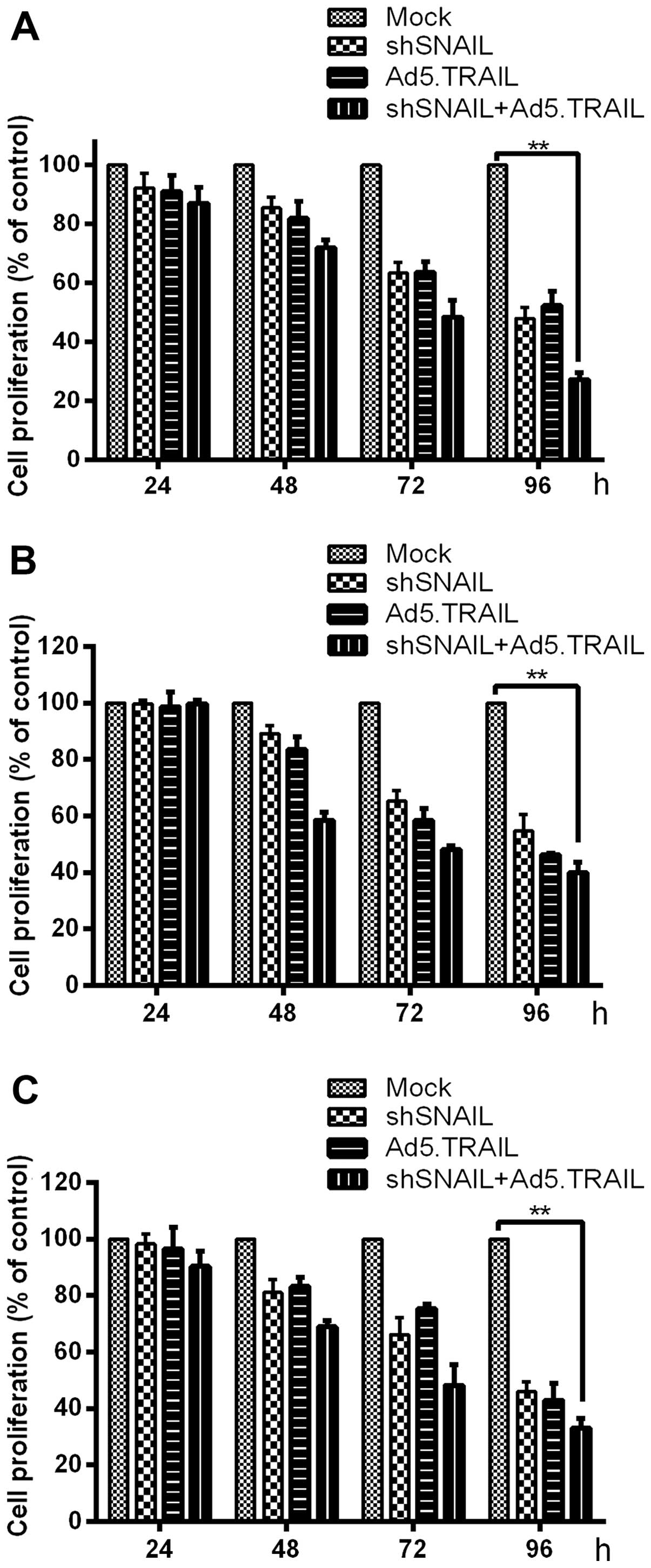
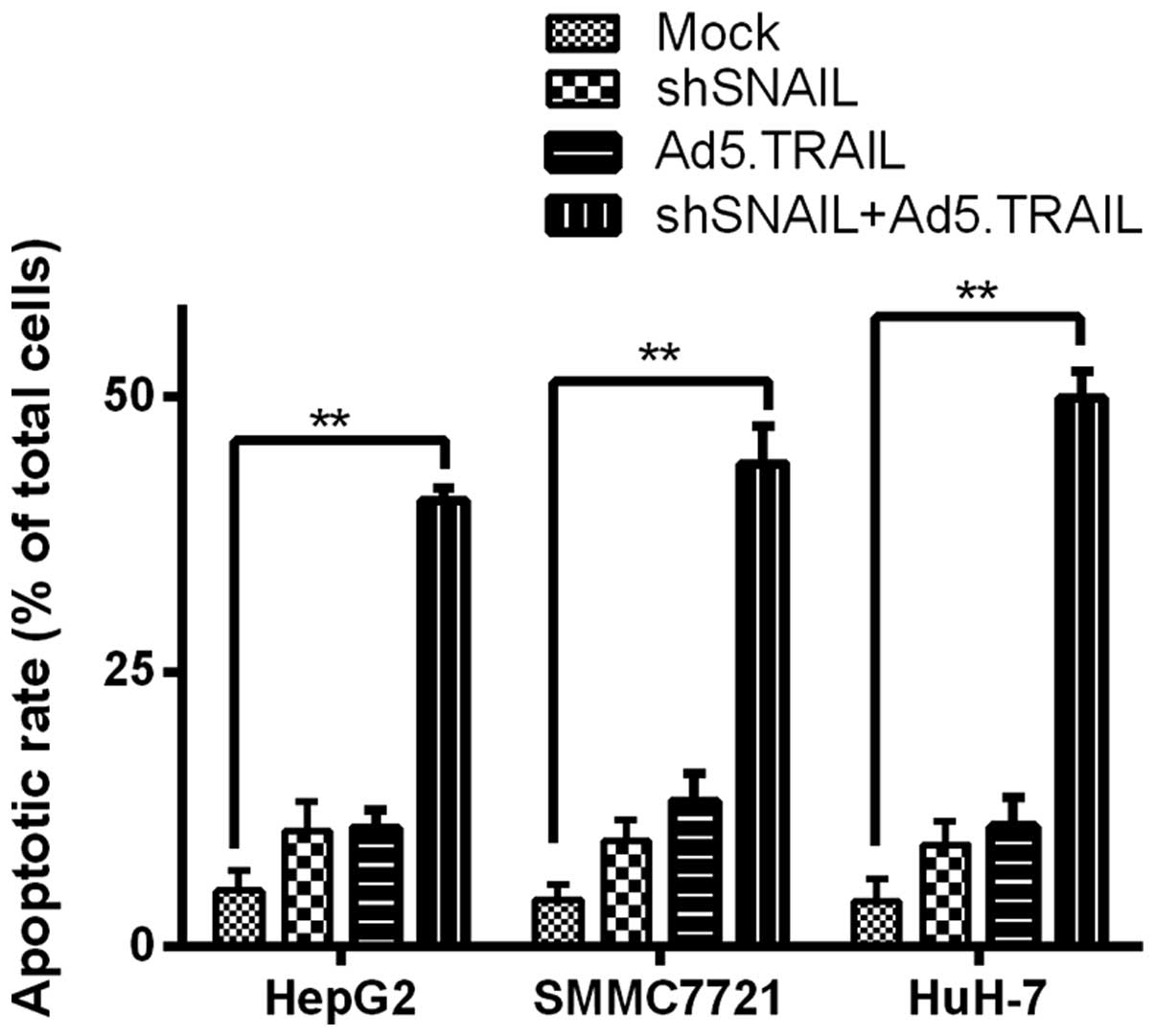
TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Int J Mol Med. 18:41–47. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chun E and Lee KY: Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL are
important for the induction of paclitaxel resistance in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
315:771–779. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ogunwobi OO and Liu C: Hepatocyte growth
factor upregulation promotes carcinogenesis and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via
Akt and COX-2 pathways. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:721–731. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang Y, Zhu J, Gou H, Cao D, Jiang M and
Hou M: Clinical significance of Cox-2, Survivin and Bcl-2
expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Med Oncol.
28:796–803. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Deng Q, Zhang Z, Feng X, et al:
TRAIL-secreting mesenchymal stem cells promote apoptosis in
heat-shock-treated liver cancer cells and inhibit tumor growth in
nude mice. Gene Ther. 21:317–327. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Apoptosis
control by death and decoy receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
11:255–260. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Benedict CA and Ware CF: TRAIL: not just
for tumors anymore? J Exp Med. 209:1903–1906. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Garimella SV, Gehlhaus K, Dine JL, Pitt
JJ, Grandin M, Chakka S, Nau MM, Caplen NJ and Lipkowitz S:
Identification of novel molecular regulators of tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis
in breast cancer cells by RNAi screening. Breast Cancer Res.
16:R412014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamanaka T, Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, Ito T,
Fujikawa K, Ito M, Takase K, Moriyama M, Nakano T and Suzuki A:
Chemotherapeutic agents augment TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Hepatology. 32:482–490. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ganten TM, Koschny R, Haas TL, Sykora J,
Li-Weber M, Herzer K and Walczak H: Proteasome inhibition
sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells, but not human
hepatocytes, to TRAIL. Hepatology. 42:588–597. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hall MA and Cleveland JL: Clearing the
TRAIL for cancer therapy. Cancer Cell. 12:4–6. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Omar HA, Arafa el-SA, Maghrabi IA and Weng
JR: Sensitization of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to Apo2L/TRAIL
by a novel Akt/NF-κB signalling inhibitor. Basic Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol. 114:464–471. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Refaat A, Abd-Rabou A and Reda A: TRAIL
combinations: The new ‘trail’ for cancer therapy (Review). Oncol
Lett. 7:1327–1332. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pioli PD and Weis JH: Snail transcription
factors in hematopoietic cell development: a model of functional
redundancy. Exp Hematol. 42:425–430. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kudo-Saito C, Shirako H, Takeuchi T and
Kawakami Y: Cancer metastasis is accelerated through
immunosuppression during Snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer
Cell. 15:195–206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Miyoshi A, Kitajima Y, Kido S, Shimonishi
T, Matsuyama S, Kitahara K and Miyazaki K: Snail accelerates cancer
invasion by upregulating MMP expression and is associated with poor
prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 92:252–258.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu J, Jiang G, Liu S, Liu Z, Pan H, Yao R
and Liang J: Lentivirus-delivered short hairpin RNA targeting SNAIL
inhibits HepG2 cell growth. Oncol Rep. 30:1483–1487.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fellmann C and Lowe SW: Stable RNA
interference rules for silencing. Nat Cell Biol. 16:10–18. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Takakura Y: Towards therapeutic
application of RNA-mediated gene regulation. Preface Adv Drug Deliv
Rev. 61:6672009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Djuranovic S, Nahvi A and Green R: A
parsimonious model for gene regulation by miRNAs. Science.
331:550–553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jinek M and Doudna JA: A three-dimensional
view of the molecular machinery of RNA interference. Nature.
457:405–412. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu X, Wang J, Wang H, Liu S, Liang Y, Lv
Z, Zhou Q and Ding W: Combination of Ad-sTRAIL with the
chemotherapeutic drug cisplatin synergistically enhances their
pro-apoptotic ability in human breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
30:1913–1919. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen D, Zheng X, Jiao X, Gao Y, Zhang K
and Liang J: Transcriptional repressor snail and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 59:1359–1365.
2012.
|
|
27
|
Smyth MJ, Takeda K, Hayakawa Y, Peschon
JJ, van den Brink MR and Yagita H: Nature’s TRAIL - on a path to
cancer immunotherapy. Immunity. 18:1–6. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Abou El Naga RN, Azab SS, El-Demerdash E,
Shaarawy S, El-Merzabani M and Ammar el-SM: Sensitization of
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2
cells by phytochemicals. Life Sci. 92:555–561. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu X, Qiu F, Liu Z, Lan Y, Wang K, Zhou
PK and Wang Y: Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor
regulates apoptotic sensitivity of colon cancer HCT116 cell line to
TRAIL via JNK-p53 pathway. Apoptosis. 19:1532–1544. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao J, Lu Y and Shen HM: Targeting p53 as
a therapeutic strategy in sensitizing TRAIL-induced apoptosis in
cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 314:8–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lee SH and Park BJ: p53 activation by
blocking Snail: a novel pharmacological strategy for cancer. Curr
Pharm Des. 17:610–617. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Finlay D, Vamos M, Gonzalez-Lopez M, et
al: Small-molecule IAP antagonists sensitize cancer cells to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis: roles of XIAP and cIAPs. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:5–15. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Dougherty MK, Müller J, Ritt DA, Zhou M,
Zhou XZ, Copelan TD, Conrads TP, Veenstra TD, Lu KP and Morrison
DK: Regulation of Raf-1 by direct feedback phosphorylation.
17:215–224. 2005.
|
|
34
|
Akram KM, Lomas NJ, Forsyth NR and Spiteri
MA: Alveolar epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
display upregulation of TRAIL, DR4 and DR5 expression with
simultaneous preferential over-expression of pro-apoptotic marker
p53. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:552–564. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yeh CH, Yang YY, Huang YF, Chow KC and
Chen MF: Induction of apoptosis in human Hep3B hepatoma cells by
norcantharidin through a p53 independent pathway via TRAIL/DR5
signal transduction. Chin J Integr Med. 18:676–682. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Inoue H, Shiraki K, Murata K, et al:
Adenoviral-mediated transfer of p53 gene enhances TRAIL-induced
apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med.
14:271–275. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cantarella G, Di Benedetto G, Ribatti D,
Saccani-Jotti G and Bernardini R: Involvement of caspase 8 and
c-FLIPL in the proangiogenic effects of the tumour necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). FEBS J.
281:1505–1513. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guo XZ, Shao XD, Liu MP, Xu JH, Ren LN,
Zhao JJ, Li HY and Wang D: Effect of bax, bcl-2 and bcl-xL on
regulating apoptosis in tissues of normal liver and hepatocellular
carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 8:1059–1062. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bansal H, Seifert T, Bachier C, Rao M,
Tomlinson G, Iyer SP and Bansal S: The transcription factor Wilms
tumor 1 confers resistance in myeloid leukemia cells against the
proapoptotic therapeutic agent TRAIL (tumor necrosis factor
alpha-related apoptosis-inducing ligand) by regulating the
antiapoptotic protein Bcl-xL. J Biol Chem. 287:32875–32880. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Koehler BC, Urbanik T, Vick B, Boger RJ,
Heeger S, Galle PR, Schuchmann M and Schulze-Bergkamen H:
TRAIL-induced apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells is
augmented by targeted therapies. World J Gastroenterol.
15:5924–5935. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kaler P, Galea V, Augenlicht L and
Klampfer L: Tumor associated macrophages protect colon cancer cells
from TRAIL-induced apoptosis through IL-1beta-dependent
stabilization of Snail in tumor cells. PLoS One. 5:e117002010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Baritaki S and Bonavida B: Viral infection
and cancer: the NF-kappaB/Snail/RKIP loop regulates target cell
sensitivity to apoptosis by cytotoxic lymphocytes. Crit Rev
Immunol. 30:31–46. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wu K and Bonavida B: The activated
NF-kappaB-Snail-RKIP circuitry in cancer regulates both the
metastatic cascade and resistance to apoptosis by cytotoxic drugs.
Crit Rev Immunol. 29:241–254. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|