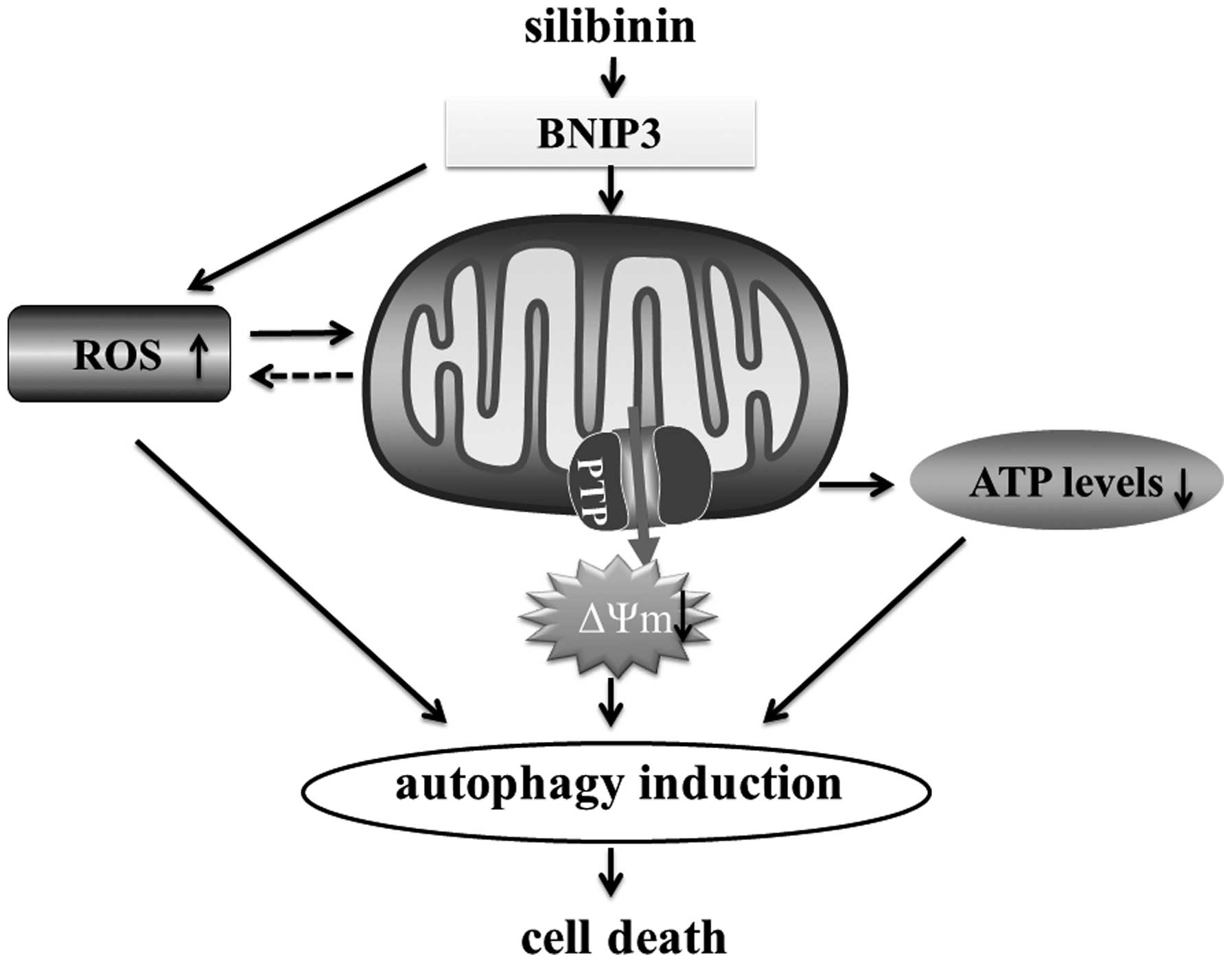
|
1
|
Tinoco G, Warsch S, Glück S, Avancha K and
Montero AJ: Treating breast cancer in the 21st century: emerging
biological therapies. J Cancer. 4:117–132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P,
Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, El-Deiry WS,
Golstein P, Green DR, et al: Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death
2009: Classification of cell death: recommendations of the
Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ.
16:3–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Reggiori F and Klionsky DJ:
Autophagosomes: biogenesis from scratch? Curr Opin Cell Biol.
17:415–422. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Klionsky DJ and Emr SD: Autophagy as a
regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science. 290:1717–1721.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liang XH, Jackson S, Seaman M, Brown K,
Kempkes B, Hibshoosh H and Levine B: Induction of autophagy and
inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature. 402:672–676. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yuan J, Lipinski M and Degterev A:
Diversity in the mechanisms of neuronal cell death. Neuron.
40:401–413. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Burton TR and Gibson SB: The role of Bcl-2
family member BNIP3 in cell death and disease: NIPping at the heels
of cell death. Cell Death Differ. 16:515–523. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gustafsson AB: Bnip3 as a dual regulator
of mitochondrial turnover and cell death in the myocardium. Pediatr
Cardiol. 32:267–274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vande Velde C, Cizeau J, Dubik D, Alimonti
J, Brown T, Israels S, Hakem R and Greenberg AH: BNIP3 and genetic
control of necrosis-like cell death through the mitochondrial
permeability transition pore. Mol Cell Biol. 20:5454–5468. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kubli DA, Ycaza JE and Gustafsson AB:
Bnip3 mediates mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death through Bax
and Bak. Biochem J. 405:407–415. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Milić N, Milosević N, Suvajdzić L, Zarkov
M and Abenavoli L: New therapeutic potentials of milk thistle
(Silybum marianum). Nat Prod Commun. 8:1801–1810. 2013.
|
|
13
|
Jeong JC, Shin WY, Kim TH, Kwon CH, Kim
JH, Kim YK and Kim KH: Silibinin induces apoptosis via
calpain-dependent AIF nuclear translocation in U87MG human glioma
cell death. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:442011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim S, Choi MG, Lee HS, Lee SK, Kim SH,
Kim WW, Hur SM, Kim JH, Choe JH, Nam SJ, et al: Silibinin
suppresses TNF-alpha-induced MMP-9 expression in gastric cancer
cells through inhibition of the MAPK pathway. Molecules.
14:4300–4311. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Meng G, Sun Y, Fu W, Guo Z and Xu L:
Microcystin-LR induces cytoskeleton system reorganization through
hyperphosphorylation of tau and HSP27 via PP2A inhibition and
subsequent activation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in
neuroendocrine (PC12) cells. Toxicology. 290:218–229. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Waterhouse NJ, Goldstein JC, von Ahsen O,
Schuler M, Newmeyer DD and Green DR: Cytochrome cmaintains
mitochondrial transmembrane potential and ATP generation after
outer mitochondrial membrane permeabilization during the apoptotic
process. J Cell Biol. 153:319–328. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gong X, Ivanov VN, Davidson MM and Hei TK:
Tetramethylpyrazine (TMP) protects against sodium arsenite-induced
nephrotoxicity by suppressing ROS production, mitochondrial
dysfunction, pro-inflammatory signaling pathways and programed cell
death. Arch Toxicol. June 25–2014.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Duan W, Jin X, Li Q, Tashiro S, Onodera S
and Ikejima T: Silibinin induced autophagic and apoptotic cell
death in HT1080 cells through a reactive oxygen species pathway. J
Pharmacol Sci. 113:48–56. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Scherz-Shouval R and Elazar Z: ROS,
mitochondria and the regulation of autophagy. Trends Cell Biol.
17:422–427. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yousefi M, Ghaffari SH, Zekri A, Hassani
S, Alimoghaddam K and Ghavamzadeh A: Silibinin induces apoptosis
and inhibits proliferation of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative
breast carcinoma cells through suppression of nuclear factor kappa
B activation. Arch Iran Med. 17:366–371. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kondo Y and Kondo S: Autophagy and cancer
therapy. Autophagy. 2:85–90. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kuma A, Mizushima N, Ishihara N and Ohsumi
Y: Formation of the approximately 350-kDa Apg12-Apg5.Apg16
multimeric complex, mediated by Apg16 oligomerization, is essential
for autophagy in yeast. J Biol Chem. 277:18619–18625. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Yamamoto A,
Oshitani-Okamoto S, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, GABARAP and
GATE16 localize to autophagosomal membrane depending on form-II
formation. J Cell Sci. 117:2805–2812. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tassa A, Roux MP, Attaix D and Bechet DM:
Class III phosphoinositide 3-kinase - Beclin1 complex mediates the
amino acid-dependent regulation of autophagy in C2C12 myotubes.
Biochem J. 376:577–586. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thorburn A: Apoptosis and autophagy:
regulatory connections between two supposedly different processes.
Apoptosis. 13:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Ferraro E and Cecconi F: Autophagic and
apoptotic response to stress signals in mammalian cells. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 462:210–219. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kiffin R, Bandyopadhyay U and Cuervo AM:
Oxidative stress and autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 8:152–162.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Scherz-Shouval R and Elazar Z: Regulation
of autophagy by ROS: physiology and pathology. Trends Biochem Sci.
36:30–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li ZY, Yang Y, Ming M and Liu B:
Mitochondrial ROS generation for regulation of autophagic pathways
in cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 414:5–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Azad MB, Chen Y and Gibson SB: Regulation
of autophagy by reactive oxygen species (ROS): implications for
cancer progression and treatment. Antioxid Redox Signal.
11:777–790. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Duan WJ, Li QS, Xia MY, Tashiro S, Onodera
S and Ikejima T: Silibinin activated p53 and induced autophagic
death in human fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells via reactive oxygen
species-p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathways. Biol Pharm Bull.
34:47–53. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fan S, Li L, Chen S, Yu Y, Qi M, Tashiro
S, Onodera S and Ikejima T: Silibinin induced-autophagic and
apoptotic death is associated with an increase in reactive oxygen
and nitrogen species in HeLa cells. Free Radic Res. 45:1307–1324.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wen S, Zhu D and Huang P: Targeting cancer
cell mitochondria as a therapeutic approach. Future Med Chem.
5:53–67. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Van Blerkom J, Davis P and Alexander S:
Inner mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsim), cytoplasmic ATP
content and free Ca2+ levels in metaphase II mouse
oocytes. Hum Reprod. 18:2429–2440. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Halestrap AP, Clarke SJ and Javadov SA:
Mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening during
myocardial reperfusion - a target for cardioprotection. Cardiovasc
Res. 61:372–385. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M and Sollott SJ:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS
release. Physiol Rev. 94:909–950. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ghavami S, Eshragi M, Ande SR, Chazin WJ,
Klonisch T, Halayko AJ, McNeill KD, Hashemi M, Kerkhoff C and Los
M: S100A8/A9 induces autophagy and apoptosis via ROS-mediated
cross-talk between mitochondria and lysosomes that involves BNIP3.
Cell Res. 20:314–331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|