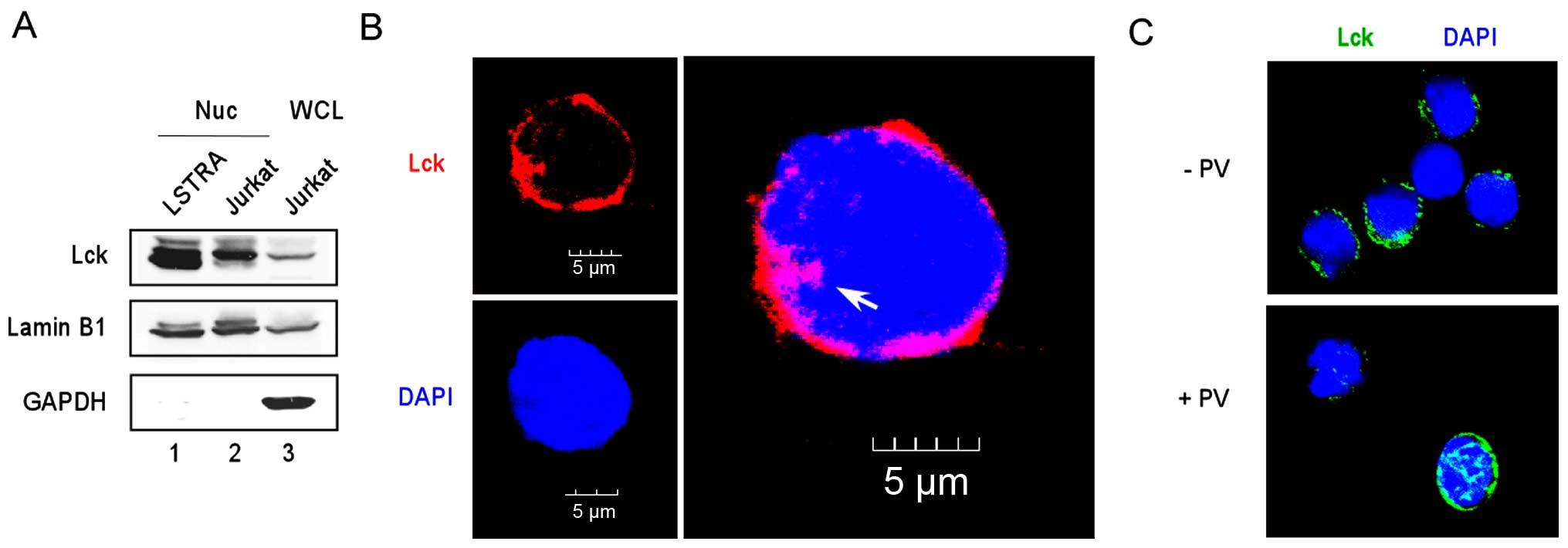
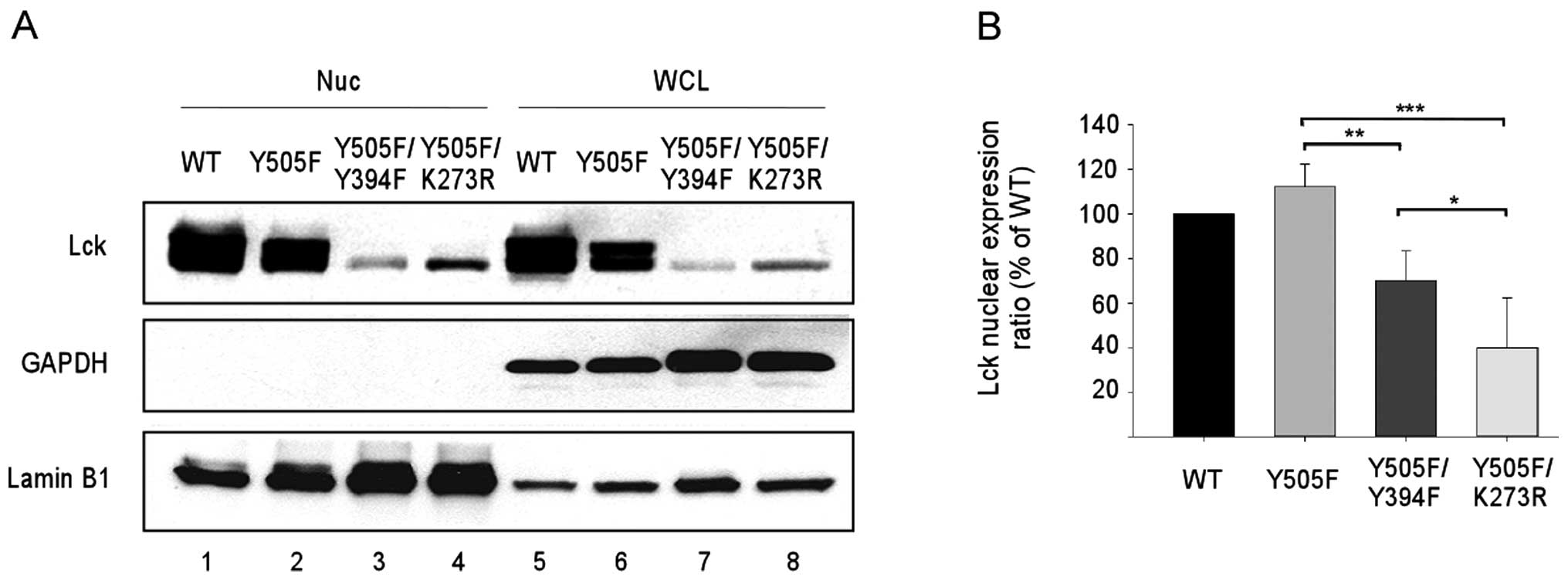
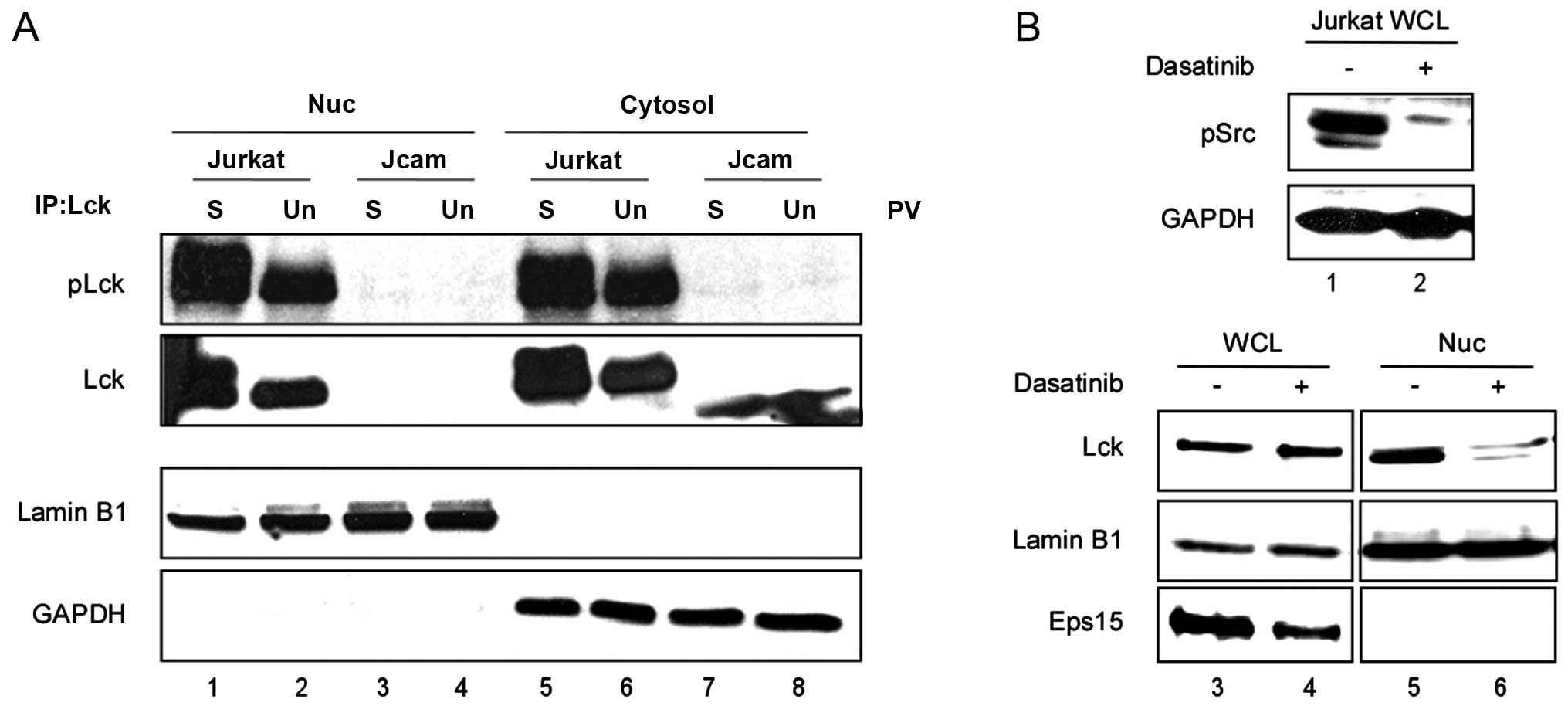
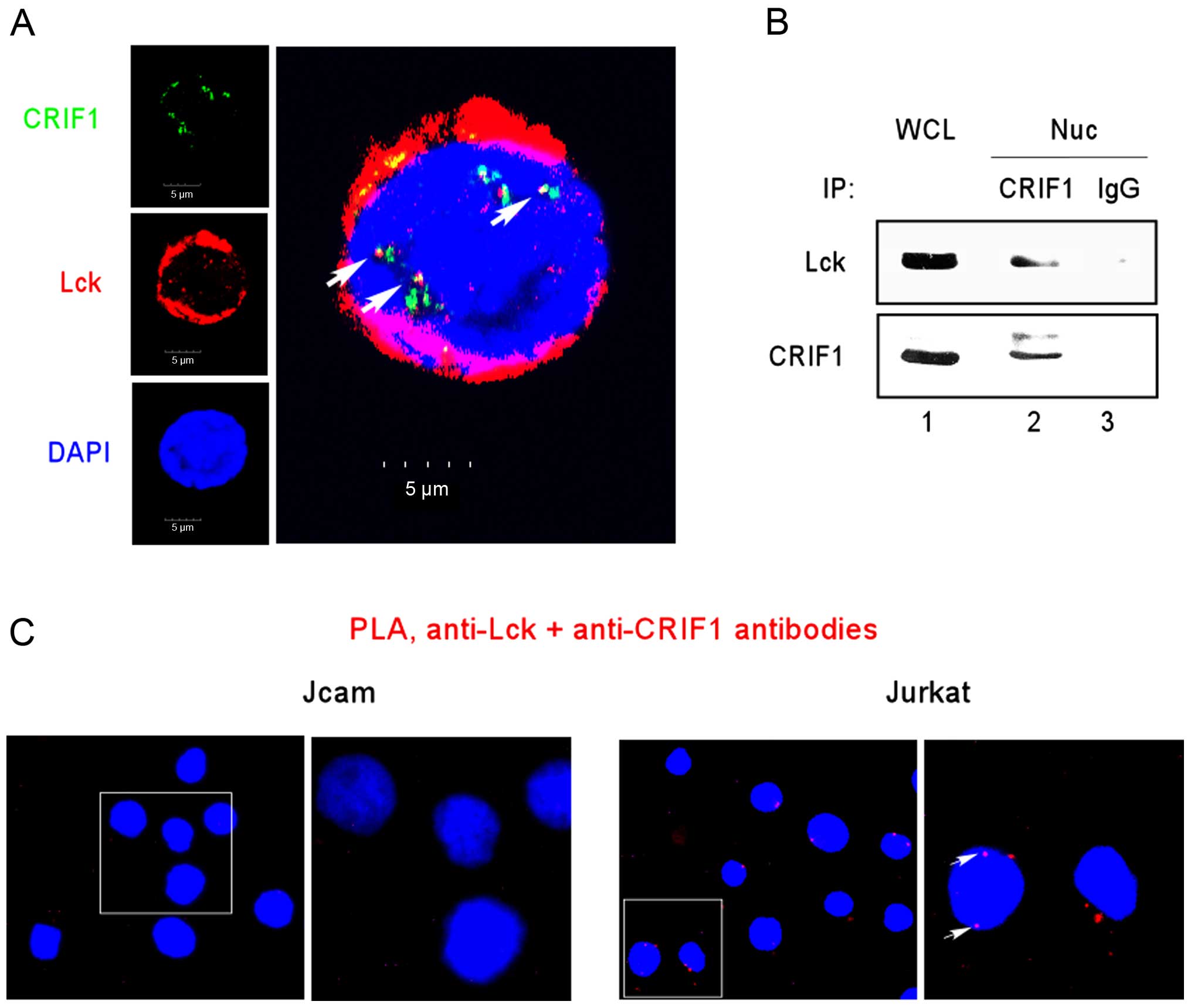
|
1
|
Krause DS and Van Etten RA: Tyrosine
kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 353:172–187.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lo HW and Hung MC: Nuclear EGFR signalling
network in cancers: Linking EGFR pathway to cell cycle progression,
nitric oxide pathway and patient survival. Br J Cancer. 94:184–188.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin SY, Makino K, Xia W, Matin A, Wen Y,
Kwong KY, Bourguignon L and Hung MC: Nuclear localization of EGF
receptor and its potential new role as a transcription factor. Nat
Cell Biol. 3:802–808. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chou RH, Wang YN, Hsieh YH, Li LY, Xia W,
Chang WC, Chang LC, Cheng CC, Lai CC, Hsu JL, et al: EGFR modulates
DNA synthesis and repair through Tyr phosphorylation of histone H4.
Dev Cell. 30:224–237. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marti U, Burwen SJ, Wells A, Barker ME,
Huling S, Feren AM and Jones AL: Localization of epidermal growth
factor receptor in hepatocyte nuclei. Hepatology. 13:15–20. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hadzisejdić I, Mustać E, Jonjić N,
Petković M and Grahovac B: Nuclear EGFR in ductal invasive breast
cancer: Correlation with cyclin-D1 and prognosis. Mod Pathol.
23:392–403. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tan M, Jing T, Lan KH, Neal CL, Li P, Lee
S, Fang D, Nagata Y, Liu J, Arlinghaus R, et al: Phosphorylation on
tyrosine-15 of p34(Cdc2) by ErbB2 inhibits p34(Cdc2) activation and
is involved in resistance to taxol-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell.
9:993–1004. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Domingues I, Rino J, Demmers JA, de
Lanerolle P and Santos SC: VEGFR2 translocates to the nucleus to
regulate its own transcription. PLoS One. 6:e256682011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Takahashi A, Obata Y, Fukumoto Y, Nakayama
Y, Kasahara K, Kuga T, Higashiyama Y, Saito T, Yokoyama KK and
Yamaguchi N: Nuclear localization of Src-family tyrosine kinases is
required for growth factor-induced euchromatinization. Exp Cell
Res. 315:1117–1141. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Van Laethem F, Tikhonova AN, Pobezinsky
LA, Tai X, Kimura MY, Le Saout C, Guinter TI, Adams A, Sharrow SO,
Bernhardt G, et al: Lck availability during thymic selection
determines the recognition specificity of the T cell repertoire.
Cell. 154:1326–1341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Palacios EH and Weiss A: Function of the
Src-family kinases, Lck and Fyn, in T-cell development and
activation. Oncogene. 23:7990–8000. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Burnett RC, David JC, Harden AM, Le Beau
MM, Rowley JD and Diaz MO: The LCK gene is involved in the
t(1;7)(p34;q34) in the T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia derived
cell line, HSB-2. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 3:461–467. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Majolini MB, Boncristiano M and Baldari
CT: Dysregulation of the protein tyrosine kinase LCK in
lymphoproliferative disorders and in other neoplasias. Leuk
Lymphoma. 35:245–254. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Accordi B, Espina V, Giordan M, VanMeter
A, Milani G, Galla L, Ruzzene M, Sciro M, Trentin L, De Maria R, et
al: Functional protein network activation mapping reveals new
potential molecular drug targets for poor prognosis pediatric
BCP-ALL. PLoS One. 5:e135522010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Veillette A, Foss FM, Sausville EA, Bolen
JB and Rosen N: Expression of the lck tyrosine kinase gene in human
colon carcinoma and other non-lymphoid human tumor cell lines.
Oncogene Res. 1:357–374. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Robinson D, He F, Pretlow T and Kung HJ: A
tyrosine kinase profile of prostate carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 93:5958–5962. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chueh FY and Yu CL: Engagement of T-cell
antigen receptor and CD4/CD8 co-receptors induces prolonged STAT
activation through autocrine/paracrine stimulation in human primary
T cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 426:242–246. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Elsberger B, Fullerton R, Zino S, Jordan
F, Mitchell TJ, Brunton VG, Mallon EA, Shiels PG and Edwards J:
Breast cancer patients’ clinical outcome measures are associated
with Src kinase family member expression. Br J Cancer. 103:899–909.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Venkitachalam S, Chueh FY and Yu CL:
Nuclear localization of lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase
(Lck) and its role in regulating LIM domain only 2 (Lmo2) gene.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 417:1058–1062. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chueh FY, Cronk RJ, Alsuwaidan AN, Mallers
TM, Jaiswal MK, Beaman KD and Yu CL: Mouse LSTRA leukemia as a
model of human natural killer T cell and highly aggressive lymphoid
malignancies. Leuk Lymphoma. 55:706–708. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chueh FY, Leong KF and Yu CL:
Mitochondrial translocation of signal transducer and activator of
transcription 5 (STAT5) in leukemic T cells and cytokine-stimulated
cells. Biochem. Biophys Res Commun. 402:778–783. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cooper JC, Shi M, Chueh FY, Venkitachalam
S and Yu CL: Enforced SOCS1 and SOCS3 expression attenuates
Lck-mediated cellular transformation. Int J Oncol. 36:1201–1208.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Venkitachalam S, Chueh FY, Leong KF,
Pabich S and Yu CL: Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 interacts
with oncogenic lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase. Oncol
Rep. 25:677–683. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu CL, Jove R and Burakoff SJ:
Constitutive activation of the Janus kinase-STAT pathway in T
lymphoma overexpressing the Lck protein tyrosine kinase. J Immunol.
159:5206–5210. 1997.
|
|
25
|
Abraham RT and Weiss A: Jurkat T cells and
development of the T-cell receptor signalling paradigm. Nat Rev
Immunol. 4:301–308. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shi M, Cooper JC and Yu CL: A
constitutively active Lck kinase promotes cell proliferation and
resistance to apoptosis through signal transducer and activator of
transcription 5b activation. Mol Cancer Res. 4:39–45. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Straus DB and Weiss A: Genetic evidence
for the involvement of the lck tyrosine kinase in signal
transduction through the T cell antigen receptor. Cell. 70:585–593.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ran Q, Hao P, Xiao Y, Xiang L, Ye X, Deng
X, Zhao J and Li Z: CRIF1 interacting with CDK2 regulates bone
marrow microenvironment-induced G0/G1 arrest of leukemia cells.
PLoS One. 9:e853282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park KC, Song KH, Chung HK, Kim H, Kim DW,
Song JH, Hwang ES, Jung HS, Park SH, Bae I, et al: CR6-interacting
factor 1 interacts with orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 and inhibits
its transactivation. Mol Endocrinol. 19:12–24. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hanada N, Lo HW, Day CP, Pan Y, Nakajima Y
and Hung MC: Co-regulation of B-Myb expression by E2F1 and EGF
receptor. Mol Carcinog. 45:10–17. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liccardi G, Hartley JA and Hochhauser D:
EGFR nuclear trans-location modulates DNA repair following
cisplatin and ionizing radiation treatment. Cancer Res.
71:1103–1114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu YL, Chou RH, Liang JH, Chang WJ, Su KJ,
Tseng YJ, Huang WC, Wang SC and Hung MC: Targeting the EGFR/PCNA
signaling suppresses tumor growth of triple-negative breast cancer
cells with cell-penetrating PCNA peptides. PLoS One. 8:e613622013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brand TM, Iida M, Li C and Wheeler DL: The
nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor signaling network and its
role in cancer. Discov Med. 12:419–432. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hsu SC and Hung MC: Characterization of a
novel tripartite nuclear localization sequence in the EGFR family.
J Biol Chem. 282:10432–10440. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chung HK, Yi YW, Jung NC, Kim D, Suh JM,
Kim H, Park KC, Song JH, Kim DW, Hwang ES, et al: CR6-interacting
factor 1 interacts with Gadd45 family proteins and modulates the
cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 278:28079–28088. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim SJ, Kwon MC, Ryu MJ, Chung HK, Tadi S,
Kim YK, Kim JM, Lee SH, Park JH, Kweon GR, et al: CRIF1 is
essential for the synthesis and insertion of oxidative
phosphorylation polypeptides in the mammalian mitochondrial
membrane. Cell Metab. 16:274–283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Byun J, Son SM, Cha MY, Shong M, Hwang YJ,
Kim Y, Ryu H, Moon M, Kim KS and Mook-Jung I: CR6-interacting
factor 1 is a key regulator in Aβ-induced mitochondrial disruption
and pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Differ. Nov
7–2014.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Demory ML, Boerner JL, Davidson R, Faust
W, Miyake T, Lee I, Hüttemann M, Douglas R, Haddad G and Parsons
SJ: Epidermal growth factor receptor translocation to the
mitochondria: Regulation and effect. J Biol Chem. 284:36592–36604.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tibaldi E, Brunati AM, Massimino ML,
Stringaro A, Colone M, Agostinelli E, Arancia G and Toninello A:
Src-tyrosine kinases are major agents in mitochondrial tyrosine
phosphorylation. J Cell Biochem. 104:840–849. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ding Y, Liu Z, Desai S, Zhao Y, Liu H,
Pannell LK, Yi H, Wright ER, Owen LB, Dean-Colomb W, et al:
Receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB2 translocates into mitochondria and
regulates cellular metabolism. Nat Commun. 3:12712012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|