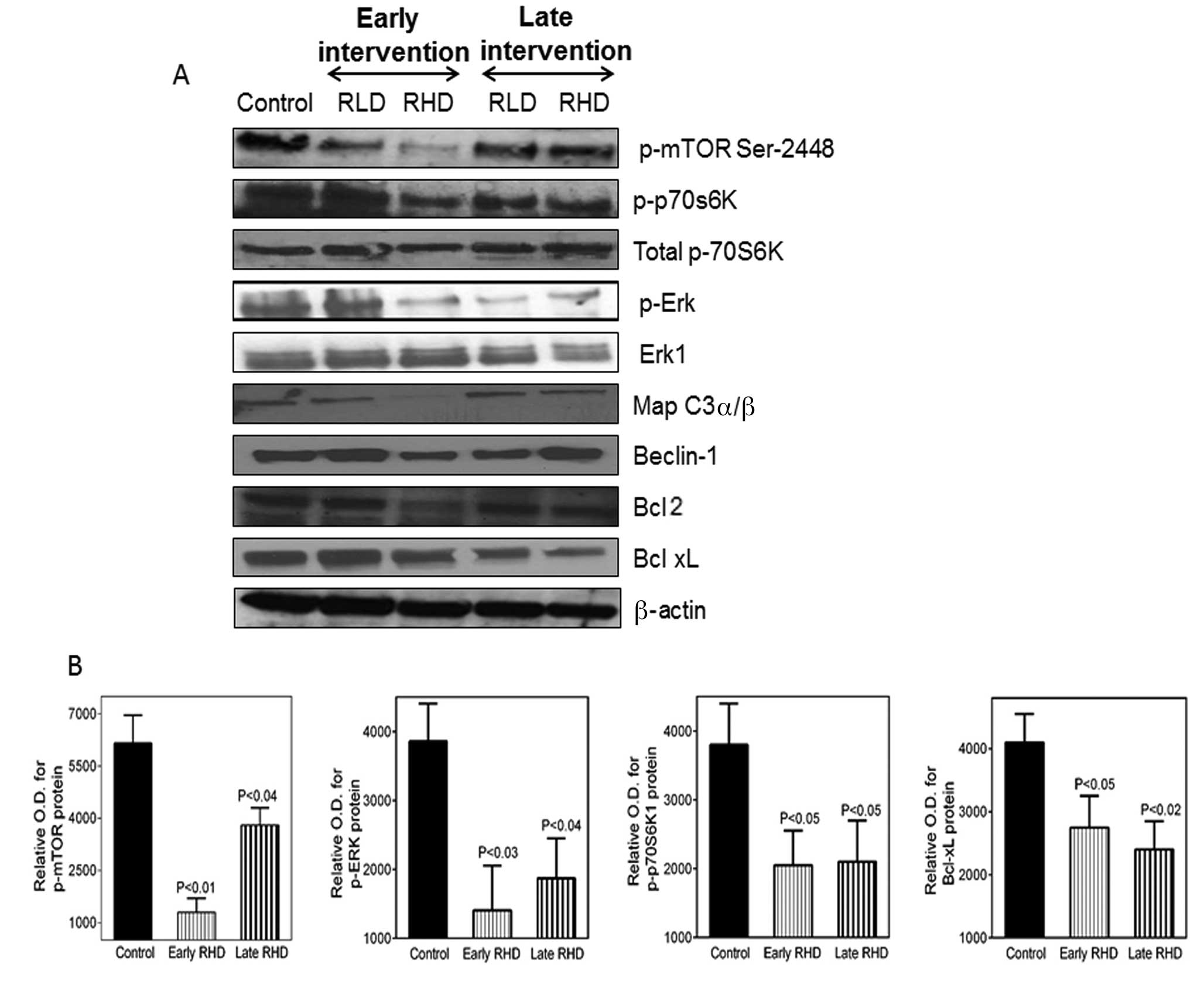
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Humphrey L, Deffebach M, Pappas M, Baumann
C, Artis K, Mitchell JP, Zakher B, Fu R and Slatore C: Screening
for Lung Cancer: Systematic Review to Update the U.S. Preventive
Services Task Force Recommendation. Rockville, MD: 2013
|
|
3
|
American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts
& Figures 2013. American Cancer Society; Atlanta, GA: 2013
|
|
4
|
Hecht SS, Kassie F and Hatsukami DK:
Chemoprevention of lung carcinogenesis in addicted smokers and
ex-smokers. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:476–488. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tsurutani J, Castillo SS, Brognard J,
Granville CA, Zhang C, Gills JJ, Sayyah J and Dennis PA: Tobacco
components stimulate Akt-dependent proliferation and
NFkappaB-dependent survival in lung cancer cells. Carcinogenesis.
26:1182–1195. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
West KA, Brognard J, Clark AS, Linnoila
IR, Yang X, Swain SM, Harris C, Belinsky S and Dennis PA: Rapid Akt
activation by nicotine and a tobacco carcinogen modulates the
phenotype of normal human airway epithelial cells. J Clin Invest.
111:81–90. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
West KA, Linnoila IR, Belinsky SA, Harris
CC and Dennis PA: Tobacco carcinogen-induced cellular
transformation increases activation of the phosphatidylinositol
3′-kinase/Akt pathway in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 64:446–451.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Markman B, Dienstmann R and Tabernero J:
Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway - beyond rapalogs. Oncotarget.
1:530–543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bjornsti MA and Houghton PJ: The TOR
pathway: A target for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:335–348.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kumar G, Dange P, Kailaje V, Vaidya MM,
Ramchandani AG and Maru GB: Polymeric black tea polyphenols
modulate the localization and activity of
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-a cetate-mediated kinases in mouse
skin: Mechanisms of their anti-tumor-promoting action. Free Radic
Biol Med. 53:1358–1370. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Foster KG and Fingar DC: Mammalian target
of rapamycin (mTOR): Conducting the cellular signaling symphony. J
Biol Chem. 285:14071–14077. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim DH, Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, King JE,
Latek RR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P and Sabatini DM: mTOR
interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that
signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell. 110:163–175. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sekulić A, Hudson CC, Homme JL, Yin P,
Otterness DM, Karnitz LM and Abraham RT: A direct linkage between
the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-AKT signaling pathway and the
mammalian target of rapamycin in mitogen-stimulated and transformed
cells. Cancer Res. 60:3504–3513. 2000.
|
|
14
|
Hsu PP, Kang SA, Rameseder J, Zhang Y,
Ottina KA, Lim D, Peterson TR, Choi Y, Gray NS, Yaffe MB, et al:
The mTOR-regulated phosphoproteome reveals a mechanism of
mTORC1-mediated inhibition of growth factor signaling. Science.
332:1317–1322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kelloff GJ: Perspectives on cancer
chemoprevention research and drug development. Adva Cancer Res.
78:199–334. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA and Lowe SW:
Apoptosis: A link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell.
108:153–164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Malaguarnera L: Implications of apoptosis
regulators in tumorigenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 23:367–387.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kumar G, Tajpara P and Maru G: Dietary
turmeric post-treatment decreases DMBA-induced hamster buccal pouch
tumor growth by altering cell proliferation and apoptosis-related
markers. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 31:295–312. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bareford MD, Park MA, Yacoub A, Hamed HA,
Tang Y, Cruickshanks N, Eulitt P, Hubbard N, Tye G, Burow ME, et
al: Sorafenib enhances pemetrexed cytotoxicity through an
autophagy-dependent mechanism in cancer cells. Cancer Res.
71:4955–4967. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thorburn A: Apoptosis and autophagy:
Regulatory connections between two supposedly different processes.
Apoptosis. 13:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Maiuri MC, Le Toumelin G, Criollo A, Rain
JC, Gautier F, Juin P, Tasdemir E, Pierron G, Troulinaki K,
Tavernarakis N, et al: Functional and physical interaction between
Bcl-X(L) and a BH3-like domain in Beclin-1. EMBO J. 26:2527–2539.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang ZF, Shao LJ, Wang WM, Yan XB and Liu
RY: Decreased expression of Beclin-1 and LC3 in human lung cancer.
Mol Biol Rep. 39:259–267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Stoner GD, Adam-Rodwell G and Morse MA:
Lung tumors in strain A mice: Application for studies in cancer
chemoprevention. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 17F:95–103. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Harrison DE, Strong R, Sharp ZD, Nelson
JF, Astle CM, Flurkey K, Nadon NL, Wilkinson JE, Frenkel K, Carter
CS, et al: Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in
genetically heterogeneous mice. Nature. 460:392–395.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nadon NL, Strong R, Miller RA, Nelson J,
Javors M, Sharp ZD, Peralba JM and Harrison DE: Design of aging
intervention studies: The NIA interventions testing program. Age
(Dordr). 30:187–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Nikitin AY, Alcaraz A, Anver MR, Bronson
RT, Cardiff RD, Dixon D, Fraire AE, Gabrielson EW, Gunning WT,
Haines DC, et al: Classification of proliferative pulmonary lesions
of the mouse: Recommendations of the mouse models of human cancers
consortium. Cancer Res. 64:2307–2316. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kumar G, Tajpara P, Bukhari AB,
Ramchandani AG, De A and Maru GB: Dietary curcumin post-treatment
enhances the disappearance of B(a)P-derived DNA adducts in mouse
liver and lungs. Toxicol Rep. 1:1181–1194. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sun SY, Rosenberg LM, Wang X, Zhou Z, Yue
P, Fu H and Khuri FR: Activation of Akt and eIF4E survival pathways
by rapamycin-mediated mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition.
Cancer Res. 65:7052–7058. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Laag E, Majidi M, Cekanova M, Masi T,
Takahashi T and Schuller HM: NNK activates ERK1/2 and CREB/ATF-1
via beta-1-AR and EGFR signaling in human lung adenocarcinoma and
small airway epithelial cells. Int J Cancer. 119:1547–1552. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vicent S, López-Picazo JM, Toledo G,
Lozano MD, Torre W, Garcia-Corchón C, Quero C, Soria JC,
Martín-Algarra S, Manzano RG, et al: ERK1/2 is activated in
non-small-cell lung cancer and associated with advanced tumours. Br
J Cancer. 90:1047–1052. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tooze SA and Yoshimori T: The origin of
the autophagosomal membrane. Nat Cell Biol. 12:831–835. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oberstein A, Jeffrey PD and Shi Y: Crystal
structure of the Bcl-XL-Beclin 1 peptide complex: Beclin 1 is a
novel BH3-only protein. J Biol Chem. 282:13123–13132. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Memmott RM and Dennis PA: The role of the
Akt/mTOR pathway in tobacco carcinogen-induced lung tumorigenesis.
Clin Cancer Res. 16:4–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Altomare DA and Testa JR: Perturbations of
the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene. 24:7455–7464.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tsurutani J, Fukuoka J, Tsurutani H, Shih
JH, Hewitt SM, Travis WD, Jen J and Dennis PA: Evaluation of two
phosphorylation sites improves the prognostic significance of Akt
activation in non-small-cell lung cancer tumors. J Clinical Oncol.
24:306–314. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Balsara BR, Pei J, Mitsuuchi Y, Page R,
Klein-Szanto A, Wang H, Unger M and Testa JR: Frequent activation
of AKT in non-small cell lung carcinomas and preneoplastic
bronchial lesions. Carcinogenesis. 25:2053–2059. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Han S, Khuri FR and Roman J: Fibronectin
stimulates non-small cell lung carcinoma cell growth through
activation of Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin/S6 kinase and
inactivation of LKB1/AMP-activated protein kinase signal pathways.
Cancer Res. 66:315–323. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Granville CA, Warfel N, Tsurutani J,
Hollander MC, Robertson M, Fox SD, Veenstra TD, Issaq HJ, Linnoila
RI and Dennis PA: Identification of a highly effective rapamycin
schedule that markedly reduces the size, multiplicity, and
phenotypic progression of tobacco carcinogen-induced murine lung
tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2281–2289. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yan Y, Wang Y, Tan Q, Hara Y, Yun TK,
Lubet RA and You M: Efficacy of polyphenon E, red ginseng, and
rapamycin on benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung tumorigenesis in A/J mice.
Neoplasia. 8:52–58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jaeschke A, Hartkamp J, Saitoh M, Roworth
W, Nobukuni T, Hodges A, Sampson J, Thomas G and Lamb R: Tuberous
sclerosis complex tumor suppressor-mediated S6 kinase inhibition by
phosphatidylinositide-3-OH kinase is mTOR independent. J Cell Biol.
159:217–224. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Khuri FR, Lee JS, Lippman SM, Lee JJ,
Kalapurakal S, Yu R, Ro JY, Morice RC, Hong WK and Hittelman WN:
Modulation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen in the bronchial
epithelium of smokers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
10:311–318. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fingar DC and Blenis J: Target of
rapamycin (TOR): An integrator of nutrient and growth factor
signals and coordinator of cell growth and cell cycle progression.
Oncogene. 23:3151–3171. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dowling RJ, Topisirovic I, Alain T,
Bidinosti M, Fonseca BD, Petroulakis E, Wang X, Larsson O, Selvaraj
A, Liu Y, et al: mTORC1-mediated cell proliferation, but not cell
growth, controlled by the 4E-BPs. Science. 328:1172–1176. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Degtyarev M, De Mazière A, Orr C, Lin J,
Lee BB, Tien JY, Prior WW, van Dijk S, Wu H, Gray DC, et al: Akt
inhibition promotes autophagy and sensitizes PTEN-null tumors to
lysosomotropic agents. J Cell Biol. 183:101–116. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bai X, Ma D, Liu A, Shen X, Wang QJ, Liu Y
and Jiang Y: Rheb activates mTOR by antagonizing its endogenous
inhibitor, FKBP38. Science. 318:977–980. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ma D, Bai X, Zou H, Lai Y and Jiang Y:
Rheb GTPase controls apoptosis by regulating interaction of FKBP38
with Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL. J Biol Chem. 285:8621–8627. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shirane M and Nakayama KI: Inherent
calcineurin inhibitor FKBP38 targets Bcl-2 to mitochondria and
inhibits apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 5:28–37. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chun KH, Kosmeder JW II, Sun S, Pezzuto
JM, Lotan R, Hong WK and Lee HY: Effects of deguelin on the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and apoptosis in
premalignant human bronchial epithelial cells. J Natl Cancer Inst.
95:291–302. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang W, Fan H, Zhou Y, Duan P, Zhao G and
Wu G: Knockdown of autophagy-related gene BECLIN1 promotes cell
growth and inhibits apoptosis in the A549 human lung cancer cell
line. Mol Med Rep. 7:1501–1505. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|