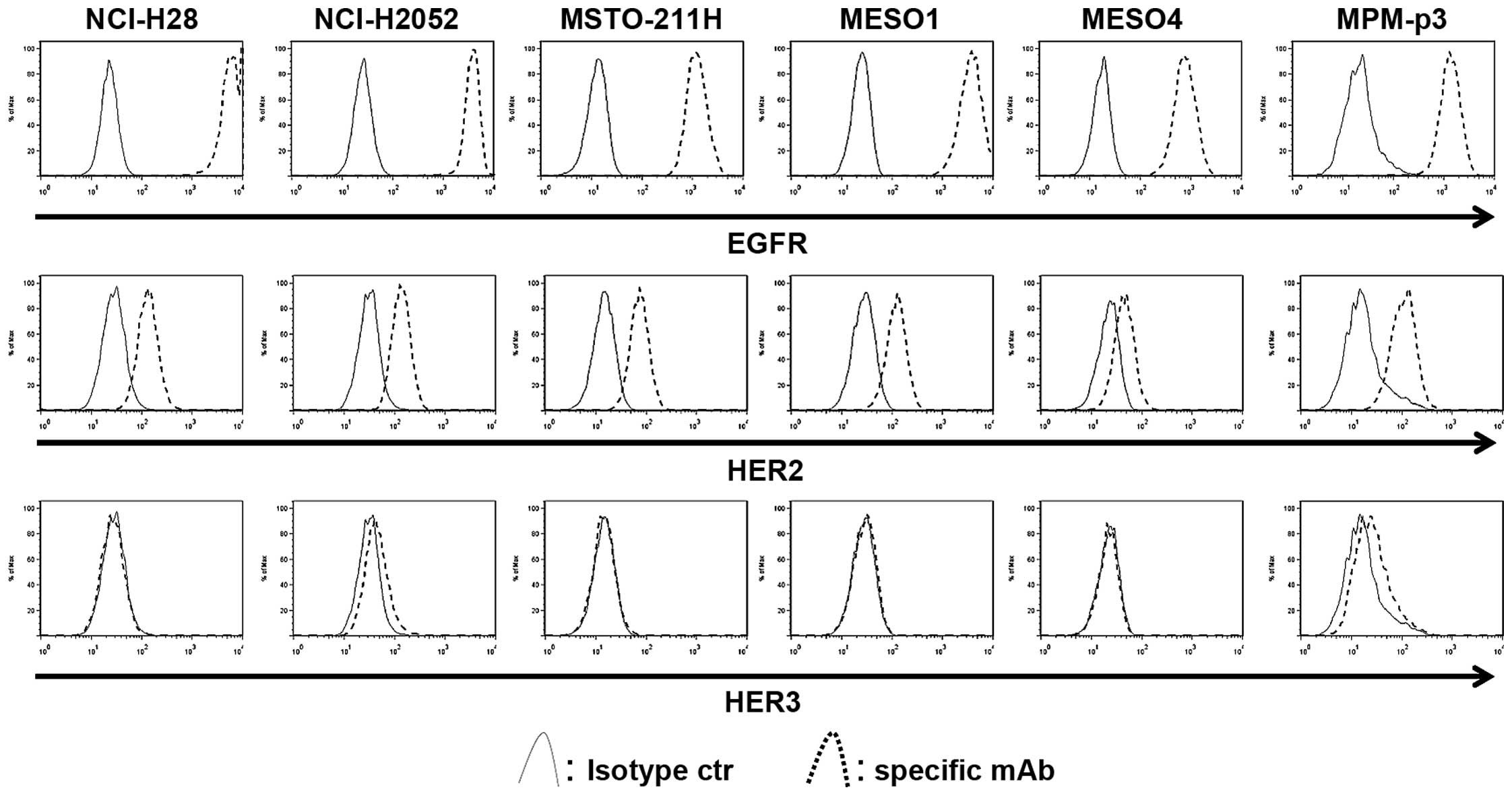
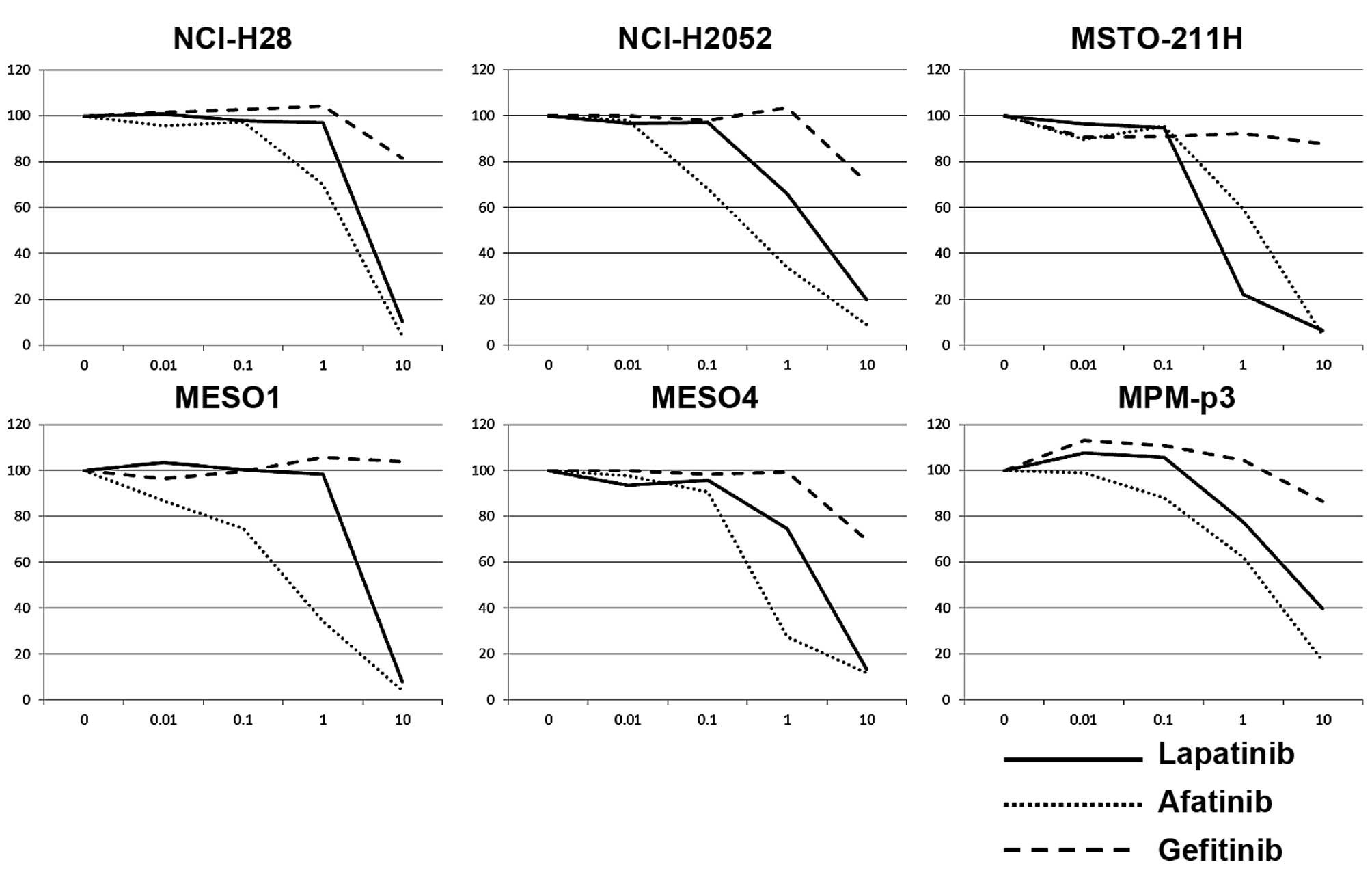
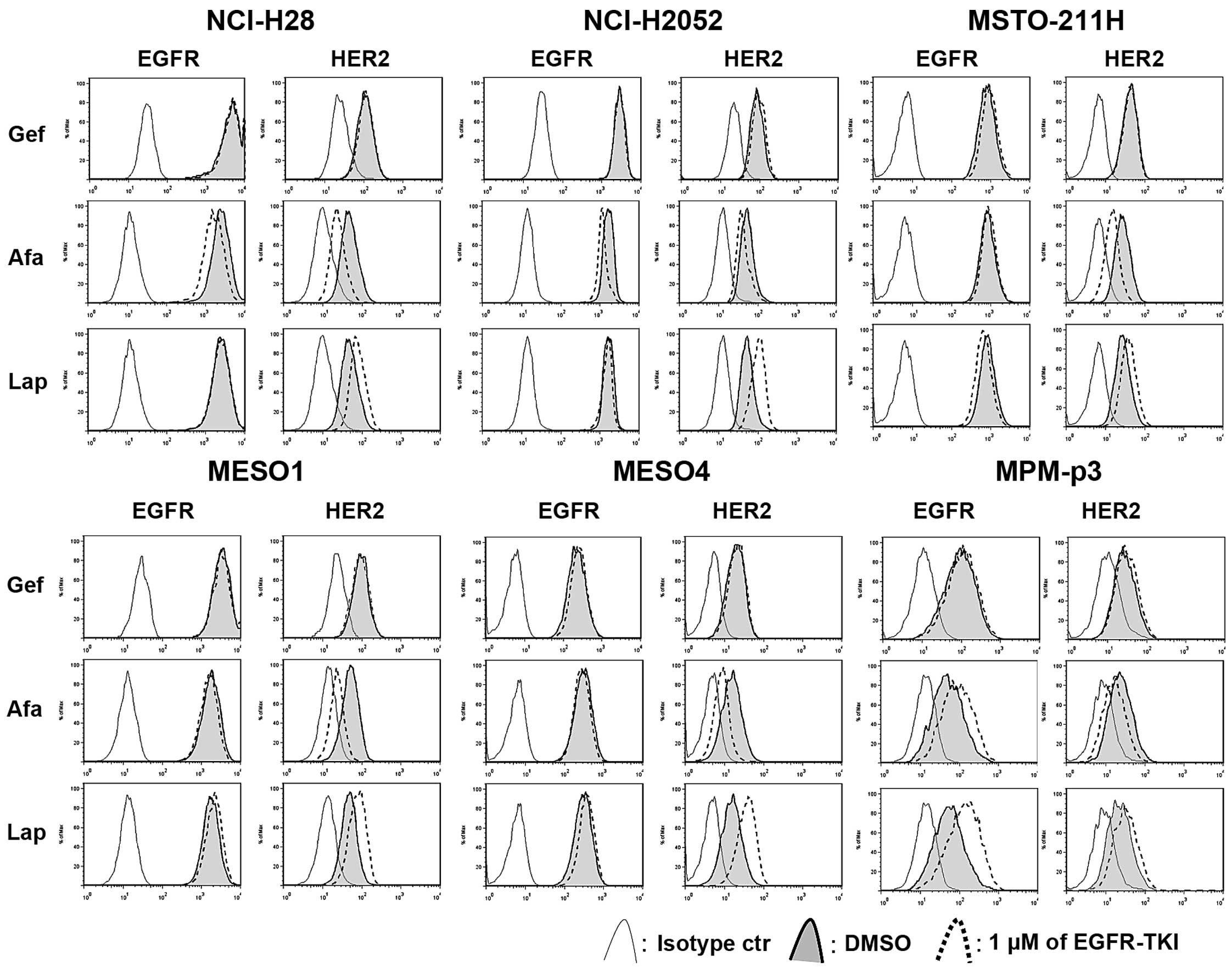
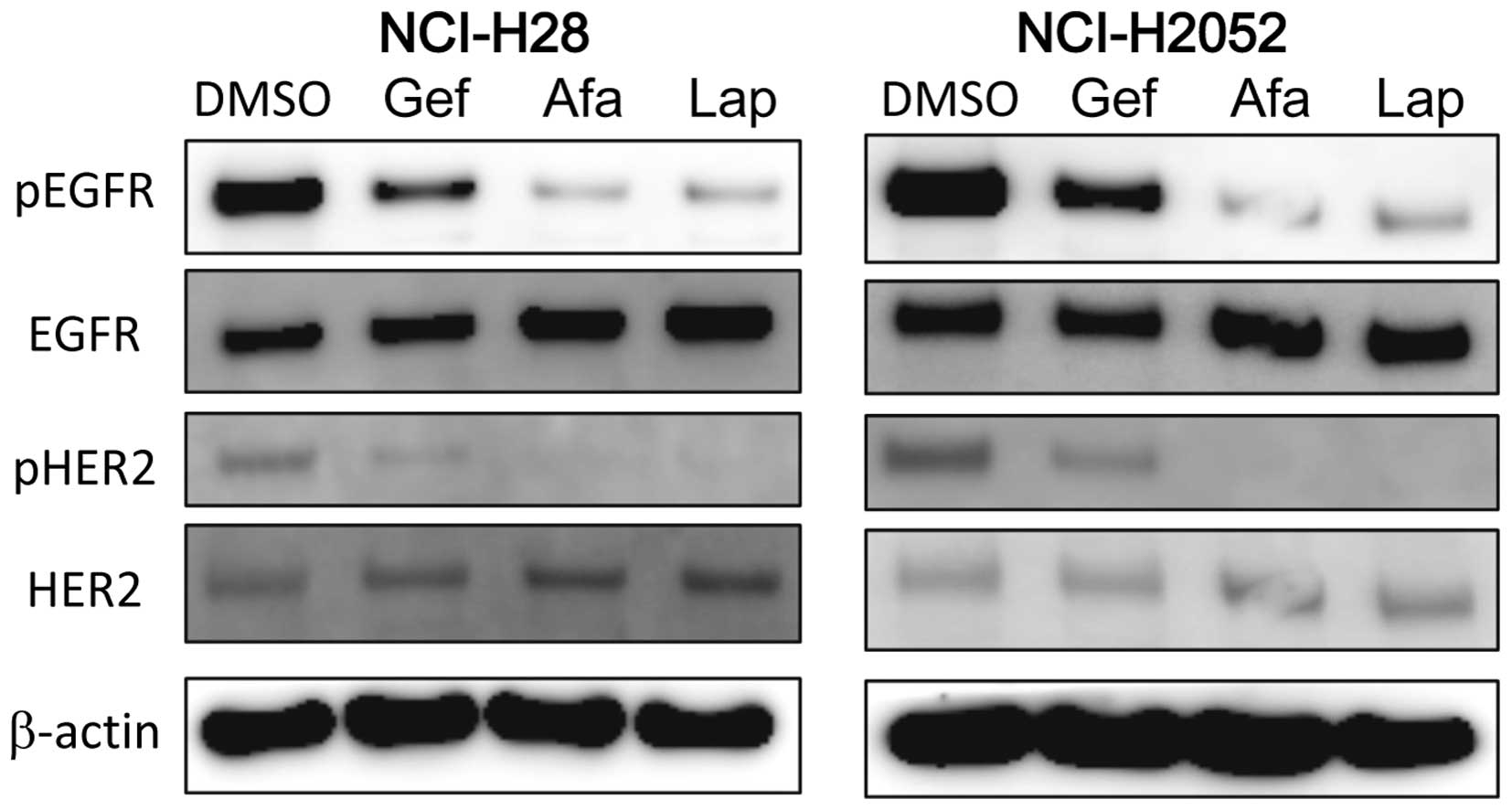
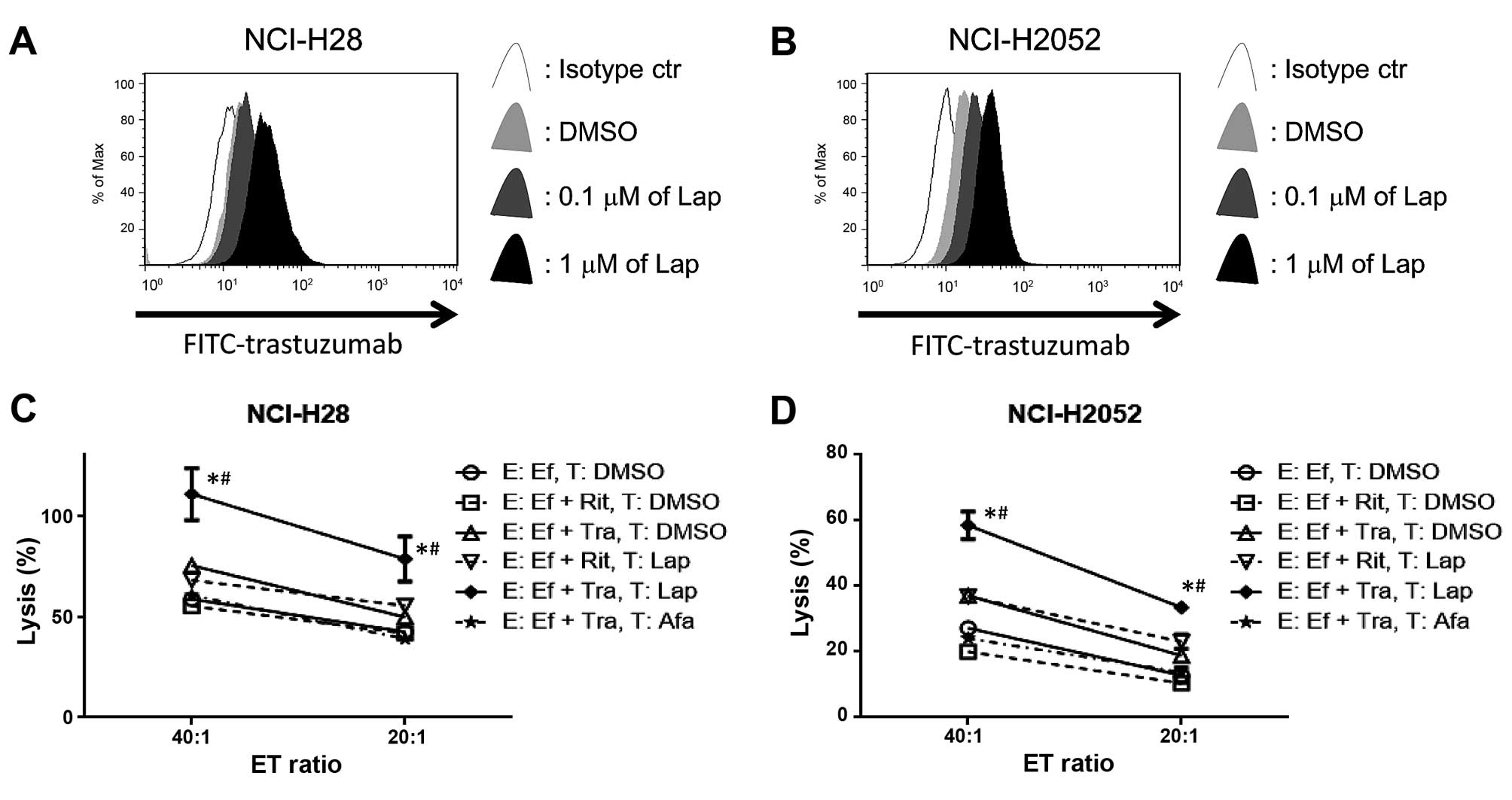
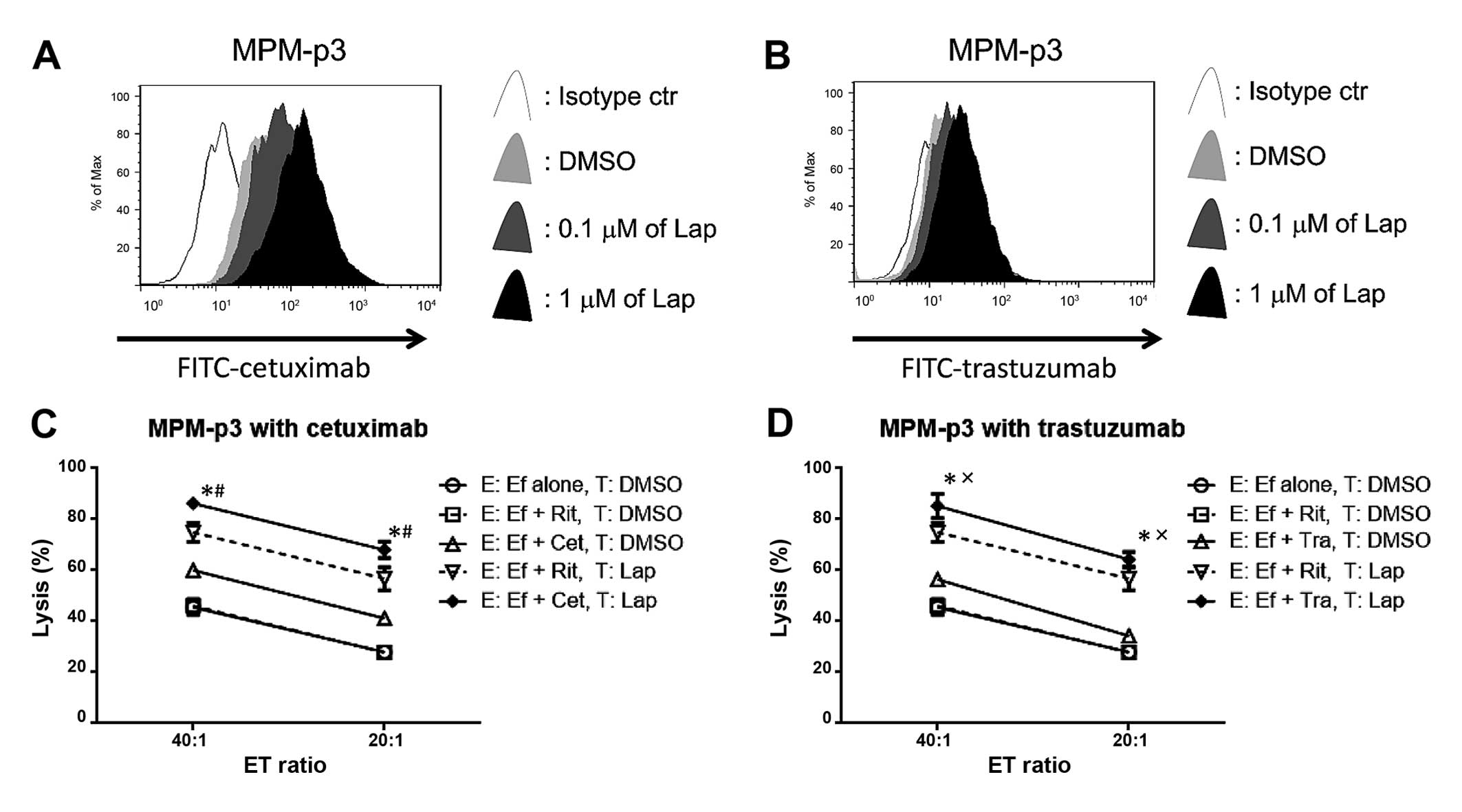
|
1
|
Rusch VW and Venkatraman ES: Important
prognostic factors in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma,
managed surgically. Ann Thorac Surg. 68:1799–1804. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vogelzang NJ, Rusthoven JJ, Symanowski J,
Denham C, Kaukel E, Ruffie P, Gatzemeier U, Boyer M, Emri S,
Manegold C, et al: Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination
with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant
pleural mesothelioma. J Clin Oncol. 21:2636–2644. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Destro A, Ceresoli GL, Falleni M, Zucali
PA, Morenghi E, Bianchi P, Pellegrini C, Cordani N, Vaira V,
Alloisio M, et al: EGFR overexpression in malignant pleural
mesothelioma. An immunohistochemical and molecular study with
clinico-pathological correlations. Lung Cancer. 51:207–215. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Garland LL, Rankin C, Gandara DR, Rivkin
SE, Scott KM, Nagle RB, Klein-Szanto AJ, Testa JR, Altomare DA and
Borden EC: Phase II study of erlotinib in patients with malignant
pleural mesothelioma: A Southwest Oncology Group Study. J Clin
Oncol. 25:2406–2413. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Govindan R, Kratzke RA, Herndon JE II,
Niehans GA, Vollmer R, Watson D, Green MR and Kindler HL: Cancer
and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 30101): Gefitinib in patients with
malignant mesothelioma: A phase II study by the Cancer and Leukemia
Group B. Clin Cancer Res. 11:2300–2304. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scaltriti M, Verma C, Guzman M, Jimenez J,
Parra JL, Pedersen K, Smith DJ, Landolfi S, Ramon y Cajal S,
Arribas J, et al: Lapatinib, a HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor,
induces stabilization and accumulation of HER2 and potentiates
trastuzumab-dependent cell cytotoxicity. Oncogene. 28:803–814.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mimura K, Kono K, Maruyama T, Watanabe M,
Izawa S, Shiba S, Mizukami Y, Kawaguchi Y, Inoue M, Kono T, et al:
Lapatinib inhibits receptor phosphorylation and cell growth and
enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of EGFR-and
HER2-overexpressing esophageal cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer.
129:2408–2416. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shiraishi K, Mimura K, Izawa S, Inoue A,
Shiba S, Maruyama T, Watanabe M, Kawaguchi Y, Inoue M, Fujii H, et
al: Lapatinib acts on gastric cancer through both antiproliferative
function and augmentation of trastuzumab-mediated
antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Gastric Cancer.
16:571–580. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Usami N, Fukui T, Kondo M, Taniguchi T,
Yokoyama T, Mori S, Yokoi K, Horio Y, Shimokata K, Sekido Y, et al:
Establishment and characterization of four malignant pleural
mesothelioma cell lines from Japanese patients. Cancer Sci.
97:387–394. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pao W, Miller VA, Politi KA, Riely GJ,
Somwar R, Zakowski MF, Kris MG and Varmus H: Acquired resistance of
lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a
second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain. PLoS Med. 2:e732005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li D, Ambrogio L, Shimamura T, Kubo S,
Takahashi M, Chirieac LR, Padera RF, Shapiro GI, Baum A,
Himmelsbach F, et al: BIBW2992, an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor
highly effective in preclinical lung cancer models. Oncogene.
27:4702–4711. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Geyer CE, Forster J, Lindquist D, Chan S,
Romieu CG, Pienkowski T, Jagiello-Gruszfeld A, Crown J, Chan A,
Kaufman B, et al: Lapatinib plus capecitabine for HER2-positive
advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2733–2743. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gilmer TM, Cable L, Alligood K, Rusnak D,
Spehar G, Gallagher KT, Woldu E, Carter HL, Truesdale AT, Shewchuk
L, et al: Impact of common epidermal growth factor receptor and
HER2 variants on receptor activity and inhibition by lapatinib.
Cancer Res. 68:571–579. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Clynes RA, Towers TL, Presta LG and
Ravetch JV: Inhibitory Fc receptors modulate in vivo cytotoxicity
against tumor targets. Nat Med. 6:443–446. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kurai J, Chikumi H, Hashimoto K, Yamaguchi
K, Yamasaki A, Sako T, Touge H, Makino H, Takata M, Miyata M, et
al: Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mediated by cetuximab
against lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1552–1561.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kurai J, Chikumi H, Hashimoto K, Takata M,
Sako T, Yamaguchi K, Kinoshita N, Watanabe M, Touge H, Makino H, et
al: Therapeutic antitumor efficacy of anti-epidermal growth factor
receptor antibody, cetuximab, against malignant pleural
mesothelioma. Int J Oncol. 41:1610–1618. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rimawi MF, Aleixo SB, Rozas AA, Nunes de
Matos Neto J, Caleffi M, Figueira AC, Souza SC, Reiriz AB,
Gutierrez C, Arantes H, et al: A neoadjuvant, randomized,
open-label phase II trial of afatinib versus trastuzumab versus
lapatinib in patients with locally advanced HER2-positive breast
cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 15:101–109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|