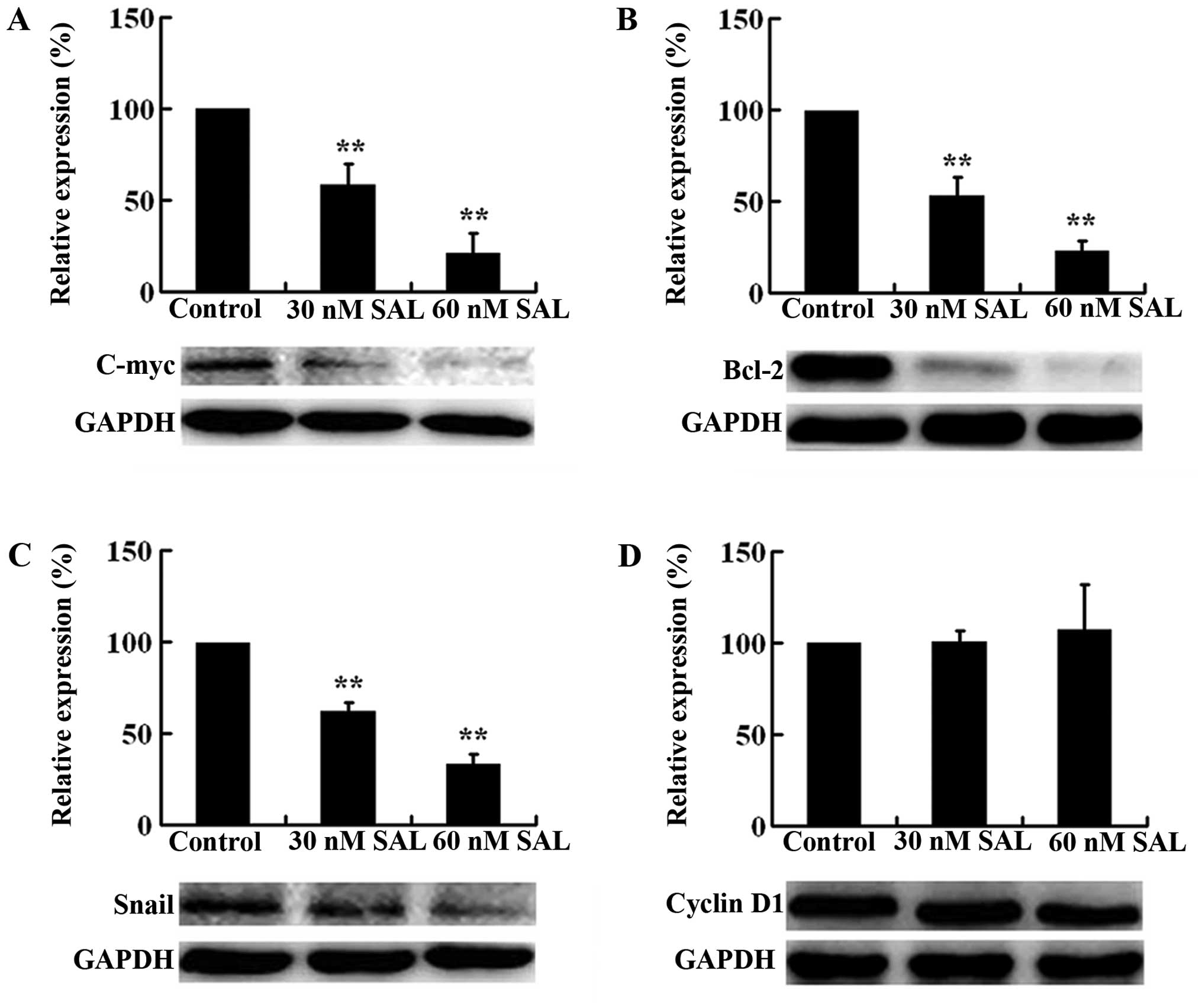
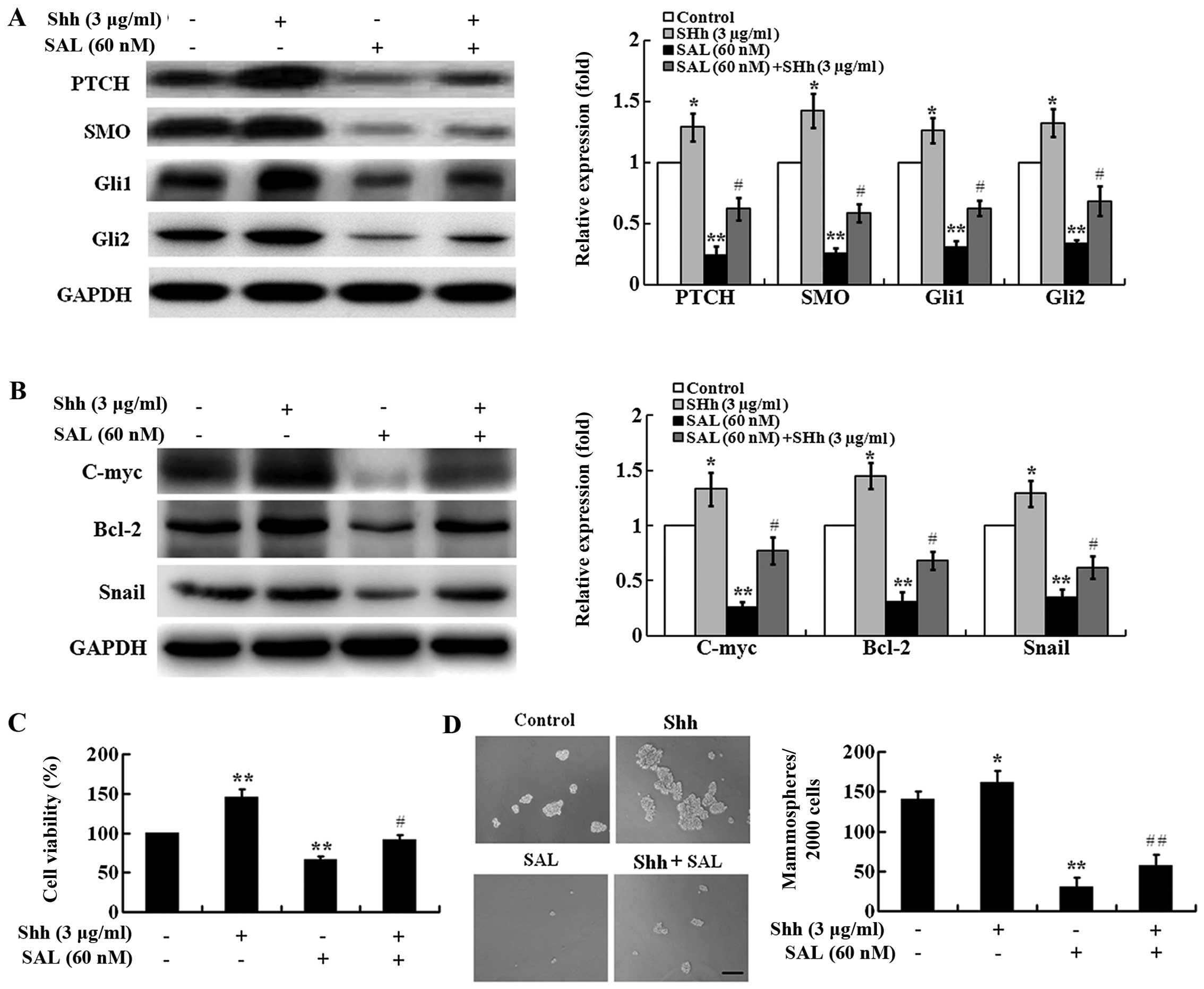
|
1
|
DeSantis C, Siegel R, Bandi P and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:409–418. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marquette C and Nabell L:
Chemotherapy-resistant metastatic breast cancer. Curr Treat Options
Oncol. 13:263–275. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhou J, Zhang H, Gu P, Bai J, Margolick JB
and Zhang Y: NF-kappaB pathway inhibitors preferentially inhibit
breast cancer stem-like cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
111:419–427. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Diehn M, Cho RW, Lobo NA, Kalisky T, Dorie
MJ, Kulp AN, Qian D, Lam JS, Ailles LE, Wong M, et al: Association
of reactive oxygen species levels and radioresistance in cancer
stem cells. Nature. 458:780–783. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sampieri K and Fodde R: Cancer stem cells
and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:187–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Varjosalo M and Taipale J: Hedgehog:
Functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev. 22:2454–2472. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dontu G, Jackson KW, McNicholas E,
Kawamura MJ, Abdallah WM and Wicha MS: Role of Notch signaling in
cell-fate determination of human mammary stem/progenitor cells.
Breast Cancer Res. 6:R605–R615. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Taipale J and Beachy PA: The Hedgehog and
Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature. 411:349–354. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Watkins DN, Berman DM, Burkholder SG, Wang
B, Beachy PA and Baylin SB: Hedgehog signalling within airway
epithelial progenitors and in small-cell lung cancer. Nature.
422:313–317. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma X, Sheng T, Zhang Y, Zhang X, He J,
Huang S, Chen K, Sultz J, Adegboyega PA, Zhang H, et al: Hedgehog
signaling is activated in subsets of esophageal cancers. Int J
Cancer. 118:139–148. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Fukaya M, Isohata N, Ohta H, Aoyagi K,
Ochiya T, Saeki N, Yanagihara K, Nakanishi Y, Taniguchi H, Sakamoto
H, et al: Hedgehog signal activation in gastric pit cell and in
diffuse-type gastric cancer. Gastroenterology. 131:14–29. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kayed H, Kleeff J, Keleg S, Guo J,
Ketterer K, Berberat PO, Giese N, Esposito I, Giese T, Büchler MW,
et al: Indian hedgehog signaling pathway: Expression and regulation
in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 110:668–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Clement V, Sanchez P, de Tribolet N,
Radovanovic I and Ruiz i Altaba A: HEDGEHOG-GLI1 signaling
regulates human glioma growth, cancer stem cell self-renewal, and
tumorigenicity. Curr Biol. 17:165–172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tanaka H, Nakamura M, Kameda C, Kubo M,
Sato N, Kuroki S, Tanaka M and Katano M: The Hedgehog signaling
pathway plays an essential role in maintaining the
CD44+CD24−/low subpopulation and the side
population of breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 29:2147–2157.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sheikh A, Alvi AA, Aslam HM and Haseeb A:
Hedgehog pathway inhibitors - current status and future prospects.
Infect Agent Cancer. 7:292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K,
Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA and Lander ES: Identification of
selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput
screening. Cell. 138:645–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dong TT, Zhou HM, Wang LL, Feng B, Lv B
and Zheng MH: Salinomycin selectively targets 'CD133+'
cell subpopulations and decreases malignant traits in colorectal
cancer lines. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1797–1804. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhi QM, Chen XH, Ji J, Zhang JN, Li JF,
Cai Q, Liu BY, Gu QL, Zhu ZG and Yu YY: Salinomycin can effectively
kill ALDH(high) stem-like cells on gastric cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 65:509–515. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang GN, Liang Y, Zhou LJ, Chen SP, Chen
G, Zhang TP, Kang T and Zhao YP: Combination of salinomycin and
gemci-tabine eliminates pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
313:137–144. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kuo SZ, Blair KJ, Rahimy E, Kiang A,
Abhold E, Fan JB, Wang-Rodriguez J, Altuna X and Ongkeko WM:
Salinomycin induces cell death and differentiation in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma stem cells despite activation of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and Akt. BMC Cancer. 12:5562012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kusunoki S, Kato K, Tabu K, Inagaki T,
Okabe H, Kaneda H, Suga S, Terao Y, Taga T and Takeda S: The
inhibitory effect of salinomycin on the proliferation, migration
and invasion of human endometrial cancer stem-like cells. Gynecol
Oncol. 129:598–605. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ketola K, Hilvo M, Hyötyläinen T, Vuoristo
A, Ruskeepää AL, Orešič M, Kallioniemi O and Iljin K: Salinomycin
inhibits prostate cancer growth and migration via induction of
oxidative stress. Br J Cancer. 106:99–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim KY, Yu SN, Lee SY, Chun SS, Choi YL,
Park YM, Song CS, Chatterjee B and Ahn SC: Salinomycin-induced
apoptosis of human prostate cancer cells due to accumulated
reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial membrane depolarization.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 413:80–86. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lieke T, Ramackers W, Bergmann S,
Klempnauer J, Winkler M and Klose J: Impact of salinomycin on human
cholangiocarcinoma: Induction of apoptosis and impairment of tumor
cell proliferation in vitro. BMC Cancer. 12:4662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang F, He L, Dai WQ, Xu YP, Wu D, Lin CL,
Wu SM, Cheng P, Zhang Y, Shen M, et al: Salinomycin inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 7:e506382012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Verdoodt B, Vogt M, Schmitz I, Liffers ST,
Tannapfel A and Mirmohammadsadegh A: Salinomycin induces autophagy
in colon and breast cancer cells with concomitant generation of
reactive oxygen species. PLoS One. 7:e441322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lu D, Choi MY, Yu J, Castro JE, Kipps TJ
and Carson DA: Salinomycin inhibits Wnt signaling and selectively
induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:13253–13257. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tang QL, Zhao ZQ, Li JC, Liang Y, Yin JQ,
Zou CY, Xie XB, Zeng YX, Shen JN, Kang T, et al: Salinomycin
inhibits osteo-sarcoma by targeting its tumor stem cells. Cancer
Lett. 311:113–121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ponti D, Costa A, Zaffaroni N, Pratesi G,
Petrangolini G, Coradini D, Pilotti S, Pierotti MA and Daidone MG:
Isolation and in vitro propagation of tumorigenic breast cancer
cells with stem/progenitor cell properties. Cancer Res.
65:5506–5511. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fan X, Chen X, Deng W, Zhong G, Cai Q and
Lin T: Up-regulated microRNA-143 in cancer stem cells
differentiation promotes prostate cancer cells metastasis by
modulating FNDC3B expression. BMC Cancer. 13:612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
He M, Sun HG, Hao JY, Li YL, Yu JK, Yan
YY, Zhao L, Li N, Wang Y, Bai XF, et al: RNA interference-mediated
FANCF silencing sensitizes OVCAR3 ovarian cancer cells to
adriamycin through increased adriamycin-induced apoptosis dependent
on JNK activation. Oncol Rep. 29:1721–1729. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hatton BA, Knoepfler PS, Kenney AM,
Rowitch DH, de Alborán IM, Olson JM and Eisenman RN: N-myc is an
essential downstream effector of Shh signaling during both normal
and neoplastic cerebellar growth. Cancer Res. 66:8655–8661. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bigelow RL, Chari NS, Unden AB, Spurgers
KB, Lee S, Roop DR, Toftgard R and McDonnell TJ: Transcriptional
regulation of bcl-2 mediated by the sonic hedgehog signaling
pathway through gli-1. J Biol Chem. 279:1197–1205. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Duman-Scheel M, Weng L, Xin S and Du W:
Hedgehog regulates cell growth and proliferation by inducing cyclin
D and cyclin E. Nature. 417:299–304. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li X, Deng W, Nail CD, Bailey SK, Kraus
MH, Ruppert JM and Lobo-Ruppert SM: Snail induction is an early
response to Gli1 that determines the efficiency of epithelial
transformation. Oncogene. 25:609–621. 2006.
|
|
37
|
Liu S, Dontu G, Mantle ID, Patel S, Ahn
NS, Jackson KW, Suri P and Wicha MS: Hedgehog signaling and Bmi-1
regulate self-renewal of normal and malignant human mammary stem
cells. Cancer Res. 66:6063–6071. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu H, Patel MR, Prescher JA, Patsialou A,
Qian D, Lin J, Wen S, Chang YF, Bachmann MH, Shimono Y, et al:
Cancer stem cells from human breast tumors are involved in
spontaneous metastases in orthotopic mouse models. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 107:18115–18120. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cariati M, Naderi A, Brown JP, Smalley MJ,
Pinder SE, Caldas C and Purushotham AD: Alpha-6 integrin is
necessary for the tumourigenicity of a stem cell-like subpopulation
within the MCF7 breast cancer cell line. Int J Cancer. 122:298–304.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhao XQ, Dai CL, Ohnuma S, Liang YJ, Deng
W, Chen JJ, Zeng MS, Ambudkar SV, Chen ZS and Fu LW: Tandutinib
(MLN518/CT53518) targeted to stem-like cells by inhibiting the
function of ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2. Eur J Pharm
Sci. 49:441–450. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Takashima S, Mkrtchyan M,
Younossi-Hartenstein A, Merriam JR and Hartenstein V: The behaviour
of Drosophila adult hindgut stem cells is controlled by Wnt and Hh
signalling. Nature. 454:651–655. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lu Y, Ma W, Mao J, Yu X, Hou Z, Fan S,
Song B, Wang H, Li J, Kang L, et al: Salinomycin exerts anticancer
effects on human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cancer stem cells via
modulation of Hedgehog signaling. Chem Biol Interact. 228:100–107.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wang J, Wang H, Li Z, Wu Q, Lathia JD,
McLendon RE, Hjelmeland AB and Rich JN: c-Myc is required for
maintenance of glioma cancer stem cells. PLoS One. 3:e37692008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Murphy MJ, Wilson A and Trumpp A: More
than just proliferation: Myc function in stem cells. Trends Cell
Biol. 15:128–137. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fu J, Rodova M, Roy SK, Sharma J, Singh
KP, Srivastava RK and Shankar S: GANT-61 inhibits pancreatic cancer
stem cell growth in vitro and in NOD/SCID/IL2R gamma null mice
xenograft. Cancer Lett. 330:22–32. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesen-chymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Haslehurst AM, Koti M, Dharsee M, Nuin P,
Evans K, Geraci J, Childs T, Chen J, Li J, Weberpals J, et al: EMT
transcription factors snail and slug directly contribute to
cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 12:912012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Feldmann G, Dhara S, Fendrich V, Bedja D,
Beaty R, Mullendore M, Karikari C, Alvarez H, Iacobuzio-Donahue C,
Jimeno A, et al: Blockade of hedgehog signaling inhibits pancreatic
cancer invasion and metastases: A new paradigm for combination
therapy in solid cancers. Cancer Res. 67:2187–2196. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fuchs D, Heinold A, Opelz G, Daniel V and
Naujokat C: Sali-nomycin induces apoptosis and overcomes apoptosis
resistance in human cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
390:743–749. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Koo KH, Kim H, Bae YK, Kim K, Park BK, Lee
CH and Kim YN: Salinomycin induces cell death via inactivation of
Stat3 and downregulation of Skp2. Cell Death Dis. 4:e6932013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|