|
1
|
Gupta GP and Massagué J: Cancer
metastasis: Building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Steeg PS: Tumor metastasis: Mechanistic
insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 12:895–904. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Al-Mehdi AB, Tozawa K, Fisher AB, Shientag
L, Lee A and Muschel RJ: Intravascular origin of metastasis from
the proliferation of endothelium-attached tumor cells: A new model
for metastasis. Nat Med. 6:100–102. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fidler IJ: The pathogenesis of cancer
metastasis: The 'seed and soil' hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:453–458. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fukushima-Nakase Y, Naoe Y, Taniuchi I,
Hosoi H, Sugimoto T and Okuda T: Shared and distinct roles mediated
through C-terminal subdomains of acute myeloid
leukemia/Runt-related transcription factor molecules in murine
development. Blood. 105:4298–4307. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wotton S, Terry A, Kilbey A, Jenkins A,
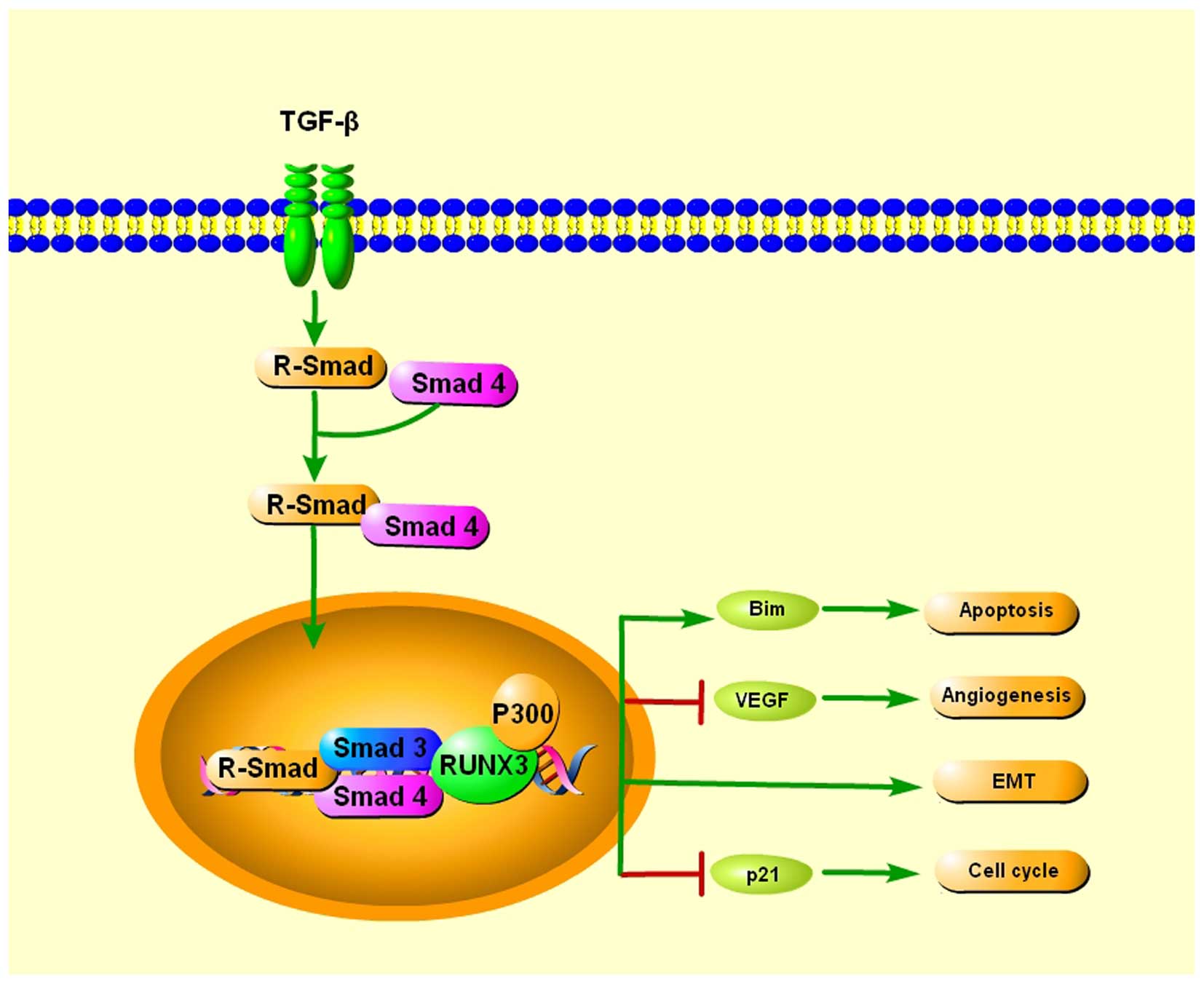
Herzyk P, Cameron E and Neil JC: Gene array analysis reveals a
common Runx transcriptional programme controlling cell adhesion and
survival. Oncogene. 27:5856–5866. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
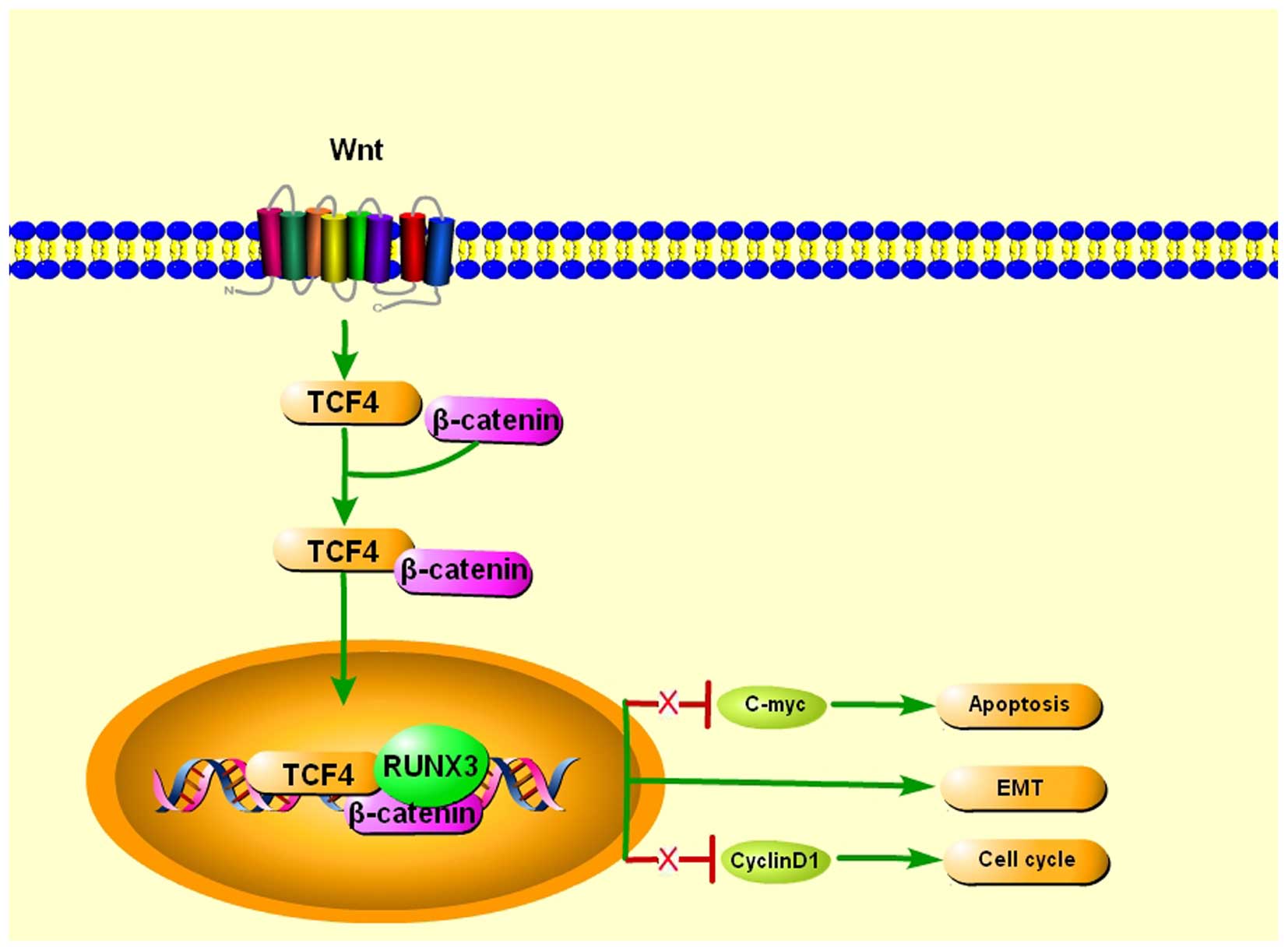
|
7
|
Brady G and Farrell PJ: RUNX3-mediated
repression of RUNX1 in B cells. J Cell Physiol. 221:283–287. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
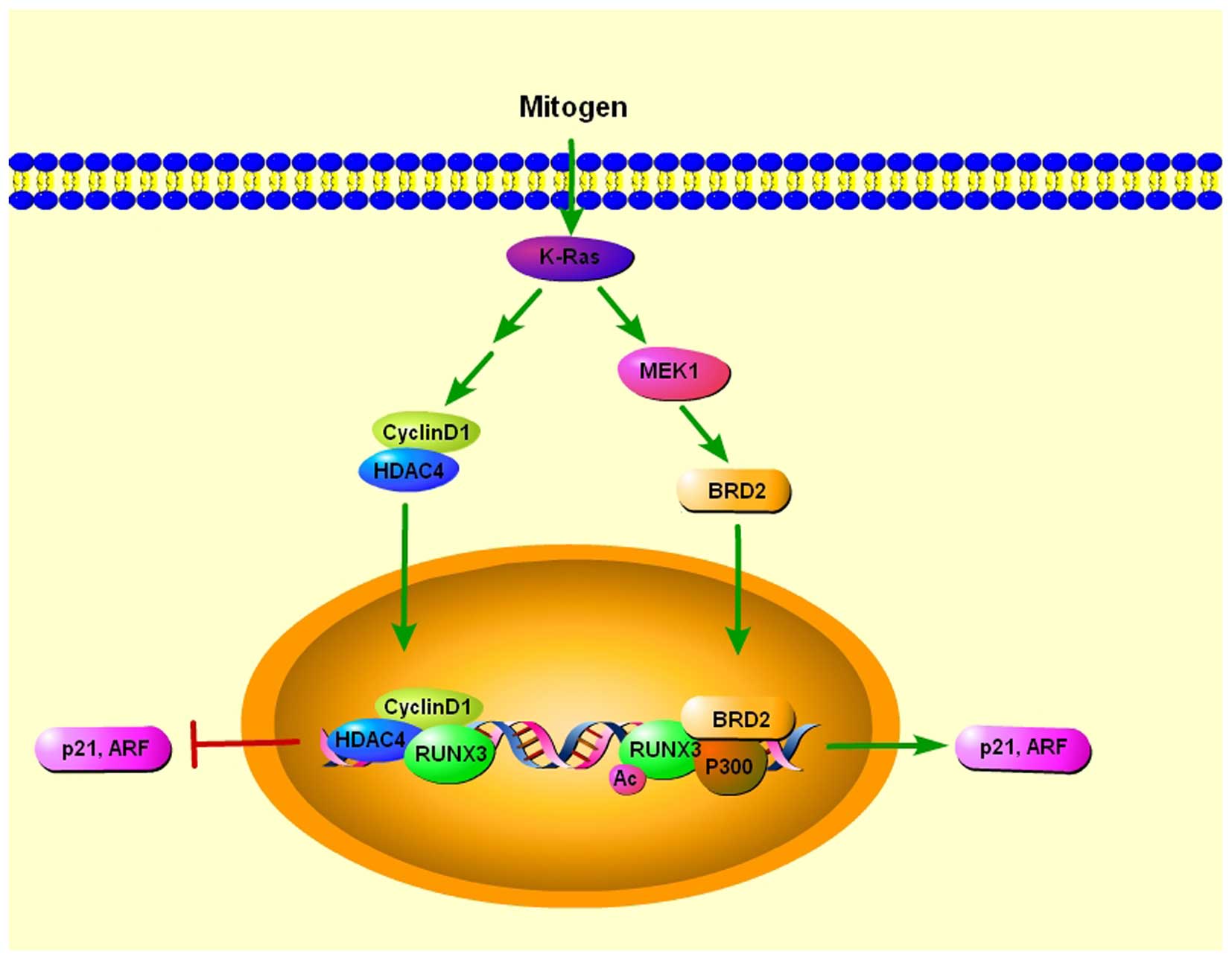
8
|
Fukamachi H and Ito K: Growth regulation
of gastric epithelial cells by Runx3. Oncogene. 23:4330–4335. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Levanon D, Bettoun D, Harris-Cerruti C,
Woolf E, Negreanu V, Eilam R, Bernstein Y, Goldenberg D, Xiao C,
Fliegauf M, et al: The Runx3 transcription factor regulates
development and survival of TrkC dorsal root ganglia neurons. EMBO
J. 21:3454–3463. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Woolf E, Brenner O, Goldenberg D, Levanon
D and Groner Y: Runx3 regulates dendritic epidermal T cell
development. Dev Biol. 303:703–714. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bagchi A and Mills AA: The quest for the
1p36 tumor suppressor. Cancer Res. 68:2551–2556. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Subramaniam MM, Chan JY, Yeoh KG, Quek T,
Ito K and Salto-Tellez M: Molecular pathology of RUNX3 in human
carcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:315–331. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oshimo Y, Oue N, Mitani Y, Nakayama H,
Kitadai Y, Yoshida K, Ito Y, Chayama K and Yasui W: Frequent loss
of RUNX3 expression by promoter hypermethylation in gastric
carcinoma. Pathobiology. 71:137–143. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lau QC, Raja E, Salto-Tellez M, Liu Q, Ito
K, Inoue M, Putti TC, Loh M, Ko TK, Huang C, et al: RUNX3 is
frequently inactivated by dual mechanisms of protein
mislocalization and promoter hypermethylation in breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 66:6512–6520. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ahlquist T, Lind GE, Costa VL, Meling GI,
Vatn M, Hoff GS, Rognum TO, Skotheim RI, Thiis-Evensen E and Lothe
RA: Gene methylation profiles of normal mucosa, and benign and
malignant colorectal tumors identify early onset markers. Mol
Cancer. 7:942008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ito K, Liu Q, Salto-Tellez M, Yano T, Tada
K, Ida H, Huang C, Shah N, Inoue M, Rajnakova A, et al: RUNX3, a
novel tumor suppressor, is frequently inactivated in gastric cancer
by protein mislocalization. Cancer Res. 65:7743–7750.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Voon DC, Wang H, Koo JK, Nguyen TA, Hor
YT, Chu YS, Ito K, Fukamachi H, Chan SL, Thiery JP, et al: Runx3
protects gastric epithelial cells against epithelial-mesenchymal
transition-induced cellular plasticity and tumorigenicity. Stem
Cells. 30:2088–2099. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen F, Bai J, Li W, Mei P, Liu H, Li L,
Pan Z, Wu Y and Zheng J: RUNX3 suppresses migration, invasion and
angiogenesis of human renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e562412013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sakakura C, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa K,
Nakashima S, Yoshikawa T, Kin S, Nakase Y, Yazumi S, Yamagishi H,
Okanoue T, et al: Possible involvement of RUNX3 silencing in the
peritoneal metastases of gastric cancers. Clin Cancer Res.
11:6479–6488. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yano T, Ito K, Fukamachi H, Chi XZ, Wee
HJ, Inoue K, Ida H, Bouillet P, Strasser A, Bae SC, et al: The
RUNX3 tumor suppressor upregulates Bim in gastric epithelial cells
undergoing transforming growth factor beta-induced apoptosis. Mol
Cell Biol. 26:4474–4488. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peng Z, Wei D, Wang L, Tang H, Zhang J, Le
X, Jia Z, Li Q and Xie K: RUNX3 inhibits the expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor and reduces the angiogenesis, growth, and
metastasis of human gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6386–6394.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mei PJ, Bai J, Liu H, Li C, Wu YP, Yu ZQ
and Zheng JN: RUNX3 expression is lost in glioma and its
restoration causes drastic suppression of tumor invasion and
migration. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:1823–1830. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Chen G, Cheng Y, Martinka M and
Li G: Prognostic significance of RUNX3 expression in human
melanoma. Cancer. 117:2719–2727. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen F, Wang M, Bai J, Liu Q, Xi Y, Li W
and Zheng J: Role of RUNX3 in suppressing metastasis and
angiogenesis of human prostate cancer. PLoS One. 9:e869172014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen W, Salto-Tellez M, Palanisamy N,
Ganesan K, Hou Q, Tan LK, Sii LH, Ito K, Tan B, Wu J, et al:
Targets of genome copy number reduction in primary breast cancers
identified by integrative genomics. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
46:288–301. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Finak G, Bertos N, Pepin F, Sadekova S,
Souleimanova M, Zhao H, Chen H, Omeroglu G, Meterissian S, Omeroglu
A, et al: Stromal gene expression predicts clinical outcome in
breast cancer. Nat Med. 14:518–527. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sakakura C, Miyagawa K, Fukuda KI,
Nakashima S, Yoshikawa T, Kin S, Nakase Y, Ida H, Yazumi S,
Yamagishi H, et al: Frequent silencing of RUNX3 in esophageal
squamous cell carcinomas is associated with radioresistance and
poor prognosis. Oncogene. 26:5927–5938. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chuang LS and Ito Y: RUNX3 is
multifunctional in carcinogenesis of multiple solid tumors.
Oncogene. 29:2605–2615. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu YY, Chen C, Kong FF and Zhang W:
Clinicopathological significance and potential drug target of RUNX3
in breast cancer. Drug Des Devel Ther. 8:2423–2430. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang D, Cui W, Wu X, Qu Y, Wang N, Shi B
and Hou P: RUNX3 site-specific hypermethylation predicts papillary
thyroid cancer recurrence. Am J Cancer Res. 4:725–737.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Katayama Y, Takahashi M and Kuwayama H:
Helicobacter pylori causes runx3 gene methylation and its loss of
expression in gastric epithelial cells, which is mediated by nitric
oxide produced by macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
388:496–500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cheng AS, Culhane AC, Chan MW, Venkataramu
CR, Ehrich M, Nasir A, Rodriguez BA, Liu J, Yan PS, Quackenbush J,
et al: Epithelial progeny of estrogen-exposed breast progenitor
cells display a cancer-like methylome. Cancer Res. 68:1786–1796.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fujii S, Ito K, Ito Y and Ochiai A:
Enhancer of zeste homologue 2 (EZH2) down-regulates RUNX3 by
increasing histone H3 methylation. J Biol Chem. 283:17324–17332.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee SH, Kim J, Kim WH and Lee YM: Hypoxic
silencing of tumor suppressor RUNX3 by histone modification in
gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:184–194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Varambally S, Cao Q, Mani RS, Shankar S,
Wang X, Ateeq B, Laxman B, Cao X, Jing X, Ramnarayanan K, et al:
Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone
methyl-transferase EZH2 in cancer. Science. 322:1695–1699. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lai KW, Koh KX, Loh M, Tada K, Subramaniam
MM, Lim XY, Vaithilingam A, Salto-Tellez M, Iacopetta B, Ito Y, et
al Singapore Gastric Cancer Consortium: MicroRNA-130b regulates the
tumour suppressor RUNX3 in gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer.
46:1456–1463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kitago M, Martinez SR, Nakamura T, Sim MS
and Hoon DS: Regulation of RUNX3 tumor suppressor gene expression
in cutaneous melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2988–2994. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Goh YM, Cinghu S, Hong ET, Lee YS, Kim JH,
Jang JW, Li YH, Chi XZ, Lee KS, Wee H, et al: Src kinase
phosphorylates RUNX3 at tyrosine residues and localizes the protein
in the cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 285:10122–10129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim HR, Oh BC, Choi JK and Bae SC: Pim-1
kinase phosphorylates and stabilizes RUNX3 and alters its
subcellular localization. J Cell Biochem. 105:1048–1058. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim JH, Choi JK, Cinghu S, Jang JW, Lee
YS, Li YH, Goh YM, Chi XZ, Lee KS, Wee H, et al: Jab1/CSN5 induces
the cytoplasmic localization and degradation of RUNX3. J Cell
Biochem. 107:557–565. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sheen YY, Kim MJ, Park SA, Park SY and Nam
JS: Targeting the transforming growth factor-β signaling in cancer
therapy. Biomol Ther. 21:323–331. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ito Y and Miyazono K: RUNX transcription
factors as key targets of TGF-beta superfamily signaling. Curr Opin
Genet Dev. 13:43–47. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chi XZ, Yang JO, Lee KY, Ito K, Sakakura
C, Li QL, Kim HR, Cha EJ, Lee YH, Kaneda A, et al: RUNX3 suppresses
gastric epithelial cell growth by inducing p21WAF1/Cip1
expression in cooperation with transforming growth factor
β-activated SMAD. Mol Cell Biol. 25:8097–8107. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yamamura Y, Lee WL, Inoue K, Ida H and Ito
Y: RUNX3 cooperates with FoxO3a to induce apoptosis in gastric
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 281:5267–5276. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yao H, Ashihara E and Maekawa T: Targeting
the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human cancers. Expert Opin
Ther Targets. 15:873–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tanaka S, Shiraha H, Nakanishi Y, Nishina
S, Matsubara M, Horiguchi S, Takaoka N, Iwamuro M, Kataoka J,
Kuwaki K, et al: Runt-related transcription factor 3 reverses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int
J Cancer. 131:2537–2546. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ito K, Lim AC, Salto-Tellez M, Motoda L,
Osato M, Chuang LS, Lee CW, Voon DC, Koo JK, Wang H, et al: RUNX3
attenuates beta-catenin/T cell factors in intestinal tumorigenesis.
Cancer Cell. 14:226–237. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ju X, Ishikawa TO, Naka K, Ito K, Ito Y
and Oshima M: Context-dependent activation of Wnt signaling by
tumor suppressor RUNX3 in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Sci.
105:418–424. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Palmero I, Pantoja C and Serrano M:
p19ARF links the tumour suppressor p53 to Ras. Nature.
395:125–126. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee KS, Lee YS, Lee JM, Ito K, Cinghu S,
Kim JH, Jang JW, Li YH, Goh YM, Chi XZ, et al: Runx3 is required
for the differentiation of lung epithelial cells and suppression of
lung cancer. Oncogene. 29:3349–3361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kruse JP and Gu W: Modes of p53
regulation. Cell. 137:609–622. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chi XZ, Kim J, Lee YH, Lee JW, Lee KS, Wee
H, Kim WJ, Park WY, Oh BC, Stein GS, et al: Runt-related
transcription factor RUNX3 is a target of MDM2-mediated
ubiquitination. Cancer Res. 69:8111–8119. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Efeyan A and Serrano M: p53: Guardian of
the genome and policeman of the oncogenes. Cell Cycle. 6:1006–1010.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lee YS, Lee JW, Jang JW, Chi XZ, Kim JH,
Li YH, Kim MK, Kim DM, Choi BS, Kim EG, et al: Runx3 inactivation
is a crucial early event in the development of lung adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Cell. 24:603–616. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hnilicová J, Hozeifi S, Stejskalová E,
Dušková E, Poser I, Humpolíčková J, Hof M and Staněk D: The
C-terminal domain of Brd2 is important for chromatin interaction
and regulation of transcription and alternative splicing. Mol Biol
Cell. 24:3557–3568. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Jin YH, Jeon EJ, Li QL, Lee YH, Choi JK,
Kim WJ, Lee KY and Bae SC: Transforming growth factor-beta
stimulates p300-dependent RUNX3 acetylation, which inhibits
ubiquitination-mediated degradation. J Biol Chem. 279:29409–29417.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Padua D and Massagué J: Roles of TGFbeta
in metastasis. Cell Res. 19:89–102. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lee JM, Shin JO, Cho KW, Hosoya A, Cho SW,
Lee YS, Ryoo HM, Bae SC and Jung HS: Runx3 is a crucial regulator
of alveolar differentiation and lung tumorigenesis in mice.
Differentiation. 81:261–268. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chang CJ, Chao CH, Xia W, Yang JY, Xiong
Y, Li CW, Yu WH, Rehman SK, Hsu JL, Lee HH, et al: p53 regulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell properties through
modulating miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 13:317–323. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kumarswamy R, Mudduluru G, Ceppi P,
Muppala S, Kozlowski M, Niklinski J, Papotti M and Allgayer H:
MicroRNA-30a inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by
targeting Snai1 and is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer.
Int J Cancer. 130:2044–2053. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Yamasaki T, Seki N, Yamada Y, Yoshino H,
Hidaka H, Chiyomaru T, Nohata N, Kinoshita T, Nakagawa M and
Enokida H: Tumor suppressive microRNA-138 contributes to cell
migration and invasion through its targeting of vimentin in renal
cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 41:805–817. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Cheng CW, Wang HW, Chang CW, Chu HW, Chen
CY, Yu JC, Chao JI, Liu HF, Ding SL and Shen CY: MicroRNA-30a
inhibits cell migration and invasion by downregulating vimentin
expression and is a potential prognostic marker in breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 134:1081–1093. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Liu Z, Chen L, Zhang X, Xu X, Xing H,
Zhang Y, Li W, Yu H, Zeng J and Jia J: RUNX3 regulates vimentin
expression via miR-30a during epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
gastric cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 18:610–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Nishida N, Yano H, Nishida T, Kamura T and
Kojiro M: Angiogenesis in cancer. Vasc Health Risk Manag.
2:213–219. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Hanahan D and Folkman J: Patterns and
emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis.
Cell. 86:353–364. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Jain RK: Antiangiogenesis strategies
revisited: From starving tumors to alleviating hypoxia. Cancer
Cell. 26:605–622. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yang M, Kuang X, Pan Y, Tan M, Lu B, Lu J,
Cheng Q and Li J: Clinicopathological characteristics of vascular
endothelial growth factor expression in uveal melanoma: A
meta-analysis. Mol Clin Oncol. 2:363–368. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lee JM, Lee DJ, Bae SC and Jung HS:
Abnormal liver differentiation and excessive angiogenesis in mice
lacking Runx3. Histochem Cell Biol. 139:751–758. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lee JM, Kwon HJ, Lai WF and Jung HS:
Requirement of Runx3 in pulmonary vasculogenesis. Cell Tissue Res.
356:445–449. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Semenza GL: Angiogenesis in ischemic and
neoplastic disorders. Annu Rev Med. 54:17–28. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Harris AL: Hypoxia - a key regulatory
factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:38–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lee SH, Bae SC, Kim KW and Lee YM: RUNX3
inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1α protein stability by
interacting with prolyl hydroxylases in gastric cancer cells.
Oncogene. 33:1458–1467. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Meng S, Cao J, Zhang X, Fan Y, Fang L,
Wang C, Lv Z, Fu D and Li Y: Downregulation of microRNA-130a
contributes to endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction in diabetic
patients via its target Runx3. PLoS One. 8:e686112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Luzzi KJ, MacDonald IC, Schmidt EE,
Kerkvliet N, Morris VL, Chambers AF and Groom AC: Multistep nature
of metastatic inefficiency: Dormancy of solitary cells after
successful extravasation and limited survival of early
micrometastases. Am J Pathol. 153:865–873. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Nagasaka A, Kawane K, Yoshida H and Nagata
S: Apaf-1-independent programmed cell death in mouse development.
Cell Death Differ. 17:931–941. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Burgess DJ: Apoptosis: Refined and lethal.
Nat Rev Cancer. 13:792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Nakanishi Y, Shiraha H, Nishina S, Tanaka
S, Matsubara M, Horiguchi S, Iwamuro M, Takaoka N, Uemura M, Kuwaki
K, et al: Loss of runt-related transcription factor 3 expression
leads hepatocellular carcinoma cells to escape apoptosis. BMC
Cancer. 11:32011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhai FX, Liu XF, Fan RF, Long ZJ, Fang ZG,
Lu Y, Zheng YJ and Lin DJ: RUNX3 is involved in caspase-3-dependent
apoptosis induced by a combination of 5-aza-CdR and TSA in
leukaemia cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:439–449. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Liu Z, Zhang X, Xu X, Chen L, Li W, Yu H,
Sun Y, Zeng J and Jia J: RUNX3 inhibits survivin expression and
induces cell apoptosis in gastric cancer. Eur J Cell Biol.
93:118–126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Meng X, Franklin DA, Dong J and Zhang Y:
MDM2-p53 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res.
74:7161–7167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Yamada C, Ozaki T, Ando K, Suenaga Y,
Inoue K, Ito Y, Okoshi R, Kageyama H, Kimura H, Miyazaki M, et al:
RUNX3 modulates DNA damage-mediated phosphorylation of tumor
suppressor p53 at Ser-15 and acts as a co-activator for p53. J Biol
Chem. 285:16693–16703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Lai CB and Mager DL: Role of runt-related
transcription factor 3 (RUNX3) in transcription regulation of
natural cytotoxicity receptor 1 (NCR1/NKp46), an activating natural
killer (NK) cell receptor. J Biol Chem. 287:7324–7334. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Levanon D, Negreanu V, Lotem J, Bone KR,
Brenner O, Leshkowitz D and Groner Y: Transcription factor Runx3
regulates interleukin-15-dependent natural killer cell activation.
Mol Cell Biol. 34:1158–1169. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhang Y, Lu Q and Cai X: MicroRNA-106a
induces multidrug resistance in gastric cancer by targeting RUNX3.
FEBS Lett. 587:3069–3075. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Li Q, Wang JX, He YQ, Feng C, Zhang XJ,
Sheng JQ and Li PF: MicroRNA-185 regulates chemotherapeutic
sensitivity in gastric cancer by targeting apoptosis repressor with
caspase recruitment domain. Cell Death Dis. 5:e11972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Boya P, Reggiori F and Codogno P: Emerging
regulation and functions of autophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 15:713–720.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kenific CM, Thorburn A and Debnath J:
Autophagy and metastasis: Another double-edged sword. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 22:241–245. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
91
|
Xu Q, Meng S, Liu B, Li MQ, Li Y, Fang L
and Li YG: MicroRNA-130a regulates autophagy of endothelial
progenitor cells through Runx3. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
41:351–357. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Denhardt DT, Lopez CA, Rollo EE, Hwang SM,
An XR and Walther SE: Osteopontin-induced modifications of cellular
functions. Ann NY Acad Sci. 760:127–142. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Anborgh PH, Mutrie JC, Tuck AB and
Chambers AF: Role of the metastasis-promoting protein osteopontin
in the tumour microenvironment. J Cell Mol Med. 14:2037–2044. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Fong YC, Liu SC, Huang CY, Li TM, Hsu SF,
Kao ST, Tsai FJ, Chen WC, Chen CY and Tang CH: Osteopontin
increases lung cancer cells migration via activation of the
alphavbeta3 integrin/FAK/Akt and NF-kappaB-dependent pathway. Lung
Cancer. 64:263–270. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Wang Y, Yan W, Lu X, Qian C, Zhang J, Li
P, Shi L, Zhao P, Fu Z, Pu P, et al: Overexpression of osteopontin
induces angiogenesis of endothelial progenitor cells via the
avβ3/PI3K/AKT/eNOS/NO signaling pathway in glioma cells. Eur J Cell
Biol. 90:642–648. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Singhal H, Bautista DS, Tonkin KS,
O'Malley FP, Tuck AB, Chambers AF and Harris JF: Elevated plasma
osteopontin in metastatic breast cancer associated with increased
tumor burden and decreased survival. Clin Cancer Res. 3:605–611.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Schneider S, Yochim J, Brabender J, Uchida
K, Danenberg KD, Metzger R, Schneider PM, Salonga D, Hölscher AH
and Danenberg PV: Osteopontin but not osteonectin messenger RNA
expression is a prognostic marker in curatively resected non-small
cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:1588–1596. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ue T, Yokozaki H, Kitadai Y, Yamamoto S,
Yasui W, Ishikawa T and Tahara E: Co-expression of osteopontin and
CD44v9 in gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 79:127–132. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Cheng HC, Liu YP, Shan YS, Huang CY, Lin
FC, Lin LC, Lee L, Tsai CH, Hsiao M and Lu PJ: Loss of RUNX3
increases osteopontin expression and promotes cell migration in
gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:2452–2459. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Min KW, Kim DH, Do SI, Kim K, Lee HJ, Chae
SW, Sohn JH, Pyo JS, Oh YH, Kim WS, et al: Expression patterns of
stromal MMP-2 and tumoural MMP-2 and -9 are significant prognostic
factors in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. APMIS.
122:1196–1206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Stellas D and Patsavoudi E: Inhibiting
matrix metalloproteinases, an old story with new potentials for
cancer treatment. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 12:707–717. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Galis ZS and Khatri JJ: Matrix
metalloproteinases in vascular remodeling and atherogenesis: The
good, the bad, and the ugly. Circ Res. 90:251–262. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Zuo JH, Zhu W, Li MY, Li XH, Yi H, Zeng
GQ, Wan XX, He QY, Li JH, Qu JQ, et al: Activation of EGFR promotes
squamous carcinoma SCC10A cell migration and invasion via inducing
EMT-like phenotype change and MMP-9-mediated degradation of
E-cadherin. J Cell Biochem. 112:2508–2517. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Murphy DA and Courtneidge SA: The 'ins'
and 'outs' of podosomes and invadopodia: Characteristics, formation
and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:413–426. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Bai ZK, Guo B, Tian XC, Li DD, Wang ST,
Cao H, Wang QY and Yue ZP: Expression and regulation of Runx3 in
mouse uterus during the peri-implantation period. J Mol Histol.
44:519–526. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Jinga DC, Blidaru A, Condrea I, Ardeleanu
C, Dragomir C, Szegli G, Stefanescu M and Matache C: MMP-9 and
MMP-2 gelatinases and TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 inhibitors in breast
cancer: Correlations with prognostic factors. J Cell Mol Med.
10:499–510. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|