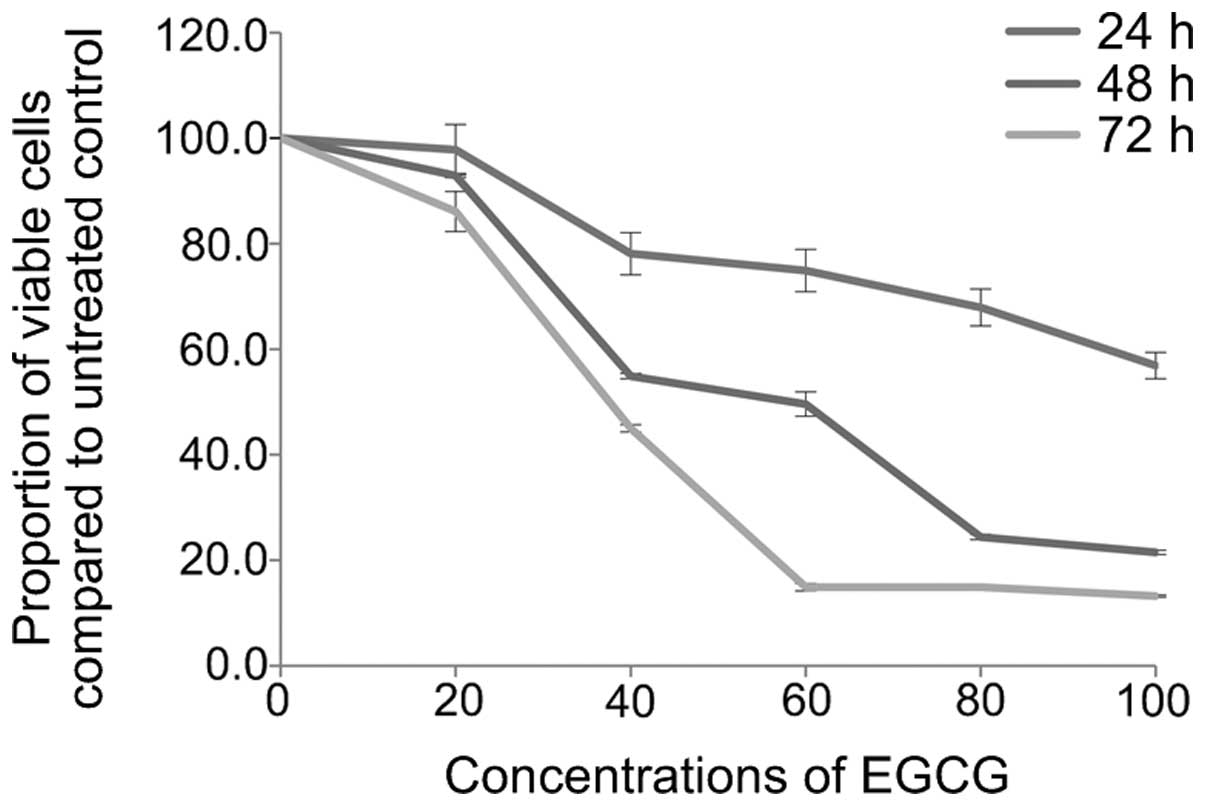
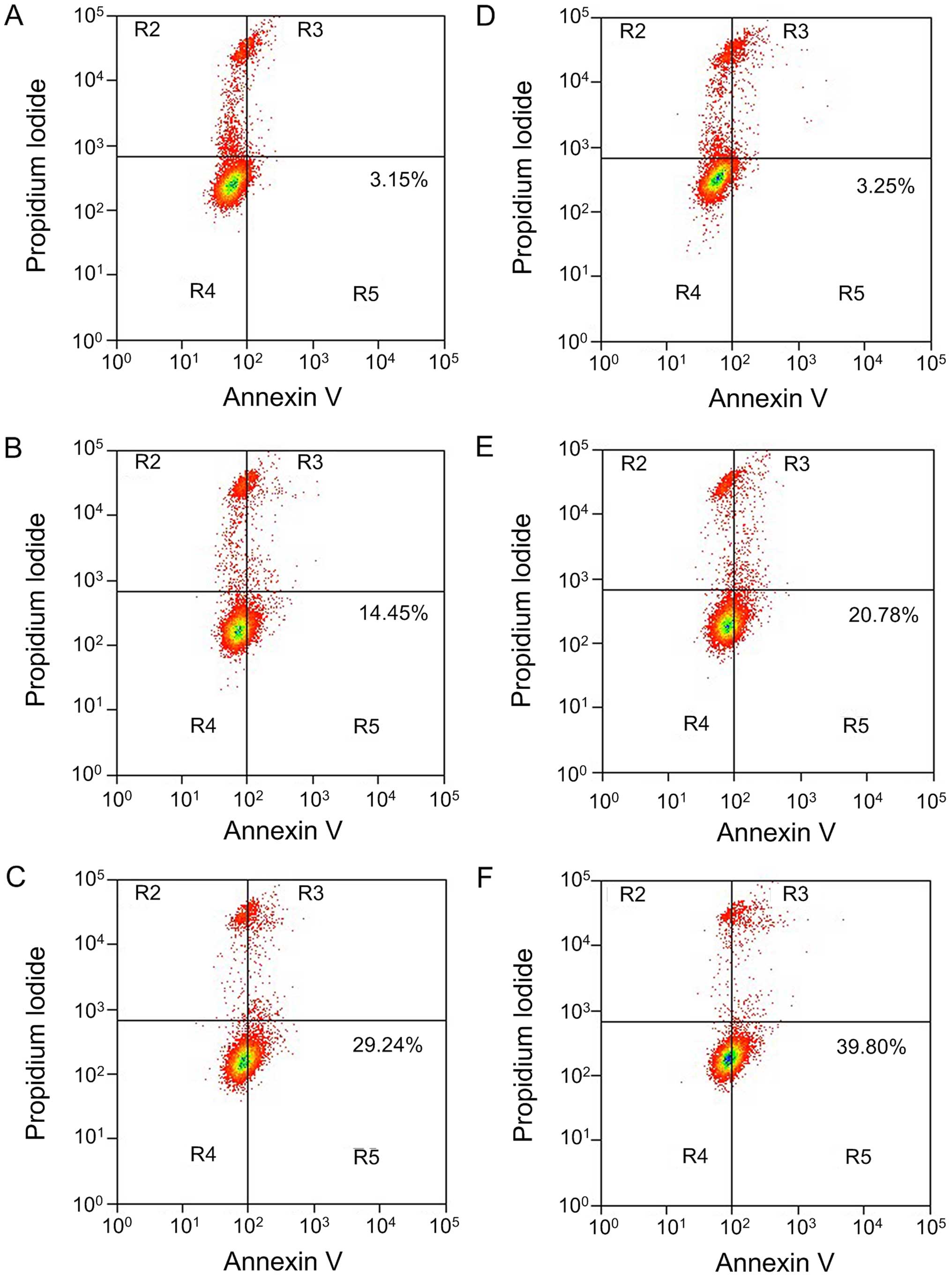
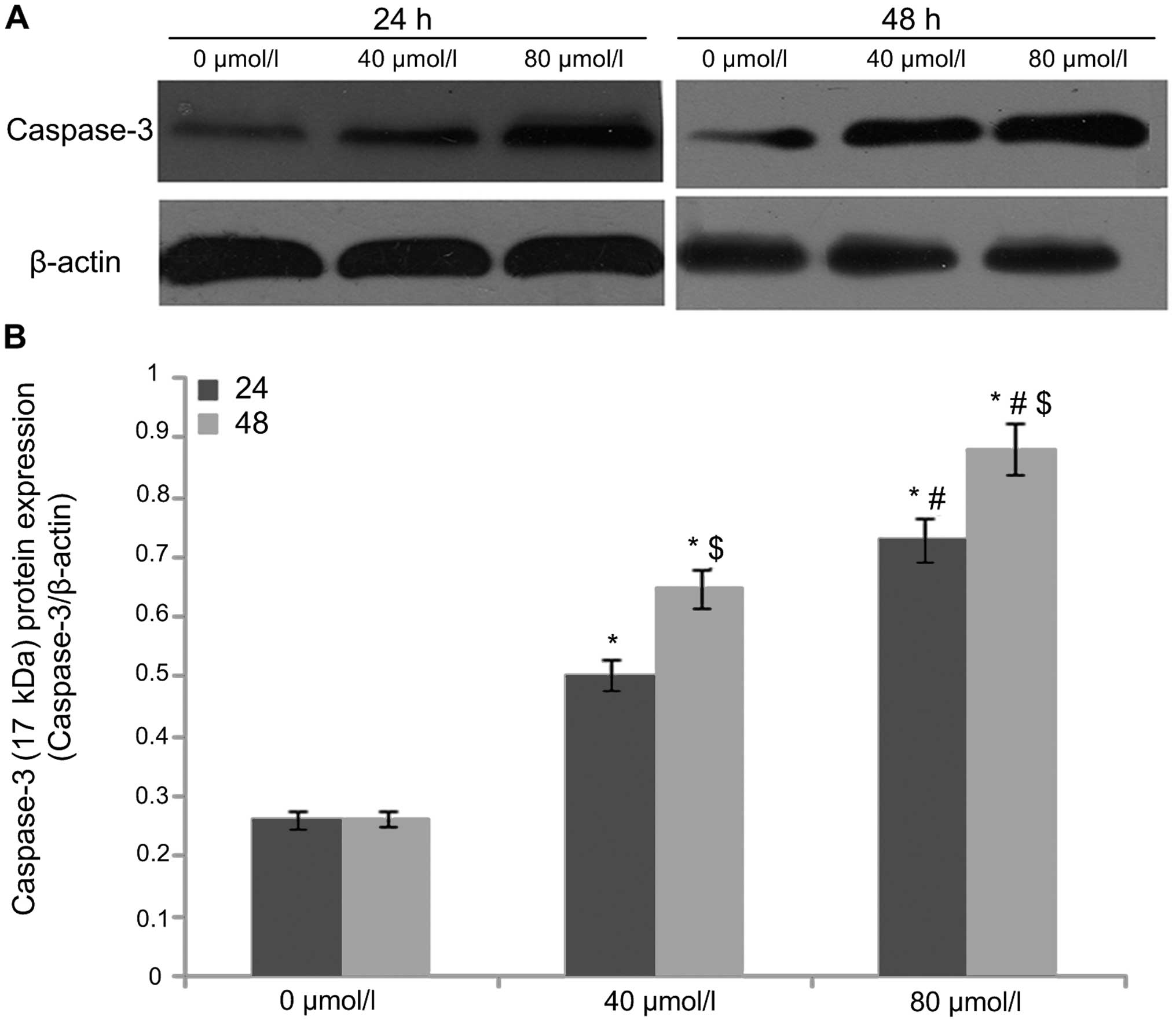
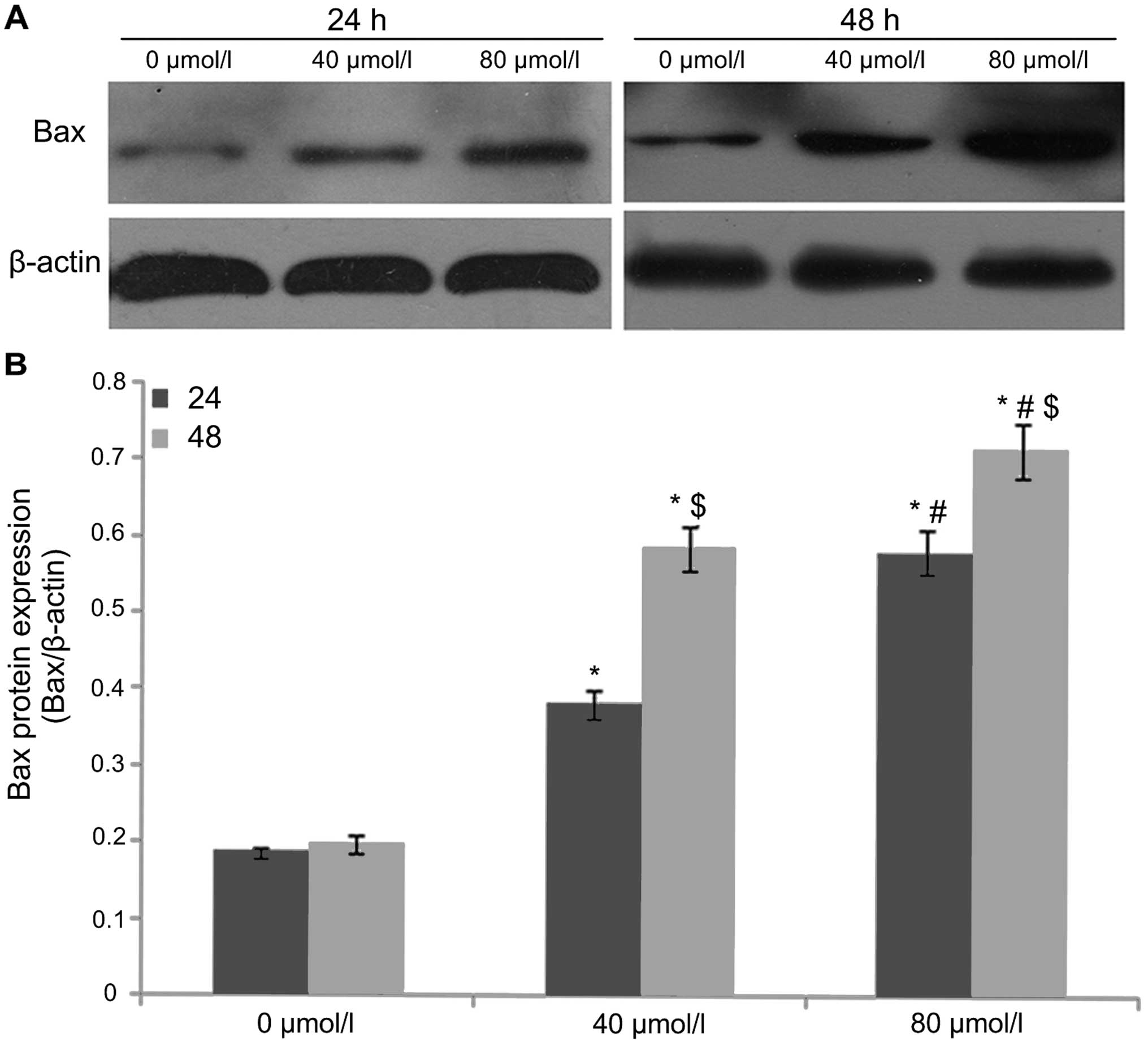
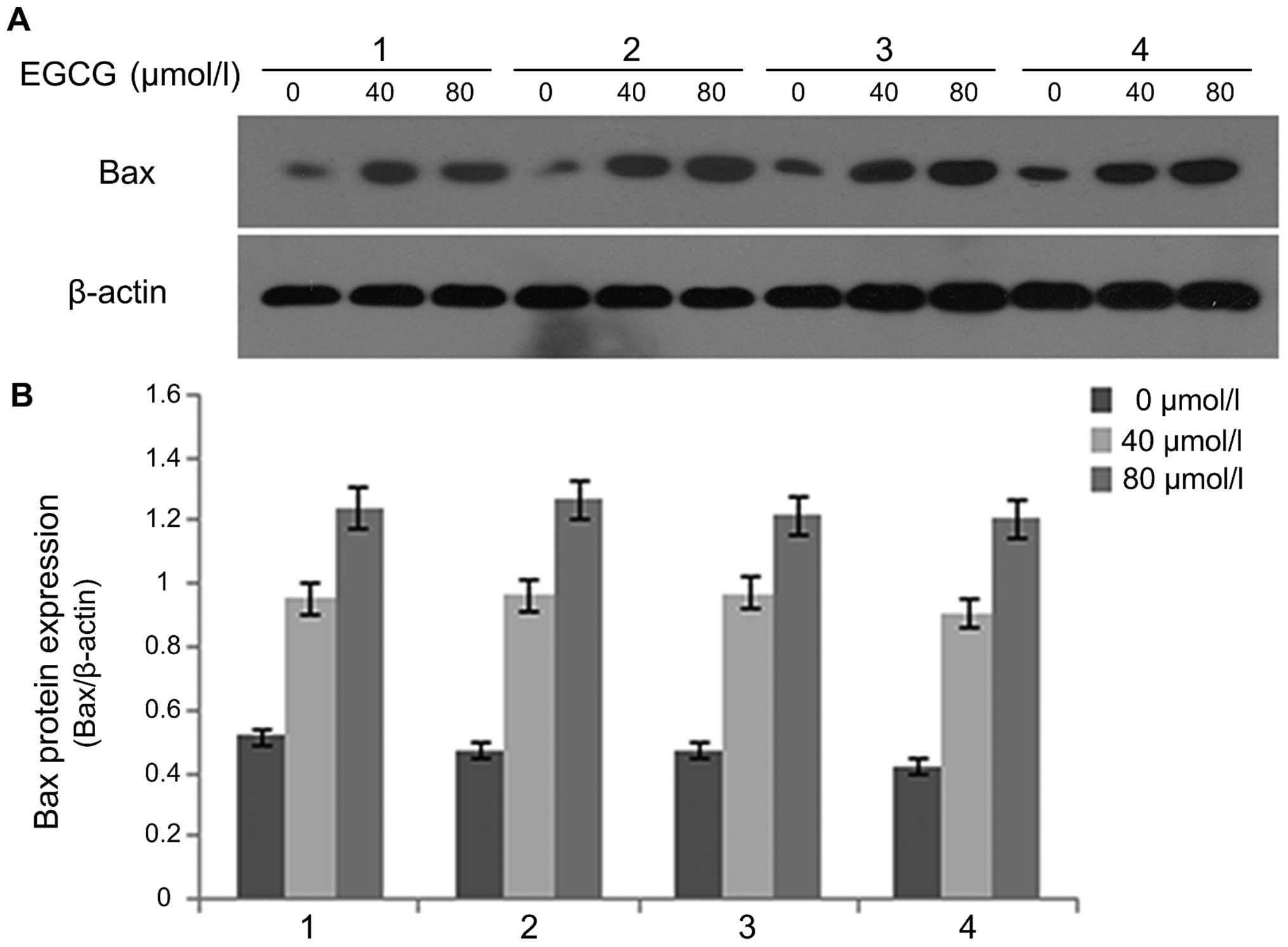
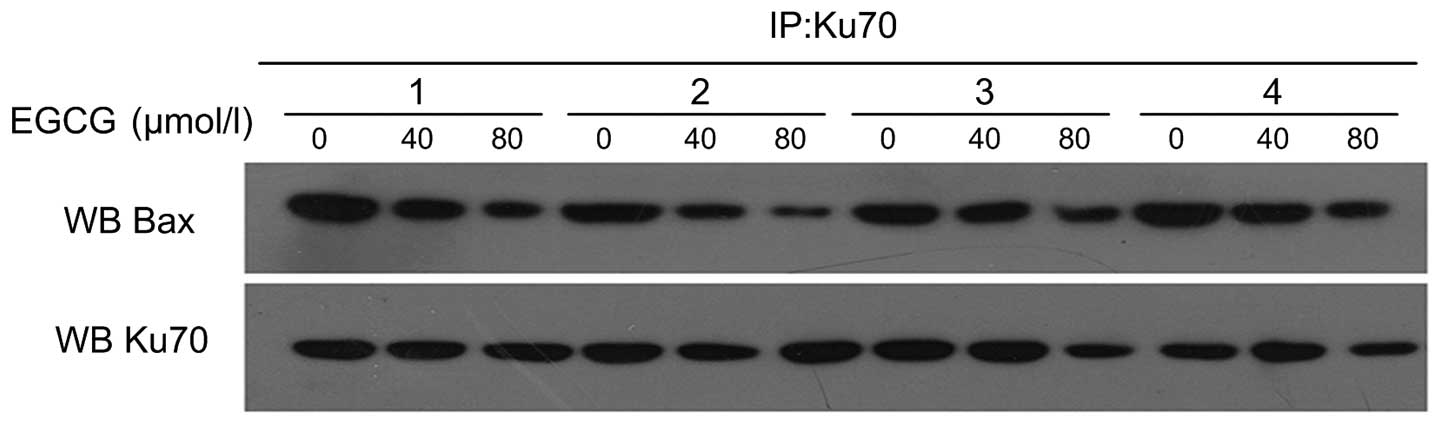
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kushi LH, Doyle C, McCullough M, Rock CL,
Demark-Wahnefried W, Bandera EV, Gapstur S, Patel AV, Andrews K and
Gansler T; American Cancer Society 2010 Nutrition and Physical
Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee: American Cancer Society
Guidelines on nutrition and physical activity for cancer
prevention: Reducing the risk of cancer with healthy food choices
and physical activity. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:30–67. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jin L, Li C, Xu Y, Wang L, Liu J, Wang D,
Hong C, Jiang Z, Ma Y, Chen Q, et al: Epigallocatechin gallate
promotes p53 accumulation and activity via the inhibition of
MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination in human lung cancer cells. Oncol
Rep. 29:1983–1990. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma YC, Li C, Gao F, Xu Y, Jiang ZB, Liu JX
and Jin LY: Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits the growth of human
lung cancer by directly targeting the EGFR signaling pathway. Oncol
Rep. 31:1343–1349. 2014.
|
|
5
|
Lee YH, Kwak J, Choi HK, Choi KC, Kim S,
Lee J, Jun W, Park HJ and Yoon HG: EGCG suppresses prostate cancer
cell growth modulating acetylation of androgen receptor by
anti-histone acetyltransferase activity. Int J Mol Med. 30:69–74.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tang Y, Zhao DY, Elliott S, Zhao W, Curiel
TJ, Beckman BS and Burow ME: Epigallocatechin-3 gallate induces
growth inhibition and apoptosis in human breast cancer cells
through survivin suppression. Int J Oncol. 31:705–711.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang CS and Wang ZY: Tea and cancer. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 85:1038–1049. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu H, Xin Y, Xiao Y and Zhao J: Low-dose
docetaxel combined with (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits
angiogenesis and tumor growth in nude mice with gastric cancer
xenografts. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 27:204–209. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang G, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wan X, Li J, Liu
K, Wang F, Liu K, Liu Q, Yang C, et al: Anti-cancer activities of
tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate in breast cancer patients under
radiotherapy. Curr Mol Med. 12:163–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tudoran O, Soritau O, Balacescu O,
Balacescu L, Braicu C, Rus M, Gherman C, Virag P, Irimie F and
Berindan-Neagoe I: Early transcriptional pattern of angiogenesis
induced by EGCG treatment in cervical tumour cells. J Cell Mol Med.
16:520–530. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lu YP, Lou YR, Xie JG, Peng QY, Liao J,
Yang CS, Huang MT and Conney AH: Topical applications of caffeine
or (−)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) inhibit carcinogenesis and
selectively increase apoptosis in UVB-induced skin tumors in mice.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:12455–12460. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Syed DN, Afaq F, Kweon MH, Hadi N, Bhatia
N, Spiegelman VS and Mukhtar H: Green tea polyphenol EGCG
suppresses cigarette smoke condensate-induced NF-kappaB activation
in normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Oncogene. 26:673–682.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lee MH, Han DW, Hyon SH and Park JC:
Apoptosis of human fibrosarcoma HT-1080 cells by
epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate via induction of p53 and caspases as
well as suppression of Bcl-2 and phosphorylated nuclear factor-κB.
Apoptosis. 16:75–85. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tsukamoto S, Hirotsu K, Kumazoe M, Goto Y,
Sugihara K, Suda T, Tsurudome Y, Suzuki T, Yamashita S, Kim Y, et
al: Green tea polyphenol EGCG induces lipid-raft clustering and
apoptotic cell death by activating protein kinase Cδ and acid
sphingomyelinase through a 67 kDa laminin receptor in multiple
myeloma cells. Biochem J. 443:525–534. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Adachi S, Nagao T, Ingolfsson HI, Maxfield
FR, Andersen OS, Kopelovich L and Weinstein IB: The inhibitory
effect of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate on activation of the
epidermal growth factor receptor is associated with altered lipid
order in HT29 colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 67:6493–6501. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wei LH, Kuo ML, Chen CA, Chou CH, Lai KB,
Lee CN and Hsieh CY: Interleukin-6 promotes cervical tumor growth
by VEGF-dependent angiogenesis via a STAT3 pathway. Oncogene.
22:1517–1527. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Hao MW, Dong K, Lin F, Ren JH and
Zhang HZ: Apoptosis induction effects of EGCG in laryngeal squamous
cell carcinoma cells through telomerase repression. Arch Pharm Res.
32:1263–1269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang J, Xie Y, Feng Y, Zhang L, Huang X,
Shen X and Luo X: (−)-Epigallocatechingallate induces apoptosis in
B lymphoma cells via caspase-dependent pathway and Bcl-2 family
protein modulation. Int J Oncol. 46:1507–1515. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sonoda JI, Ikeda R, Baba Y, Narumi K,
Kawachi A, Tomishige E, Nishihara K, Takeda Y, Yamada K, Sato K, et
al: Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate, attenuates the
cell viability of human non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cells via
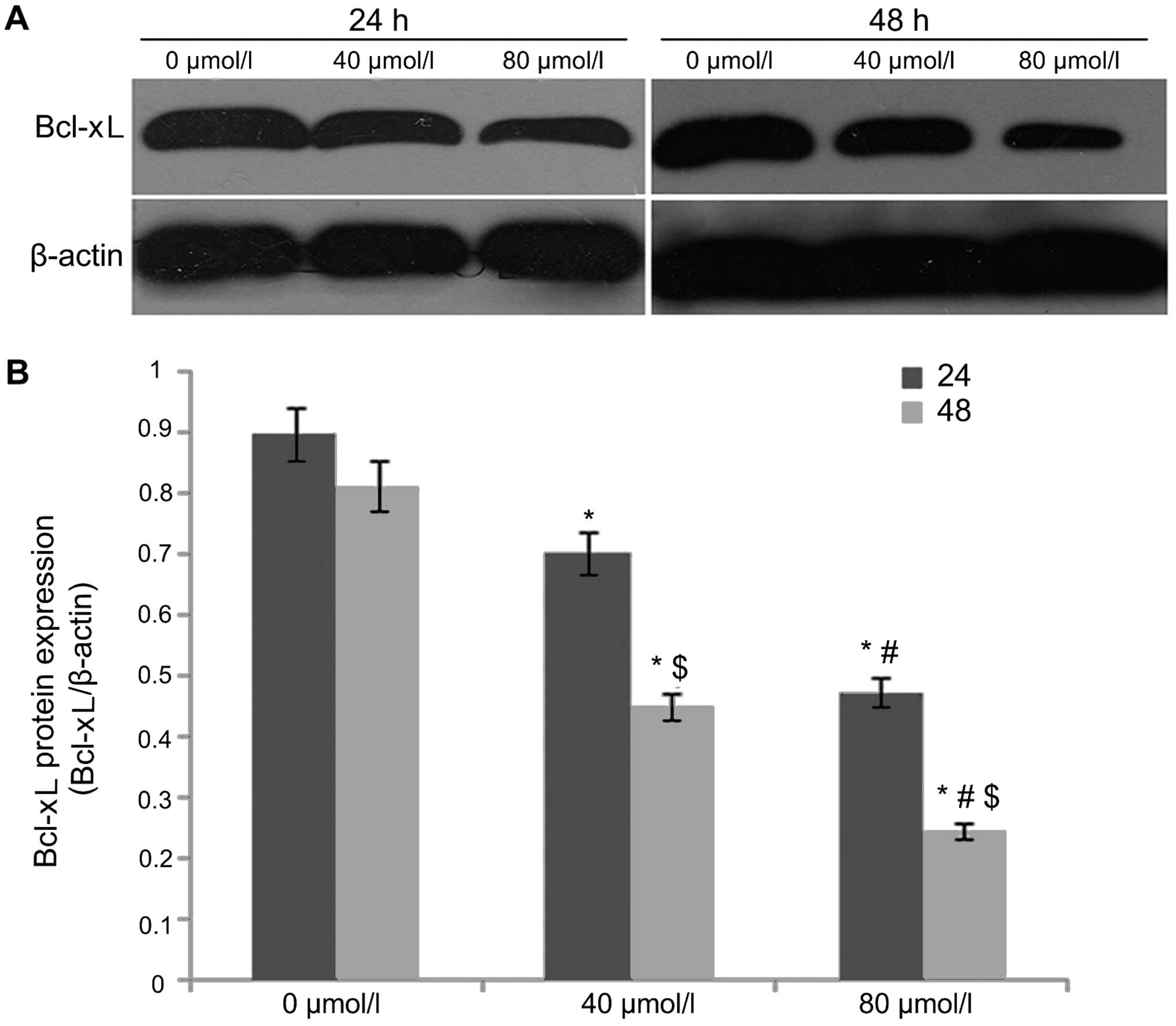
reducing Bcl-xL expression. Exp Ther Med. 8:59–63. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hurwitz JL, Stasik I, Kerr EM, Holohan C,
Redmond KM, McLaughlin KM, Busacca S, Barbone D, Broaddus VC, Gray
SG, et al: Vorinostat/SAHA-induced apoptosis in malignant
mesothelioma is FLIP/caspase 8-dependent and HR23B-independent. Eur
J Cancer. 48:1096–1107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
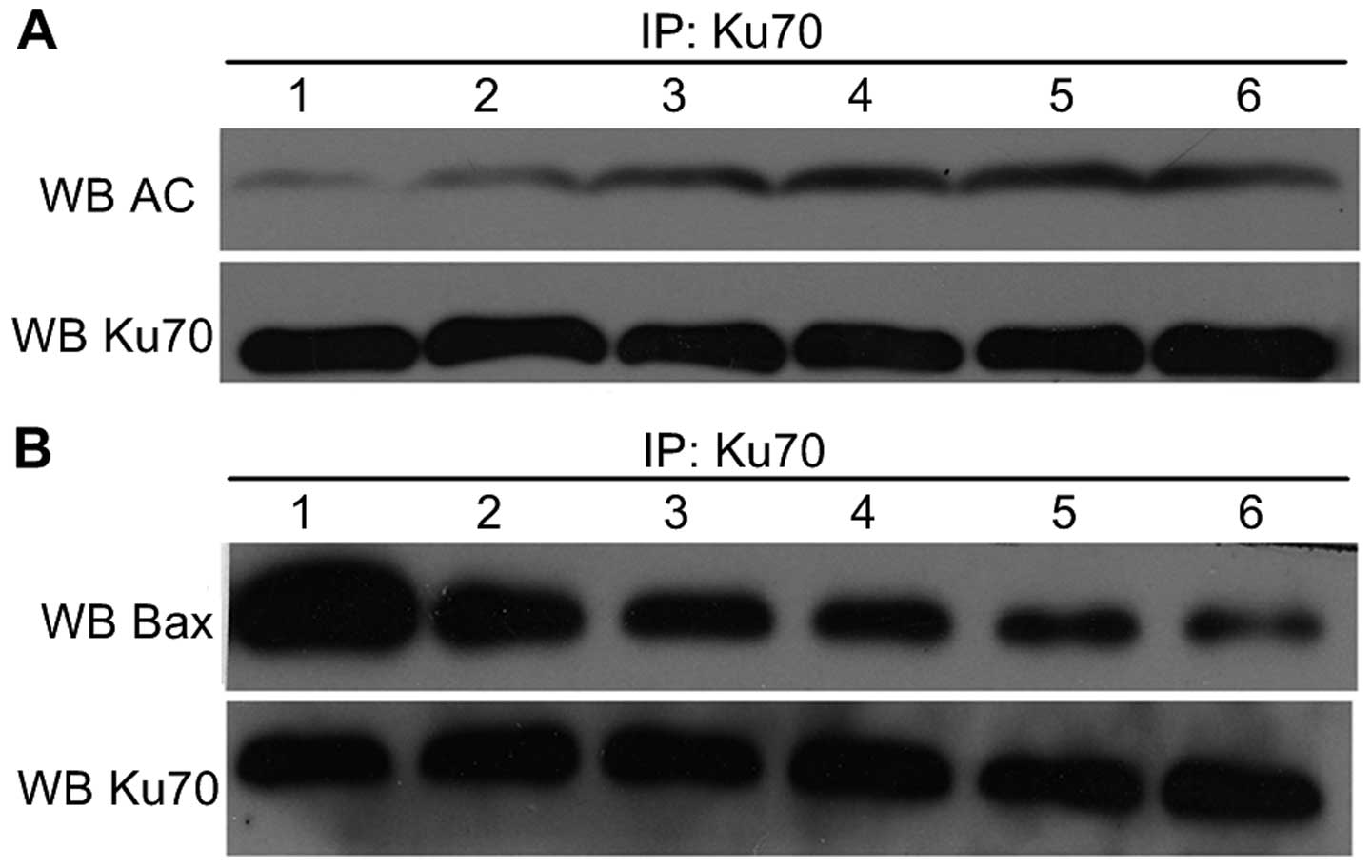
Hada M and Kwok RP: Regulation of ku70-bax
complex in cells. J Cell Death. 7:11–13. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
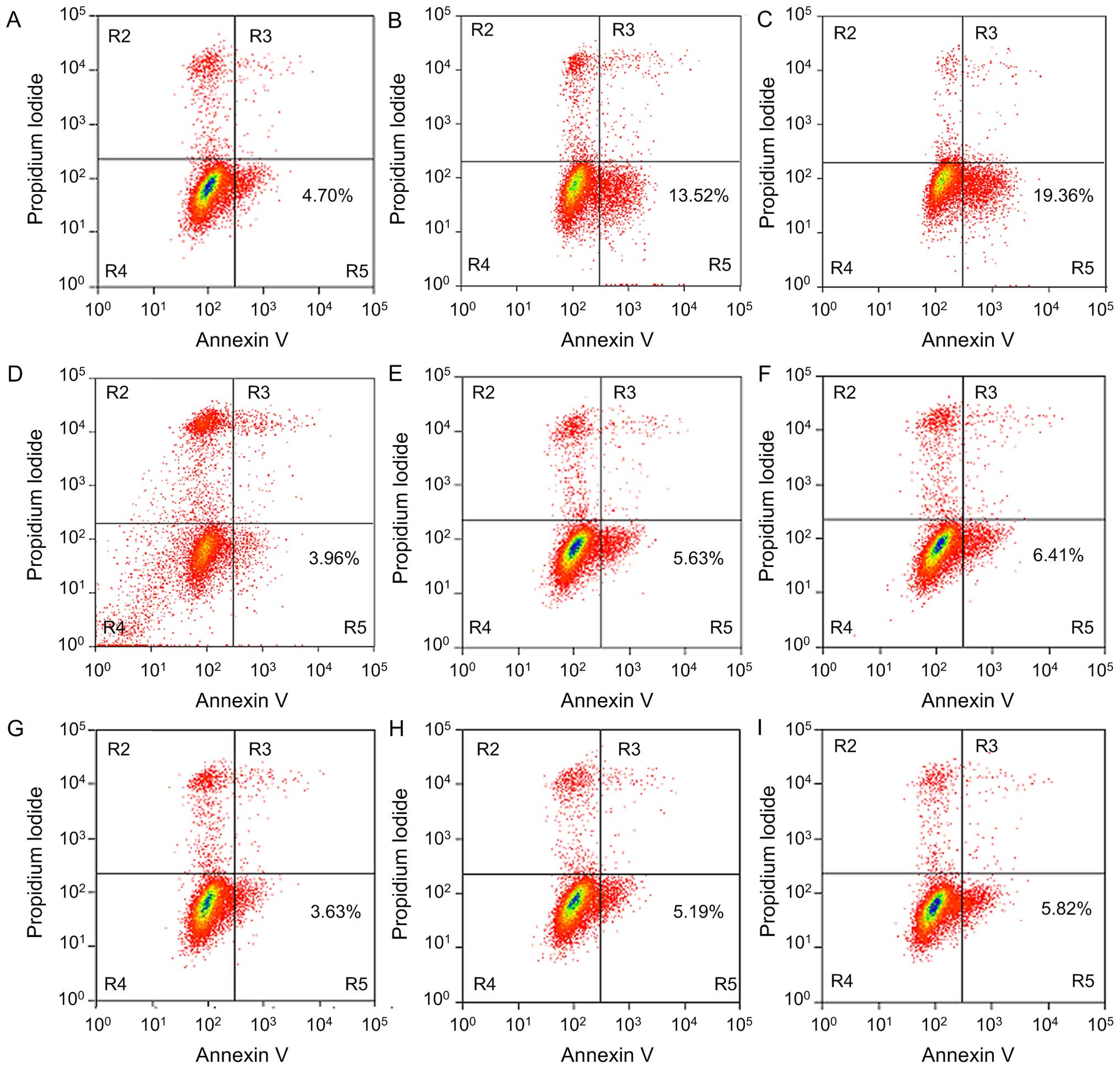
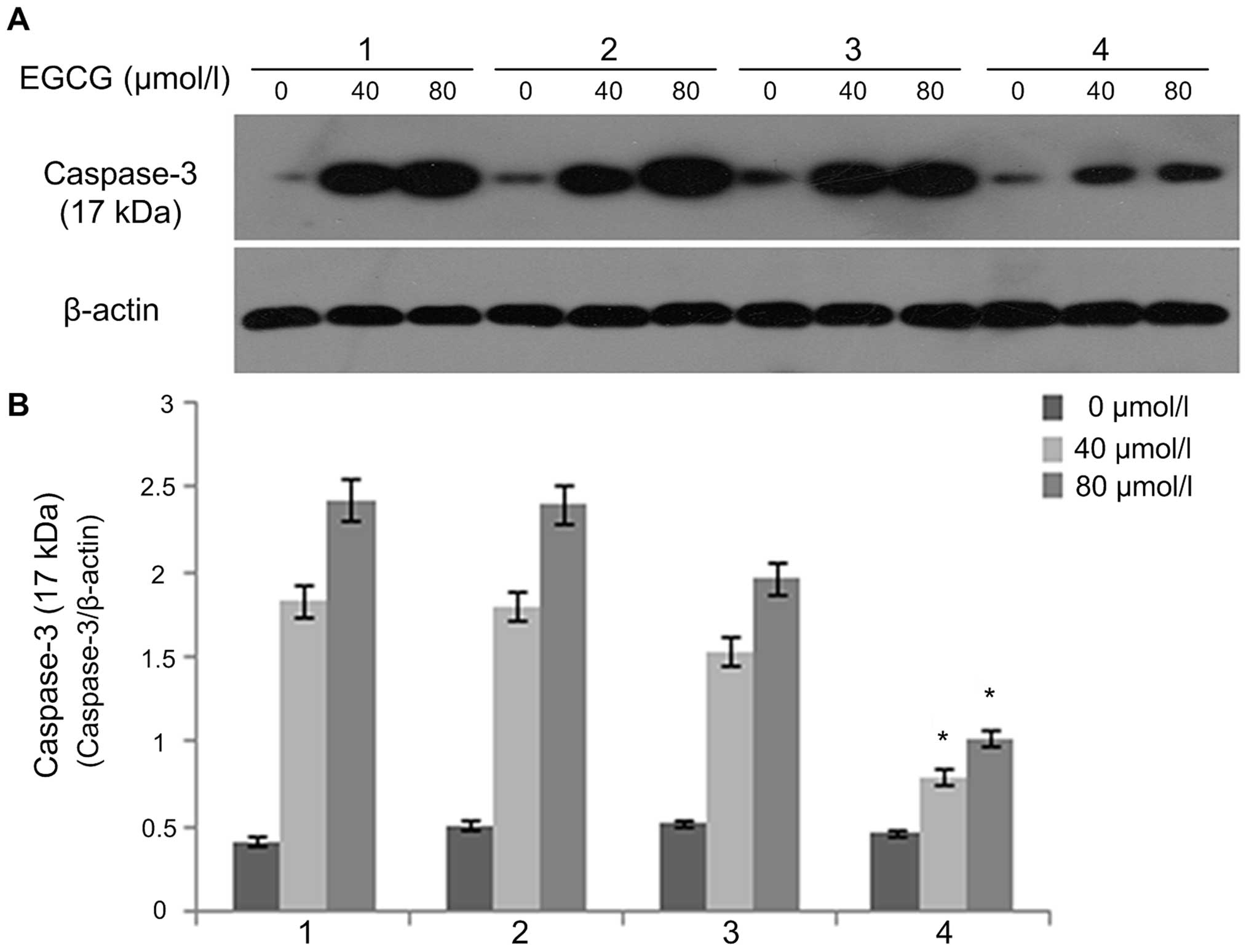
Li JJ, Gu QH, Li M, Yang HP, Cao LM and Hu
CP: Role of Ku70 and Bax in epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced
apoptosis of A549 cells in vivo. Oncol Lett. 5:101–106. 2013.
|
|
23
|
Kang HG, Jenabi JM, Liu XF, Reynolds CP,
Triche TJ and Sorensen PH: Inhibition of the insulin-like growth
factor I receptor by epigallocatechin gallate blocks proliferation
and induces the death of Ewing tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
9:1396–1407. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu PP, Kuo SC, Huang WW, Yang JS, Lai KC,
Chen HJ, Lin KL, Chiu YJ, Huang LJ and Chung JG:
(−)-Epigallocatechin gallate induced apoptosis in human adrenal
cancer NCI-H295 cells through caspase-dependent and
caspase-independent pathway. Anticancer Res. 29:1435–1442.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deveraux QL, Schendel SL and Reed JC:
Antiapoptotic proteins. The bcl-2 and inhibitor of apoptosis
protein families. Cardiol Clin. 19:57–74. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gu Q, Hu C, Chen Q and Xia Y: Tea
polyphenols prevent lung from preneoplastic lesions and effect p53
and bcl-2 gene expression in rat lung tissues. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 6:1523–1531. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hastak K, Agarwal MK, Mukhtar H and
Agarwal ML: Ablation of either p21 or Bax prevents p53-dependent
apoptosis induced by green tea polyphenol
epigallocatechin-3-gallate. FASEB J. 19:789–791. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sawada M, Sun W, Hayes P, Leskov K,
Boothman DA and Matsuyama S: Ku70 suppresses the apoptotic
translocation of Bax to mitochondria. Nat Cell Biol. 5:320–329.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sawada M, Hayes P and Matsuyama S:
Cytoprotective membrane-permeable peptides designed from the
Bax-binding domain of Ku70. Nat Cell Biol. 5:352–357. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cohen HY, Lavu S, Bitterman KJ, Hekking B,
Imahiyerobo TA, Miller C, Frye R, Ploegh H, Kessler BM and Sinclair
DA: Acetylation of the C terminus of Ku70 by CBP and PCAF controls
Bax-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell. 13:627–638. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|