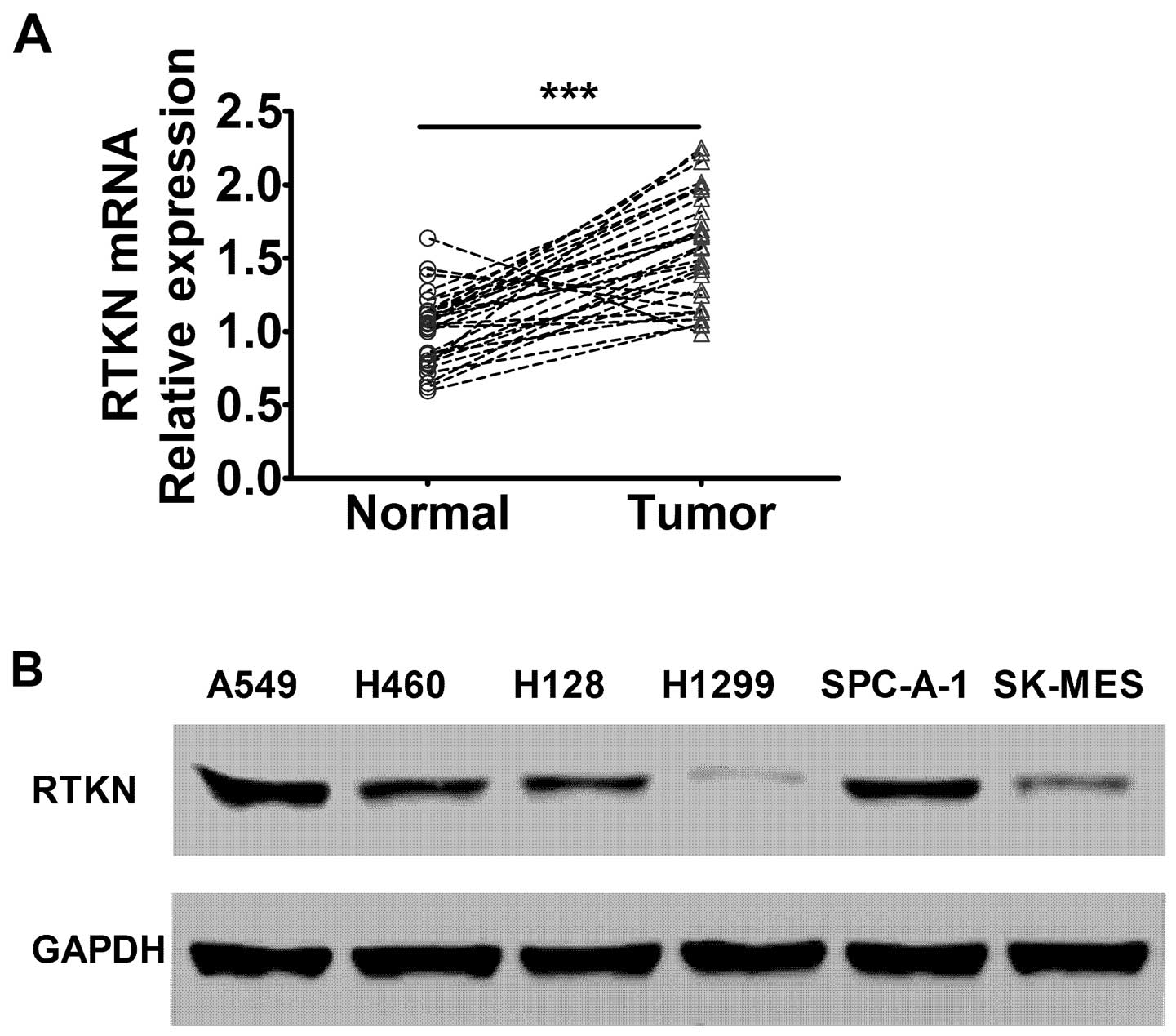
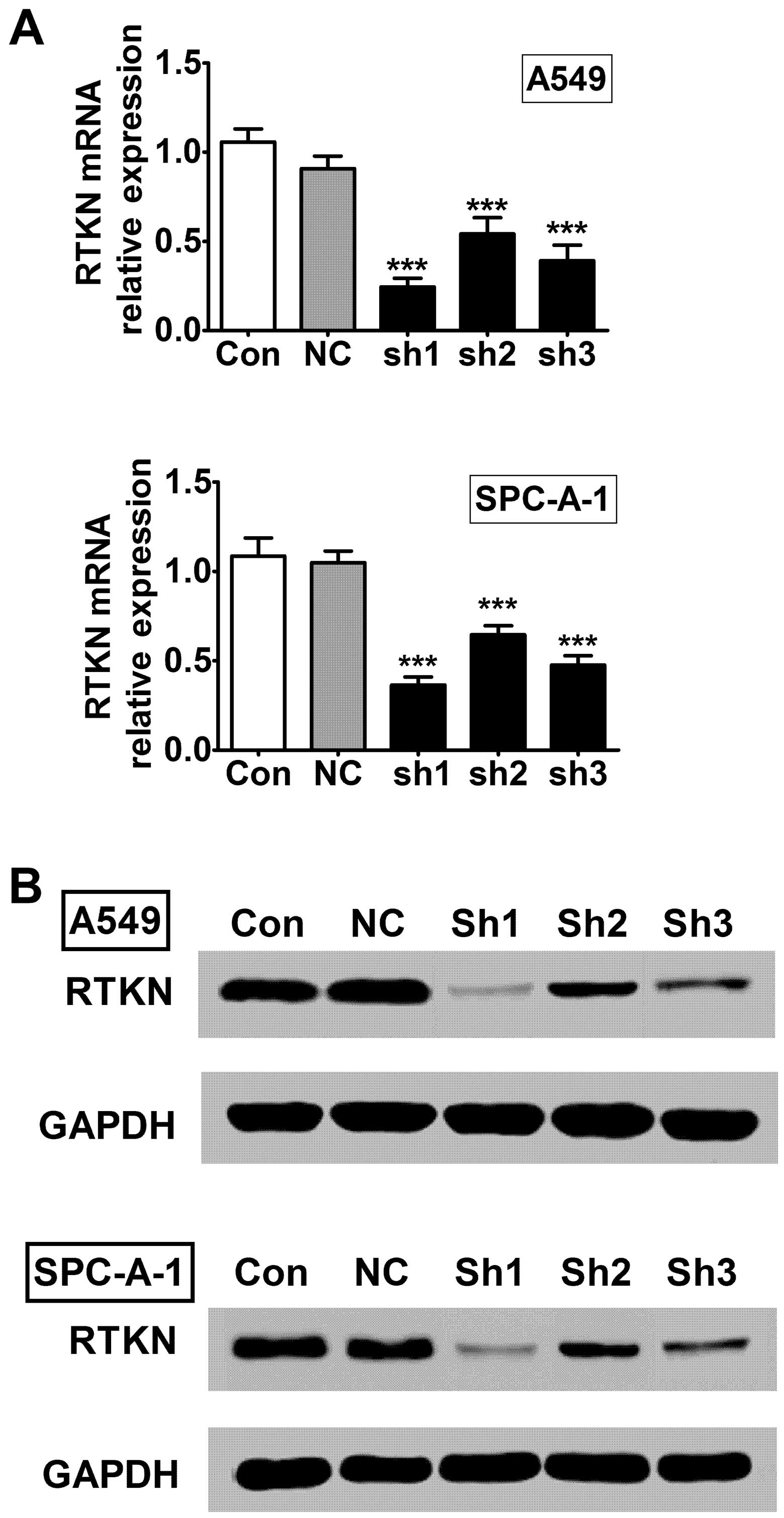
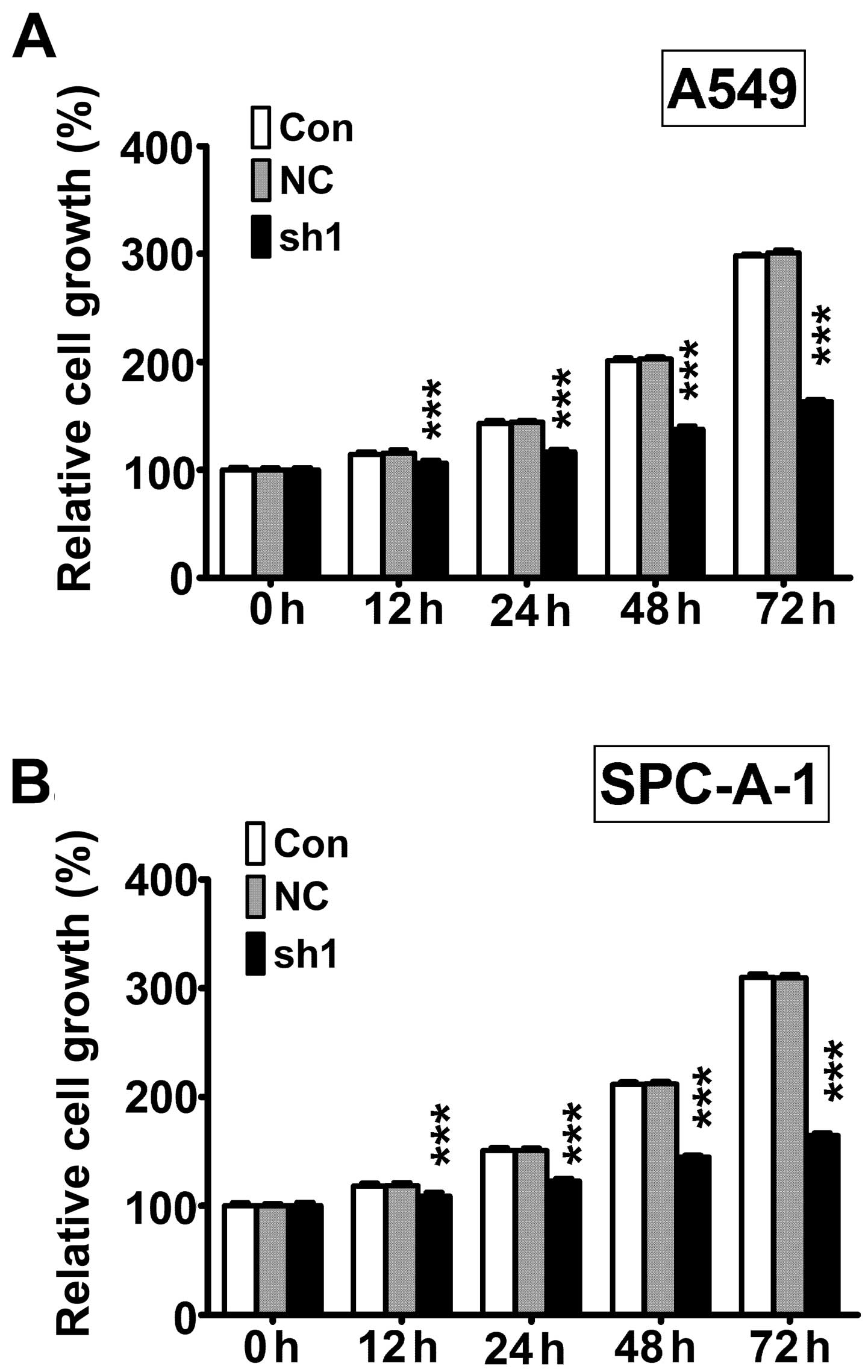
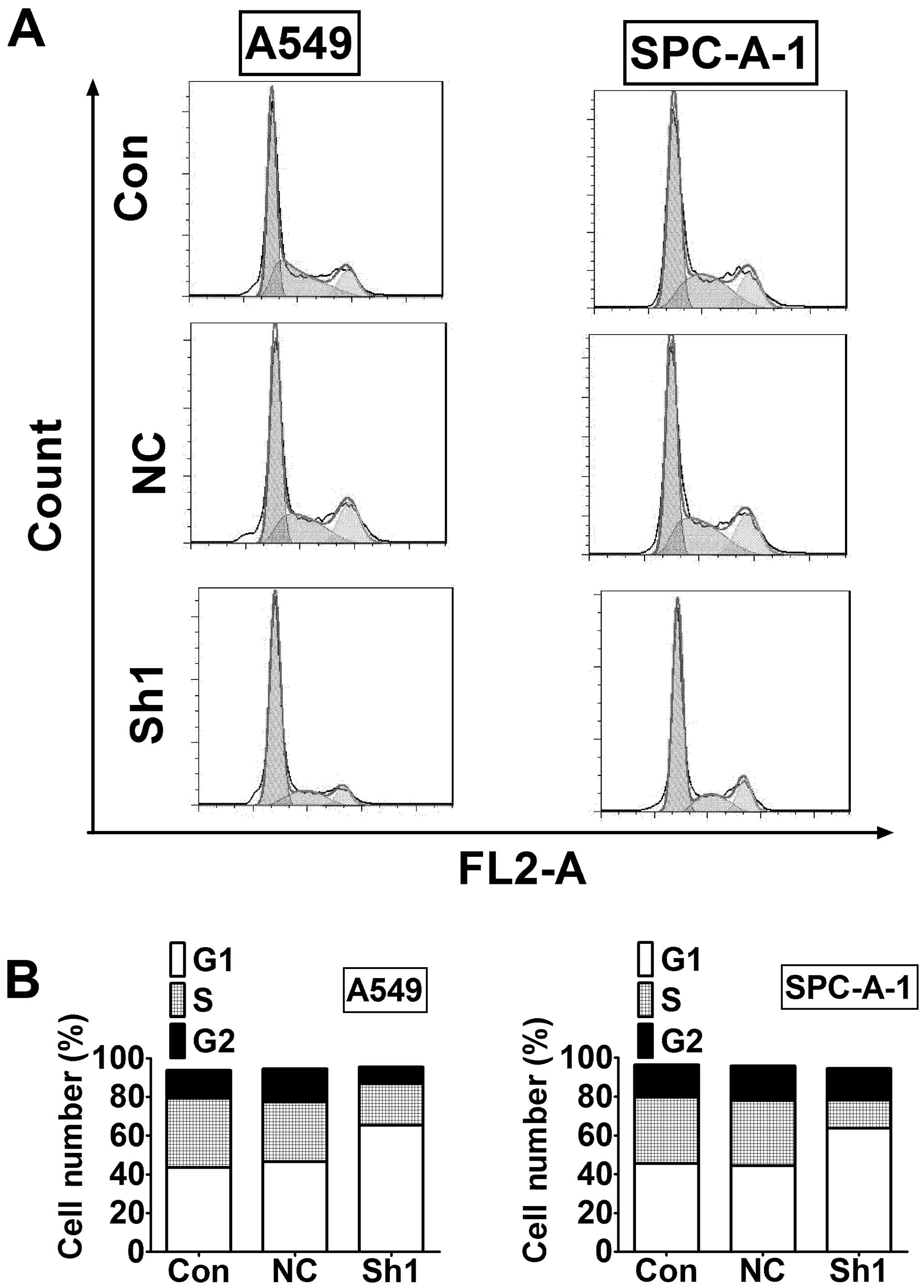
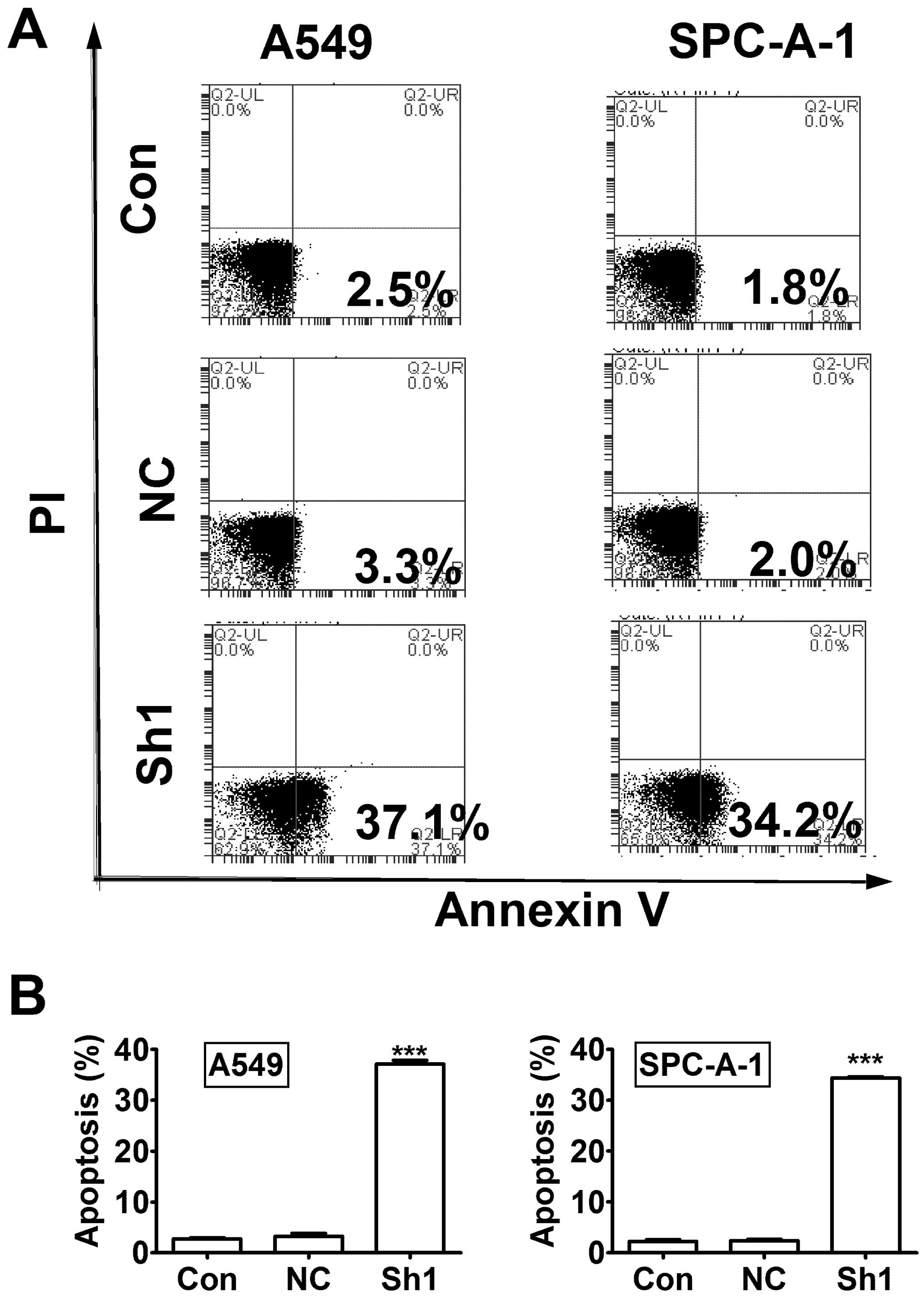
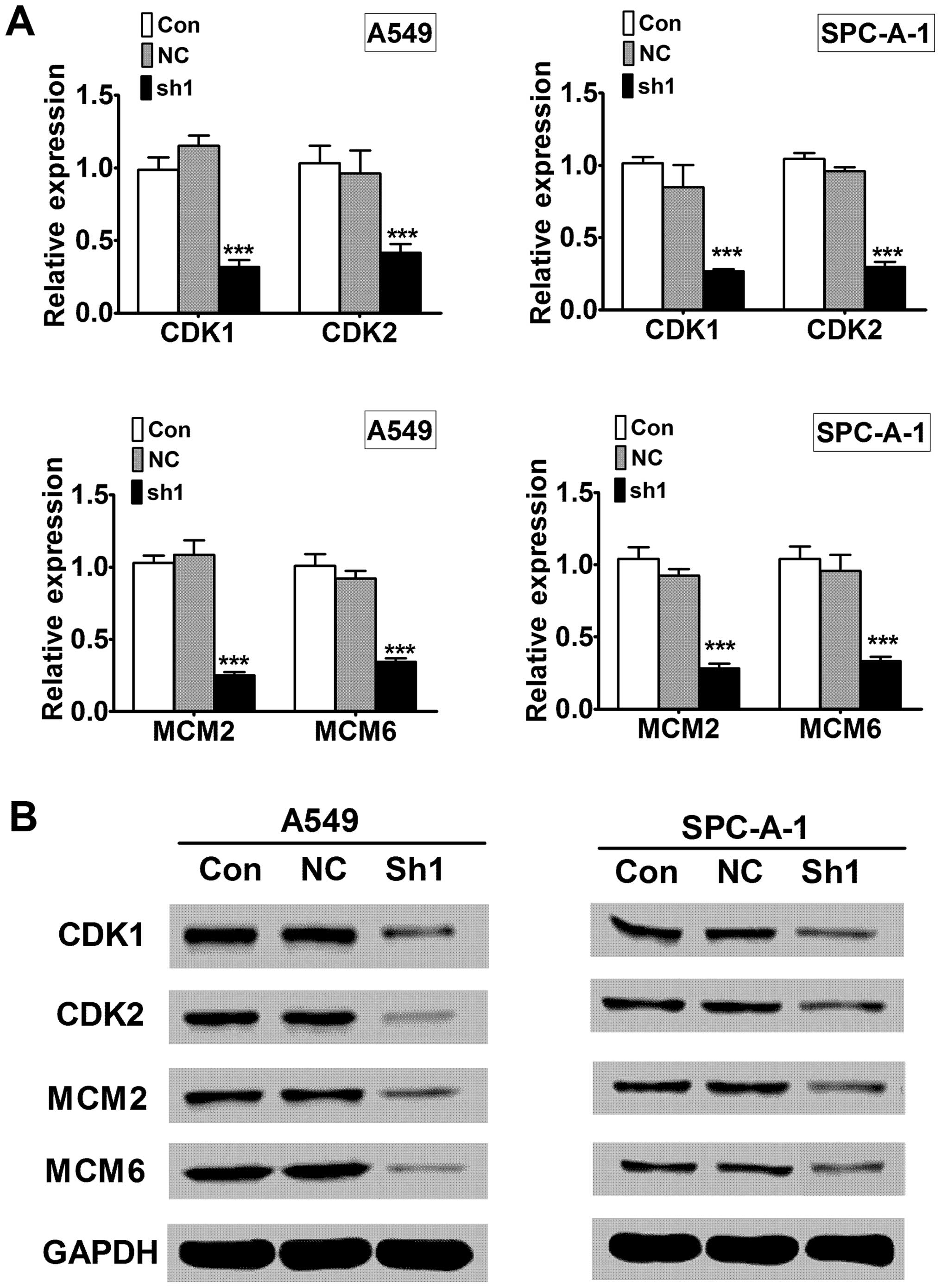
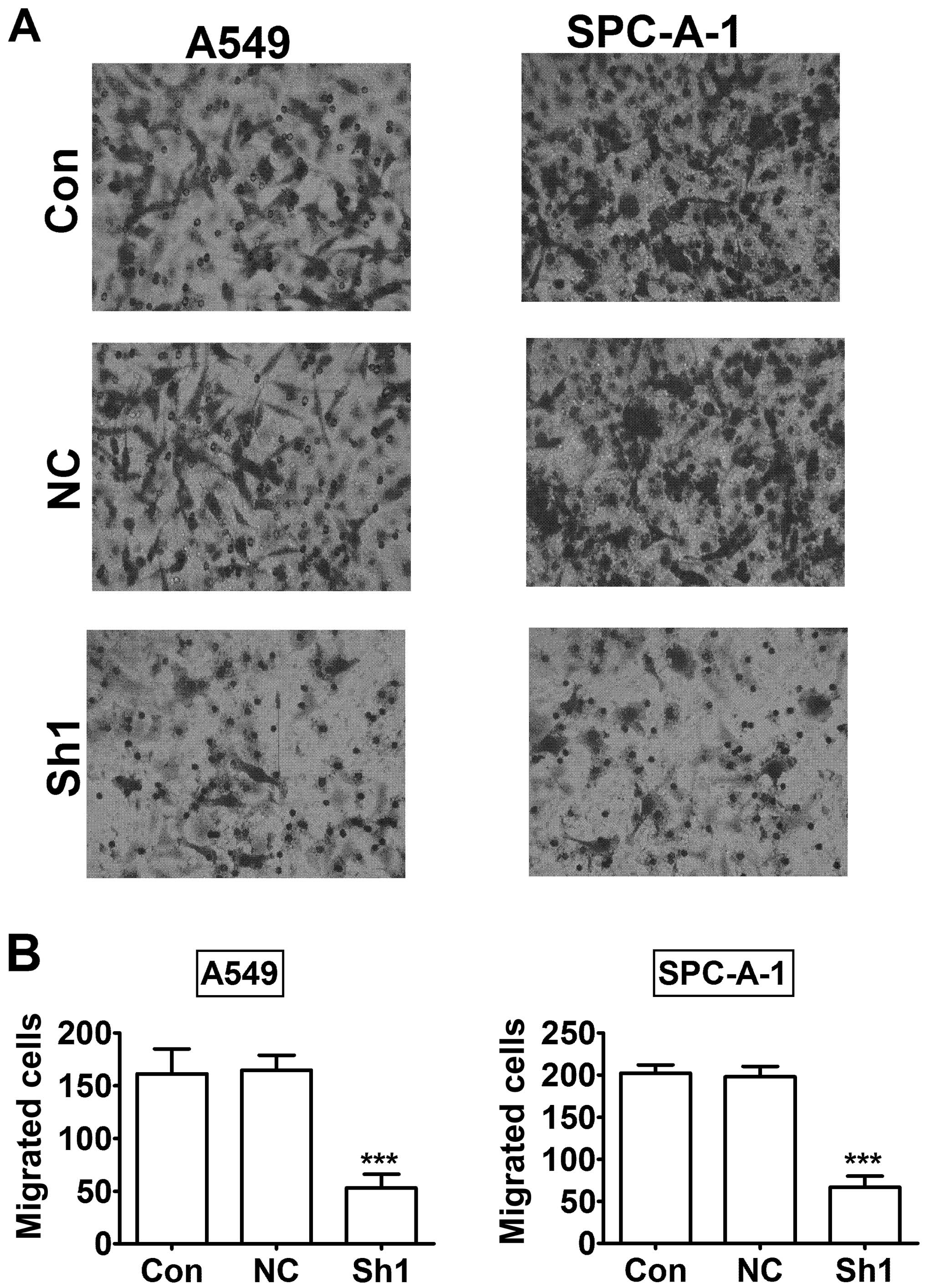
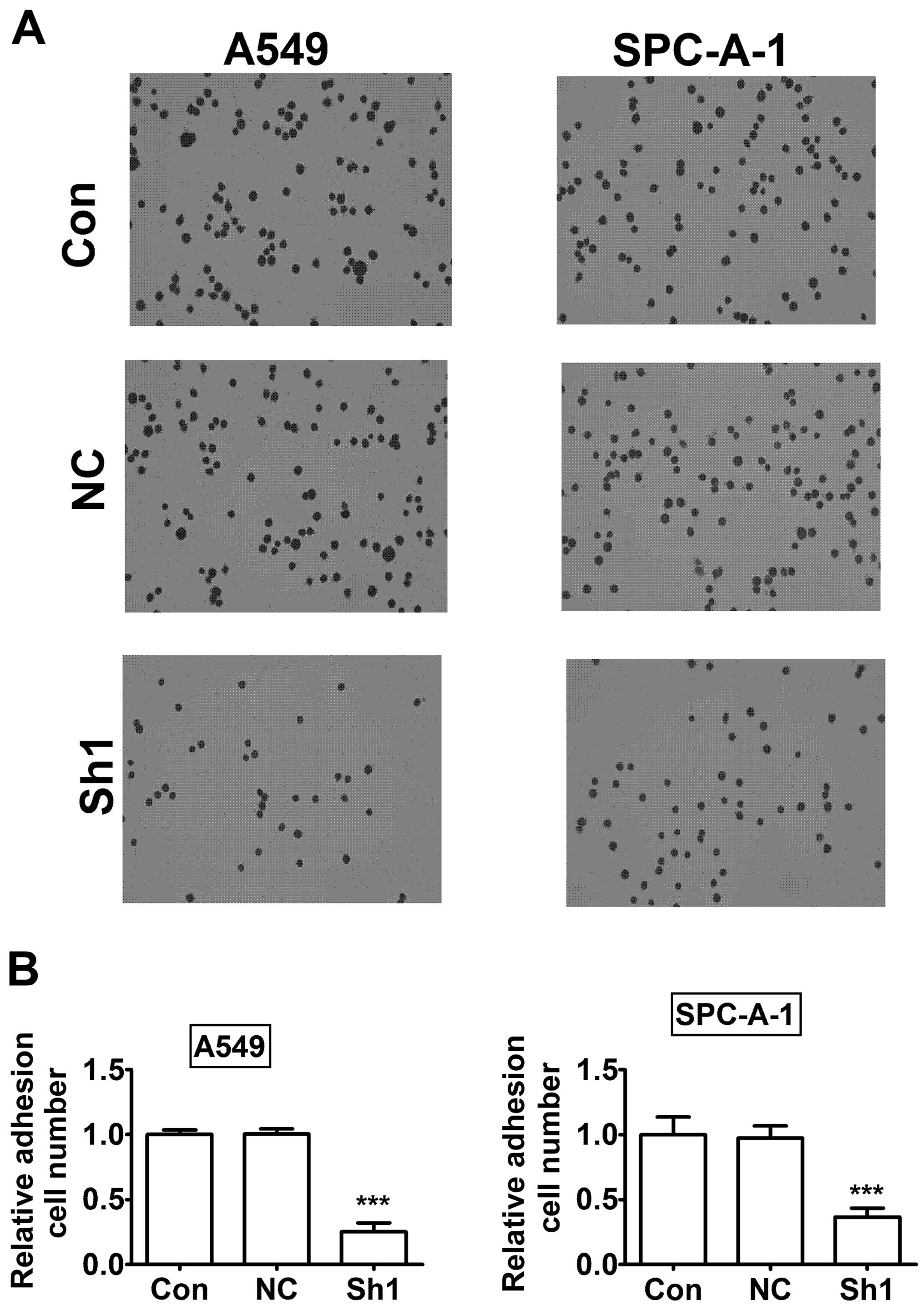
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Peters S, Adjei AA, Gridelli C, Reck M and
Kerr K: Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO
Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and
follow-up. Ann Oncol. 23(Suppl 7): vii56–vii64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kumar M, Ernani V and Owonikoko TK:
Biomarkers and targeted systemic therapies in advanced non-small
cell lung cancer. Mol Aspects Med. Jul 14–2015.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Black A and Morris D: Personalized
medicine in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: Promising
targets and current clinical trials. Curr Oncol. 19(Suppl 1):
S73–S85. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pérez-Soler R, Chachoua A, Hammond LA,
Rowinsky EK, Huberman M, Karp D, Rigas J, Clark GM, Santabárbara P
and Bonomi P: Determinants of tumor response and survival with
erlotinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 22:3238–3247. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J,
Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R and Johnson DH:
Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2542–2550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pender A and Popat S: The efficacy of
crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small cell lung
cancer. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 9:97–104. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Reid T, Furuyashiki T, Ishizaki T,
Watanabe G, Watanabe N, Fujisawa K, Morii N, Madaule P and Narumiya
S: Rhotekin, a new putative target for Rho bearing homology to a
serine/threonine kinase, PKN, and rhophilin in the rho-binding
domain. J Biol Chem. 271:13556–13560. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bishop AL and Hall A: Rho GTPases and
their effector proteins. Biochem J. 348:241–255. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen M, Bresnick AR and O'Connor KL:
Coupling S100A4 to Rhotekin alters Rho signaling output in breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 32:3754–3764. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liu CA, Wang MJ, Chi CW, Wu CW and Chen
JY: Overexpression of rho effector rhotekin confers increased
survival in gastric adenocarcinoma. J Biomed Sci. 11:661–670. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan J, Ma LJ, Xia SJ, Yu L, Fu Q, Wu CQ,
Huang XH, Jiang JM and Tang XD: Association between clinical
characteristics and expression abundance of RTKN gene in human
bladder carcinoma tissues from Chinese patients. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 131:157–162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Norbury C and Nurse P: Animal cell cycles
and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 61:441–470. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ubersax JA, Woodbury EL, Quang PN, Paraz
M, Blethrow JD, Shah K, Shokat KM and Morgan DO: Targets of the
cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk1. Nature. 425:859–864. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Morgan DO: Principles of CDK regulation.
Nature. 374:131–134. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Labib K, Tercero JA and Diffley JF:
Uninterrupted MCM2-7 function required for DNA replication fork
progression. Science. 288:1643–1647. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lygerou Z and Nurse P: Cell cycle. License
withheld - geminin blocks DNA replication. Science. 290:2271–2273.
2000.
|
|
20
|
Sahai E and Marshall CJ: ROCK and Dia have
opposing effects on adherens junctions downstream of Rho. Nat Cell
Biol. 4:408–415. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Watanabe N, Kato T, Fujita A, Ishizaki T
and Narumiya S: Cooperation between mDia1 and ROCK in Rho-induced
actin reorganization. Nat Cell Biol. 1:136–143. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ishizaki T, Naito M, Fujisawa K, Maekawa
M, Watanabe N, Saito Y and Narumiya S: p160ROCK, a
Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein kinase, works downstream
of Rho and induces focal adhesions. FEBS Lett. 404:118–124. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fu Q, Yu L, Liu Q, Zhang J, Zhang H and
Zhao S: Molecular cloning, expression characterization, and mapping
of a novel putative inhibitor of rho GTPase activity, RTKN, to
D2S145-D2S286. Genomics. 66:328–332. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Morgan DO: Cyclin-dependent kinases:
Engines, clocks, and microprocessors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
13:261–291. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stillman B: Cell cycle control of DNA
replication. Science. 274:1659–1664. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|