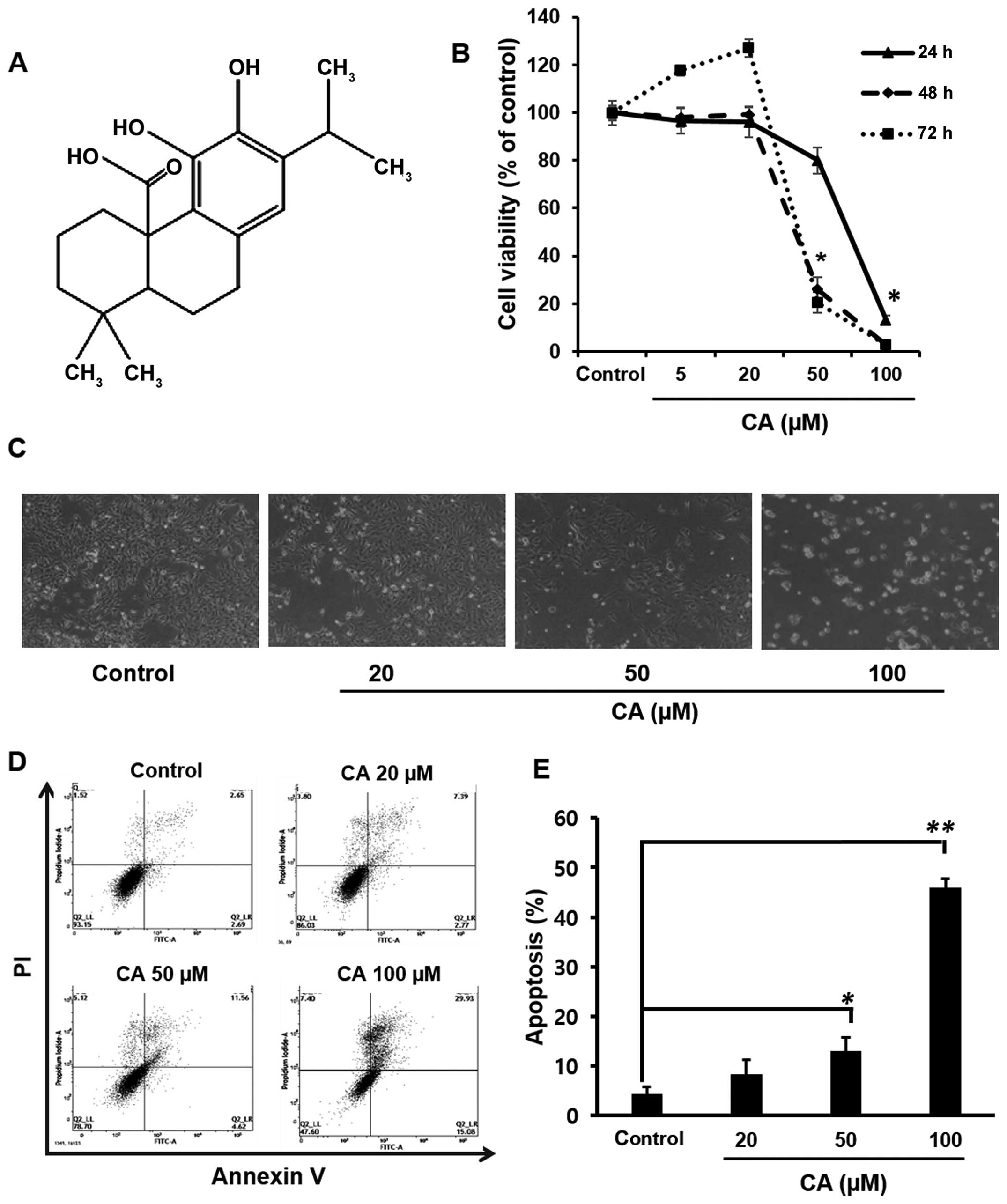
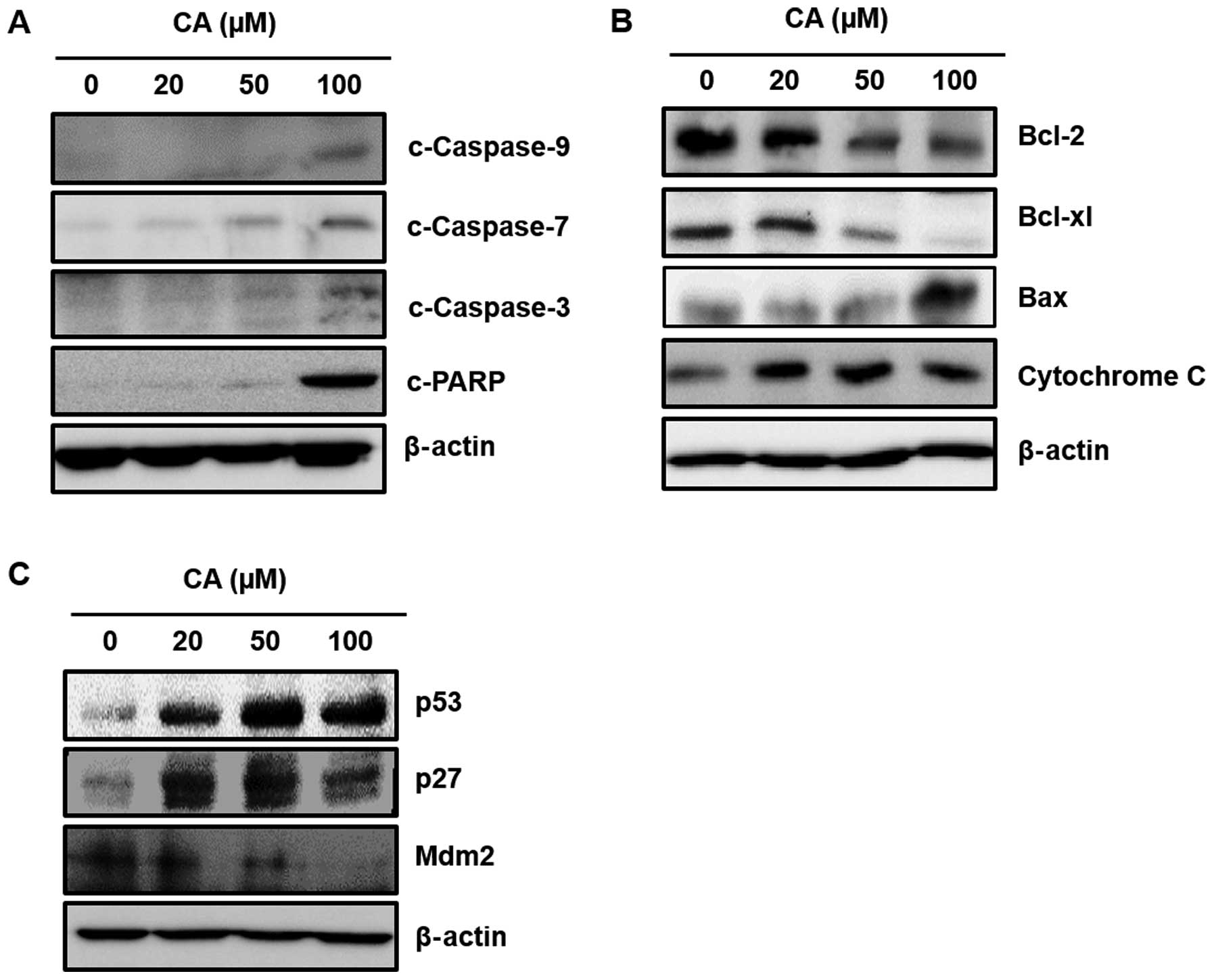
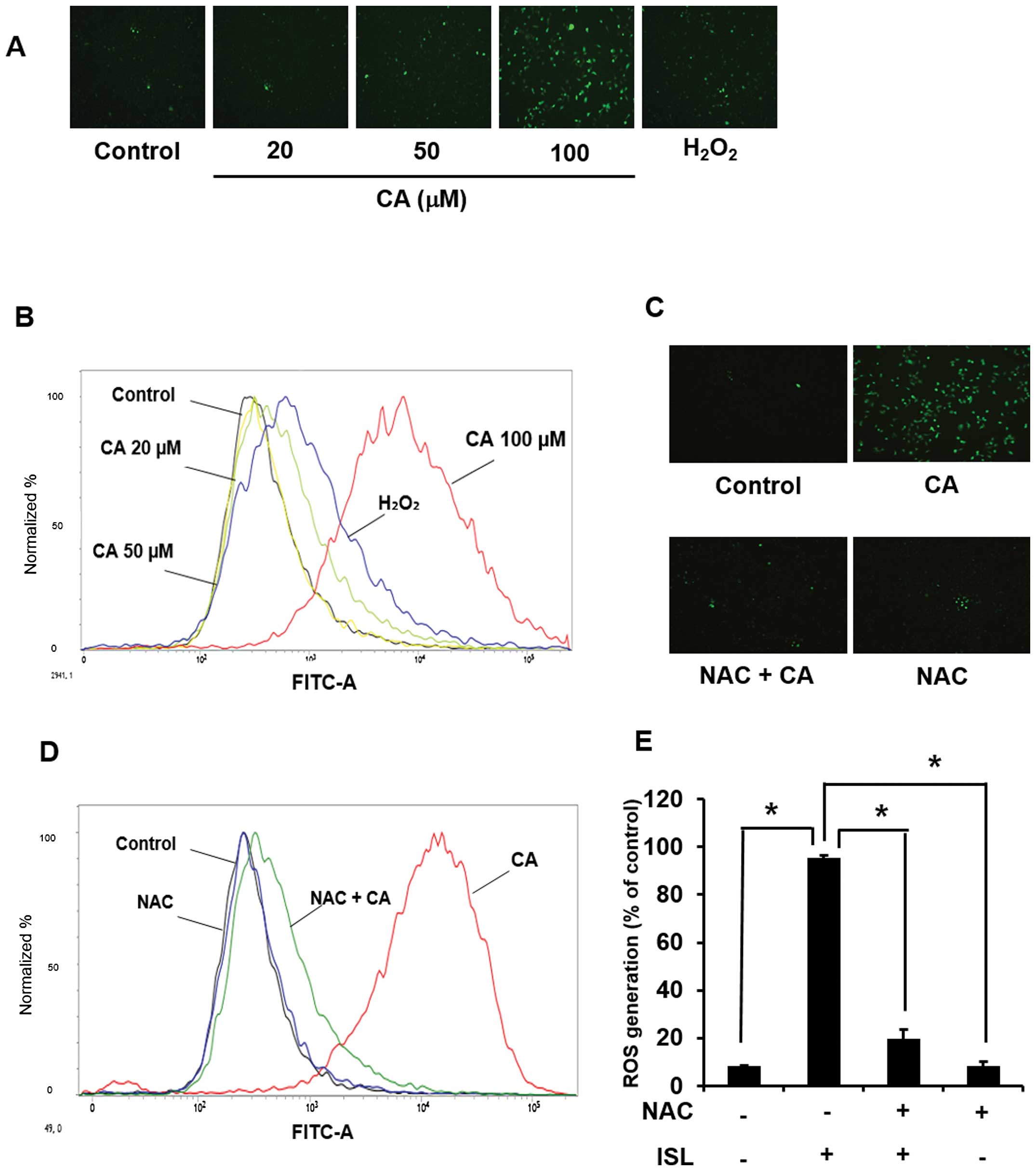
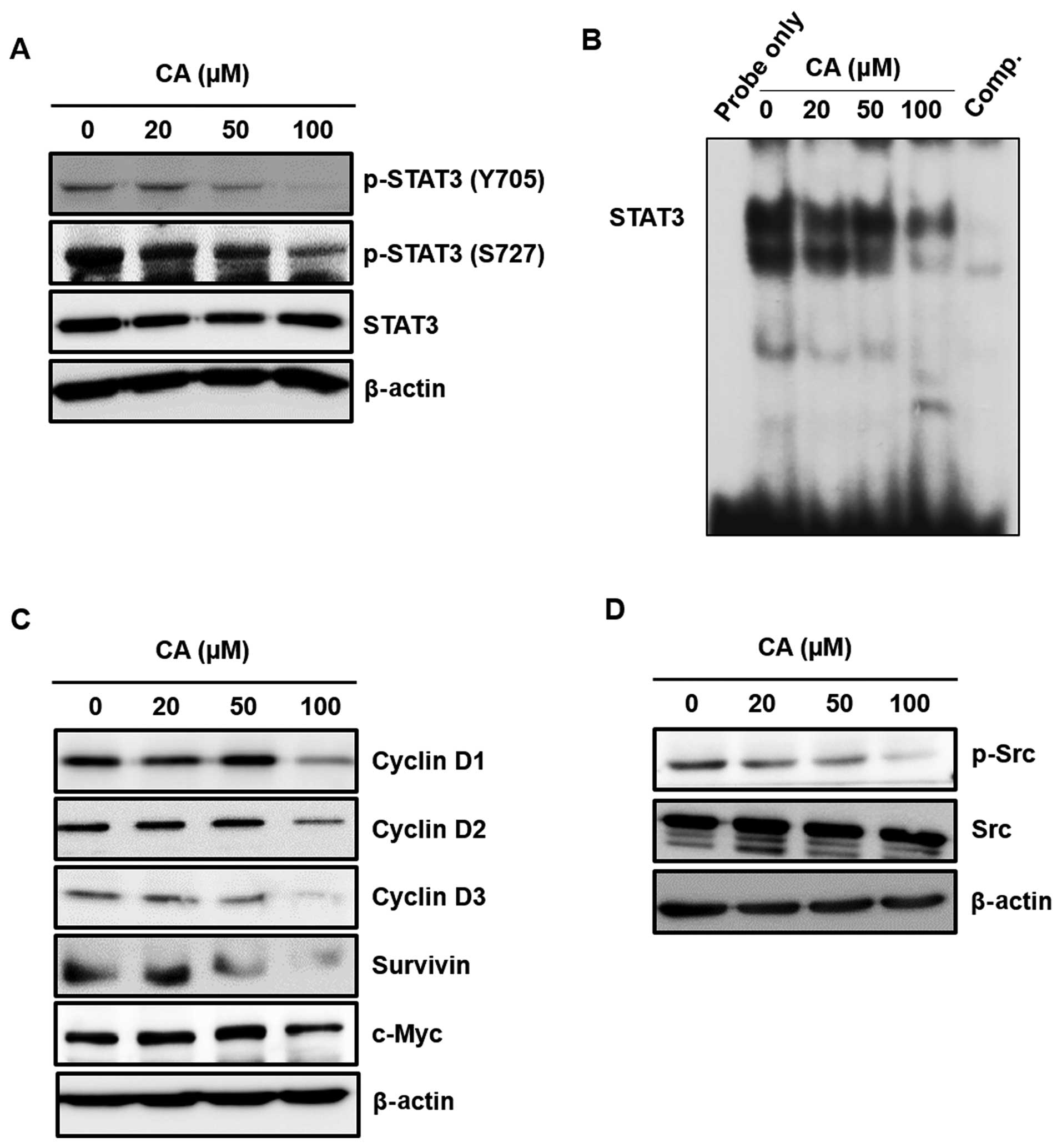
|
1
|
Motzer RJ, Bander NH and Nanus DM:
Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 335:865–875. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mulders P, Figlin R, deKernion JB,
Wiltrout R, Linehan M, Parkinson D, deWolf W and Belldegrun A:
Renal cell carcinoma: Recent progress and future directions. Cancer
Res. 57:5189–5195. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Santoni M, De Tursi M, Felici A, Lo Re G,
Ricotta R, Ruggeri EM, Sabbatini R, Santini D, Vaccaro V and
Milella M: Management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients
with poor-risk features: Current status and future perspectives.
Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 13:697–709. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang MT, Ho CT, Wang ZY, Ferraro T, Lou
YR, Stauber K, Ma W, Georgiadis C, Laskin JD and Conney AH:
Inhibition of skin tumorigenesis by rosemary and its constituents
carnosol and ursolic acid. Cancer Res. 54:701–708. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen D and Dou QP: Tea polyphenols and
their roles in cancer prevention and chemotherapy. Int J Mol Sci.
9:1196–1206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Earnshaw WC, Martins LM and Kaufmann SH:
Mammalian caspases: Structure, activation, substrates, and
functions during apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 68:383–424. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Fulda S, Galluzzi L and Kroemer G:
Targeting mitochondria for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
9:447–464. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Panaretakis T, Pokrovskaja K, Shoshan MC
and Grandér D: Interferon-alpha-induced apoptosis in U266 cells is
associated with activation of the proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members
Bak and Bax. Oncogene. 22:4543–4556. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Trachootham D, Lu W, Ogasawara MA, Nilsa
RD and Huang P: Redox regulation of cell survival. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 10:1343–1374. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Akgul C, Moulding DA and Edwards SW:
Molecular control of neutrophil apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 487:318–322.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kang YJ, Kim IY, Kim EH, Yoon MJ, Kim SU,
Kwon TK and Choi KS: Paxilline enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of
glioma cells via modulation of c-FLIP, survivin and DR5. Exp Mol
Med. 43:24–34. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Thorburn A: Death receptor-induced cell
killing. Cell Signal. 16:139–144. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ashkenazi A: Targeting the extrinsic
apoptosis pathway in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
19:325–331. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Neergheen VS, Bahorun T, Taylor EW, Jen LS
and Aruoma OI: Targeting specific cell signaling transduction
pathways by dietary and medicinal phytochemicals in cancer
chemoprevention. Toxicology. 278:229–241. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Huang S: Regulation of metastases by
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling
pathway: Clinical implications. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1362–1366.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Niu G, Wright KL, Huang M, Song L, Haura
E, Turkson J, Zhang S, Wang T, Sinibaldi D, Coppola D, et al:
Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor
angiogenesis. Oncogene. 21:2000–2008. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang T, Niu G, Kortylewski M, Burdelya L,
Shain K, Zhang S, Bhattacharya R, Gabrilovich D, Heller R, Coppola
D, et al: Regulation of the innate and adaptive immune responses by
Stat-3 signaling in tumor cells. Nat Med. 10:48–54. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Y, Ma X, Yan S, Shen S, Zhu H, Gu Y,
Wang H, Qin G and Yu Q: 17-hydroxy-jolkinolide B inhibits signal
transducers and activators of transcription 3 signaling by
covalently cross-linking Janus kinases and induces apoptosis of
human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 69:7302–7310. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu H and Jove R: The STATs of cancer - new
molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:97–105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen YF, Yang JS, Chang WS, Tsai SC, Peng
SF and Zhou YR: Houttuynia cordata Thunb extract modulates G0/G1
arrest and Fas/CD95-mediated death receptor apoptotic cell death in
human lung cancer A549 cells. J Biomed Sci. 20:182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim HG, Hwang YP and Jeong HG: Kahweol
blocks STAT3 phosphorylation and induces apoptosis in human lung
adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Toxicol Lett. 187:28–34. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jalali-Heravi M, Moazeni RS and Sereshti
H: Analysis of Iranian rosemary essential oil: Application of gas
chromatography-mass spectrometry combined with chemometrics. J
Chromatogr A. 1218:2569–2576. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ninomiya K, Matsuda H, Shimoda H, Nishida
N, Kasajima N, Yoshino T, Morikawa T and Yoshikawa M: Carnosic
acid, a new class of lipid absorption inhibitor from sage. Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 14:1943–1946. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Almela L, Sánchez-Muñoz B, Fernández-López
JA, Roca MJ and Rabe V: Liquid chromatograpic-mass spectrometric
analysis of phenolics and free radical scavenging activity of
rosemary extract from different raw material. J Chromatogr A.
1120:221–229. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ramírez P, García-Risco MR, Santoyo S,
Señoráns FJ, Ibáñez E and Reglero G: Isolation of functional
ingredients from rosemary by preparative-supercritical fluid
chromatography (Prep-SFC). J Pharm Biomed Anal. 41:1606–1613. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
López-García S, Castañeda-Sanchez JI,
Jiménez-Arellanes A, Domínguez-López L, Castro-Mussot ME,
Hernández-Sanchéz J and Luna-Herrera J: Macrophage activation by
ursolic and oleanolic acids during mycobacterial infection.
Molecules. 20:14348–14364. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ortuño J, Serrano R and Bañón S:
Antioxidant and antimicrobial effects of dietary supplementation
with rosemary diterpenes (carnosic acid and carnosol) vs vitamin E
on lamb meat packed under protective atmosphere. Meat Sci.
110:62–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gaya M, Repetto V, Toneatto J, Anesini C,
Piwien-Pilipuk G and Moreno S: Antiadipogenic effect of carnosic
acid, a natural compound present in Rosmarinus officinalis, is
exerted through the C/EBPs and PPARγ pathways at the onset of the
differentiation program. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1830:3796–3806.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ibarra A, Cases J, Roller M, Chiralt-Boix
A, Coussaert A and Ripoll C: Carnosic acid-rich rosemary
(Rosmarinus officinalis L.) leaf extract limits weight gain and
improves cholesterol levels and glycaemia in mice on a high-fat
diet. Br J Nutr. 106:1182–1189. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tsai CW, Liu KL, Lin YR and Kuo WC: The
mechanisms of carnosic acid attenuates tumor necrosis
factor-α-mediated inflammation and insulin resistance in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. Mol Nutr Food Res. 58:654–664. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang T, Takikawa Y, Satoh T, Yoshioka Y,
Kosaka K, Tatemichi Y and Suzuki K: Carnosic acid prevents obesity
and hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice. Hepatol Res. 41:87–92. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xiang Q, Liu Z, Wang Y, Xiao H, Wu W, Xiao
C and Liu X: Carnosic acid attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
liver injury in rats via fortifying cellular antioxidant defense
system. Food Chem Toxicol. 53:1–9. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kundu JK, Shin YK, Kim SH and Surh YJ:
Resveratrol inhibits phorbol ester-induced expression of COX-2 and
activation of NF-kappaB in mouse skin by blocking IkappaB kinase
activity. Carcinogenesis. 27:1465–1474. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Herr I and Debatin KM: Cellular stress
response and apoptosis in cancer therapy. Blood. 98:2603–2614.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Prasad S, Yadav VR, Kannappan R and
Aggarwal BB: Ursolic acid, a pentacyclin triterpene, potentiates
TRAIL-induced apoptosis through p53-independent up-regulation of
death receptors: Evidence for the role of reactive oxygen species
and JNK. J Biol Chem. 286:5546–5557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Ghobrial IM, Witzig TE and Adjei AA:
Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA Cancer J Clin.
55:178–194. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang X: The expanding role of mitochondria
in apoptosis. Genes Dev. 15:2922–2933. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Garrido C, Galluzzi L, Brunet M, Puig PE,
Didelot C and Kroemer G: Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from
mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 13:1423–1433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Antonsson B and Martinou JC: The Bcl-2
protein family. Exp Cell Res. 256:50–57. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Han J, Goldstein LA, Gastman BR and
Rabinowich H: Interrelated roles for Mcl-1 and BIM in regulation of
TRAIL-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
281:10153–10163. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
O'Connor PM, Jackman J, Bae I, Myers TG,
Fan S, Mutoh M, Scudiero DA, Monks A, Sausville EA, Weinstein JN,
et al: Characterization of the p53 tumor suppressor pathway in cell
lines of the National Cancer Institute anticancer drug screen and
correlations with the growth-inhibitory potency of 123 anticancer
agents. Cancer Res. 57:4285–4300. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Giaccia AJ and Kastan MB: The complexity
of p53 modulation: Emerging patterns from divergent signals. Genes
Dev. 12:2973–2983. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shieh SY, Ikeda M, Taya Y and Prives C:
DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of p53 alleviates inhibition by
MDM2. Cell. 91:325–334. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gottlieb TM, Leal JF, Seger R, Taya Y and
Oren M: Cross-talk between Akt, p53 and Mdm2: Possible implications
for the regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene. 21:1299–1303. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lotem J, Peled-Kamar M, Groner Y and Sachs
L: Cellular oxidative stress and the control of apoptosis by
wild-type p53, cytotoxic compounds, and cytokines. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 93:9166–9171. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Misra MK, Sarwat M, Bhakuni P, Tuteja R
and Tuteja N: Oxidative stress and ischemic myocardial syndromes.
Med Sci Monit. 15:RA209–RA219. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Orrenius S, Gogvadze V and Zhivotovsky B:
Mitochondrial oxidative stress: Implications for cell death. Annu
Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 47:143–183. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kim DJ, Chan KS, Sano S and Digiovanni J:
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) in
epithelial carcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog. 46:725–731. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kusaba T, Nakayama T, Yamazumi K, Yakata
Y, Yoshizaki A, Inoue K, Nagayasu T and Sekine I: Activation of
STAT3 is a marker of poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer.
Oncol Rep. 15:1445–1451. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lin L, Liu A, Peng Z, Lin HJ, Li PK, Li C
and Lin J: STAT3 is necessary for proliferation and survival in
colon cancer-initiating cells. Cancer Res. 71:7226–7237. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Johnston PA and Grandis JR: STAT3
signaling: Anticancer strategies and challenges. Mol Interv.
11:18–26. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|