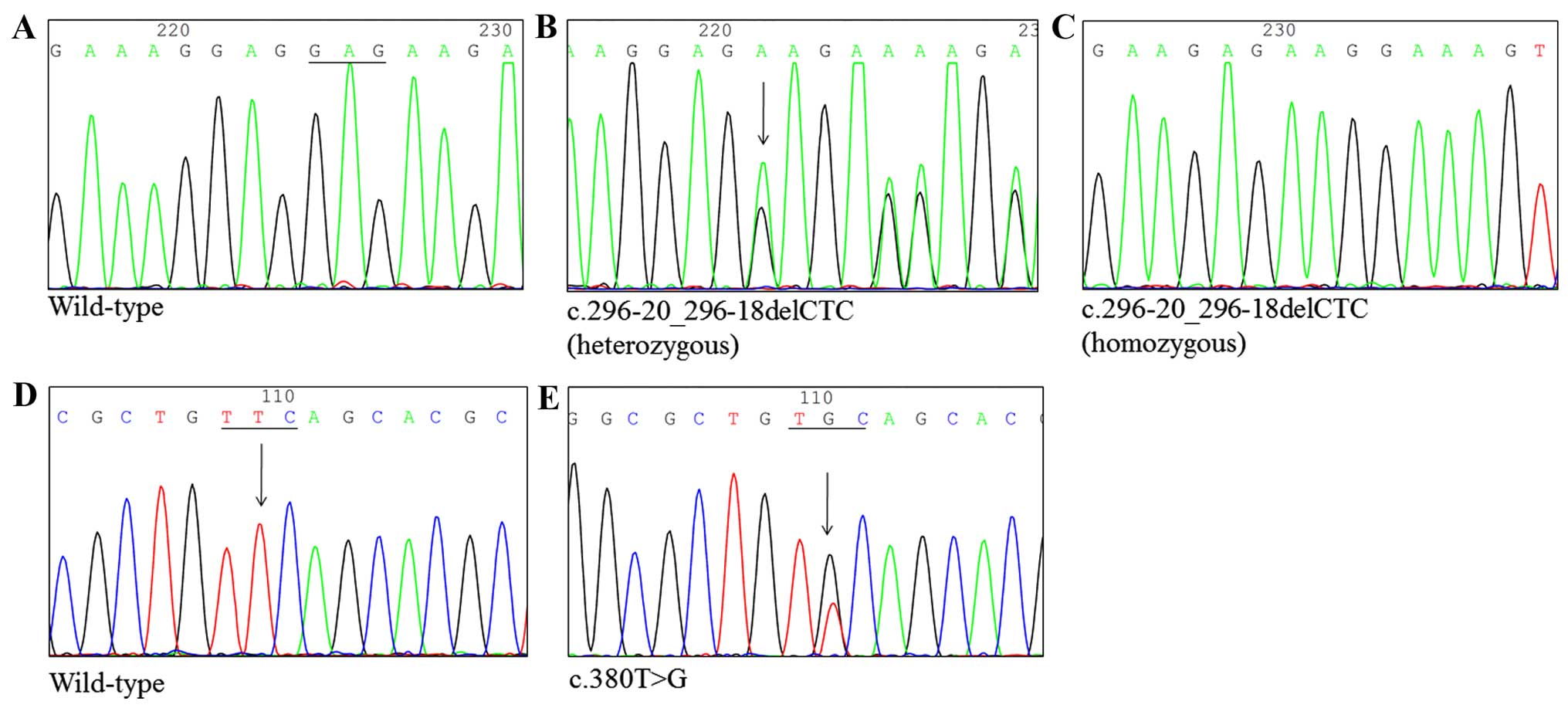
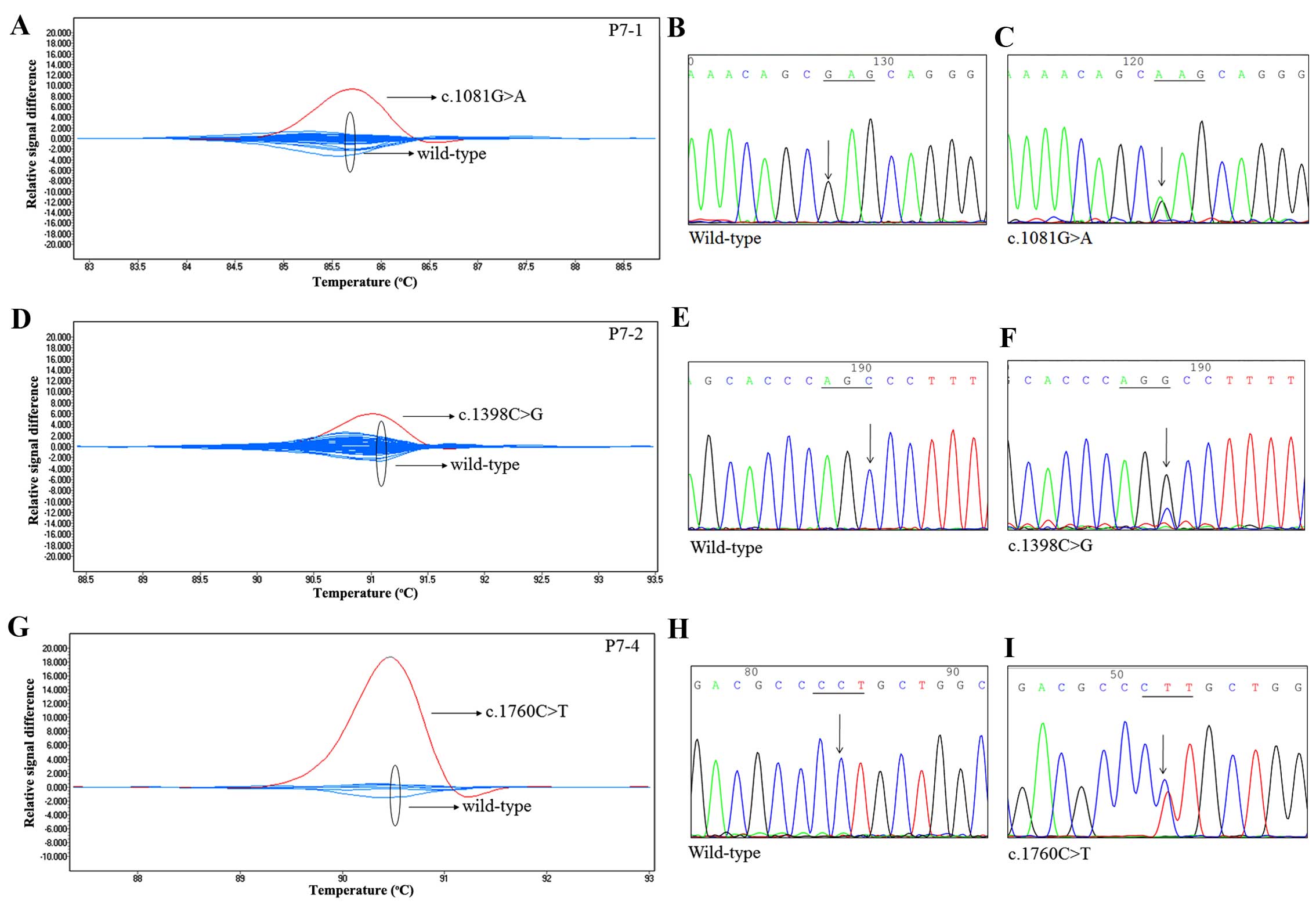
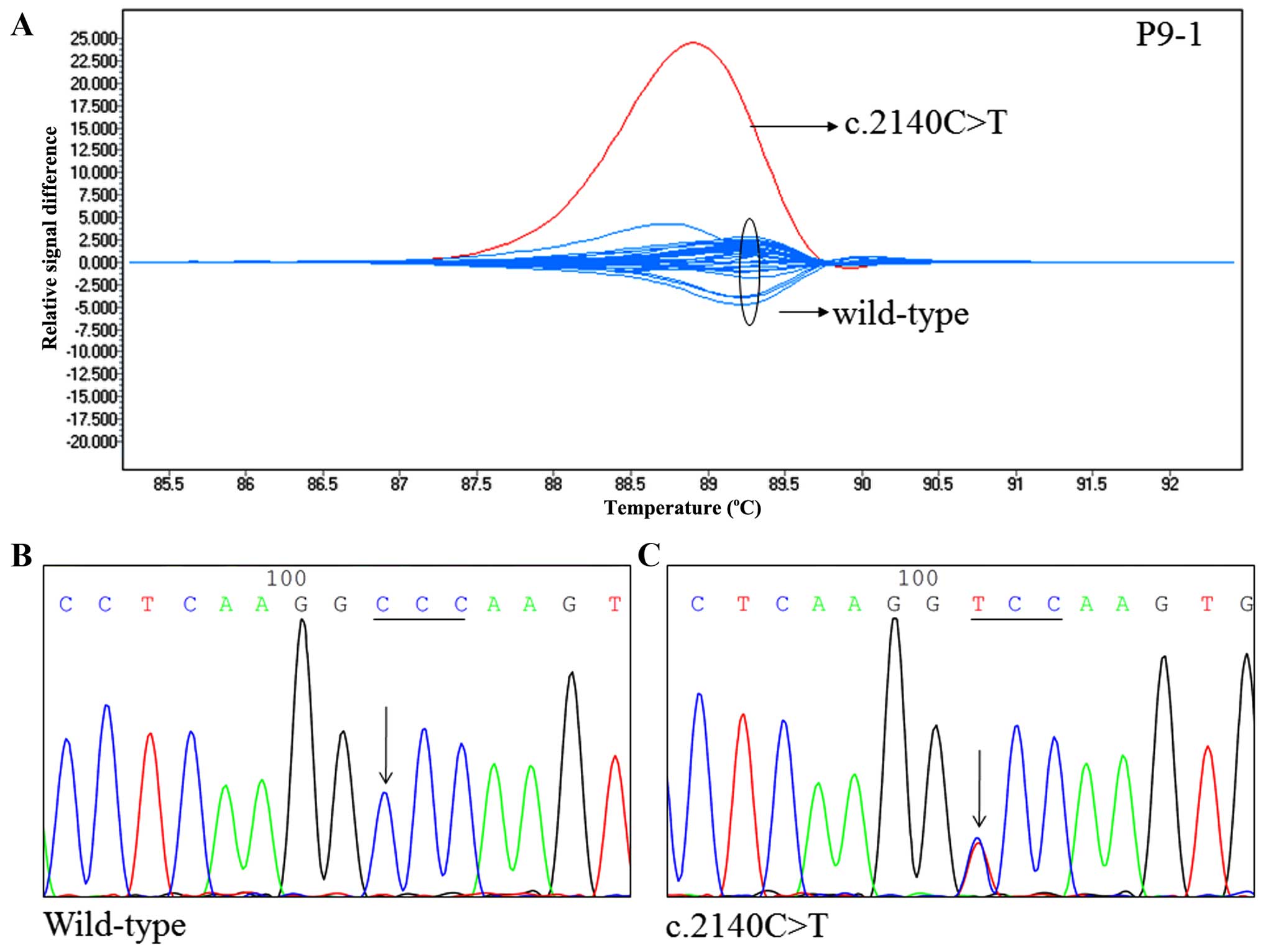
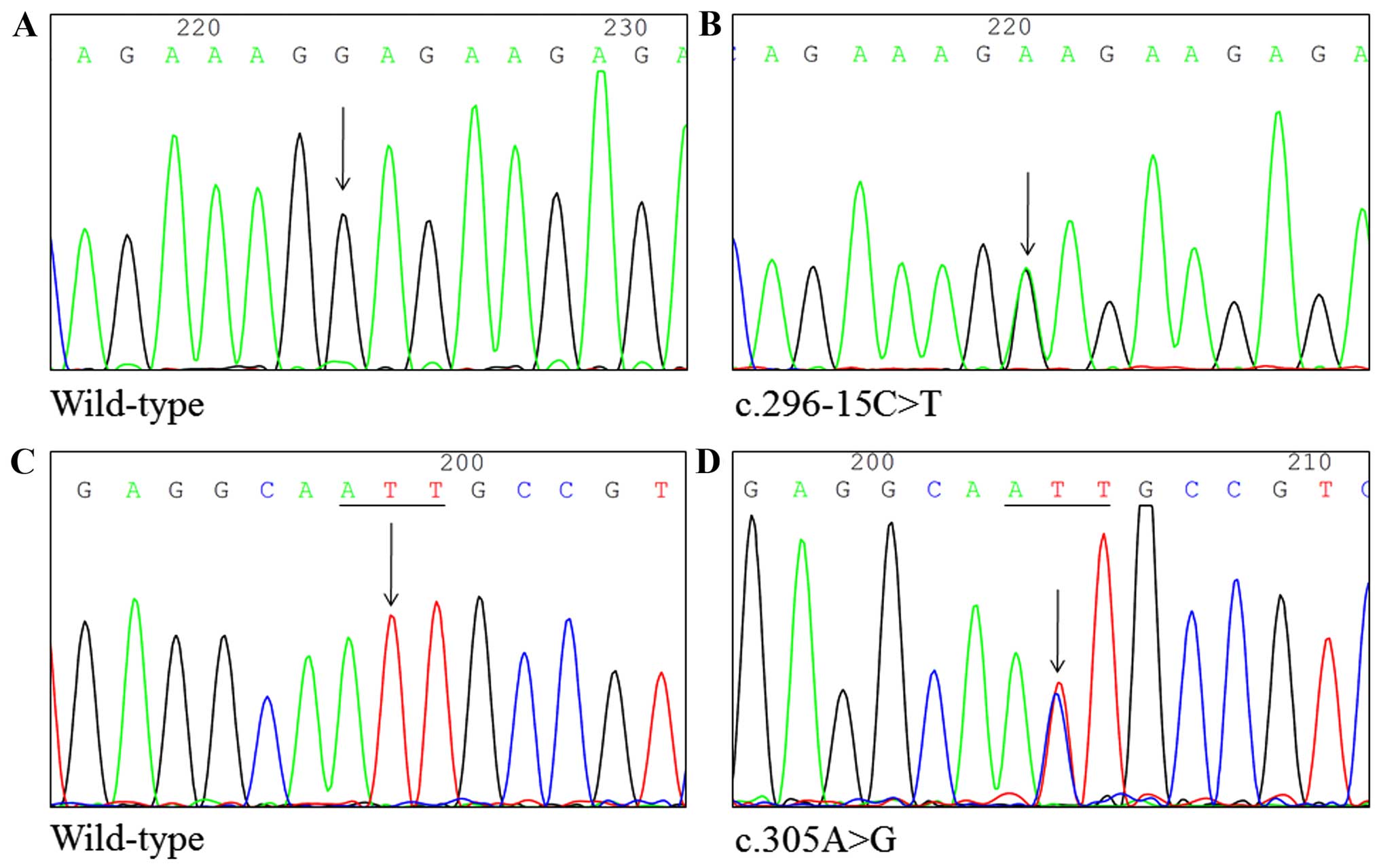
|
1
|
Molinolo AA, Amornphimoltham P, Squarize
CH, Castilho RM, Patel V and Gutkind JS: Dysregulated molecular
networks in head and neck carcinogenesis. Oral Oncol. 45:324–334.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ and Brakenhoff
RH: The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:9–22. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ko YC, Huang YL, Lee CH, Chen MJ, Lin LM
and Tsai CC: Betel quid chewing, cigarette smoking and alcohol
consumption related to oral cancer in Taiwan. J Oral Pathol Med.
24:450–453. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tanaka T, Tanaka M and Tanaka T: Oral
carcinogenesis and oral cancer chemoprevention: A review. Pathol
Res Int. 2011:4312462011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Petersen PE: Oral cancer prevention and
control - the approach of the World Health Organization. Oral
Oncol. 45:454–460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Karin M and Greten FR: NF-kappaB: Linking
inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:749–759. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oeckinghaus A, Hayden MS and Ghosh S:
Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways. Nat Immunol. 12:695–708.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Catrysse L, Vereecke L, Beyaert R and van
Loo G: A20 in inflammation and autoimmunity. Trends Immunol.
35:22–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dixit VM, Green S, Sarma V, Holzman LB,
Wolf FW, O'Rourke K, Ward PA, Prochownik EV and Marks RM: Tumor
necrosis factor-alpha induction of novel gene products in human
endothelial cells including a macrophage-specific chemotaxin. J
Biol Chem. 265:2973–2978. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wertz IE, O'Rourke KM, Zhou H, Eby M,
Aravind L, Seshagiri S, Wu P, Wiesmann C, Baker R, Boone DL, et al:
De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate
NF-kappaB signalling. Nature. 430:694–699. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kato M, Sanada M, Kato I, Sato Y, Takita
J, Takeuchi K, Niwa A, Chen Y, Nakazaki K, Nomoto J, et al:
Frequent inactivation of A20 in B-cell lymphomas. Nature.
459:712–716. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nomoto J, Hiramoto N, Kato M, Sanada M,
Maeshima AM, Taniguchi H, Hosoda F, Asakura Y, Munakata W,
Sekiguchi N, et al: Deletion of the TNFAIP3/A20 gene detected by
FICTION analysis in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. BMC Cancer.
12:4572012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Philipp C, Edelmann J, Bühler A, Winkler
D, Stilgenbauer S and Küppers R: Mutation analysis of the TNFAIP3
(A20) tumor suppressor gene in CLL. Int J Cancer. 128:1747–1750.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chanudet E, Huang Y, Ichimura K, Dong G,
Hamoudi RA, Radford J, Wotherspoon AC, Isaacson PG, Ferry J and Du
MQ: A20 is targeted by promoter methylation, deletion and
inactivating mutation in MALT lymphoma. Leukemia. 24:483–487. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ma A and Malynn BA: A20: Linking a complex
regulator of ubiquitylation to immunity and human disease. Nat Rev
Immunol. 12:774–785. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Graham RR, Hom G, Ortmann W and Behrens
TW: Review of recent genome-wide association scans in lupus. J
Intern Med. 265:680–688. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Er TK and Chang JG: High-resolution
melting: Applications in genetic disorders. Clin Chim Acta.
414:197–201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yeh KT, Shih MC, Lin TH, Chen JC, Chang
JY, Kao CF, Lin KL and Chang JG: The correlation between CpG
methylation on promoter and protein expression of E-cadherin in
oral squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 22:3971–3975.
2002.
|
|
19
|
Sobin LH and Fleming ID: TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumors, 5th edition (1997). Union
Internationale Contre le Cancer and the American Joint Committee on
Cancer. Cancer. 80:1803–1804. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stransky N, Egloff AM, Tward AD, Kostic
AD, Cibulskis K, Sivachenko A, Kryukov GV, Lawrence MS, Sougnez C,
McKenna A, et al: The mutational landscape of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Science. 333:1157–1160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shih HC, Er TK, Chang TJ, Chang YS, Liu TC
and Chang JG: Rapid identification of HBB gene mutations by
high-resolution melting analysis. Clin Biochem. 42:1667–1676. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tavares RM, Turer EE, Liu CL, Advincula R,
Scapini P, Rhee L, Barrera J, Lowell CA, Utz PJ, Malynn BA, et al:
The ubiquitin modifying enzyme A20 restricts B cell survival and
prevents autoimmunity. Immunity. 33:181–191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hövelmeyer N, Reissig S, Xuan NT,
Adams-Quack P, Lukas D, Nikolaev A, Schlüter D and Waisman A: A20
deficiency in B cells enhances B-cell proliferation and results in
the development of autoantibodies. Eur J Immunol. 41:595–601. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chu Y, Vahl JC, Kumar D, Heger K, Bertossi
A, Wójtowicz E, Soberon V, Schenten D, Mack B, Reutelshöfer M, et
al: B cells lacking the tumor suppressor TNFAIP3/A20 display
impaired differentiation and hyperactivation and cause inflammation
and autoimmunity in aged mice. Blood. 117:2227–2236. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Matmati M, Jacques P, Maelfait J,
Verheugen E, Kool M, Sze M, Geboes L, Louagie E, Mc Guire C,
Vereecke L, et al: A20 (TNFAIP3) deficiency in myeloid cells
triggers erosive polyarthritis resembling rheumatoid arthritis. Nat
Genet. 43:908–912. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kool M, van Loo G, Waelput W, De Prijck S,
Muskens F, Sze M, van Praet J, Branco-Madeira F, Janssens S, Reizis
B, et al: The ubiquitin-editing protein A20 prevents dendritic cell
activation, recognition of apoptotic cells, and systemic
autoimmunity. Immunity. 35:82–96. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hammer GE, Turer EE, Taylor KE, Fang CJ,
Advincula R, Oshima S, Barrera J, Huang EJ, Hou B, Malynn BA, et
al: Expression of A20 by dendritic cells preserves immune
homeostasis and prevents colitis and spondyloarthritis. Nat
Immunol. 12:1184–1193. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vereecke L, Sze M, Mc Guire C, Rogiers B,
Chu Y, Schmidt-Supprian M, Pasparakis M, Beyaert R and van Loo G:
Enterocyte-specific A20 deficiency sensitizes to tumor necrosis
factor-induced toxicity and experimental colitis. J Exp Med.
207:1513–1523. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ungerbäck J, Belenki D, Jawad ul-Hassan A,
Fredrikson M, Fransén K, Elander N, Verma D and Söderkvist P:
Genetic variation and alterations of genes involved in
NFκB/TNFAIP3- and NLRP3-inflammasome signaling affect
susceptibility and outcome of colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis.
33:2126–2134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lippens S, Lefebvre S, Gilbert B, Sze M,
Devos M, Verhelst K, Vereecke L, Mc Guire C, Guérin C, Vandenabeele
P, et al: Keratinocyte-specific ablation of the NF-κB regulatory
protein A20 (TNFAIP3) reveals a role in the control of epidermal
homeostasis. Cell Death Differ. 18:1845–1853. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|