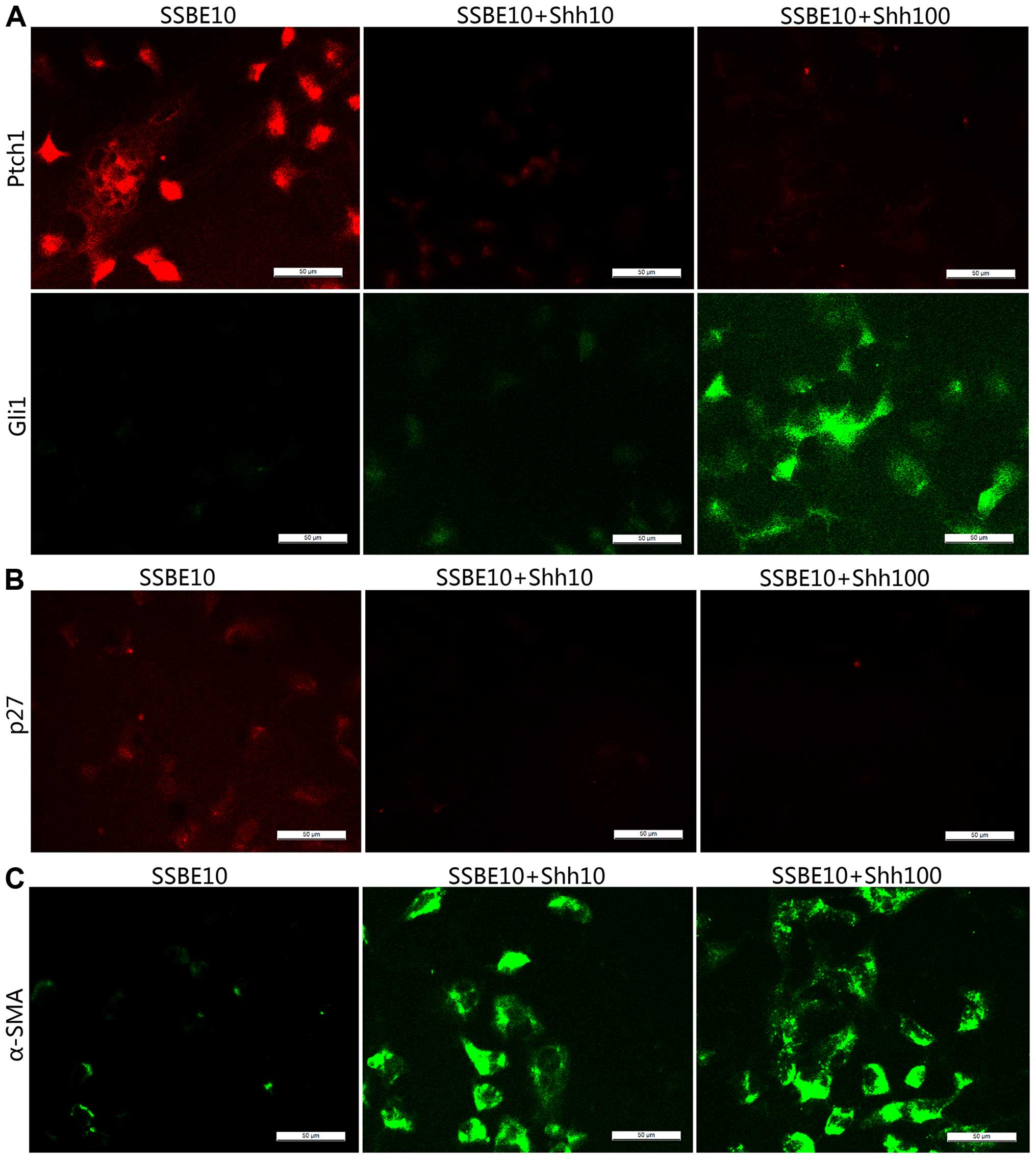
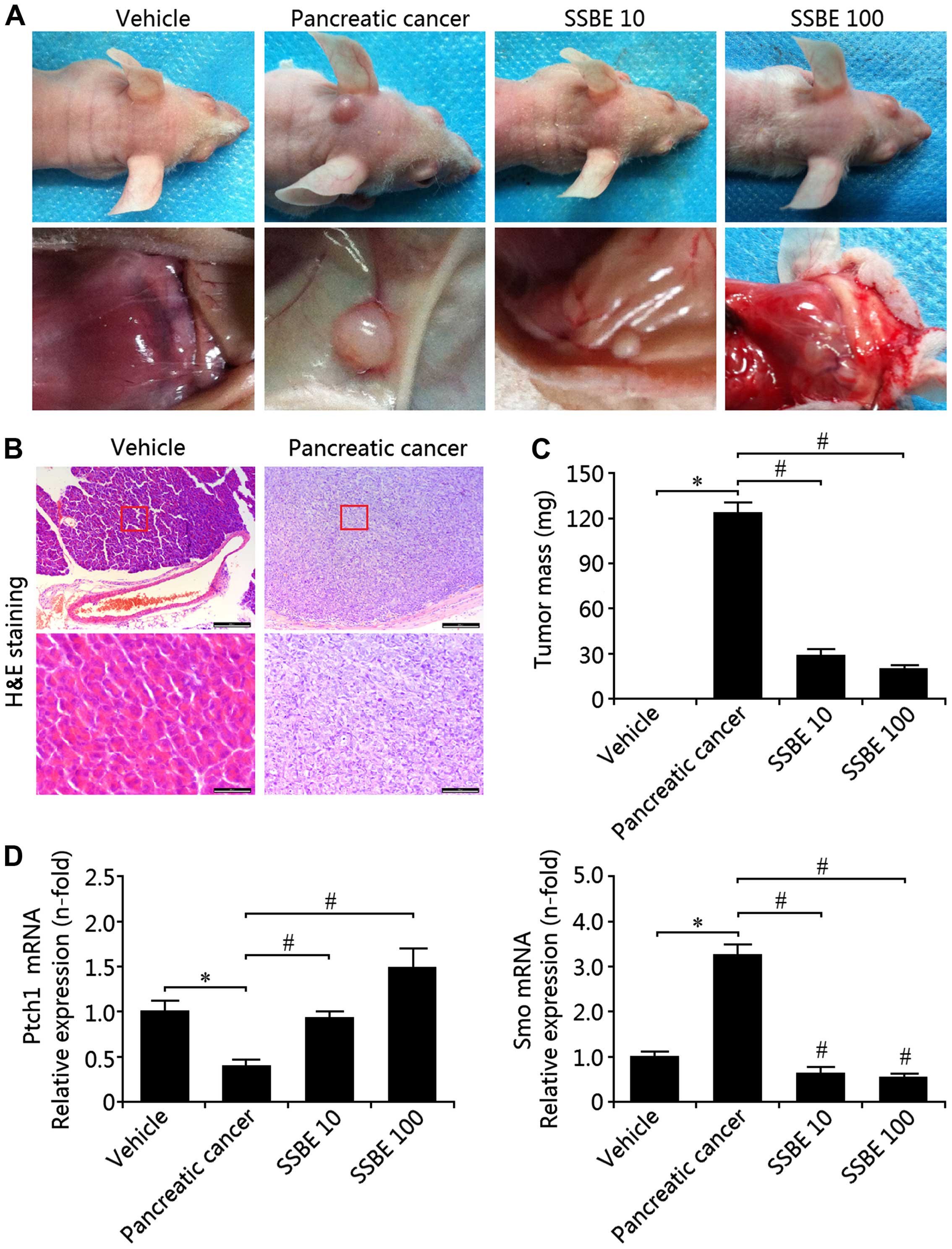
|
1
|
Douglass HO Jr: Adjuvant therapy for
pancreatic cancer. World J Surg. 19:270–274. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kayahara M, Funaki K, Tajima H, Takamura
H, Ninomiya I, Kitagawa H and Ohta T: Surgical implication of
micrometastasis for pancreatic cancer. Pancreas. 39:884–888. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Richter J and Saif MW: Updates in adjuvant
therapy in pancreatic cancer: Gemcitabine and beyond. Highlights
from the '2010 ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium'; Orlando,
FL, USA. January 22–24, 2010;
JOP. 11:144–147. 2010.
|
|
4
|
Woo JH, Li D, Wilsbach K, Orita H, Coulter
J, Tully E, Kwon TK, Xu S and Gabrielson E: Coix seed extract, a
commonly used treatment for cancer in China, inhibits NFkappaB and
protein kinase C signaling. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:2005–2011. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Habib SH, Makpol S, Abdul Hamid NA, Das S,
Ngah WZ and Yusof YA: Ginger extract (Zingiber officinale) has
anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects on ethionine-induced
hepatoma rats. Clinics. 63:807–813. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Heo BG, Park YS, Chon SU, Lee SY, Cho JY
and Gorinstein S: Antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity of methanol
extracts from aerial parts of Korean salad plants. BiofaIctors.
30:79–89. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jung HJ, Kang HJ, Song YS, Park EH, Kim YM
and Lim CJ: Anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic and anti-nociceptive
activities of Sedum sarmentosum extract. J Ethnopharmacol.
116:138–143. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Morikawa T, Zhang Y, Nakamura S, Matsuda
H, Muraoka O and Yoshikawa M: Bioactive constituents from Chinese
natural medicines. XXII Absolute structures of new megastigmane
glycosides, sedumosides E1, E2,
E3, F1, F2, and G, from Sedum
sarmentosum (Crassulaceae). Chem Pharm Bull. 55:435–441. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ninomiya K, Morikawa T, Zhang Y, Nakamura
S, Matsuda H, Muraoka O and Yoshikawa M: Bioactive constituents
from Chinese natural medicines. XXIII Absolute structures of new
megastigmane glycosides, sedumosides A4, A5,
A6, H, and I, and hepatoprotective megastigmanes from
Sedum sarmentosum. Chem Pharm Bull. 55:1185–1191. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Oh H, Kang DG, Kwon JW, Kwon TO, Lee SY,
Lee DB and Lee HS: Isolation of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)
inhibitory flavonoids from Sedum sarmentosum. Biol Pharm Bull.
27:2035–2037. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Johari J, Kianmehr A, Mustafa MR, Abubakar
S and Zandi K: Antiviral activity of baicalein and quercetin
against the Japanese encephalitis virus. Int J Mol Sci.
13:16785–16795. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang G, Song L, Wang H and Xing N:
Quercetin synergizes with 2-methoxyestradiol inhibiting cell growth
and inducing apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
30:357–363. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Youn H, Jeong JC, Jeong YS, Kim EJ and Um
SJ: Quercetin potentiates apoptosis by inhibiting nuclear
factor-kappaB signaling in H460 lung cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull.
36:944–951. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mahmoud MF, Hassan NA, El Bassossy HM and
Fahmy A: Quercetin protects against diabetes-induced exaggerated
vasoconstriction in rats: Effect on low grade inflammation. PLoS
One. 8:e637842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun J, Sun G, Meng X, Wang H, Luo Y, Qin
M, Ma B, Wang M, Cai D, Guo P, et al: Isorhamnetin protects against
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in vivo and in vitro. PLoS One.
8:e645262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bai Y, Lu H, Zhang G, Wu C, Lin C, Liang Y
and Chen B: Sedum sarmentosum Bunge extract exerts renal
anti-fibrotic effects in vivo and in vitro. Life Sci. 105:22–30.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bai Y, Lu H, Wu C, Liang Y, Wang S, Lin C,
Chen B and Xia P: Resveratrol inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and renal fibrosis by antagonizing the hedgehog
signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 92:484–493. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu F, Guo Y, Chen B, Dong P and Zheng J:
MicroRNA-17-5p activates hepatic stellate cells through targeting
of Smad7. Lab Invest. 95:781–789. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Athanasoula KC, Gogas H, Polonifi K,
Vaiopoulos AG, Polyzos A and Mantzourani M: Survivin beyond
physiology: Orchestration of multistep carcinogenesis and
therapeutic potentials. Cancer Lett. 347:175–182. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McMahon SB: MYC and the control of
apoptosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 4:a0144072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Taylor WR and Stark GR: Regulation of the
G2/M transition by p53. Oncogene. 20:1803–1815. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote MJ, Pagano M
and Draetta G: Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell
cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 7:812–821. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Diehl JA: Cycling to cancer with cyclin
D1. Cancer Biol Ther. 1:226–231. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Savagner P: The epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) phenomenon. Ann Oncol. 21(Suppl 7): vii89–vii92.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Edwards PC, Ruggiero S, Fantasia J,
Burakoff R, Moorji SM, Paric E, Razzano P, Grande DA and Mason JM:
Sonic hedgehog gene-enhanced tissue engineering for bone
regeneration. Gene Ther. 12:75–86. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Thayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW,
Nielsen CM, Roberts DJ, Lauwers GY, Qi YP, Gysin S, Fernández-del
Castillo C, Yajnik V, et al: Hedgehog is an early and late mediator
of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature. 425:851–856. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Varjosalo M and Taipale J: Hedgehog:
Functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev. 22:2454–2472. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Katoh Y and Katoh M: Hedgehog signaling
pathway and gastric cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:1050–1054. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
El-Zaatari M, Daignault S, Tessier A,
Kelsey G, Travnikar LA, Cantu EF, Lee J, Plonka CM, Simeone DM,
Anderson MA, et al: Plasma Shh levels reduced in pancreatic cancer
patients. Pancreas. 41:1019–1028. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li X, Wang Z, Ma Q, Xu Q, Liu H, Duan W,
Lei J, Ma J, Wang X, Lv S, et al: Sonic hedgehog paracrine
signaling activates stromal cells to promote perineural invasion in
pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:4326–4338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang Y, Tian X, Xie X, Zhuang Y, Wu W and
Wang W: Expression and regulation of hedgehog signaling pathway in
pancreatic cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 395:515–525. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Martin ST, Sato N, Dhara S, Chang R,
Hustinx SR, Abe T, Maitra A and Goggins M: Aberrant methylation of
the human Hedgehog interacting protein (HHIP) gene in pancreatic
neoplasms. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:728–733. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu Y, An Y, Wang X, Zha W and Li X:
Inhibition of the Hedgehog pathway induces autophagy in pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 31:707–712. 2014.
|
|
35
|
Guo J, Gao J, Li Z, Gong Y, Man X, Jin J
and Wu H: Adenovirus vector-mediated Gli1 siRNA induces growth
inhibition and apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer with
Smo-dependent or Smo-independent Hh pathway activation in vitro and
in vivo. Cancer Lett. 339:185–194. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang D, Zhang W, Huang D and Wu J:
Antitumor activity of the aqueous extract from Sedum sarmentosum
Bunge in vitro. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 25:81–88. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|