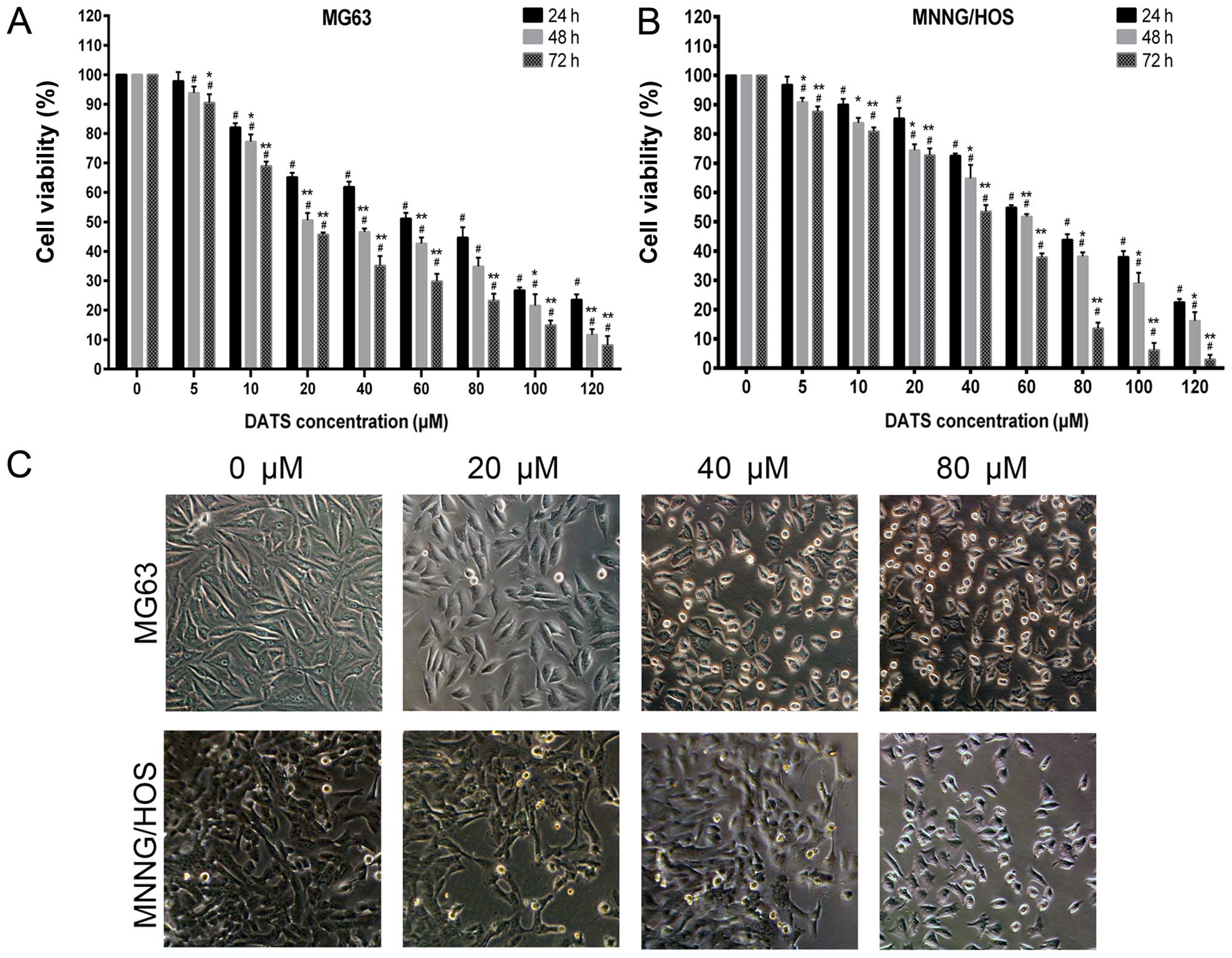
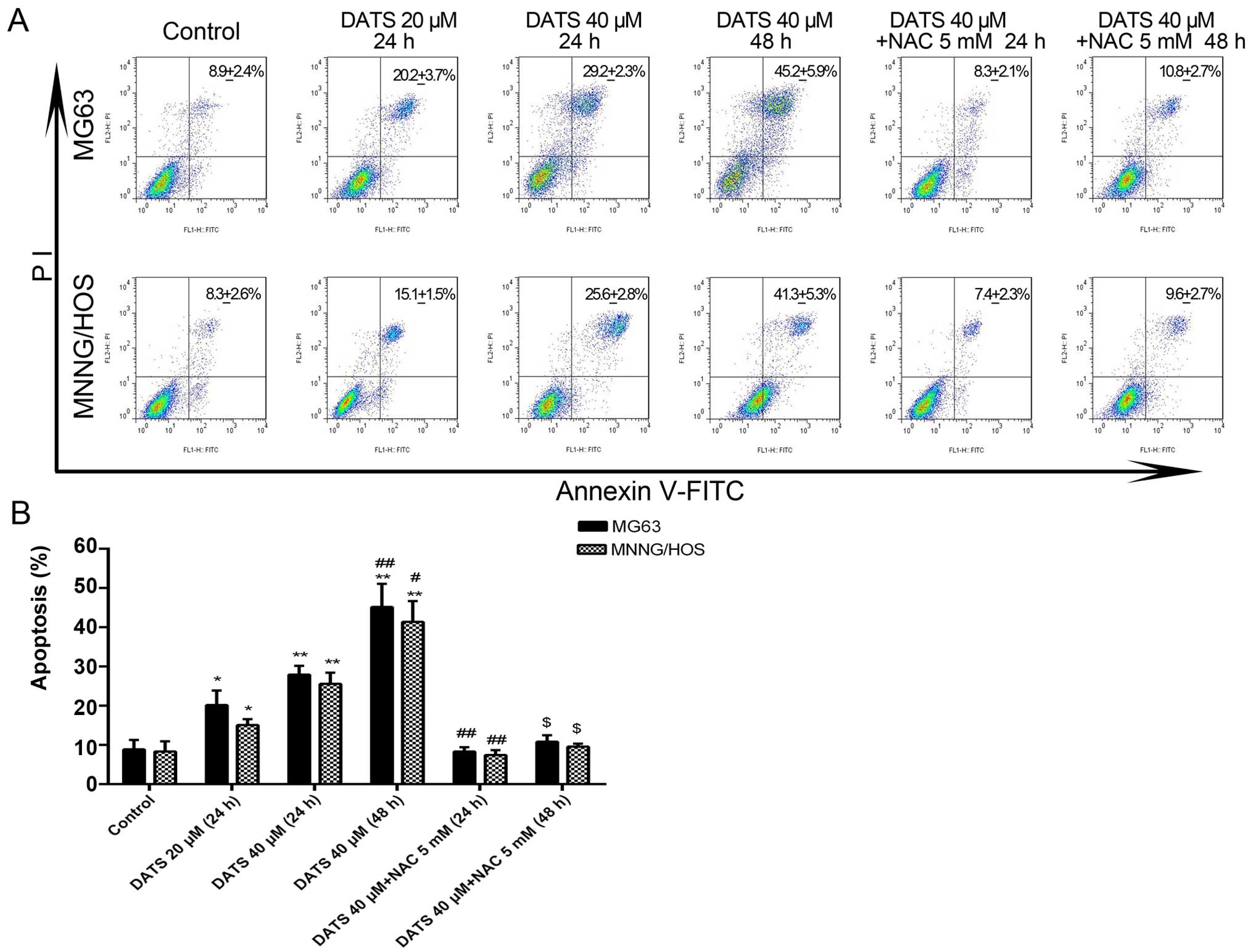
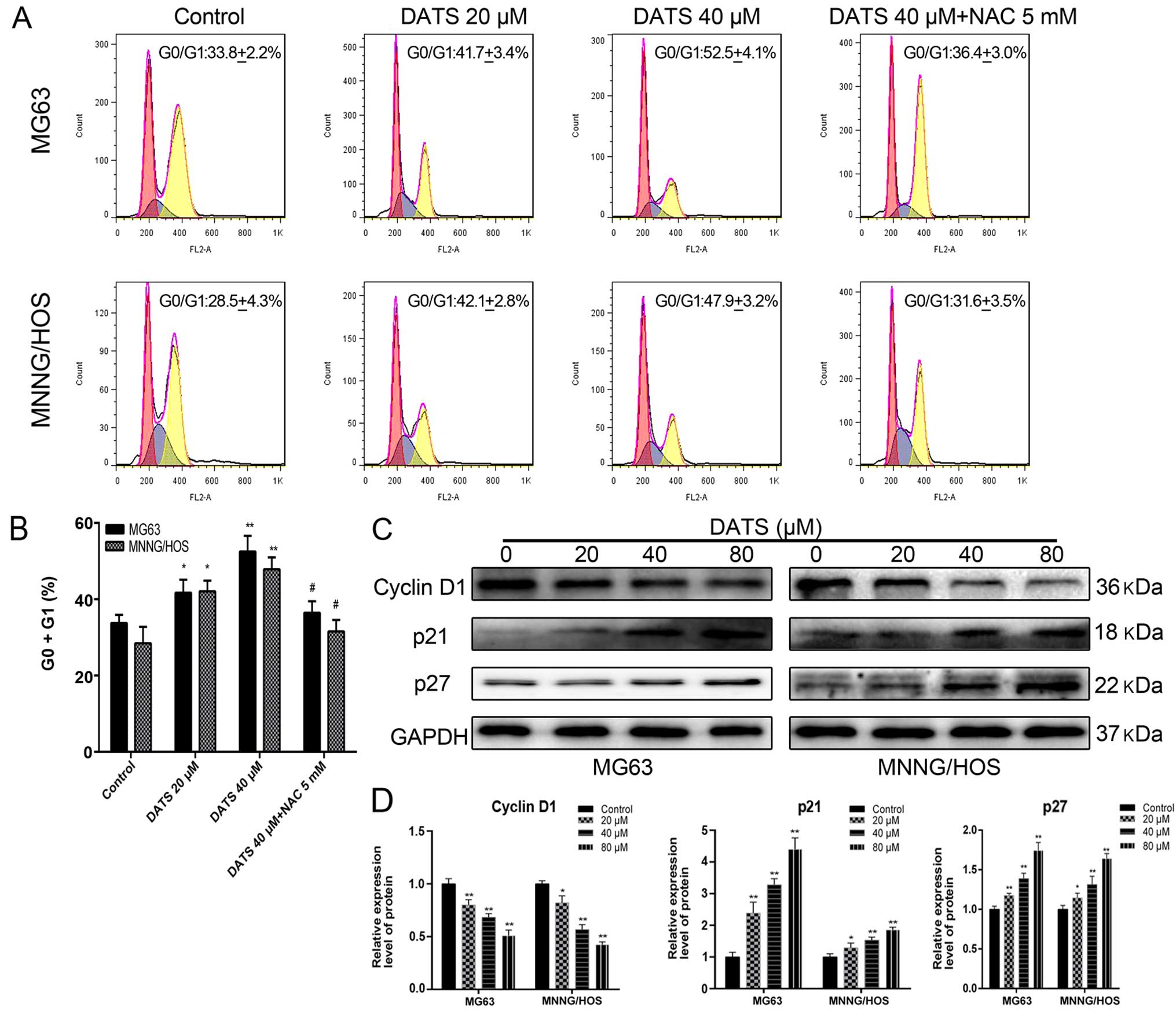
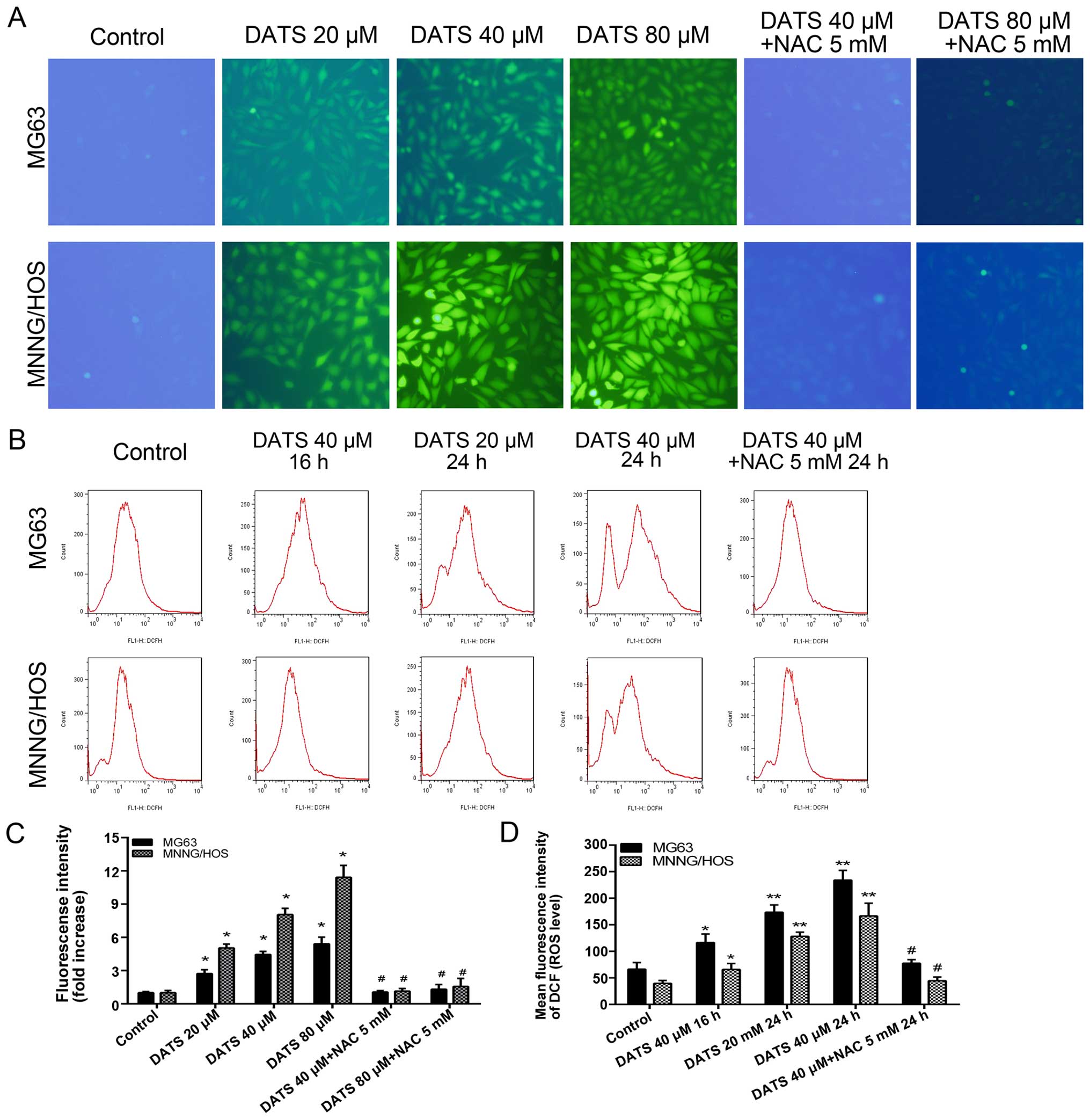
|
1
|
Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G,
Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Werner M,
Winkelmann W, et al: Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosar-coma
of the extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1,702 patients treated
on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J
Clin Oncol. 20:776–790. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boos G and Stopper H: Genotoxicity of
several clinically used topoisomerase II inhibitors. Toxicol Lett.
116:7–16. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fleischauer AT, Poole C and Arab L: Garlic
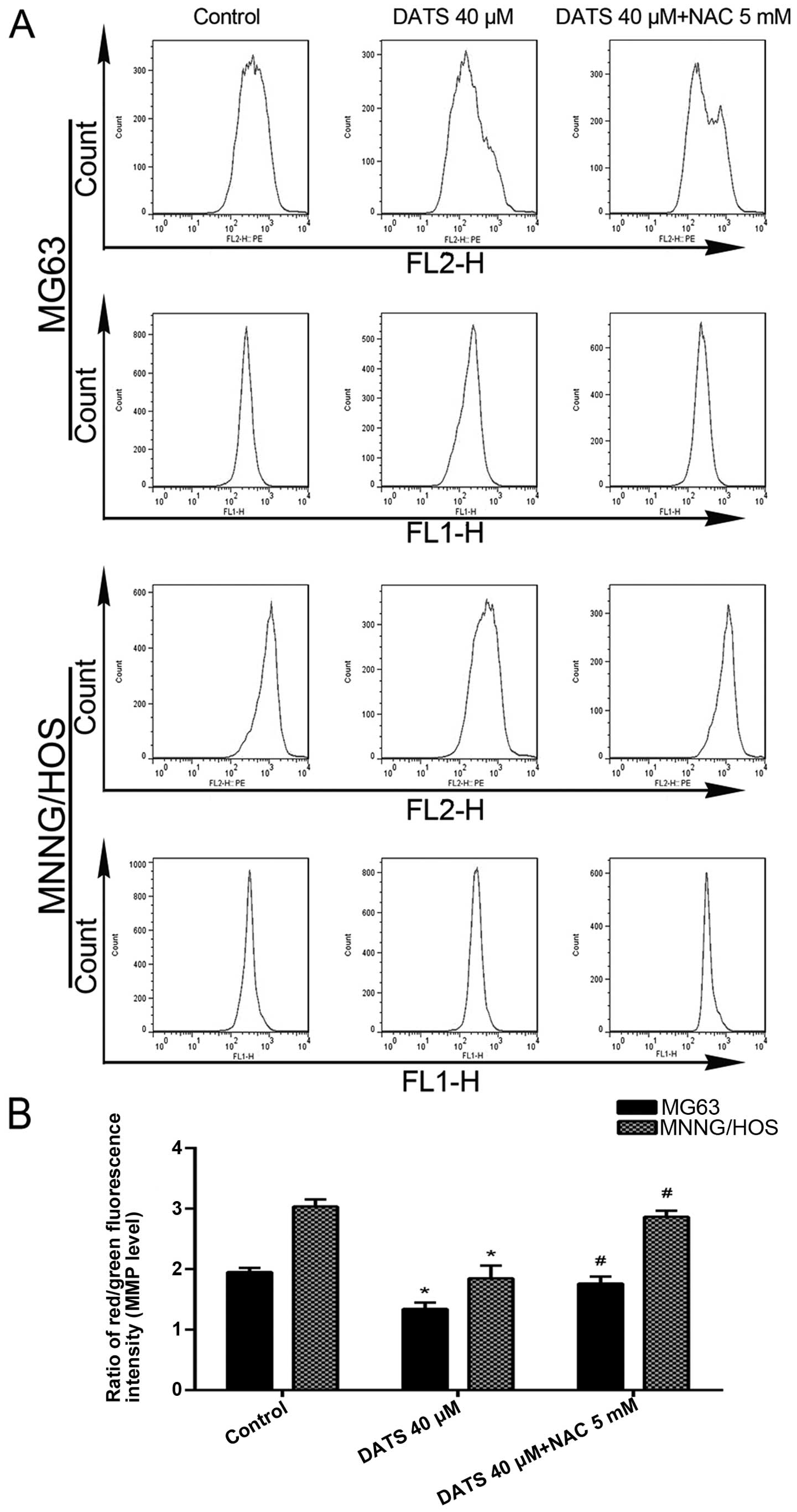
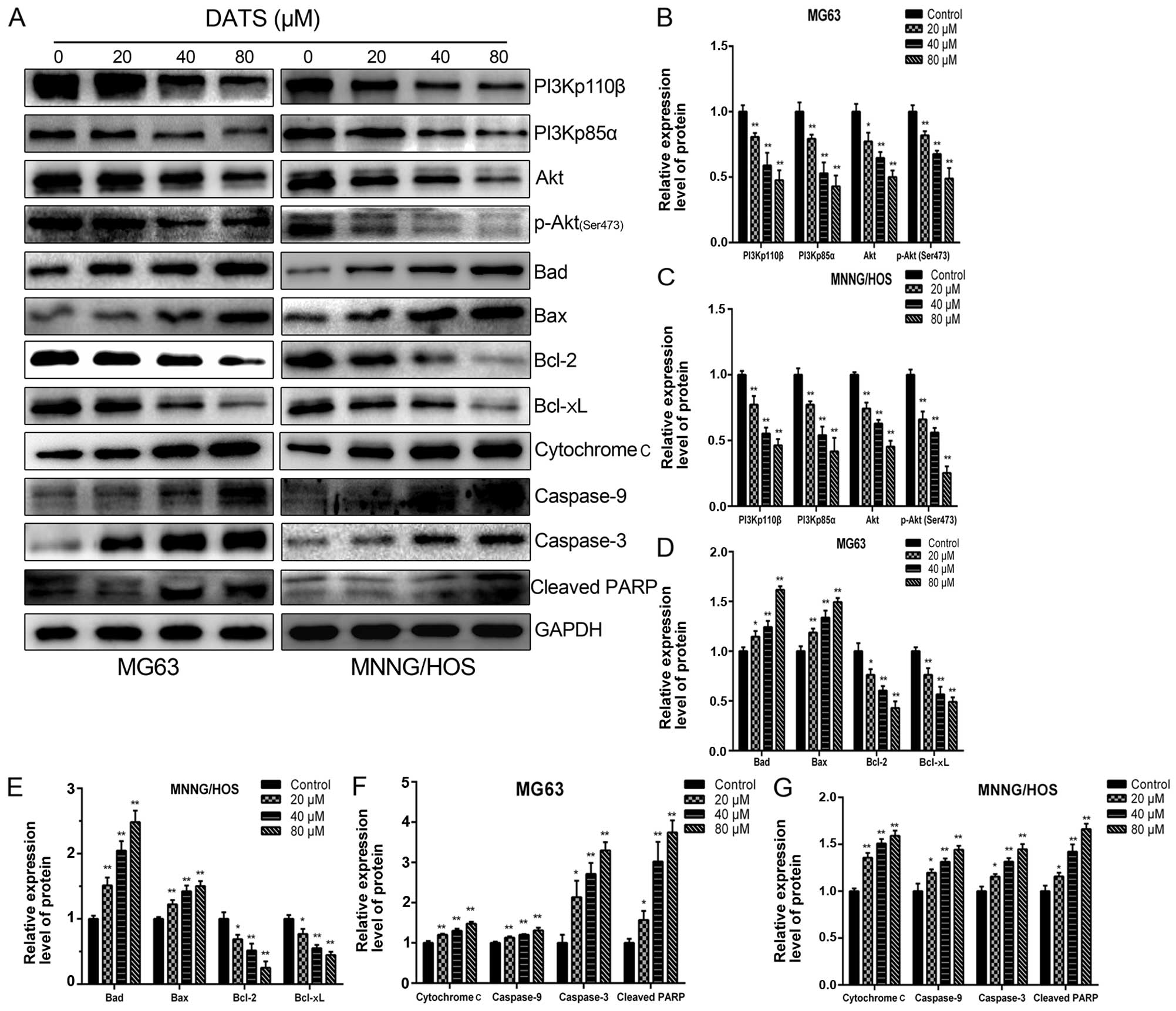
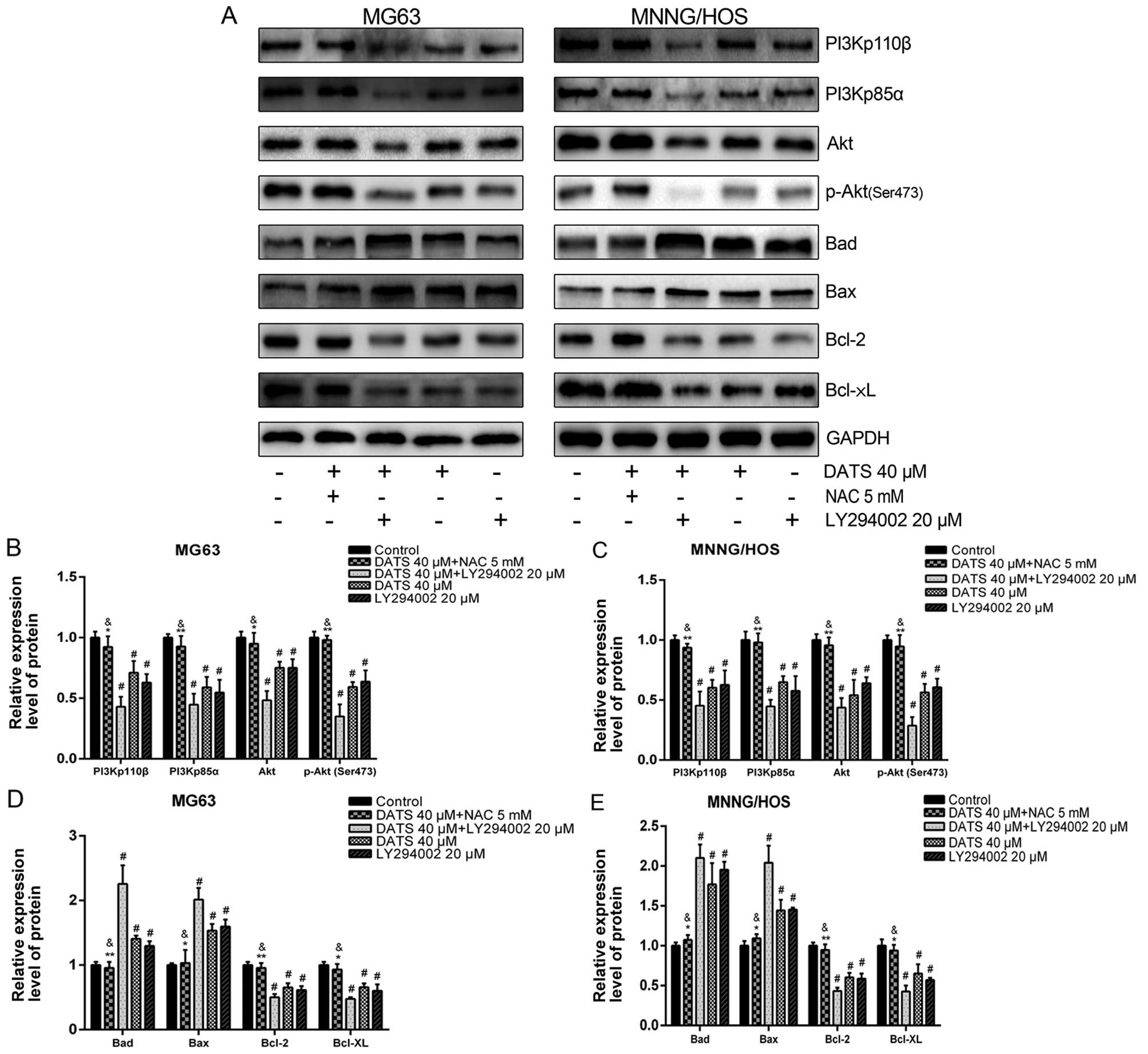
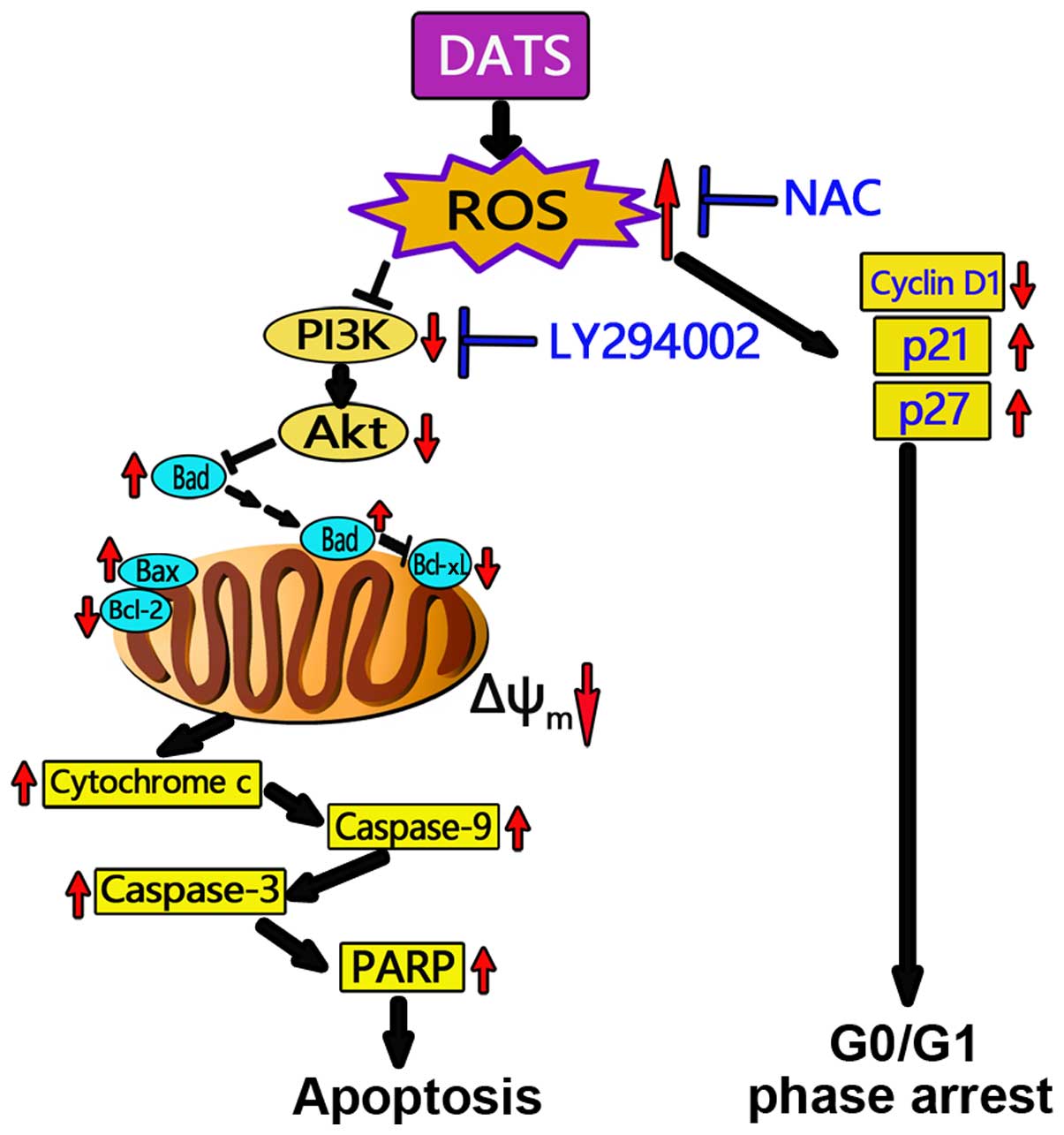
consumption and cancer prevention: Meta-analyses of colorectal and
stomach cancers. Am J Clin Nutr. 72:1047–1052. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hsing AW, Chokkalingam AP, Gao YT, Madigan
MP, Deng J, Gridley G and Fraumeni JF Jr: Allium vegetables and
risk of prostate cancer: A population-based study. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 94:1648–1651. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang X, Zhu Y, Duan W, Feng C and He X:
Allicin induces apoptosis of the MGC-803 human gastric carcinoma
cell line through the p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase/caspase-3 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 11:2755–2760.
2015.
|
|
6
|
Lai KC, Hsu SC, Yang JS, Yu CC, Lein JC
and Chung JG: Diallyl trisulfide inhibits migration, invasion and
angiogenesis of human colon cancer HT-29 cells and umbilical vein
endothelial cells, and suppresses murine xenograft tumour growth. J
Cell Mol Med. 19:474–484. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Chandra-Kuntal K and Singh SV: Diallyl
trisulfide inhibits activation of signal transducer and activator
of transcription 3 in prostate cancer cells in culture and in vivo.
Cancer Prev Res. 3:1473–1483. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wu PP, Liu KC, Huang WW, Chueh FS, Ko YC,
Chiu TH, Lin JP, Kuo JH, Yang JS and Chung JG: Diallyl trisulfide
(DATS) inhibits mouse colon tumor in mouse CT-26 cells allograft
model in vivo. Phytomedicine. 18:672–676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li W, Tian H, Li L, Li S, Yue W, Chen Z,
Qi L, Hu W, Zhu Y, Hao B, et al: Diallyl trisulfide induces
apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of A549 cells in vitro and in
vivo. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 44:577–583. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim SH, Bommareddy A and Singh SV: Garlic
constituent diallyl trisulfide suppresses x-linked inhibitor of
apoptosis protein in prostate cancer cells in culture and in vivo.
Cancer Prev Res. 4:897–906. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Zhu P, Wang Y, Wei Z, Tao L, Zhu Z,
Sheng X, Wang S, Ruan J, Liu Z, et al: Antimetastatic therapies of
the polysulfide diallyl trisulfide against triple-negative breast
cancer (TNBC) via suppressing MMP2/9 by blocking NF-κB and ERK/MAPK
signaling pathways. PLoS One. 10:e01237812015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Shin DY, Cha HJ, Kim GY, Kim WJ and Choi
YH: Inhibiting invasion into human bladder carcinoma 5637 cells
with diallyl trisulfide by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase
activities and tightening tight junctions. Int J Mol Sci.
14:19911–19922. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chandra-Kuntal K, Lee J and Singh SV:
Critical role for reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induction
and cell migration inhibition by diallyl trisulfide, a cancer
chemopreventive component of garlic. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
138:69–79. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Choi YH and Park HS: Apoptosis induction
of U937 human leukemia cells by diallyl trisulfide induces through
generation of reactive oxygen species. J Biomed Sci. 19:502012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim YA, Xiao D, Xiao H, Powolny AA, Lew
KL, Reilly ML, Zeng Y, Wang Z and Singh SV: Mitochondria-mediated
apoptosis by diallyl trisulfide in human prostate cancer cells is
associated with generation of reactive oxygen species and regulated
by Bax/Bak. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:1599–1609. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shin DY, Kim GY, Hwang HJ, Kim WJ and Choi
YH: Diallyl trisulfide-induced apoptosis of bladder cancer cells is
caspase-dependent and regulated by PI3K/Akt and JNK pathways.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 37:74–83. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang YB, Qin J, Zheng XY, Bai Y, Yang K
and Xie LP: Diallyl trisulfide induces Bcl-2 and
caspase-3-dependent apoptosis via downregulation of Akt
phosphorylation in human T24 bladder cancer cells. Phytomedicine.
17:363–368. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhou W, Hao M, Du X, Chen K, Wang G and
Yang J: Advances in targeted therapy for osteosarcoma. Discov Med.
17:301–307. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang YK, Zhang XH, Li JM, Sun S, Yang Q
and Diao DM: A proteomic study on a human osteosarcoma cell line
Saos-2 treated with diallyl trisulfide. Anticancer Drugs.
20:702–712. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li J, Liu W, Zhao K, Zhang Y, Li X, Yang
Q, Li Z and Li J: Diallyl trisulfide reverses drug resistance and
lowers the ratio of CD133+ cells in conjunction with
methotrexate in a human osteosarcoma drug-resistant cell subline.
Mol Med Rep. 2:245–252. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Salvioli S, Ardizzoni A, Franceschi C and
Cossarizza A: JC-1, but not DiOC6 (3) or rhodamine 123,
is a reliable fluorescent probe to assess ΔΨ changes in intact
cells: Implications for studies on mitochondrial functionality
during apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 411:77–82. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou C, Mao XP, Guo Q and Zeng FQ: Diallyl
trisulphide-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells involves
downregulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL expression and activation of
caspases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 34:e537–e543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xu L, Yu J, Zhai D, Zhang D, Shen W, Bai
L, Cai Z and Yu C: Role of JNK activation and mitochondrial Bax
translocation in allicin-induced apoptosis in human ovarian cancer
SKOV3 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:3786842014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Antico Arciuch VG, Elguero ME, Poderoso JJ
and Carreras MC: Mitochondrial regulation of cell cycle and
proliferation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:1150–1180. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang L, Si M, Yin H and Li
J: Diallyl trisulfide inhibits proliferation, invasion and
angiogenesis of osteosarcoma cells by switching on suppressor
microRNAs and inactivating of Notch-1 signaling. Carcinogenesis.
34:1601–1610. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma HB, Huang S, Yin XR, Zhang Y and Di ZL:
Apoptotic pathway induced by diallyl trisulfide in pancreatic
cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 20:193–203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang HC, Yang JH, Hsieh SC and Sheen LY:
Allyl sulfides inhibit cell growth of skin cancer cells through
induction of DNA damage mediated G2/M arrest and apoptosis. J Agric
Food Chem. 58:7096–7103. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xiao D, Zeng Y, Hahm ER, Kim YA,
Ramalingam S and Singh SV: Diallyl trisulfide selectively causes
Bax- and Bak-mediated apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Environ
Mol Mutagen. 50:201–212. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Kyomoto R, Kumazawa H, Toda Y, Sakaida N,
Okamura A, Iwanaga M, Shintaku M, Yamashita T, Hiai H and Fukumoto
M: Cyclin-D1-gene amplification is a more potent prognostic factor
than its protein overexpression in human head-and-neck
squamous-cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 74:576–581. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Karimian H, Moghadamtousi SZ, Fadaeinasab
M, Golbabapour S, Razavi M, Hajrezaie M, Arya A, Abdulla MA, Mohan
S, Ali HM, et al: Ferulago angulata activates intrinsic pathway of
apoptosis in MCF-7 cells associated with G1 cell cycle
arrest via involvement of p21/p27. Drug Des Devel Ther.
8:1481–1497. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Park HS, Han MH, Kim GY, Moon SK, Kim WJ,
Hwang HJ, Park KY and Choi YH: Sulforaphane induces reactive oxygen
species-mediated mitotic arrest and subsequent apoptosis in human
bladder cancer 5637 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 64:157–165. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jeong JB, Choi J, Baek SJ and Lee SH:
Reactive oxygen species mediate tolfenamic acid-induced apoptosis
in human colorectal cancer cells. Arch Biochem Biophys.
537:168–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rasul A, Di J, Millimouno FM, Malhi M,
Tsuji I, Ali M, Li J and Li X: Reactive oxygen species mediate
isoalantolactone-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells.
Molecules. 18:9382–9396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Na HK, Kim EH, Choi MA, Park JM, Kim DH
and Surh YJ: Diallyl trisulfide induces apoptosis in human breast
cancer cells through ROS-mediated activation of JNK and AP-1.
Biochem Pharmacol. 84:1241–1250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee BC, Park BH, Kim SY and Lee YJ: Role
of Bim in diallyl trisulfide-induced cytotoxicity in human cancer
cells. J Cell Biochem. 112:118–127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang J, Yu XH, Yan YG, Wang C and Wang
WJ: PI3K/Akt signaling in osteosarcoma. Clin Chim Acta.
444:182–192. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hahne JC, Honig A, Meyer SR, Gambaryan S,
Walter U, Wischhusen J, Häussler SF, Segerer SE, Fujita N, Dietl J,
et al: Downregulation of AKT reverses platinum resistance of human
ovarian cancers in vitro. Oncol Rep. 28:2023–2028. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Peng SF, Lee CY, Hour MJ, Tsai SC, Kuo DH,
Chen FA, Shieh PC and Yang JS: Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles
enhance apoptotic cell death of U2OS human osteosarcoma cells
through the Akt-Bad signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 44:238–246.
2014.
|