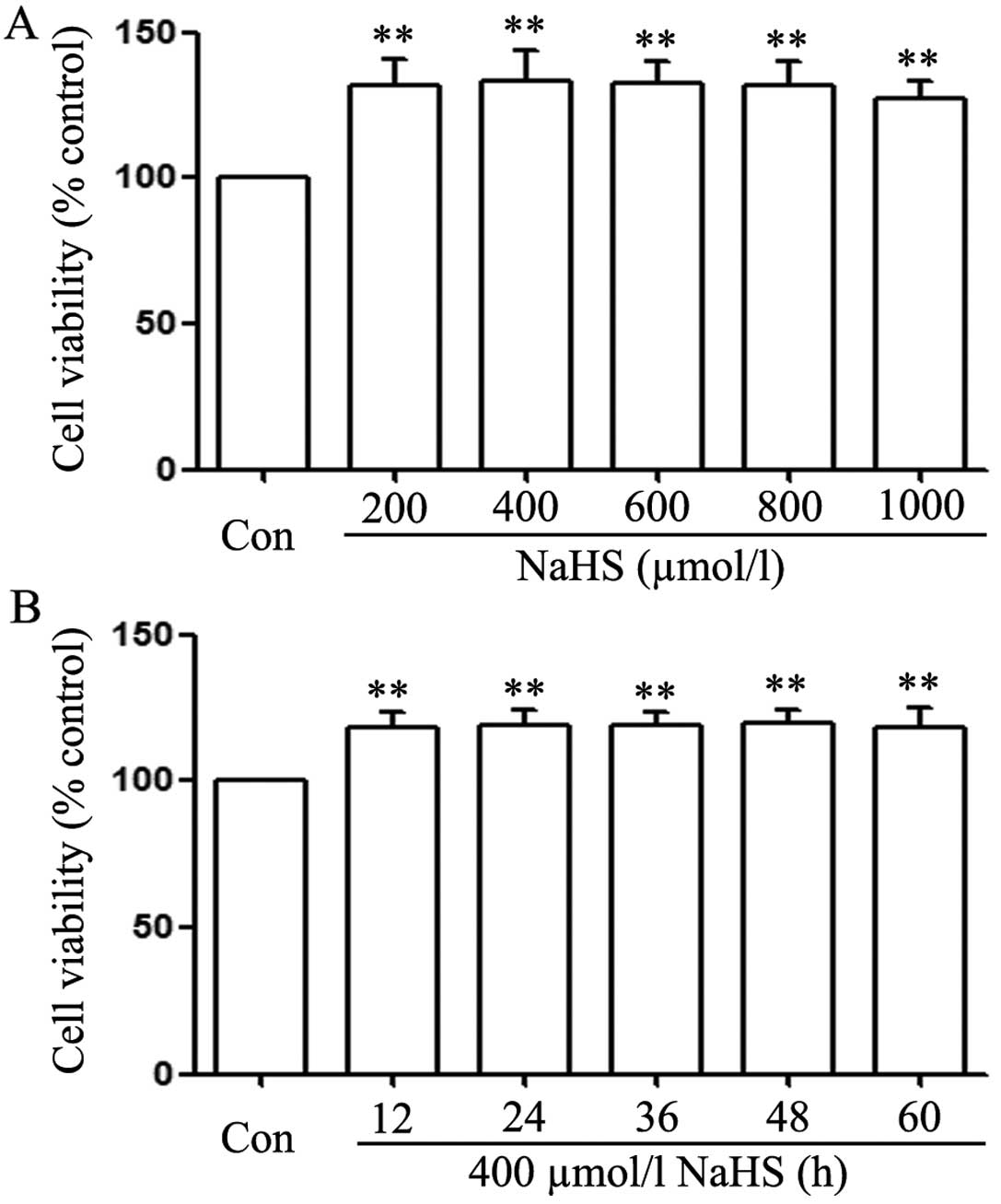
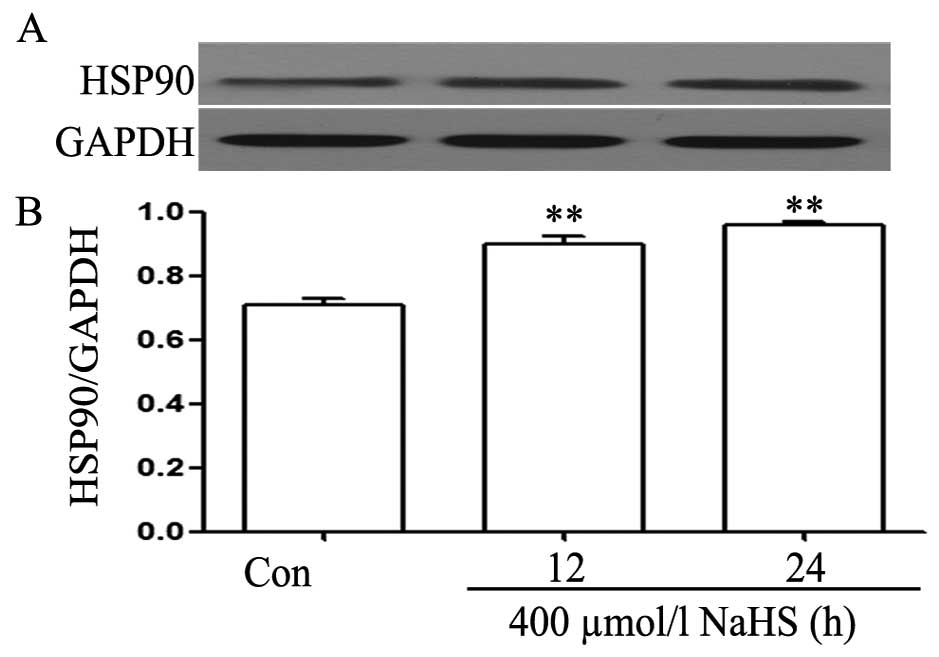
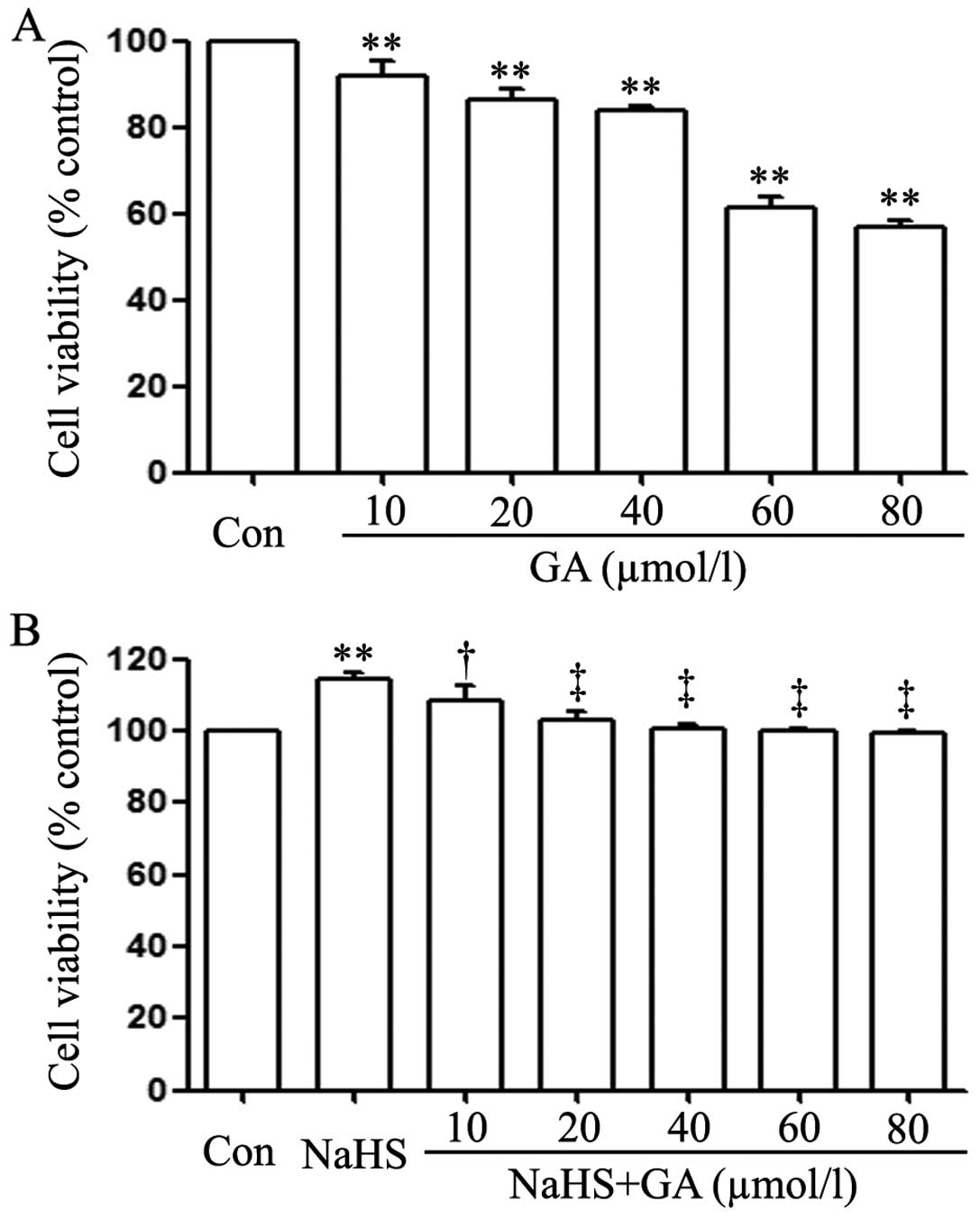
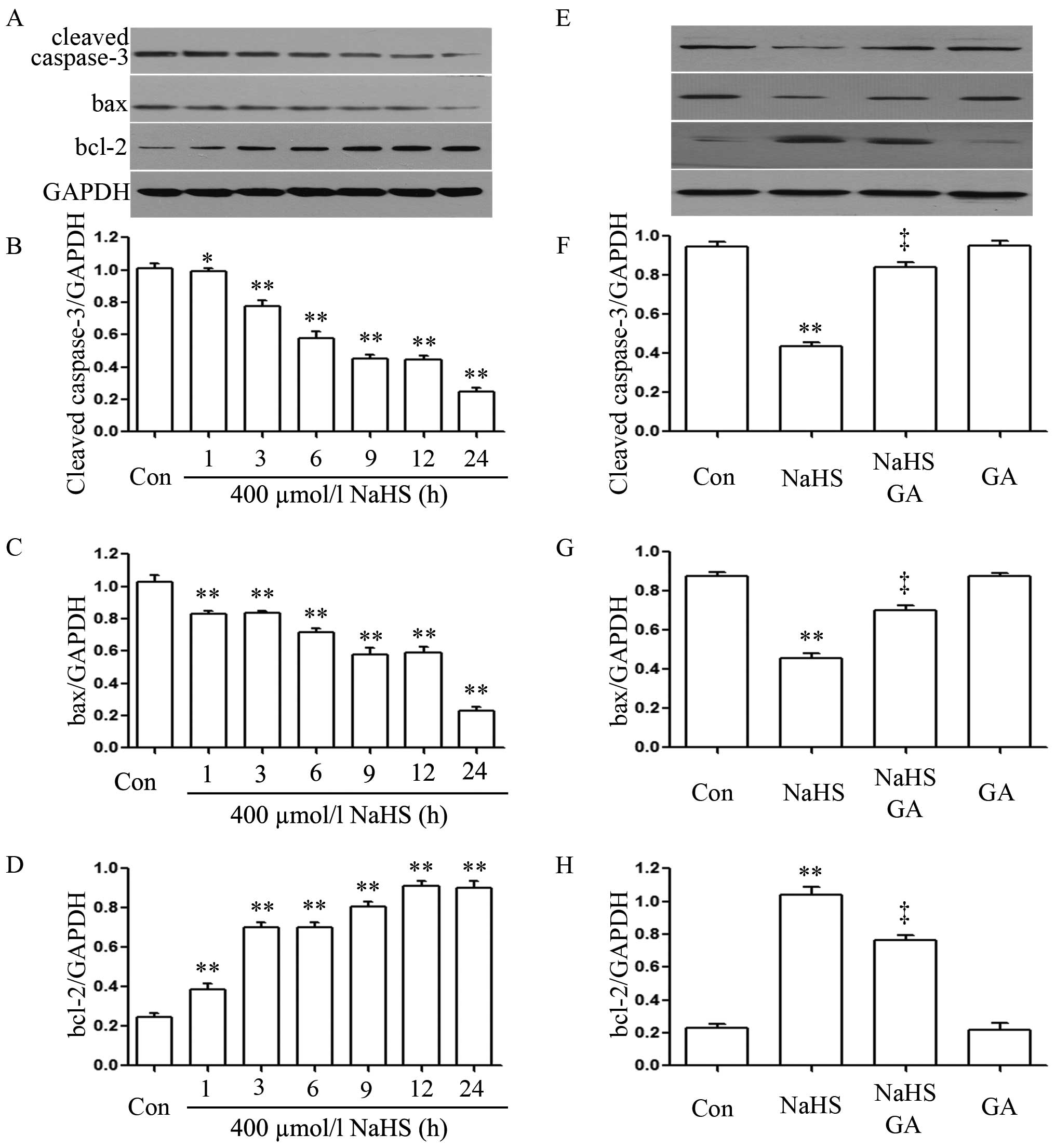
|
1
|
Kamangar F, Dores GM and Anderson WF:
Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five
continents: Defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in
different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol.
24:2137–2150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wheeler JB and Reed CE: Epidemiology of
esophageal cancer. Surg Clin North Am. 92:1077–1087. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hongo M, Nagasaki Y and Shoji T:
Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: Orient to Occident. Effects of
chronology, geography and ethnicity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
24:729–735. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kaneko K, Kumekawa Y, Makino R, Nozawa H,
Hirayama Y, Kogo M, Konishi K, Katagiri A, Kubota Y, Muramoto T, et
al: EGFR gene alterations as a prognostic biomarker in advanced
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Front Biosci. 15:65–72. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Delektorskaya VV, Chemeris GY, Zavalishina
LE, Ryazantseva AA, Grigorchuk AY, Kononets PV and Davydov MI:
Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: Evaluation of the status
of epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR and HER-2) by
immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. Bull Exp Biol Med.
149:615–620. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Berg D, Wolff C, Langer R, Schuster T,
Feith M, Slotta-Huspenina J, Malinowsky K and Becker KF: Discovery
of new molecular subtypes in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. PLoS One.
6:e239852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Langer R, Ott K, Specht K, Becker K,
Lordick F, Burian M, Herrmann K, Schrattenholz A, Cahill MA,
Schwaiger M, et al: Protein expression profiling in esophageal
adenocarcinoma patients indicates association of heat-shock protein
27 expression and chemotherapy response. Clin Cancer Res.
14:8279–8287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Morimoto RI: Cells in stress:
Transcriptional activation of heat shock genes. Science.
259:1409–1410. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Beere HM: 'The stress of dying': The role
of heat shock proteins in the regulation of apoptosis. J Cell Sci.
117:2641–2651. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mehta TA, Greenman J, Ettelaie C,
Venkatasubramaniam A, Chetter IC and McCollum PT: Heat shock
proteins in vascular disease - a review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg.
29:395–402. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cohen SM, Mukerji R, Samadi AK, Zhang X,
Zhao H, Blagg BS and Cohen MS: Novel C-terminal Hsp90 inhibitor for
head and neck squamous cell cancer (HNSCC) with in vivo efficacy
and improved toxicity profiles compared with standard agents. Ann
Surg Oncol. 19(Suppl 3): S483–S490. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Drecoll E, Nitsche U, Bauer K, Berezowska
S, Slotta-Huspenina J, Rosenberg R and Langer R: Expression
analysis of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) and Her2 in colon
carcinoma. Int J Colorectal Dis. 29:663–671. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jego G, Hazoumé A, Seigneuric R and
Garrido C: Targeting heat shock proteins in cancer. Cancer Lett.
332:275–285. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lu X, Xiao L, Wang L and Ruden DM: Hsp90
inhibitors and drug resistance in cancer: The potential benefits of
combination therapies of Hsp90 inhibitors and other anti-cancer
drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 83:995–1004. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Den RB and Lu B: Heat shock protein 90
inhibition: Rationale and clinical potential. Ther Adv Med Oncol.
4:211–218. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chehab M, Caza T, Skotnicki K, Landas S,
Bratslavsky G, Mollapour M and Bourboulia D: Targeting Hsp90 in
urothelial carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:8454–8473. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang R: Two's company, three's a crowd:
Can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter?
FASEB J. 16:1792–1798. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kilburn KH, Thrasher JD and Gray MR:
Low-level hydrogen sulfide and central nervous system dysfunction.
Toxicol Ind Health. 26:387–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guidotti TL: Hydrogen sulfide: Advances in
understanding human toxicity. Int J Toxicol. 29:569–581. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Han YF, Huang X, Guo X, Wu YS, Liu DH, Lu
HL, Kim YC and Xu WX: Evidence that endogenous hydrogen sulfide
exerts an excitatory effect on gastric motility in mice. Eur J
Pharmacol. 673:85–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schicho R, Krueger D, Zeller F, Von
Weyhern CW, Frieling T, Kimura H, Ishii I, De Giorgio R, Campi B
and Schemann M: Hydrogen sulfide is a novel prosecretory
neuromodulator in the Guinea-pig and human colon. Gastroenterology.
131:1542–1552. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cai WJ, Wang MJ, Ju LH, Wang C and Zhu YC:
Hydrogen sulfide induces human colon cancer cell proliferation:
Role of Akt, ERK and p21. Cell Biol Int. 34:565–572. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cao Q, Zhang L, Yang G, Xu C and Wang R:
Butyrate-stimulated H2S production in colon cancer
cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 12:1101–1109. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Du SX, Xiao J, Guan F, Sun LM, Wu WS, Tang
H, Du JB, Tang CS and Jin HF: Predictive role of cerebrospinal
fluid hydrogen sulfide in central nervous system leukemia. Chin Med
J. 124:3450–3454. 2011.
|
|
26
|
Levine J, Ellis CJ, Furne JK, Springfield
J and Levitt MD: Fecal hydrogen sulfide production in ulcerative
colitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 93:83–87. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pupo E, Pla AF, Avanzato D, Moccia F, Cruz
JE, Tanzi F, Merlino A, Mancardi D and Munaron L: Hydrogen sulfide
promotes calcium signals and migration in tumor-derived endothelial
cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1765–1773. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rose P, Moore PK, Ming SH, Nam OC,
Armstrong JS and Whiteman M: Hydrogen sulfide protects colon cancer
cells from chemopreventative agent beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate
induced apoptosis. World J Gastroenterol. 11:3990–3997. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Szabo C, Coletta C, Chao C, Módis K,
Szczesny B, Papapetropoulos A and Hellmich MR: Tumor-derived
hydrogen sulfide, produced by cystathionine-β-synthase, stimulates
bioenergetics, cell proliferation, and angiogenesis in colon
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:12474–12479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhen Y, Pan W, Hu F, Wu H, Feng J, Zhang Y
and Chen J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide exerts
proliferation/anti-apoptosis/angiogenesis/migration effects via
amplifying the activation of NF-κB pathway in PLC/PRF/5 hepatoma
cells. Int J Oncol. 46:2194–2204. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhen Y, Zhang W, Liu C, He J, Lu Y, Guo R,
Feng J, Zhang Y and Chen J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide promotes C6
glioma cell growth through activation of the p38 MAPK/ERK1/2-COX-2
pathways. Oncol Rep. 34:2413–2422. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tan BH, Wong PT and Bian JS: Hydrogen
sulfide: A novel signaling molecule in the central nervous system.
Neurochem Int. 56:3–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang X and Bian JS: Hydrogen sulfide: A
neuromodulator and neuroprotectant in the central nervous system.
ACS Chem Neurosci. 5:876–883. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang JM, Zhou CF, Gao SL, Tian Y, Wang
CY, Wang L, Gu HF and Tang XQ: BDNF-TrkB pathway mediates
neuroprotection of hydrogen sulfide against formaldehyde-induced
toxicity to PC12 cells. PLoS One. 10:e01194782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kashfi K: Anti-cancer activity of new
designer hydrogen sulfide-donating hybrids. Antioxid Redox Signal.
20:831–846. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Ma K, Liu Y, Zhu Q, Liu CH, Duan JL, Tan
BK and Zhu YZ: H2S donor, S-propargyl-cysteine,
increases CSE in SGC-7901 and cancer-induced mice: Evidence for a
novel anti-cancer effect of endogenous H2S? PLoS One.
6:e205252011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bir SC, Kolluru GK, McCarthy P, Shen X,
Pardue S, Pattillo CB and Kevil CG: Hydrogen sulfide stimulates
ischemic vascular remodeling through nitric oxide synthase and
nitrite reduction activity regulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
and vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent angiogenesis. J Am
Heart Assoc. 1:e0040932012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Holwerda KM, Burke SD, Faas MM, Zsengeller
Z, Stillman IE, Kang PM, van Goor H, McCurley A, Jaffe IZ,
Karumanchi SA, et al: Hydrogen sulfide attenuates sFlt1-induced
hypertension and renal damage by upregulating vascular endothelial
growth factor. J Am Soc Nephrol. 25:717–725. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Köhn C, Dubrovska G, Huang Y and Gollasch
M: Hydrogen sulfide: Potent regulator of vascular tone and
stimulator of angiogenesis. Int J Biomed Sci. 8:81–86. 2012.
|
|
40
|
Polhemus DJ, Kondo K, Bhushan S, Bir SC,
Kevil CG, Murohara T, Lefer DJ and Calvert JW: Hydrogen sulfide
attenuates cardiac dysfunction after heart failure via induction of
angiogenesis. Circ Heart Fail. 6:1077–1086. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tao BB, Liu SY, Zhang CC, Fu W, Cai WJ,
Wang Y, Shen Q, Wang MJ, Chen Y, Zhang LJ, et al: VEGFR2 functions
as an H2S-targeting receptor protein kinase with its
novel Cys1045-Cys1024 disulfide bond serving as a specific
molecular switch for hydrogen sulfide actions in vascular
endothelial cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 19:448–464. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Leung WK, To KF, Go MY, Chan KK, Chan FK,
Ng EK, Chung SC and Sung JJ: Cyclooxygenase-2 upregulates vascular
endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis in human
gastric carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 23:1317–1322. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jones JL, Shaw JA, Pringle JH and Walker
RA: Primary breast myoepithelial cells exert an invasion-suppressor
effect on breast cancer cells via paracrine down-regulation of MMP
expression in fibroblasts and tumour cells. J Pathol. 201:562–572.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li C, Li F, Zhao K, Yao J, Cheng Y, Zhao
L, Li Z, Lu N and Guo Q: LFG-500 inhibits the invasion of cancer
cells via downregulation of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway. PLoS
One. 9:e913322014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Puzovic V, Brcic I, Ranogajec I and
Jakic-Razumovic J: Prognostic values of ETS-1, MMP-2 and MMP-9
expression and co-expression in breast cancer patients. Neoplasma.
61:439–446. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ruan M, Zhang Z, Li S, Yan M, Liu S, Yang
W, Wang L and Zhang C: Activation of Toll-like receptor-9 promotes
cellular migration via up-regulating MMP-2 expression in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e927482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|