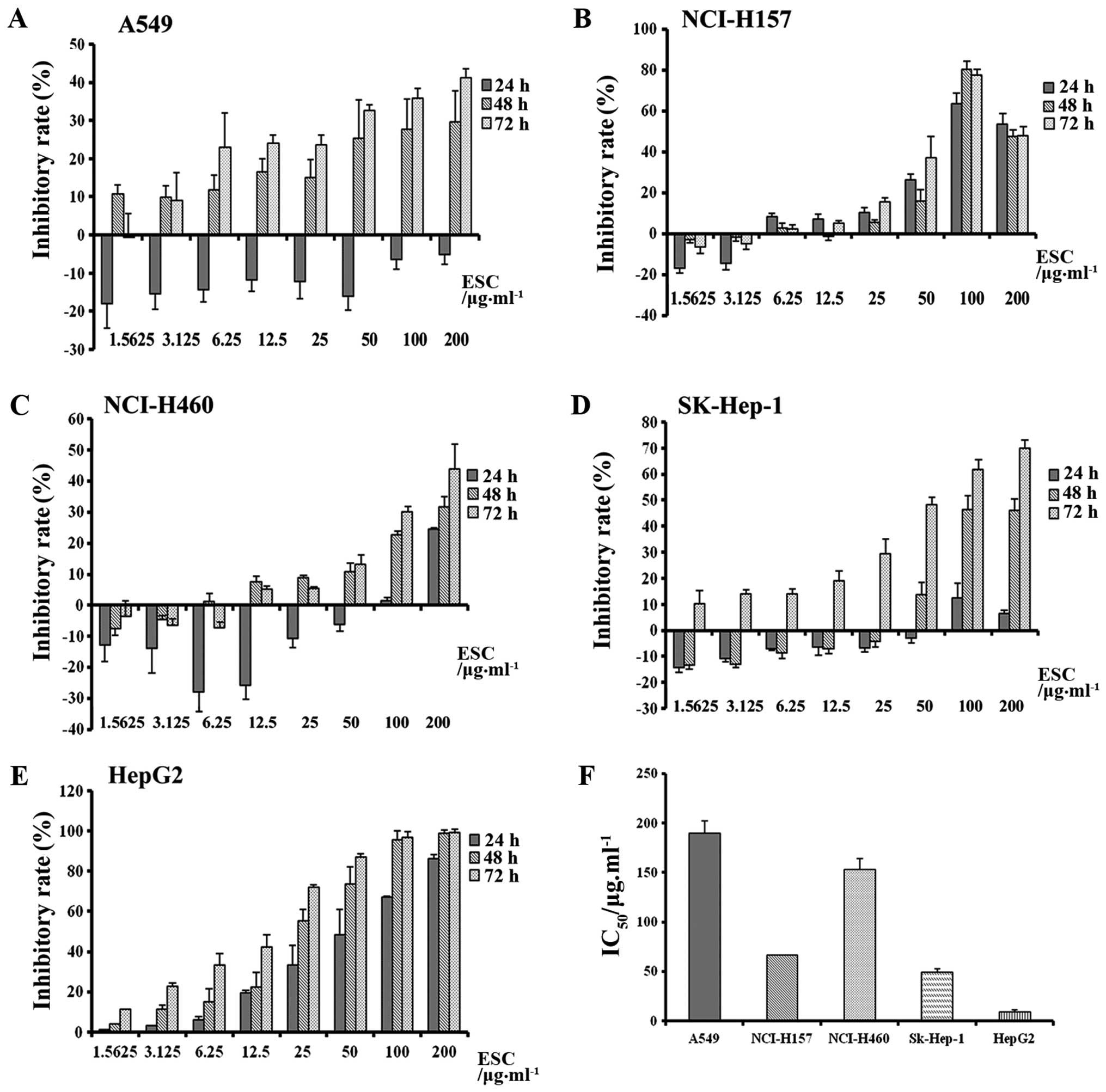
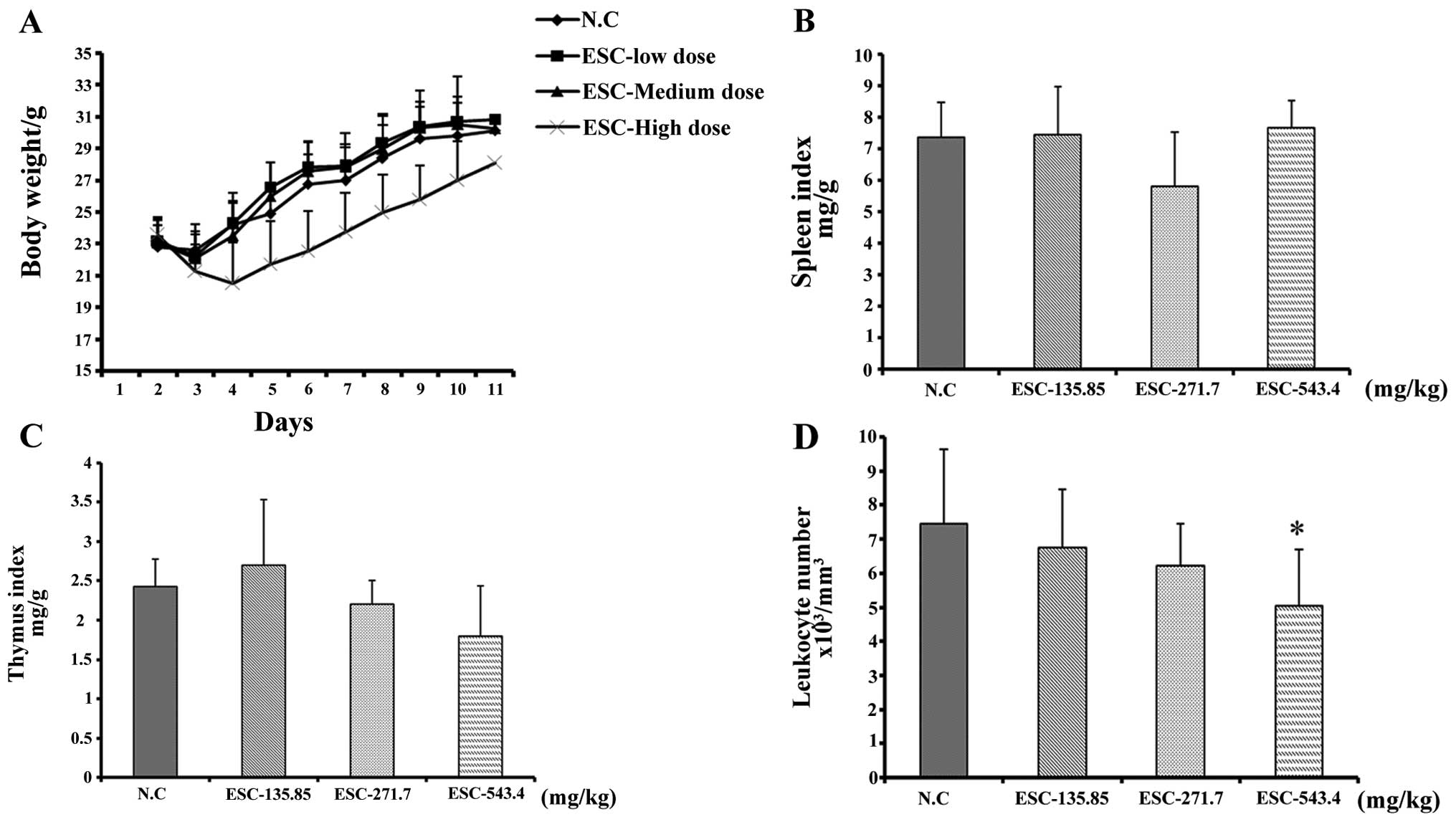
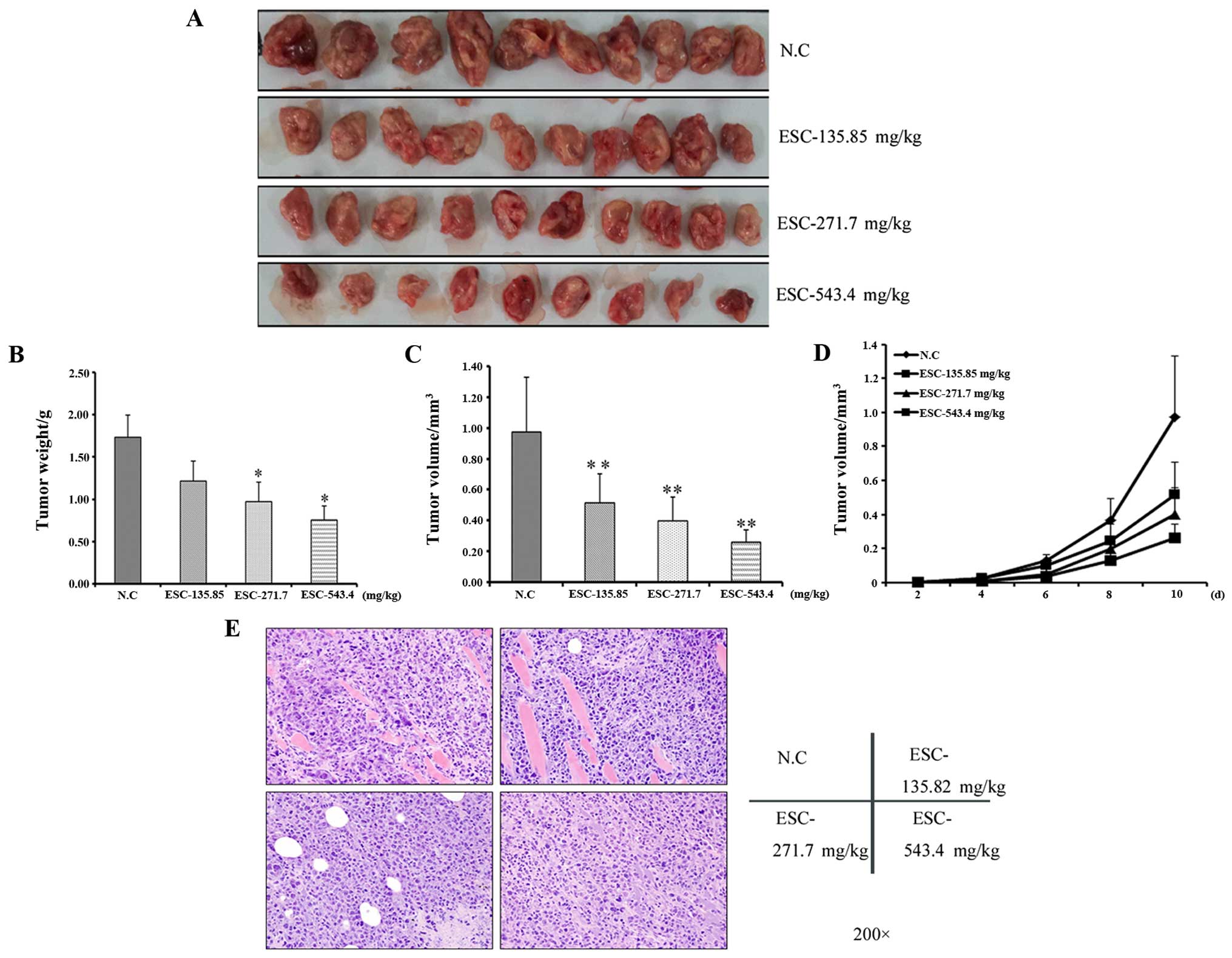
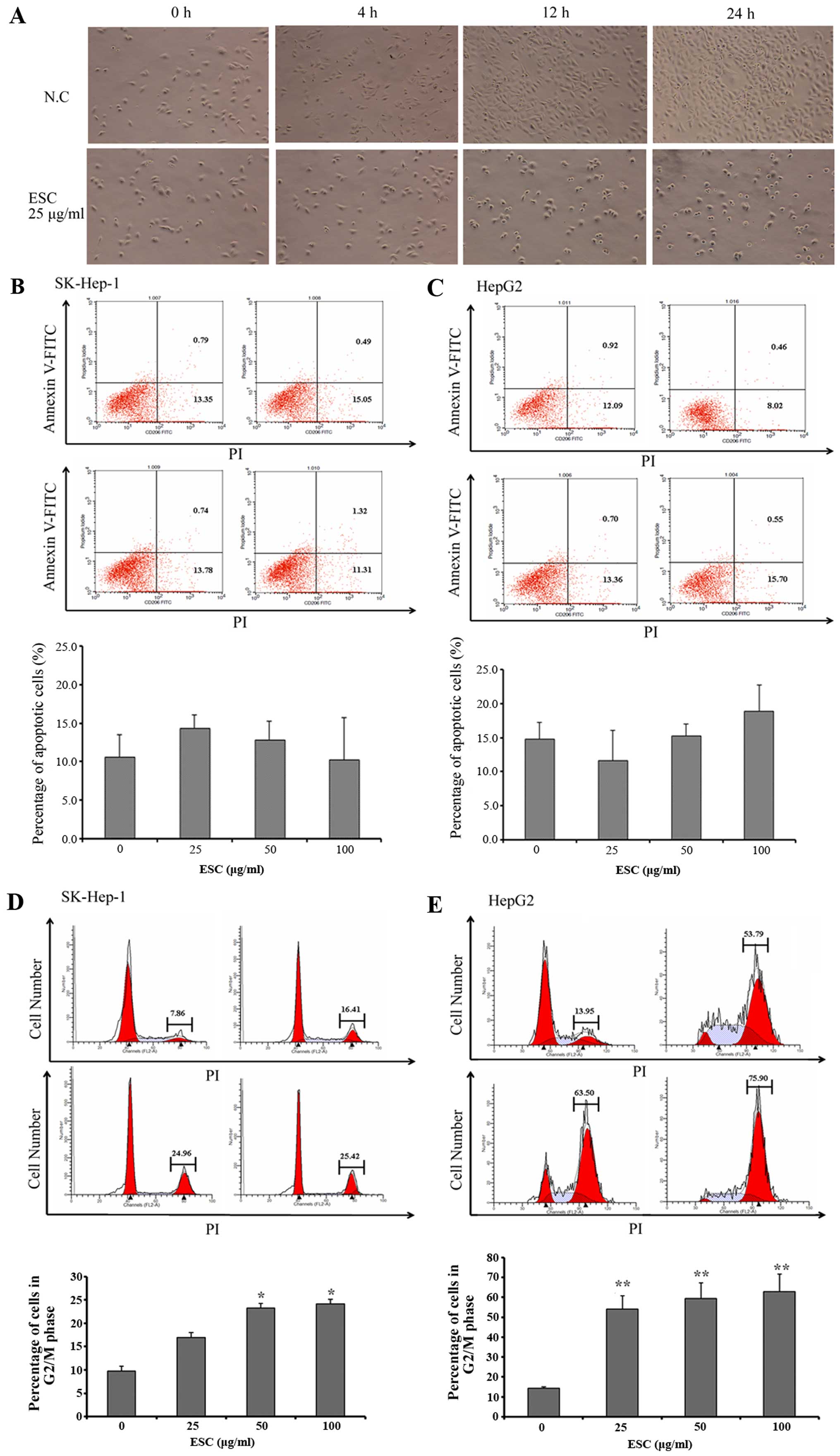
|
1
|
Wu F, Lin GZ and Zhang JX: An overview of
cancer incidence and trend in China. China Cancer. 81–85. 2012.
|
|
2
|
Rabindran SK, Ross DD, Doyle LA, Yang W
and Greenberger LM: Fumitremorgin C reverses multidrug resistance
in cells transfected with the breast cancer resistance protein.
Cancer Res. 60:47–50. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Florea AM and Büsselberg D: Cisplatin as
an anti-tumor drug: Cellular mechanisms of activity, drug
resistance and induced side effects. Cancers (Basel). 3:1351–1371.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer.
94:153–156. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li J and Luo R: Advances of
biochemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Mol Diagnostics
Therapy. 1:602009.
|
|
7
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hasegawa K, Kokudo N and Makuuchi M:
Surgical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver resection
and liver transplantation. Saudi Med J. 28:1171–1179.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Poon RT, Fan ST, Tsang FH and Wong J:
Locoregional therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: A critical
review from the surgeon's perspective. Ann Surg. 235:466–486. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thomas MB and Zhu AX: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: The need for progress. J Clin Oncol. 23:2892–2899. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dizon DS and Kemeny NE: Intrahepatic
arterial infusion of chemotherapy: Clinical results. Semin Oncol.
29:126–135. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Harvey AL: Natural products in drug
discovery. Drug Discov Today. 13:894–901. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi GL, Liu SQ, Cao H, Zhao LL, Li J and
Li SY: Acaricidal activities of extracts of Stellera chamaejasme
against Tetranychus viennensis (Acari: Tetranychidae). J Econ
Entomol. 97:1912–1916. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang BY: Inhibitory effects of Stellera
chamaejasme on the growth of a transplantable tumor in mice. Zhong
Yao Tong Bao. 11:58–59. 1986.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yoshida M, Feng W, Saijo N and Ikekawa T:
Antitumor activity of daphnane-type diterpene gnidimacrin isolated
from Stellera chamaejasme L. Int J Cancer. 66:268–273. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang G, Liao Z, Xu Z, Zhang H and Chen D:
Antimitotic and antifungal C-3/C-3″-biflavanones from Stellera
chamaejasme. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 53:776–779. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yang G and Chen D: Biflavanones,
flavonoids, and coumarins from the roots of Stellera chamaejasme
and their antiviral effect on hepatitis B virus. Chem Biodivers.
5:1419–1424. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Naito S, von Eschenbach AC, Giavazzi R and
Fidler IJ: Growth and metastasis of tumor cells isolated from a
human renal cell carcinoma implanted into different organs of nude
mice. Cancer Res. 46:4109–4115. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wittekind C: The new WHO classification of
liver tumors - what is really new? Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol.
85:212–218. 2001.In German.
|
|
20
|
Pozarowski P and Darzynkiewicz Z: Analysis
of cell cycle by flow cytometry. Methods Mol Biol. 281:301–311.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Novotny-Diermayr V, Sangthongpitag K, Hu
CY, et al: SB939, a novel potent and orally active histone
deacetylase inhibitor with high tumor exposure and efficacy in
mouse models of colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:642–652.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yim HJ, Suh SJ and Um SH: Current
management of hepatocellular carcinoma: An Eastern perspective.
World J Gastroenterol. 21:3826–3842. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Okuda K, Ohtsuki T, Obata H, Tomimatsu M,
Okazaki N, Hasegawa H, Nakajima Y and Ohnishi K: Natural history of
hepatocellular carcinoma and prognosis in relation to treatment.
Study of 850 patients. Cancer. 56:918–928. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nagasue N, Yukaya H, Hamada T, Hirose S,
Kanashima R and Inokuchi K: The natural history of hepatocellular
carcinoma. A study of 100 untreated cases. Cancer. 54:1461–1465.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park SH, Lee Y, Han SH, Kwon SY, Kwon OS,
Kim SS, Kim JH, Park YH, Lee JN, Bang SM, et al: Systemic
chemotherapy with doxorubicin, cisplatin and capecitabine for
metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 6:32006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boucher E, Corbinais S, Brissot P,
Boudjema K and Raoul JL: Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
(HCC) with systemic chemotherapy combining epirubicin, cisplatinum
and infusional 5-fluorouracil (ECF regimen). Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 50:305–308. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pohl J, Zuna I, Stremmel W and Rudi J:
Systemic chemotherapy with epirubicin for treatment of advanced or
multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma. Chemotherapy. 47:359–365.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Feun LG, O'Brien C, Molina E, Rodriguez M,
Jeffers L, Schiff ER, Marini A, Savaraj N and Ardalan B:
Recombinant leukocyte interferon, doxorubicin, and 5FUDR in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma-A phase II trial. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 129:17–20. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alexandre J, Tigaud JM, Gross-Goupil M,
Gornet JM, Romain D, Azoulay D, Misset JL and Goldwasser F:
Combination of topotecan and oxaliplatin in inoperable
hepatocellular cancer patients. Am J Clin Oncol. 25:198–203. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hsu JL, Chiang PC and Guh JH: Tunicamycin
induces resistance to camptothecin and etoposide in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells: Role of cell-cycle arrest and
GRP78. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 380:373–382. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ueda H, Fukuchi H and Tanaka C: Toxicity
and efficacy of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Oncol Lett. 3:259–263.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Basile A, Carrafiello G, Ierardi AM,
Tsetis D and Brountzos E: Quality-improvement guidelines for
hepatic transarterial chemoembolization. Cardiovasc Intervent
Radiol. 35:765–774. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gerunda GE, Neri D, Merenda R, Barbazza F,
Zangrandi F, Meduri F, Bisello M, Valmasoni M, Gangemi A and
Faccioli AM: Role of transarterial chemoembolization before liver
resection for hepatocarcinoma. Liver Transpl. 6:619–626. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Y, Ji P, Liu J, Broaddus RR, Xue F
and Zhang W: Centrosome-associated regulators of the G(2)/M
checkpoint as targets for cancer therapy. Mol Cancer. 8:82009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|