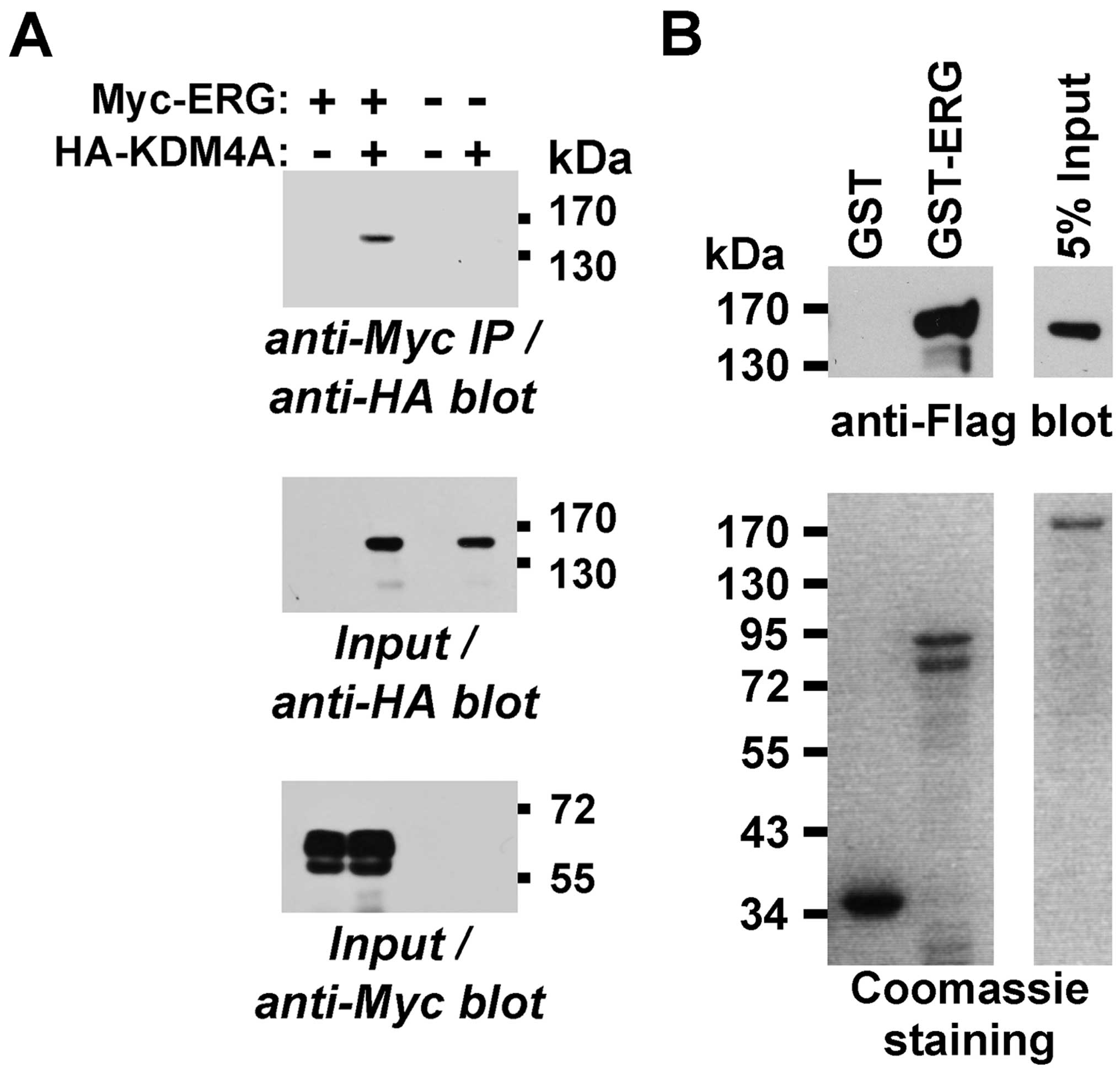
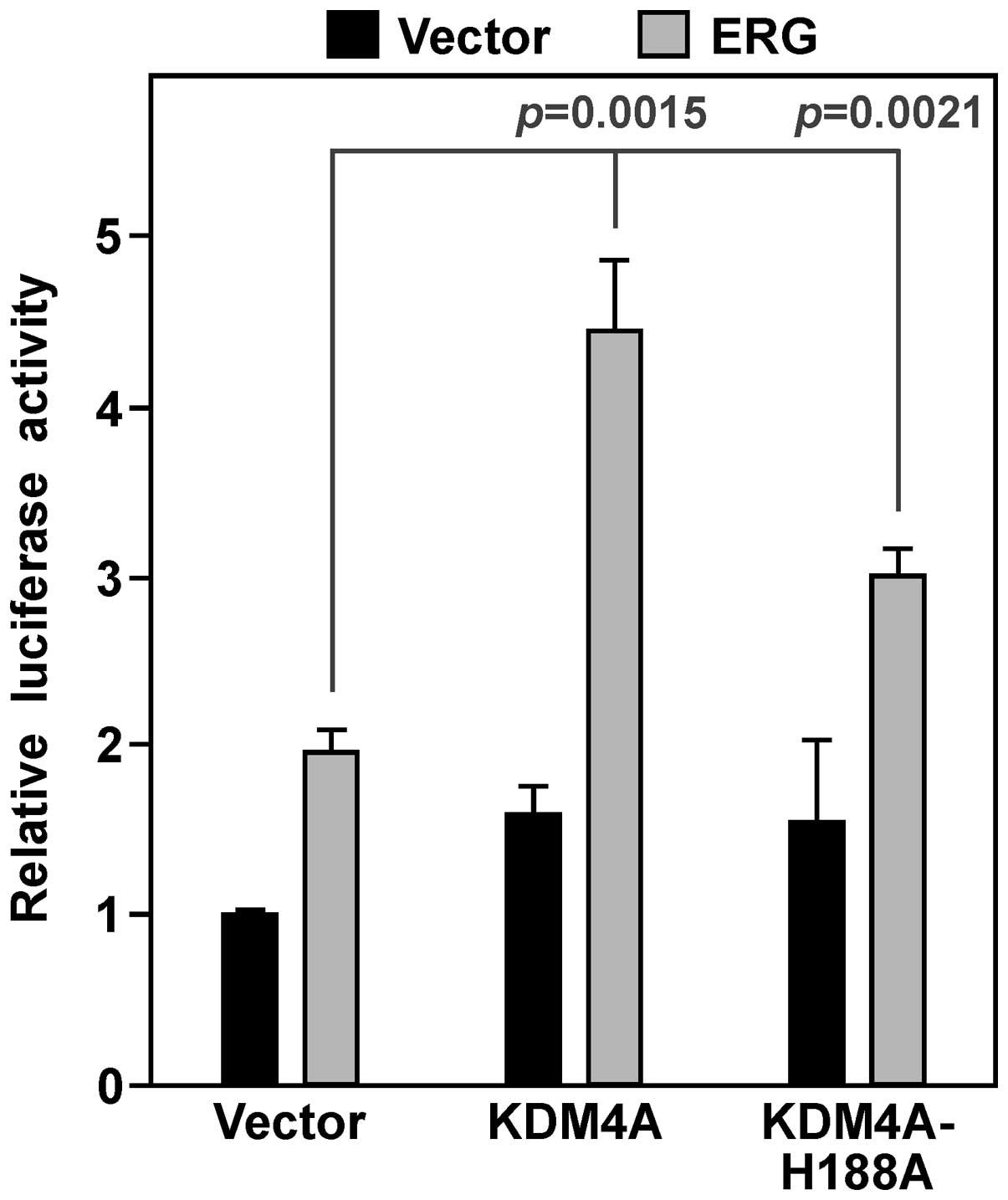
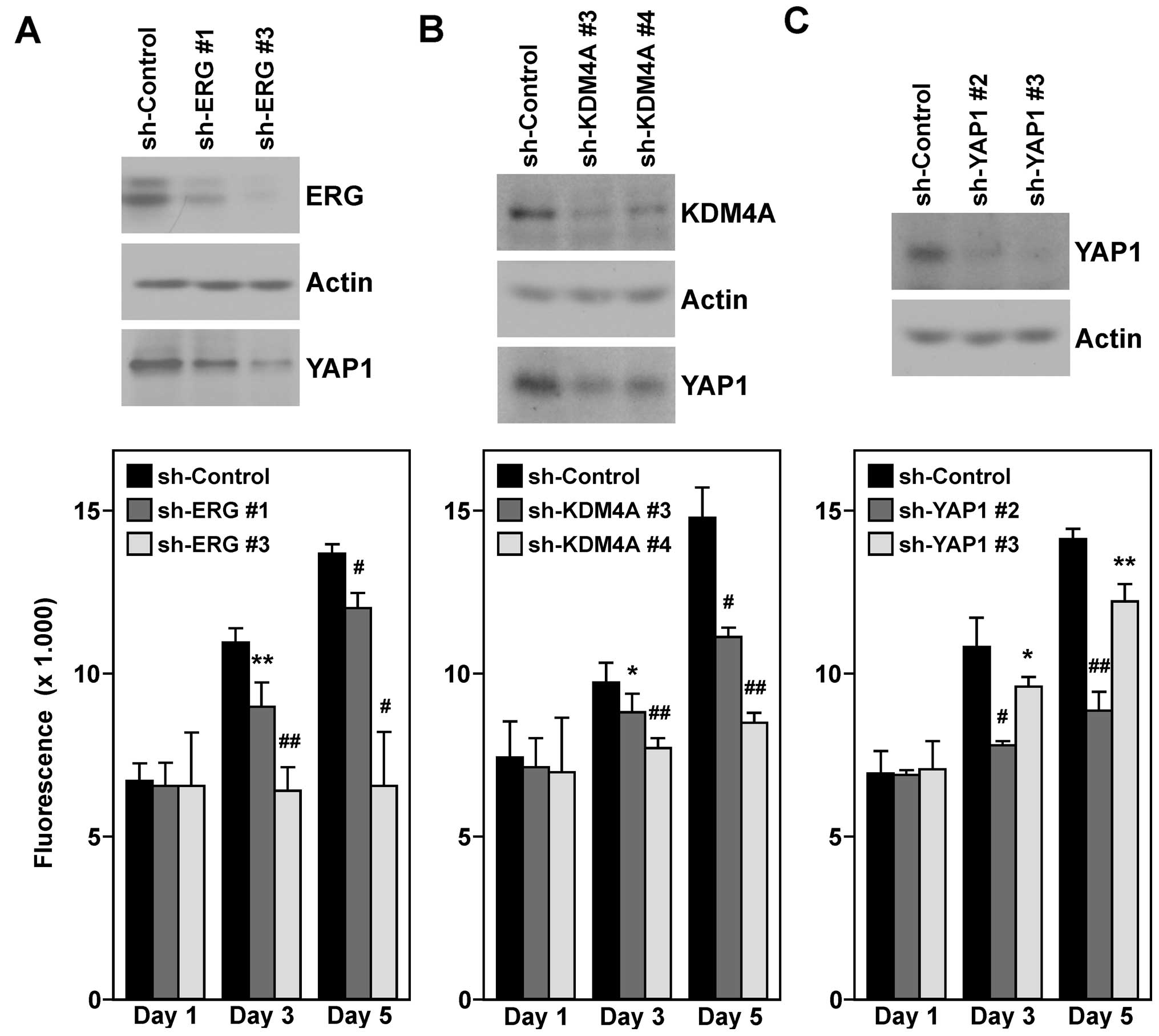
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ryan CJ and Tindall DJ: Androgen receptor
rediscovered: The new biology and targeting the androgen receptor
therapeutically. J Clin Oncol. 29:3651–3658. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S,
Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun XW, Varambally S, Cao X, Tchinda J,
Kuefer R, et al: Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription
factor genes in prostate cancer. Science. 310:644–648. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clark JP and Cooper CS: ETS gene fusions
in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 6:429–439. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Klezovitch O, Risk M, Coleman I, Lucas JM,
Null M, True LD, Nelson PS and Vasioukhin V: A causal role for ERG
in neoplastic transformation of prostate epithelium. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:2105–2110. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tomlins SA, Laxman B, Varambally S, Cao X,
Yu J, Helgeson BE, Cao Q, Prensner JR, Rubin MA, Shah RB, et al:
Role of the TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion in prostate cancer. Neoplasia.
10:177–188. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nguyen LT, Tretiakova MS, Silvis MR, Lucas
J, Klezovitch O, Coleman I, Bolouri H, Kutyavin VI, Morrissey C,
True LD, et al: ERG activates the YAP1 transcriptional program and
induces the development of age-related prostate tumors. Cancer
Cell. 27:797–808. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carver BS, Tran J, Gopalan A, Chen Z,
Shaikh S, Carracedo A, Alimonti A, Nardella C, Varmeh S, Scardino
PT, et al: Aberrant ERG expression cooperates with loss of PTEN to
promote cancer progression in the prostate. Nat Genet. 41:619–624.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
King JC, Xu J, Wongvipat J, Hieronymus H,
Carver BS, Leung DH, Taylor BS, Sander C, Cardiff RD, Couto SS, et
al: Cooperativity of TMPRSS2-ERG with PI3-kinase pathway activation
in prostate oncogenesis. Nat Genet. 41:524–526. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baena E, Shao Z, Linn DE, Glass K, Hamblen
MJ, Fujiwara Y, Kim J, Nguyen M, Zhang X, Godinho FJ, et al: ETV1
directs androgen metabolism and confers aggressive prostate cancer
in targeted mice and patients. Genes Dev. 27:683–698. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen Y, Chi P, Rockowitz S, Iaquinta PJ,
Shamu T, Shukla S, Gao D, Sirota I, Carver BS, Wongvipat J, et al:
ETS factors reprogram the androgen receptor cistrome and prime
prostate tumorigenesis in response to PTEN loss. Nat Med.
19:1023–1029. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Harvey KF, Zhang X and Thomas DM: The
Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:246–257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Varelas X: The Hippo pathway effectors TAZ
and YAP in development, homeostasis and disease. Development.
141:1614–1626. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dowdy SC, Mariani A and Janknecht R:
HER2/Neu- and TAK1-mediated up-regulation of the transforming
growth factor beta inhibitor Smad7 via the ETS protein ER81. J Biol
Chem. 278:44377–44384. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mooney SM, Grande JP, Salisbury JL and
Janknecht R: Sumoylation of p68 and p72 RNA helicases affects
protein stability and transactivation potential. Biochemistry.
49:1–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Oh S, Shin S, Lightfoot SA and Janknecht
R: 14-3-3 proteins modulate the ETS transcription factor ETV1 in
prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 73:5110–5119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu J and Janknecht R: Regulation of the
ETS transcription factor ER81 by the 90-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase 1
and protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. 277:42669–42679. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Papoutsopoulou S and Janknecht R:
Phosphorylation of ETS transcription factor ER81 in a complex with
its coactivators CREB-binding protein and p300. Mol Cell Biol.
20:7300–7310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De Haro L and Janknecht R: Cloning of the
murine ER71 gene (Etsrp71) and initial characterization of its
promoter. Genomics. 85:493–502. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
DiTacchio L, Bowles J, Shin S, Lim DS,
Koopman P and Janknecht R: Transcription factors ER71/ETV2 and SOX9
participate in a positive feedback loop in fetal and adult mouse
testis. J Biol Chem. 287:23657–23666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
De Haro L and Janknecht R: Functional
analysis of the transcription factor ER71 and its activation of the
matrix metal-loproteinase-1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res.
30:2972–2979. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mooney SM, Goel A, D'Assoro AB, Salisbury
JL and Janknecht R: Pleiotropic effects of p300-mediated
acetylation on p68 and p72 RNA helicase. J Biol Chem.
285:30443–30452. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Knebel J, De Haro L and Janknecht R:
Repression of transcription by TSGA/Jmjd1a, a novel interaction
partner of the ETS protein ER71. J Cell Biochem. 99:319–329. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shin S and Janknecht R: Concerted
activation of the Mdm2 promoter by p72 RNA helicase and the
coactivators p300 and P/CAF. J Cell Biochem. 101:1252–1265. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goel A and Janknecht R:
Acetylation-mediated transcriptional activation of the ETS protein
ER81 by p300, P/CAF, and HER2/Neu. Mol Cell Biol. 23:6243–6254.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Goel A and Janknecht R: Concerted
activation of ETS protein ER81 by p160 coactivators, the
acetyltransferase p300 and the receptor tyrosine kinase HER2/Neu. J
Biol Chem. 279:14909–14916. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Berry WL, Kim TD and Janknecht R:
Stimulation of β-catenin and colon cancer cell growth by the KDM4B
histone demethylase. Int J Oncol. 44:1341–1348. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Janknecht R: Regulation of the ER81
transcription factor and its coactivators by mitogen- and
stress-activated protein kinase 1 (MSK1). Oncogene. 22:746–755.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shin S, Bosc DG, Ingle JN, Spelsberg TC
and Janknecht R: Rcl is a novel ETV1/ER81 target gene upregulated
in breast tumors. J Cell Biochem. 105:866–874. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Goueli BS and Janknecht R: Regulation of
telomerase reverse transcriptase gene activity by upstream
stimulatory factor. Oncogene. 22:8042–8047. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shin S, Rossow KL, Grande JP and Janknecht
R: Involvement of RNA helicases p68 and p72 in colon cancer. Cancer
Res. 67:7572–7578. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shin S, Oh S, An S and Janknecht R: ETS
variant 1 regulates matrix metalloproteinase-7 transcription in
LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 29:306–314. 2013.
|
|
33
|
Goueli BS and Janknecht R: Upregulation of
the catalytic telomerase subunit by the transcription factor ER81
and oncogenic HER2/Neu, Ras, or Raf. Mol Cell Biol. 24:25–35. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Shin S, Kim TD, Jin F, van Deursen JM,
Dehm SM, Tindall DJ, Grande JP, Munz JM, Vasmatzis G and Janknecht
R: Induction of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and modulation
of androgen receptor by ETS variant 1/ETS-related protein 81.
Cancer Res. 69:8102–8110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim TD, Oh S, Shin S and Janknecht R:
Regulation of tumor suppressor p53 and HCT116 cell physiology by
histone demethylase JMJD2D/KDM4D. PLoS One. 7:e346182012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu H, Xiao Y, Zhang S, Ji S, Wei L, Fan F,
Geng J, Tian J, Sun X, Qin F, et al: The Ets transcription factor
GABP is a component of the hippo pathway essential for growth and
antioxidant defense. Cell Reports. 3:1663–1677. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Haffner MC, Aryee MJ, Toubaji A, Esopi DM,
Albadine R, Gurel B, Isaacs WB, Bova GS, Liu W, Xu J, et al:
Androgen-induced TOP2B-mediated double-strand breaks and prostate
cancer gene rearrangements. Nat Genet. 42:668–675. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hollenhorst PC, McIntosh LP and Graves BJ:
Genomic and biochemical insights into the specificity of ETS
transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 80:437–471. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Regan MC, Horanyi PS, Pryor EE Jr, Sarver
JL, Cafiso DS and Bushweller JH: Structural and dynamic studies of
the transcription factor ERG reveal DNA binding is allosterically
autoinhibited. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:13374–13379. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wei GH, Badis G, Berger MF, Kivioja T,
Palin K, Enge M, Bonke M, Jolma A, Varjosalo M, Gehrke AR, et al:
Genome-wide analysis of ETS-family DNA-binding in vitro and in
vivo. EMBO J. 29:2147–2160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bosc DG, Goueli BS and Janknecht R:
HER2/Neu-mediated activation of the ETS transcription factor ER81
and its target gene MMP-1. Oncogene. 20:6215–6224. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Janknecht R, Monté D, Baert JL and de
Launoit Y: The ETS-related transcription factor ERM is a nuclear
target of signaling cascades involving MAPK and PKA. Oncogene.
13:1745–1754. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Black JC, Van Rechem C and Whetstine JR:
Histone lysine methylation dynamics: Establishment, regulation, and
biological impact. Mol Cell. 48:491–507. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kooistra SM and Helin K: Molecular
mechanisms and potential functions of histone demethylases. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 13:297–311. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Berry WL and Janknecht R: KDM4/JMJD2
histone demeth-ylases: Epigenetic regulators in cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 73:2936–2942. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Whetstine JR, Nottke A, Lan F, Huarte M,
Smolikov S, Chen Z, Spooner E, Li E, Zhang G, Colaiacovo M, et al:
Reversal of histone lysine trimethylation by the JMJD2 family of
histone demethylases. Cell. 125:467–481. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shin S and Janknecht R: Diversity within
the JMJD2 histone demethylase family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
353:973–977. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sun C, Dobi A, Mohamed A, Li H,
Thangapazham RL, Furusato B, Shaheduzzaman S, Tan SH, Vaidyanathan
G, Whitman E, et al: TMPRSS2-ERG fusion, a common genomic
alteration in prostate cancer activates C-MYC and abrogates
prostate epithelial differentiation. Oncogene. 27:5348–5353. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang J, Cai Y, Yu W, Ren C, Spencer DM and
Ittmann M: Pleiotropic biological activities of alternatively
spliced TMPRSS2/ERG fusion gene transcripts. Cancer Res.
68:8516–8524. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Barry ER, Morikawa T, Butler BL, Shrestha
K, de la Rosa R, Yan KS, Fuchs CS, Magness ST, Smits R, Ogino S, et
al: Restriction of intestinal stem cell expansion and the
regenerative response by YAP. Nature. 493:106–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Cottini F, Hideshima T, Xu C, Sattler M,
Dori M, Agnelli L, ten Hacken E, Bertilaccio MT, Antonini E, Neri
A, et al: Rescue of Hippo coactivator YAP1 triggers DNA
damage-induced apoptosis in hematological cancers. Nat Med.
20:599–606. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao B, Wei X, Li W, Udan RS, Yang Q, Kim
J, Xie J, Ikenoue T, Yu J, Li L, et al: Inactivation of YAP
oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact
inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 21:2747–2761.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu-Chittenden Y, Huang B, Shim JS, Chen
Q, Lee SJ, Anders RA, Liu JO and Pan D: Genetic and pharmacological
disruption of the TEAD-YAP complex suppresses the oncogenic
activity of YAP. Genes Dev. 26:1300–1305. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jiao S, Wang H, Shi Z, Dong A, Zhang W,
Song X, He F, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Wang W, et al: A peptide mimicking
VGLL4 function acts as a YAP antagonist therapy against gastric
cancer. Cancer Cell. 25:166–180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Labbé RM, Holowatyj A and Yang ZQ: Histone
lysine demeth-ylase (KDM) subfamily 4: Structures, functions and
therapeutic potential. Am J Transl Res. 6:1–15. 2013.
|
|
56
|
Klose RJ, Yamane K, Bae Y, Zhang D,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Wong J and Zhang Y: The
transcriptional repressor JHDM3A demethylates trimethyl histone H3
lysine 9 and lysine 36. Nature. 442:312–316. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Trojer P, Zhang J, Yonezawa M, Schmidt A,
Zheng H, Jenuwein T and Reinberg D: Dynamic histone H1 isotype 4
methylation and demethylation by histone lysine methyltransferase
G9a/KMT1C and the Jumonji domain-containing JMJD2/KDM4 proteins. J
Biol Chem. 284:8395–8405. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Crona F, Dahlberg O, Lundberg LE, Larsson
J and Mannervik M: Gene regulation by the lysine demethylase KDM4A
in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 373:453–463. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Mallette FA, Mattiroli F, Cui G, Young LC,
Hendzel MJ, Mer G, Sixma TK and Richard S: RNF8- and
RNF168-dependent degradation of KDM4A/JMJD2A triggers 53BP1
recruitment to DNA damage sites. EMBO J. 31:1865–1878. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hamada S, Kim TD, Suzuki T, Itoh Y,
Tsumoto H, Nakagawa H, Janknecht R and Miyata N: Synthesis and
activity of N-oxalylglycine and its derivatives as Jumonji
C-domain-containing histone lysine demethylase inhibitors. Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 19:2852–2855. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Hamada S, Suzuki T, Mino K, Koseki K,
Oehme F, Flamme I, Ozasa H, Itoh Y, Ogasawara D, Komaarashi H, et
al: Design, synthesis, enzyme-inhibitory activity, and effect on
human cancer cells of a novel series of jumonji domain-containing
protein 2 histone demethylase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 53:5629–5638.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Rose NR, Woon EC, Kingham GL, King ON,
Mecinović J, Clifton IJ, Ng SS, Talib-Hardy J, Oppermann U,
McDonough MA, et al: Selective inhibitors of the JMJD2 histone
demethylases: Combined nondenaturing mass spectrometric screening
and crystallographic approaches. J Med Chem. 53:1810–1818. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
King ON, Li XS, Sakurai M, Kawamura A,
Rose NR, Ng SS, Quinn AM, Rai G, Mott BT, Beswick P, et al:
Quantitative high-throughput screening identifies
8-hydroxyquinolines as cell-active histone demethylase inhibitors.
PLoS One. 5:e155352010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Luo X, Liu Y, Kubicek S, Myllyharju J,
Tumber A, Ng S, Che KH, Podoll J, Heightman TD, Oppermann U, et al:
A selective inhibitor and probe of the cellular functions of
Jumonji C domain-containing histone demethylases. J Am Chem Soc.
133:9451–9456. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wang L, Chang J, Varghese D, Dellinger M,
Kumar S, Best AM, Ruiz J, Bruick R, Peña-Llopis S, Xu J, et al: A
small molecule modulates Jumonji histone demethylase activity and
selectively inhibits cancer growth. Nat Commun.
4:20352013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kim TD, Fuchs JR, Schwartz E, Abdelhamid
D, Etter J, Berry WL, Li C, Ihnat MA, Li PK and Janknecht R:
Pro-growth role of the JMJD2C histone demethylase in HCT-116 colon
cancer cells and identification of curcuminoids as JMJD2
inhibitors. Am J Transl Res. 6:236–247. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cloos PA, Christensen J, Agger K, Maiolica
A, Rappsilber J, Antal T, Hansen KH and Helin K: The putative
oncogene GASC1 demethylates tri- and dimethylated lysine 9 on
histone H3. Nature. 442:307–311. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Patani N, Jiang WG, Newbold RF and Mokbel
K: Histone-modifier gene expression profiles are associated with
pathological and clinical outcomes in human breast cancer.
Anticancer Res. 31:4115–4125. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Berry WL, Shin S, Lightfoot SA and
Janknecht R: Oncogenic features of the JMJD2A histone demethylase
in breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 41:1701–1706. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Slee RB, Steiner CM, Herbert BS, Vance GH,
Hickey RJ, Schwarz T, Christan S, Radovich M, Schneider BP,
Schindelhauer D, et al: Cancer-associated alteration of
pericentromeric heterochromatin may contribute to chromosome
instability. Oncogene. 31:3244–3253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Mallette FA and Richard S: JMJD2A promotes
cellular transformation by blocking cellular senescence through
transcriptional repression of the tumor suppressor CHD5. Cell
Reports. 2:1233–1243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Shin S and Janknecht R: Activation of
androgen receptor by histone demethylases JMJD2A and JMJD2D.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 359:742–746. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kim TD, Shin S, Berry WL, Oh S and
Janknecht R: The JMJD2A demethylase regulates apoptosis and
proliferation in colon cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 113:1368–1376.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Black JC, Manning AL, Van Rechem C, Kim J,
Ladd B, Cho J, Pineda CM, Murphy N, Daniels DL, Montagna C, et al:
KDM4A lysine demethylase induces site-specific copy gain and
rereplication of regions amplified in tumors. Cell. 154:541–555.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|